How long does radiotherapy last for non small cell lung cancer?
Jan 28, 2022 · While radiation therapy is a routine part of treatment for limited-stage cancer, a few analyses attempted to figure out the survival benefit of adding radiation therapy to the combined treatment. The addition of radiation therapy to chemotherapy appears to have a 5.4% survival benefit at two to three years after treatment.
How long does radiation therapy take to work for cancer?
Most often, radiation treatments to the lungs are given 5 days a week for 5 to 7 weeks, but this can vary based on the type of EBRT and the reason it’s being given. Newer EBRT techniques have been shown to help doctors treat lung cancers more accurately while lowering the radiation exposure to nearby healthy tissues. These include:
What are the side effects of radiation therapy for lung cancer?
Oct 22, 2021 · Radiation is a type of lung cancer treatment designed to only target cancer cells and not affect other parts of the body. Lung cancer radiation therapy uses powerful, high-energy X-rays to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. Radiation may come from outside the body (external) or from radioactive materials placed directly inside the ...
How is radiation therapy used to treat lung tumors?
Radiation therapy for limited-stage small cell lung cancer can be administered either once or twice a day. The treatment course lasts between three and seven weeks.
How many sessions of radiation is needed for lung cancer?
It typically uses three to five treatments to deliver very high doses of radiation to patients with localized, early-stage lung cancer who cannot have surgery.
What is the success rate of radiation for lung cancer?
The overall survival rate at 24 months for those receiving radiation plus chemotherapy and immunotherapy was 66.3% compared to 55.6% for those only receiving radiation and chemotherapy.Jan 28, 2022
What happens after radiotherapy for lung cancer?
Radiotherapy to the chest area might cause some inflammation of your lungs. Soon after the treatment, you might have a dry cough or shortness of breath. This is called acute radiation pneumonitis (pronounced new-mon-eye-tiss). Let your doctor or radiographer know if you feel breathless.
How long does a person go through radiation therapy?
Most patients get radiation treatments daily, 5 days a week (Monday through Friday) for 5 to 8 weeks. Weekend rest breaks allow time for normal cells to recover.
How long does it take for radiation to shrink a lung tumor?
Most often, radiation treatments to the lungs are given 5 days a week for 5 to 7 weeks, but this can vary based on the type of EBRT and the reason it's being given. Newer EBRT techniques have been shown to help doctors treat lung cancers more accurately while lowering the radiation exposure to nearby healthy tissues.Oct 1, 2019
How long does it take for radiation to work on lung cancer?
Both deliver super-high-dose radiation to small targets in a very short period of time — usually four to 10 treatments within one to two weeks. “That makes them very effective at killing cancer cells,” Liao says.Mar 17, 2021
What is the success rate of radiation therapy?
When it comes to early stages of disease, patients very frequently do well with either brachytherapy or external beam radiation. Success rates of around 90% or higher can be achieved with either approach.Oct 25, 2016
Where does lung cancer usually spread to first?
Most lung cancers first spread to lymph nodes within the lung or around the major airways. 4 Lymph nodes are tiny organs clustered throughout the body that trap and filter foreign substances.Dec 8, 2021
Is lung cancer always terminal?
It is common to go through strong feelings of blame, guilt and anger. However, getting a incurable lung cancer diagnosis is not automatically the same as being told you have a terminal illness. Your lung cancer may be incurable, but, with good treatment and ongoing care, you can lead a relatively normal life.
Is 6 weeks of radiation a lot?
Treatments are usually given five days a week for six to seven weeks. If the goal of treatment is palliative (to control symptoms) treatment will last 2-3 weeks in length. Using many small doses (fractions) for daily radiation, rather than a few large doses, helps to protect the healthy cells in the treatment area.
Do tumors grow back after radiation?
Normal cells close to the cancer can also become damaged by radiation, but most recover and go back to working normally. If radiotherapy doesn't kill all of the cancer cells, they will regrow at some point in the future.Jul 6, 2020
Can you drive yourself to radiation treatments?
Almost all patients are able to drive while receiving radiotherapy treatment. However, with some types of cancer, driving may NOT be recommended due to fatigue or strong pain medication.
How long does radiation treatment last in the lungs?
Most often, radiation treatments to the lungs are given 5 days a week for 5 to 7 weeks, but this can vary based on the type of EBRT and the reason it’s being given. Newer EBRT techniques have been shown to help doctors treat lung cancers more accurately while lowering the radiation exposure to nearby healthy tissues.
How long does radiation last?
Less often, small radioactive “seeds” are left in place permanently, and the radiation gets weaker over several weeks.
What is EBRT in cancer?
