
What is the life expectancy of a person with leukemia?
What is the outlook for chronic lymphocytic leukemia?
- CLL overview. CLL does not usually present symptoms, and older adults are more likely to be affected by it. ...
- Survival rates. Survival rates can give a person more information about the outlook for their illness and help them to plan treatment and care.
- Factors that influence life expectancy. ...
- Living with CLL. ...
- Takeaway. ...
How to cure leukemia naturally?
Leukemia Symptoms
- swollen lymph nodes (neck, underarm, groin or stomach)
- enlarged spleen or liver
- frequent infections
- fever
- pale skin tone
- night sweats
- fatigue (feeling very tired)
- unplanned weight loss (10% of body weight over 6 months)
- bone or joint pain and/or tenderness
- easy bruising or bleeding
How long can you live with chronic myeloid leukemia?
The five-year survival rate of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) has more than doubled in recent years with 70 percent of patients surviving for more than 5 years. Previously, the typical survival rate of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) was three to five years.
Can you cure leukemia?
Since receiving the cord blood to treat her acute myeloid leukemia - a cancer that starts in blood-forming cells in the bone marrow - the woman has been in remission and free of the virus for 14 months, without the need for potent HIV treatments known as ...
How long is chemotherapy for ALL leukemia?
Chemo treatment for ALL is typically divided into 3 phases: Induction, which is short and intensive, usually lasts about a month. Consolidation (intensification), which is also intensive, typically lasts for a few months. Maintenance (post-consolidation), which is less intensive, typically lasts for about 2 years.
How long does ALL treatment last?
The entire length of treatment is typically about 2 to 3 years, with the most intense treatment in the first few months. Children with ALL are typically classified by risk group to make sure that the correct types and doses of drugs are given. Treatment may be more or less intense, depending on the risk group.
How many rounds of chemo does it take for ALL?
During a course of treatment, you usually have around 4 to 8 cycles of treatment. A cycle is the time between one round of treatment until the start of the next. After each round of treatment you have a break, to allow your body to recover.
How long is maintenance therapy for leukemia?
Standard ALL treatment usually takes between 2 to 3 years altogether. The maintenance phase takes up most of this time as it lasts 2 years. During the maintenance phase people are often back to work or college. If you have a stem cell or bone marrow transplant the treatment time is shorter but more intensive.
How many cycles of chemo do you need for leukemia?
The treatment usually consists of four cycles of intensive chemotherapy that includes high doses of cytarabine and one or more other drugs.
Why is leukemia treatment so long?
Although there may not be detectable leukemia cells in your child's blood or bone marrow at the end of induction, there still might be some leukemia cells that doctors cannot detect. This is why the treatment continues. The consolidation phase lasts for 4 to 8 weeks, depending on the ALL risk type and protocol.
What is the life expectancy after chemotherapy?
During the 3 decades, the proportion of survivors treated with chemotherapy alone increased from 18% in 1970-1979 to 54% in 1990-1999, and the life expectancy gap in this chemotherapy-alone group decreased from 11.0 years (95% UI, 9.0-13.1 years) to 6.0 years (95% UI, 4.5-7.6 years).
Does ALL chemo cause hair loss?
Most people think that chemotherapy drugs always cause hair loss. But some don't cause any hair loss at all or only slight thinning. Other types of chemotherapy may cause complete hair loss. It might include your eyelashes, eyebrows, underarm, leg and sometimes pubic hair.
Which type of leukemia is most curable?
While it is similar in many ways to the other subtypes, APL is distinctive and has a specific treatment regime. Treatment outcomes for APL are very good, and it is considered the most curable type of leukemia, with cure rates as high as 90%.
How long does leukemia take to go into remission?
For ALL, Gruber says, cure is typically defined as five years of remission after diagnosis. For AML, she says, cure is typically defined as retaining remission for three years after diagnosis. Helping kids stay as healthy as possible throughout their treatment is the first step.
Can you be on chemo for years?
Still, it's important to know that even those who are not cured of cancer may go on living for months or years, even though there may be changes in their lives. Many families adjust to this kind of treatment schedule.
Is ALL leukemia curable?
About 98% of children with ALL go into remission within weeks after starting treatment. About 90% of those children can be cured. Patients are considered cured after 10 years in remission.
What is intrathecal chemo?
Intrathecal chemotherapy: All children also get chemo into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to kill any leukemia cells that might have spread to the brain and spinal cord. This treatment, known as intrathecal chemotherapy, is given through a lumbar puncture (spinal tap).
How long does the consolidation phase of chemo last?
