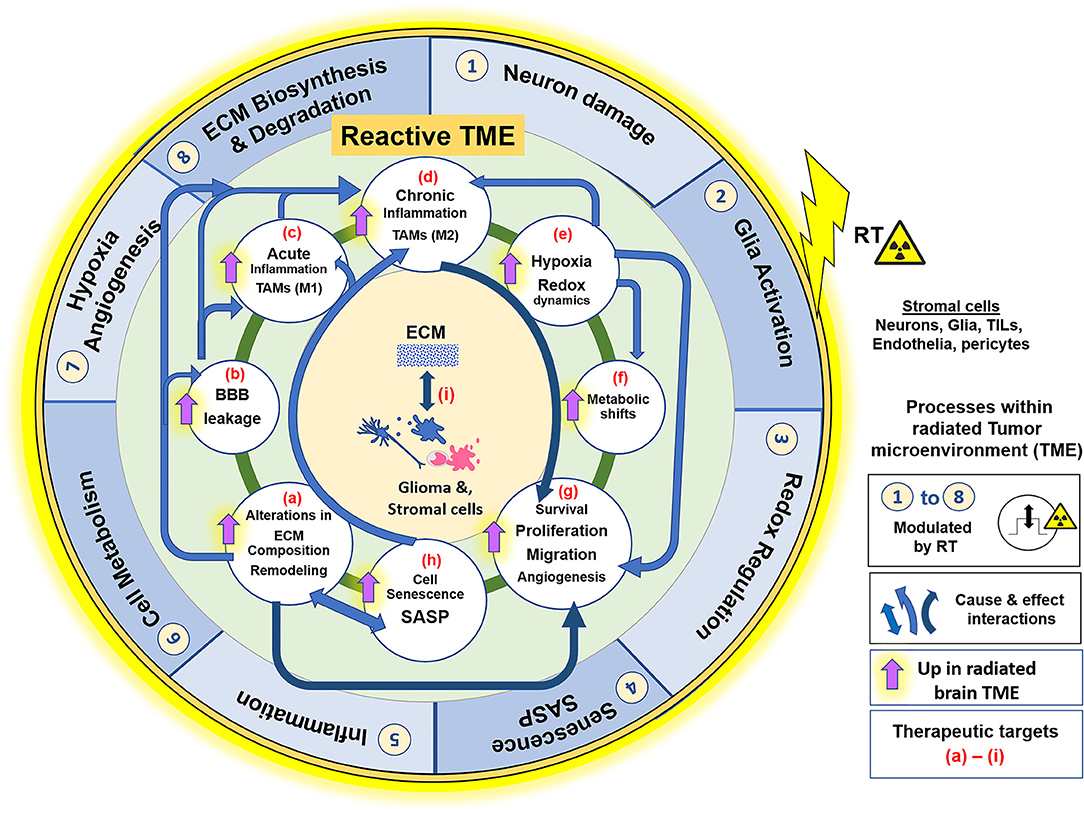
What is the typical radiation therapy schedule for a glioblastoma?
The most common schedule of radiation therapy for a glioblastoma is six weeks of daily treatment with a low dose of radiation. This amount of radiation is well tolerated by most people. It causes few side effects.
How is proton therapy used to treat glioblastoma?
Sometimes we recommend proton therapy, a type of radiation that uses charged particles called protons instead of the X-rays that are used in conventional radiation therapy. This is most frequently used for glioblastoma tumors that are deep in the brain. It is occasionally used after a tumor has come back after previous treatment.
What is the treatment for glioblastoma multiforme?
What's the treatment for GBM? The standard of treatment for a GBM is surgery, followed by daily radiation and oral chemotherapy for six and a half weeks, then a six-month regimen of oral chemotherapy given five days a month.
Where can I get radiation therapy for glioblastoma?
Moffitt Cancer Center not only offers some of the most advanced radiation therapy options for glioblastoma, but we also have some of the most experienced radiation oncologists, radiation therapists, dosimetrists and physicists in the field.
What is the success rate of radiation therapy for glioblastoma?
Among GBM patients, overall response rate was 50% with a 6-month progression-free survival of 65%. Median overall survival was 12.5 months and 1-year survival was 54%.
How long is chemo and radiation for glioblastoma?