External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) focuses radiation from outside the body onto the cancer. This is the type of radiation therapy most often used to treat NSCLC or its spread to other organs. Treatment is much like getting an x-ray, but the radiation dose is stronger.
What is the treatment for non-small cell lung cancer?
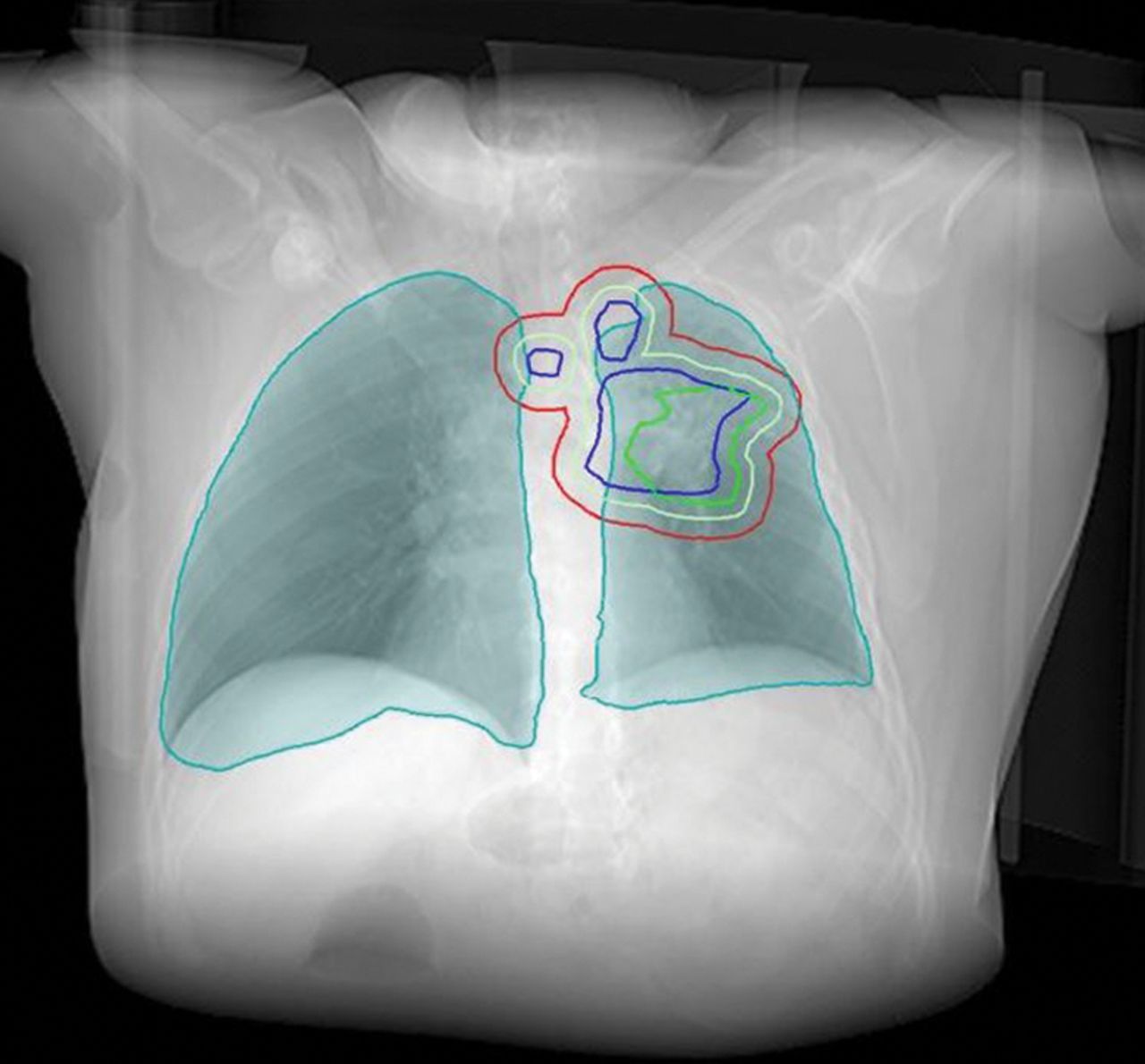
Radiation Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays or particles to kill cancer cells. Depending on the stage of the non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and other factors, radiation therapy might be used: As the main treatment (sometimes along with chemotherapy ), especially if the lung tumor can’t be removed ...
What is the purpose of chemo after surgery?
After surgery (alone or along with chemotherapy) to try to kill any small areas of cancer that surgery might have missed. Before surgery (usually along with chemotherapy) to try to shrink a lung tumor to make it easier to operate on. To treat cancer spread to other areas such as the brain or bone. To relieve (palliate) symptoms ...
What are the side effects of radiation therapy for NSCLC?