Consolidation (intensification) The next, and usually more intense, consolidation phase of chemo starts once the leukemia is in remission and typically lasts for several months. This phase further reduces the number of leukemia cells still in the body.
How often is methotrexate given?
It is usually given twice (or more if the leukemia is high risk or leukemia cells have been found in the CSF) during the first month and several times during the next 1 or 2 months. It is then repeated less often during the rest of treatment. Usually, methotrexate is the drug used for intrathecal chemo.
What is the best treatment for leukemia?
If the leukemia remains in remission after induction and consolidation, maintenance therapy can begin. Most treatment plans use daily 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) and weekly methotrexate, given as pills, often along with vincristine, which is given into a vein (IV), and a steroid (prednisone or dexamethasone). These latter 2 drugs are given ...
What is the goal of induction chemotherapy?
Induction. The goal of induction chemotherapy is to achieve a remission. This means that leukemia cells are no longer found in bone marrow samples, the normal marrow cells return, and the blood counts become normal. (A remission is not necessarily a cure.) More than 95% of children with ALL enter remission after 1 month of induction treatment.
How long does it take to get rid of lymphocytic leukemia?
The main treatment for children with acute lymphocytic (lymphoblastic) leukemia (ALL) is chemotherapy, which is usually given in 3 main phases: The entire length of treatment is typically about 2 to 3 years, with the most intense treatment in the first few months. Children with ALL are typically classified by risk group to make sure ...
Why do children spend their first month in the hospital?
Your child may spend some or much of this time in the hospital, because serious infections or other complications can occur . It is very important to take all medicines as prescribed.
How long does it take to cure lymphoblastic leukaemia?
Treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) is divided into 3 phases. These are: Treatment for ALL usually takes between 2 and 3 years. The maintenance phase of treatment takes up most of this time.
Where do leukaemia cells travel?
Leukaemia cells can sometimes travel to the brain and spinal cord (the central nervous system, CNS). So as part of your induction treatment you have chemotherapy and possibly a steroid into the fluid that circulates around the spinal cord and brain. This is called intrathecal chemotherapy.
How long before chemotherapy do you start taking steroids?
There are different combinations of drugs your doctors might use. You usually start taking steroids for up to a week before you start chemotherapy. This starts to get rid of some of the leukaemia cells while your doctor gets all your test results and plans your treatment. Find out about steroids.
How long do you have to stay in hospital after chemo?
Chemotherapy kills off many of your healthy bone marrow cells as well as the leukaemia cells. So you need to stay in hospital for about a month until you have recovered. There are different combinations of drugs your doctors might use.
How often do you see your doctor for chemo?
You also have intrathecal chemotherapy. You have your treatment in cycles, also known as blocks. You see your doctor every few months to check how you are getting on and to keep an eye on your blood counts. Sometimes you may need blood transfusions or antibiotics if you have an infection.
What happens if you are not in remission?
You move on to the next phase of treatment if you are in remission (consolidation). If you’re not in remission you usually have more chemotherapy.
What is the aim of consolidation therapy?
Your doctor might also call it the intensification phase. The aim is to get rid of any leukaemia cells that might still be there and to stop it from coming back. This phase of treatment might take a few months.
What tests can you do for leukemia?
If this happens, or if you have signs or symptoms that suggest leukemia, you may undergo the following diagnostic exams: Physical exam. Your doctor will look for physical signs of leukemia, such as pale skin from anemia, swelling of your lymph nodes, and enlargement of your liver and spleen. Blood tests. By looking at a sample of your blood, your ...
Why is leukemia confusing?
The term "leukemia" can be confusing because it refers to a group of cancers that aren't all that similar except for the fact that they affect the bone marrow and blood.
How to remove bone marrow from hip?
Bone marrow test. Your doctor may recommend a procedure to remove a sample of bone marrow from your hipbone. The bone marrow is removed using a long, thin needle. The sample is sent to a laboratory to look for leukemia cells.
What is the treatment for bone marrow transplant?
Radiation therapy may be used to prepare for a bone marrow transplant. Bone marrow transplant. A bone marrow transplant, also called a stem cell transplant, helps reestablish healthy stem cells by replacing unhealthy bone marrow with leukemia-free stem cells that will regenerate healthy bone marrow.
How does immunotherapy work?
Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process. Engineering immune cells to fight leukemia.
What is clinical trial?
Clinical trials are experiments to test new cancer treatments and new ways of using existing treatments. While clinical trials give you or your child a chance to try the latest cancer treatment, treatment benefits and risks may be uncertain. Discuss the benefits and risks of clinical trials with your doctor.