The standard of treatment for a GBM is surgery, followed by daily radiation and oral chemotherapy for six and a half weeks, then a six-month regimen of oral chemotherapy given five days a month.
How long is radiation therapy for brain tumor?
It is also used for some meningiomas, pituitary tumours and schwannomas, and is occasionally used for gliomas that have come back after other treatment. Often, only 1–5 doses of SRS are needed. A treatment session may last between 15 minutes and two hours, depending on the type of radiosurgery given.
What happens after radiation treatment for glioblastoma?
Specifically for patients going through radiation therapy for glioblastoma, they may experience headaches, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss, seizures and trouble with memory or speech. Some of these side effects may appear during the treatment while others don't show up until a year or two afterward.
How fast does glioblastoma grow back after radiation?
However, we now know that GBM is a heterogeneous group of tumors (it behaves differently in different people) and the time when it comes back or recurs can vary. In the majority of patients it has a tendency to recur within 6-8 months.
Does glioblastoma ever go into remission?
In remission, symptoms may let up or disappear for a time. Glioblastomas often regrow. If that happens, doctors may be able to treat it with surgery and a different form of radiation and chemotherapy.
What is the best treatment for glioblastoma?
The best treatment for glioblastoma currently is surgery to remove as much of the tumour as possible, followed by a combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy.Surgery for glioblastomas. The first treatment for glioblastomas is usually neurosurgery. ... Treating glioblastoma with chemoradiation. ... Gliadel® wafers. ... Avastin®
How long does it take for radiation to shrink brain tumors?
This can occur six months to a few years after treatment. However, there is less risk of necrosis today because of newer, targeted radiation therapies and the emergence of powerful imaging, brain mapping and information technologies.
How long do daily radiation treatments take?
Each radiation therapy treatment takes about 10 minutes. Radiation therapy to try and cure cancer is usually delivered daily, Monday through Friday, for about five to eight weeks. Weekend breaks allow normal cells to recover. Shorter durations of radiation therapy may be used to relieve symptoms.
What can you not do during radiation treatment?
Avoid raw vegetables and fruits, and other hard, dry foods such as chips or pretzels. It's also best to avoid salty, spicy or acidic foods if you are experiencing these symptoms. Your care team can recommend nutrient-based oral care solutions if you are experiencing mucositis or mouth sores caused by cancer treatment.
How long after brain radiation will I feel better?
Radiotherapy to the brain can cause short term side effects such as tiredness and sickness. These side effects usually improve a few weeks after treatment. You may also have long term side effects which can continue for a lot longer and sometimes might be permanent.
What can I expect after my first radiation treatment?
The most common early side effects are fatigue (feeling tired) and skin changes. Other early side effects usually are related to the area being treated, such as hair loss and mouth problems when radiation treatment is given to this area. Late side effects can take months or even years to develop.
How long does it take to get rid of glioblastoma?
The most common schedule of radiation therapy for a glioblastoma is six weeks of daily treatment with a low dose of radiation. This amount of radiation is well tolerated by most people. It causes few side effects.
What is the treatment for glioblastoma?
Radiation also may be used as the sole treatment when a glioblastoma tumor is in an area that is not appropriate for surgery. Radiation is usually given along with a chemotherapy drug called temozolomide (Temodar ® ). The drug makes the tumor more sensitive to the radiation .
What is IMRT radiation?
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) use s sophisticated software and 3-D images from CT scans to focus radiation directly on a tumor. These pencil-thin beams vary in intensity and conform to the specific shape and size of the tumor. This highly focused approach reduces radiation exposure to healthy tissue in the brain. IMRT can also decrease the chance of side effects.
Where is Proton Therapy done?
In 2019, Memorial Sloan Kettering began delivering proton therapy at the New York Proton Center, a state-of-the-art facility in upper Manhattan.
Can you get radiation therapy for gliomas?
We may also recommend it for tumors that come back after initial treatment. We use two main types of radiation therapy for gliomas. Which is the best for you depends on the type, size, and location of the tumor.
Can radiation be directed precisely to the tumor?
Radiation can be directed precisely to the tumor, sparing the nearby healthy tissue and leading to better outcomes. We can verify within millimeters that the setup for each MSK patient is accurate and can be reproduced from treatment to treatment.