Common side effects depend on where the radiation is aimed and can include: Fatigue. Nausea and vomiting.
What is the treatment for NSCLC?
Brachytherapy (internal radiation therapy) In people with NSCLC, brachytherapy is sometimes used to shrink tumors in the airway to relieve symptoms. The doctor places a small source of radioactive material (often in the form of small pellets) directly into the cancer or into the airway next to the cancer.
How long does it take to get rid of lung cancer?
If you have advanced non-small cell lung cancer that is confined to the chest and have your tumor surgically removed, you may be treated with a five-to-six-week course of radiation therapy before or after your surgery depending on your specific situation.
How does radiation therapy work for lung cancer?
Radiation therapy for lung cancer uses high-energy beams called x-rays to destroy cancer cells by damaging their DNA. It’s very effective at controlling or eliminating tumors at specific sites in the body. The treatment can be given to cure patients whose lung cancers are confined to the chest but cannot be removed surgically.
What is a lung cancer IMRT?
Some people with lung cancer may be treated with a specialized form of IMRT called image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT). IGRT involves the use of sophisticated imaging tests to verify the position of the patient and the location of the tumor prior to and during the delivery of the treatment.
What is the treatment for lung cancer?
Radiation Therapy for Lung Cancer. Radiation oncologist Andreas Rimner delivers radiation to lung cancer patients using a GPS-type approach that tracks the tumor’s precise location at all times. Radiation therapy for lung cancer uses high-energy beams called x-rays to destroy cancer cells by damaging their DNA.
What is proton therapy?
For some cases of lung cancer, our radiation oncologists can use proton therapy, an advanced form of radiation therapy, to deliver high doses of radiation to tumors that may be resistant to conventional forms while minimizing exposure to the surrounding healthy tissues. Proton therapy directs its cancer-fighting energy to precise locations within ...
How long does radiation therapy last?
The treatment course typically lasts two to three weeks, with five daily treatments per week.
How does proton therapy work?
Proton therapy directs its cancer-fighting energy to precise locations within the body, allowing our doctors to deliver the necessary dose to the tumor — maximizing the chance of destroying it — while simultaneously lowering the dose to normal tissues and thereby reducing the risk of treatment-related side effects .
How long does radiation treatment last?
Most often, radiation treatments are given 5 days a week for several weeks, but this can vary based on the reason it’s being given.
What type of radiation is used for lung cancer?
External beam radiation therapy. External beam radiation therapy uses a machine that delivers a beam of radiation to a specific part of the body. This is the type of radiation used most often for lung carcinoid tumors.
How is radiation carried to cancer cells?
It is carried to the cancer cells by dotatate where it attaches to carcinoid tumor cells. This lets doctors deliver high doses of radiation directly to the tumors. It is given as an infusion into a vein (IV).
What is the treatment for lung cancer?
Radiation Therapy for Lung Carcinoid Tumors. Radiation therapy is the use of high-energy rays (such as x-rays) or radioactive particles to kill cancer cells. Surgery is the main treatment for most carcinoid tumors, but radiation therapy may be an option for those who can’t have surgery for some reason. It may also be given after surgery in some ...
What are the side effects of radiation therapy?
The most common side effects are nausea, kidney and liver problems, low white blood counts, low platelet counts, and vomiting. Since this therapy involves radiation that is injected into the bloodstream, you will be given special instructions on how to minimize the radiation exposure during and after treatment.
Can radiation therapy be given after surgery?
It may also be given after surgery in some cases if there’s a chance some of the tumor was not removed. Radiation therapy can also be used to help relieve symptoms such as pain if the cancer has spread to the bones or other areas.
How long does it take for lung cancer to heal after radiation?
Most can be expected to improve within a few weeks after radiation therapy is completed. Throughout the course of your radiation therapy for lung cancer, it will be important for you to communicate candidly with your physician. If you experience any unpleasant side effects, there may be options to help you manage them.
What are the side effects of radiation therapy?
With that said, some common side effects of radiation therapy for lung cancer include: General weakness and fatigue. Dry, red, itchy or peeling skin. Shortness of breath. Swallowing difficulties. Sore throat. Shoulder stiffness.
How to contact a radiation oncologist at Moffitt Cancer Center?
Call 1-888-663-3488 or complete our new patient registration form online.
What does a radiation oncologist do?
As part of the planning process for your therapy, your radiation oncologist will explain what you can expect and recommend ways to prevent or alleviate any associated discomfort. Your experience will be influenced by a variety of unique factors, such as the location and type of your tumor, your radiation dosage, your general health and any other treatments you may be receiving, such as chemotherapy.
Can radiation therapy cause cancer?