What is car T cell therapy?
A specialized treatment called chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy takes your body's germ-fighting T cells, engineers them to fight cancer and infuses them back into your body. CAR -T cell therapy might be an option for certain types of leukemia. Clinical trials.
How long does chemo last?
Chemo treatment for ALL is typically divided into 3 phases: Induction, which is short and intensive, usually lasts about a month . Consolidation (intensification), which is also intensive, typically lasts for a few months. Maintenance (post-consolidation), which is less intensive, typically lasts for about 2 years.
How long does it take for chemo side effects to go away?
Fatigue and shortness of breath (from having too few red blood cells) Most side effects from chemo go away once treatment is finished. Low blood cell counts can last weeks, but then should return to normal. There are often ways to lessen chemo side effects.
What happens when you have chemo?
Tumor lysis syndrome: This side effect of chemo is most common in patients who have large numbers of leukemia cells in the body, so it is seen most often in the first (induction) phase of treatment. When chemo kills the leukemia cells, they break open and release their contents into the bloodstream.
What is the name of the fluid that is injected into the brain to kill cancer cells?
Most chemo drugs have trouble reaching the area around the brain and spinal cord, so chemo may need to be injected into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to kill cancer cells in that area. This is called intrathecal chemo. Intrathecal chemo can be given during a spinal tap or by using a special catheter called an Ommaya reservoir.
How is chemo given?
Chemo is typically given in cycles, with each period of treatment followed by a rest period to allow the body time to recover. Most often, chemo drugs are injected into a vein (IV), into a muscle, or under the skin, or are taken by mouth. These drugs enter the blood and can reach leukemia cells all over the body.
What is chemo in children?
To learn about ALL in children, see Leukemia in Children .) Chemotherapy (chemo) is the use of drugs to treat cancer. Chemo drugs travel through the bloodstream to reach cancer cells all over the body. This makes chemo useful for cancers such as leukemia that has spread throughout the body.
What is chemo for all?
Chemo for ALL uses a combination of anti-cancer drugs. The most commonly used chemo drugs include: People typically get several of these drugs at different times during the course of treatment, but they do not get all of them.
What exams would be Performed?
As mentioned, your doctor will be requiring to perform series of exams to come up with the best treatment plan. Some of these exams may be anything from the following:
Treatment of Leukemia
Keep in mind that the treatment procedure for leukemia would be dictated by a number of different factors. Your doctor will be determining your options for leukemia treatment based on overall health and age, type of leukemia that you have and whether it began spreading in several parts of your body.
How long do children live with leukemia?
More than four out of five children live at least 5 years. The prognosis for adults is not as good.
How old is the average person with leukemia?
In adults, leukemia is most common in people older than 55 years, with the average age of diagnosis being 66 years. It is also one of the most common cancers in children and adults younger than 20 years. The survival rate is higher for younger people. According to the National Cancer Institute, the percentage of deaths by age group is as follows: ...
What are the different types of leukemia?
There are four common types of leukemia which include: Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL): In this type of leukemia, immature lymphoid cells grow rapidly in the blood. It is the most common type of leukemia in children and rarely affects adults. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML):
What is the name of the cancer that affects the white blood cells?
Leukemia is a group of cancers of the blood affecting the white blood cells. White blood cells are the infection-fighting cells of the body. In leukemia , white blood cell production becomes abnormal in the bone marrow. The abnormal white blood cells divide uncontrollably and eventually outnumber the healthy white blood cells.
How long does it take for cancer to go into remission?
About 80 percent who go into remission will do so within 1 month of therapy . In some people, however, the disease will return, lowering the cure rate. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): On average, people with this cancer survive 9 years, although some have lived for decades, cancer always comes back at some point.
What are the symptoms of childhood leukemia?
Symptoms and signs include fever, easy bruising, bone or joint pain, weakness, loss of appetite, and painless lumps in the neck, underarm, stomach, or groin.
How do you know if you have leukemia?
If the fever symptoms continue for longer than usual, it is important to consult your doctor. Other early symptoms of leukemia include: Fever of unknown origin.
What to do if you have chronic lymphocytic leukemia?
It’s important that you think carefully about each of your choices. Weigh the benefits of each treatment option against the possible risks and side effects.
Why is it important to take time to think about CLL?
Common treatment approaches. It's important to take time and think about your choices. Because CLL often grows slowly, not everyone needs to be treated right away. In choosing a treatment plan, the stage of the leukemia and other prognostic factors are important.
Why is it important to discuss treatment options with your doctor?