Is radiation safe for MSK?
Keeping you as safe as possible during radiation therapy is as important to your MSK care team as the treatment itself. Our medical physicists work closely with radiation oncologists to carefully plan radiation dosages before treatment. Medical physicists are also there during treatment to ensure that the radiation is delivered correctly and in the best possible places.
What is glioblastoma multiforme?
Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM): Advancing Treatment for a Dangerous Brain Tumor. If brain tumors were sharks, the glioblastoma multiforme, or GBM, would be the great white. More than any other brain cancer, GBM inspires fear because of its almost unstoppable aggression.
What is a grade 4 glioma?
GBM is a grade 4 glioma brain tumor arising from brain cells called glial cells. A brain tumor's grade refers to how likely the tumor is to grow and spread. Grade 4 is the most aggressive and serious type of tumor. The tumor's cells are abnormal, and the tumor creates new blood vessels as it grows.
What is the drug used for brain cancer?
Another chemotherapy drug called temozolomide was approved by the FDA in 2013 and is commonly used to treat GBMs and other advanced brain cancers. The drug is taken in pill form and works by slowing down tumor growth.
Can a neurosurgeon remove a tumor?
To start, the neurosurgeon will remove as much of the tumor as possible and may implant medicated wafers right into the brain. Developed at Johns Hopkins, these wafers dissolve naturally and gradually release chemotherapy drugs into the tumor area over time.
What is the treatment for glioblastoma?
Immunotherapy. Immunotherapy is a type of treatment that uses the immune system, or principles of the immune system, to treat cancer. There are, however, many different types of immunotherapy with a few options offering hope in treating recurrent glioblastoma.
How long does it take to live with glioblastoma?
Without treatment, the median survival with glioblastoma is only a few months, but even with treatment, survival is frequently only around one year. The five-year survival rate from the disease is roughly 5.0%. For people who have surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible along with radiation and chemotherapy, the overall median survival (the time after which 50% of people have died and 50% are still alive) is only 14 months. 2
Why is glioblastoma important?
With glioblastoma, it's also important for people to understand the purpose, potential risks, and potential benefits of clinical trials. Many of the newer treatments that are being used for glioblastoma are only being used in clinical trials at the current time.
What are the factors that affect the prognosis of a tumor?
There are several factors that affect prognosis, including: 1 Age at diagnosis (children tend to have a better prognosis than adults, especially older adults) 2 Performance status (how well a person is able to carry on normal daily activities) 3 Tumor volume (how big and how extensive the tumor) 4 The location of the tumor in the brain 5 The specific treatments used 6 The amount of tumor that could be surgically removed 7 MBMT (O-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase) promoter methylation 8 IDH1 status 9 Timing of recurrence (earlier recurrence may have a poorer prognosis) 5
Can you take immunotherapy before surgery?
As noted above under surgery, combining one type of immunotherapy (a checkpoint inhibitor) before surgery has a significant benefit on survival rate with recurrent glioblastoma. However, the kind of responses sometimes seen with melanoma and lung cancer to these drugs have yet to be seen with glioblastoma. It's thought that part of the reason is that glioblastomas have fewer of a type of immune cells known as T cells in the tumor.
Does glioblastoma recur?
Glioblastoma Recurrence. Unfortunately, even when glioblastoma is discovered and treated aggressively, it almost always recurs. 1 It is this very high recurrence rate that is the reason there are so few long term survivors of the disease.
Is glioblastoma recurrence a rule or exception?
Coping. Glioblastoma recurrence is, unfortunately, the rule rather than the exception. Even when it appears a tumor has been eliminated with treatment, there is a high chance it will return. Sadly, there have also been relatively few treatment options when these cancers come back. Several newer treatments have been approved or are in clinical ...
How long can you live with glioblastoma?
Life Expectancy Without Treatment. Without treatment of any kind, the typical glioblastoma life expectancy is generally accepted to be around 3 months. This is generally for people who have inoperable tumors and are too sick to undergo radiation or chemo.
What is the life expectancy of a cancer patient?
Life expectancy with for a cancer patient seems to be defined as “median survival time since diagnosis”, or the amount of time that 50% of patients survive after diagnosis. Median survival time is usually measured in months for glioblastoma.