However, like many other treatments, it can cause certain side effects. Specifically, when healthy cells are exposed to radiation, they can be damaged in the same way that cancerous cells are, leading to adverse effects at the site of exposure. Because radiation therapy is a localized treatment, most side effects develop in the treatment area ...
Does radiation therapy affect lung cancer?
What Are the Side Effects of Radiation Therapy for Lung Cancer? Radiation therapy for lung cancer can be very effective for destroying cancerous cells and shrinking tumors. However, like many other treatments, it can cause certain side effects. Specifically, when healthy cells are exposed to radiation, they can be damaged in the same way ...
How does radiation affect the bladder?
Just like radiation harms cells in your bones, it also affects the cells in your bowel and bladder. You might experience blood in your urine, reduced bladder control, sexual dysfunction, and interruptions to your daily routine.
Can radiation cause burns?
The concentrated exposure of X-rays during radiation therapy often causes painful burns across the skin. As X-rays pass through the skin, they produce dangerous free radicals that damage DNA, injure skin tissue, and trigger inflammation. This side effect is so common that about 85% of radiation patients experience moderate to severe burns during and after treatment
Does radiation weaken bones?
Radiation is so potent that it can weaken the bones and cause osteoporosis and osteonecrosis. Since bones are living and growing organisms, radiation harms their active cells and stunts their strength. The ribs in your chest or bones in your leg may become far more vulnerable to fractures and breaks.
How long does radiation therapy last?
It is the most common radiation therapy treatment for cancer. Each session is quick, lasting about 15 minutes. Radiation does not hurt, sting, or burn when it enters the body.
How long does it take for radiation to go away?
The 2-day break in treatment each week allows your body some time to repair this damage. Some of the effects may not go away until the treatment period is completed. Let the health care professionals if you are experiencing side effects. Read more about the side effects of radiation therapy.
What type of doctor is responsible for radiation therapy?
Radiation oncologist. This type of doctor specializes in giving radiation therapy to treat cancer. A radiation oncologist oversees radiation therapy treatments. They work closely with other team members to develop the treatment plan. Radiation oncology nurse.
What is simulation in radiation therapy?
Simulating and planning treatment. Your first radiation therapy session is a simulation. This means it is a practice run without giving radiation therapy. Your team will use imaging scans to identify the tumor location.
Why is it important to be in the same position for radiation?
It is important for your body to be in the same position for each treatment. Your radiation oncology team cares about your comfort. Talk with the team to find a comfortable position that you can be in every time you come in for radiation therapy.
How often should you check for radiation?
During your treatment, your radiation oncologist will check how well it is working. Typically, this will happen at least once a week. If needed, they may adjust your treatment plan.
What is informed consent for radiation?
Giving permission for radiation therapy. If you choose to receive radiation therapy, your health care team will ask you to sign an "informed consent" form. Signing the document means: Your team gave you information about your treatment options. You choose to have radiation therapy.
How long does radiation side effects last?
Remember that the type of radiation side effects you might have depends on the prescribed dose and schedule. Most side effects go away within a few months of ending treatment. Some side effects may continue after treatment ends because it takes time for the healthy cells to recover from radiation. Side effects might limit your ability ...
What is the best treatment for radiation?
One way to reduce side effects is by using radioprotective drugs, but these are only used for certain types of radiation given to certain parts of the body. These drugs are given before radiation treatment to protect certain normal tissues in the treatment area. The one most commonly used today is amifostine. This drug may be used in people with head and neck cancer to reduce the mouth problems caused by radiation therapy.
How long does it take for radiation to show up in the brain?
Radiation to the brain can also have side effects that show up later – usually from 6 months to many years after treatment ends. These delayed effects can include serious problems such as memory loss, stroke-like symptoms, and poor brain function.
How long does it take for radiation to cause side effects?
Late side effects can take months or even years to develop. They can occur in any normal tissue in the body that has received radiation. The risk of late side effects depends on the area treated as well as the radiation dose that was used. Careful treatment planning can help avoid serious long-term side effects.
What is the most common drug used for radiation therapy?
The one most commonly used today is amifostine. This drug may be used in people with head and neck cancer to reduce the mouth problems caused by radiation therapy. Not all doctors agree on how these drugs should be used in radiation therapy. These drugs have their own side effects, too, so be sure you understand what to look for.
How to take care of your mouth during radiation?
Here are some tips that may help you manage mouth problems: Avoid spicy and rough foods, such as raw vegetables, dry crackers, and nuts.
How long does it take for side effects to show up after radiation?
Some side effects might show up quickly, but others might not show up until 1 to 2 years after treatment. Talk with your radiation oncologist about what to watch for and when to call your doctor. If the cancer is in many areas, sometimes the whole brain is treated with radiation.