Making treatment decisions. It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decision that best fits your needs. It’s also very important to ask questions if there's anything you’re not sure about.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
What are the services offered by the American Cancer Society?
These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help. The American Cancer Society also has programs and services – including rides to treatment, lodging, and more – to help you get through treatment.
Can you continue cancer treatment?
Whether or not you continue treatment, there are still things you can do to help maintain or improve your quality of life.
Is treatment information given here official policy of the American Cancer Society?
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor.
Induction
Consolidation
- If the leukemia goes into remission, the next phase often consists of another fairly short course of chemo, using many of the same drugs that were used for induction therapy. This typically lasts for a few months. Usually the drugs are given in high doses so that the treatment is still fairly intense. CNS prophylaxis/treatment is typically continue...
Maintenance
Treatment of Residual Disease
Treatment of Recurrent All
- The next, and usually more intense, consolidation phase of chemo starts once the leukemia is in remission and typically lasts for several months. This phase further reduces the number of leukemia cells still in the body. Several chemo drugs are combined to help prevent the remaining leukemia cells from developing resistance. Intrathecal chemo (as d...
Philadelphia Chromosome-Type All
- If the leukemia remains in remission after induction and consolidation, maintenance therapy can begin. Most treatment plans use daily 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) and weekly methotrexate, given as pills, often along with vincristine, which is given into a vein (IV), and a steroid (prednisone or dexamethasone). These latter 2 drugs are given for brief periods every 4 to 8 weeks. Other drug…
Steroid Pre Phase
- The treatment plans may change if the leukemia doesn’t go into remission during induction or consolidation. The doctor will probably check the child’s bone marrow soon after treatment starts to see if the leukemia is going away. If not, treatment might need to be more intense or prolonged. If standard lab tests show the leukemia seems to have gone away, the doctor may use more sen…
Induction
- If the ALL recurs (comes back) during or after treatment, the child will most likely be treated again with chemotherapy. Much of the treatment strategy depends on how soon the leukemia returns after the first treatment. If the relapse occurs after a long time, the same drugs might still be effective, so the same or similar treatment may be used to try to get the leukemia into a second …
Consolidation and Intensification
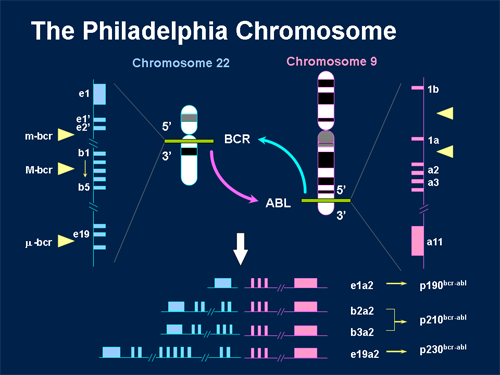
- For children with certain types of ALL, such as those with the Philadelphia chromosome, standard chemotherapy for ALL (as outlined above) might not be as effective. A stem cell transplantmay be advised if induction treatment puts the leukemia in remission and a suitable stem cell donor is available. Newer, targeted drugssuch as imatinib (Gleevec) and dasatinib (Sprycel) are designe…
Maintenance
- The aim of the steroid pre phase is to destroy as many the leukaemia cells as possible. After treatment, your doctor calls it a complete remission (CR) if: 1. there is no sign of leukaemia in your bone marrow when looked at under a microscope 2. your blood count has returned to normal
Clinical Trials
- In induction you have several chemotherapy drugs which you have over a few days. You can ask for a copy of your treatment timetable to help you follow your treatment plan and know what to expect next. Chemotherapy damages healthy cells as well as the leukaemia cells. So you will generally need to stay in hospital until you have recovered from induc...
Diagnosis
- Doctors know that even if your leukaemia is in remission after the first cycle of treatment, you have to continue treatment or it will come back. So the aims of consolidation and intensification are to get rid of any leukaemia cells that might still be there and to stop them from coming back. To work out the next part of your treatment your doctor looks at how likely your leukaemia is to …
Treatment
- The last phase of ALL treatment is maintenance therapy. It helps to keep the leukaemia away (in remission).
Clinical Trials
- Your doctor may offer you treatment as part of a clinical trial. Doctors and researchers do trials to: 1. improve treatment 2. make existing treatments better 3. develop new treatments Talk to your doctor or clinical nurse specialist if you are interested in joining a clinical trial.
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Treatment for your leukemia depends on many factors. Your doctor determines your leukemia treatment options based on your age and overall health, the type of leukemia you have, and whether it has spread to other parts of your body, including the central nervous system. Common treatments used to fight leukemia include: 1. Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy ...