
How many radiation treatments expected for breast cancer?
Nov 14, 2021 · How Does Radiation Treatment for Breast Cancer Work? You usually have radiotherapy to the whole breast after having breast conserving surgery . You generally start it about 4 to 6 weeks after surgery. If you need to have …
What is the best treatment for breast cancer?
Radiation therapy for early breast cancer most often involves treatment once a day, 5 days a week, for 3-6 weeks. Getting to and from the treatment center every day for weeks can be hard, especially if you live far away or, if children or other family members rely on you for care.
How effective is oral chemotherapy for breast cancer?
What type of radiation is used for breast cancer?
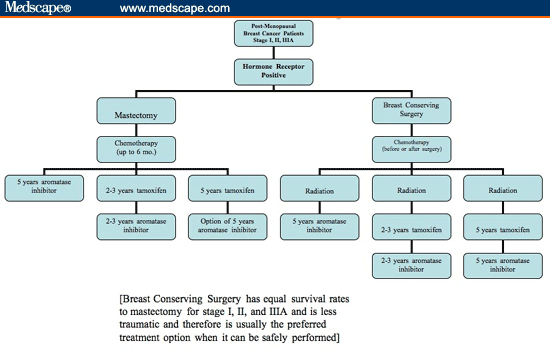
How many rounds of radiation is normal for breast cancer?
A common treatment schedule (course) historically has included one radiation treatment a day, five days a week (usually Monday through Friday), for five or six weeks. This course is still commonly used in people who require radiation to the lymph nodes.Mar 6, 2021
How long is a radiation treatment session?
In most instances, treatments are usually spread out over several weeks to allow your healthy cells to recover in between radiation therapy sessions. Expect each treatment session to last approximately 10 to 30 minutes.Jul 1, 2020
Is radiation for breast cancer painful?
The radiation treatment procedure is painless, but it may cause some skin discomfort over time. When treating early-stage breast cancer, radiation therapy is often given after surgery.Feb 2, 2022
What is the success rate of radiation therapy for breast cancer?
Radiation therapy decreased the risk of dying from cancer by approximately 33%. The probability of surviving 10 years from treatment was increased from 54% to 64% and 45% to 54% in the two studies, respectively. No significant long-term side effects of radiation therapy were reported.
What can you not do during radiation treatment?
Avoid raw vegetables and fruits, and other hard, dry foods such as chips or pretzels. It's also best to avoid salty, spicy or acidic foods if you are experiencing these symptoms. Your care team can recommend nutrient-based oral care solutions if you are experiencing mucositis or mouth sores caused by cancer treatment.Nov 8, 2021
Can you drive yourself to radiation treatments?
Almost all patients are able to drive while receiving radiotherapy treatment. However, with some types of cancer, driving may NOT be recommended due to fatigue or strong pain medication.
Do you lose hair with radiation for breast cancer?
Radiotherapy. Like chemotherapy, radiotherapy affects healthy cells as well as cancer cells so can cause hair loss, but only in the specific area being treated. This means that you will only lose hair from that area.
Is radiation worse than chemo?
Since radiation therapy is focused on one area of your body, you may experience fewer side effects than with chemotherapy. However, it may still affect healthy cells in your body.Mar 27, 2020
How will I feel after radiation for breast cancer?
The main short-term side effects of external beam radiation therapy to the breast are: Swelling in the breast. Skin changes in the treated area similar to a sunburn (redness, skin peeling, darkening of the skin) Fatigue.
Do you lose hair with radiation?
Radiation therapy also can cause hair loss Radiation therapy also attacks quickly growing cells in your body, but unlike chemotherapy, it affects only the specific area where treatment is concentrated. If you have radiation to your head, you'll likely lose the hair on your head.
Which type of breast cancer is most likely to recur?
Research suggests that estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer is more likely to come back more than five years after diagnosis. In this study, the researchers looked at the risk of late breast cancer recurrence, meaning the breast cancer came back 10 or more years after diagnosis.Feb 22, 2022
Do you need radiation for Stage 1 breast cancer?
Stage 1 is highly treatable, however, it does require treatment, typically surgery and often radiation, or a combination of the two. Additionally, you may consider hormone therapy, depending on the type of cancer cells found and your additional risk factors.
What is radiation therapy for breast cancer?
Radiation therapy for breast cancer uses high-energy X-rays, protons or other particles to kill cancer cells. Rapidly growing cells, such as cancer cells, are more susceptible to the effects of radiation therapy than are normal cells. The X-rays or particles are painless and invisible.
What is breast radiation?
Radiation to part of the breast. Radiation therapy to part of the breast (partial-breast irradiation) may be an option for some early-stage breast cancers. This technique directs internal or external radiation to the area around where the cancer was removed.
Why do we need radiation therapy?
Why it's done. Radiation therapy kills cancer cells. It's often used after surgery to reduce the risk that the cancer will come back. It can also be used to provide relief from pain and other symptoms of advanced breast cancer.
What is the treatment for breast cancer?
Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy. External beam radiation uses high-powered beams of energy to kill cancer cells. Beams of radiation are precisely aimed at the cancer using a machine that moves around your body. Radiation therapy for breast cancer uses high-energy X-rays, protons or other particles to kill cancer cells.
How big is a breast tumor?
Large tumor size. A breast cancer larger than about 2 inches (5 centimeters) generally carries a higher risk of recurrence than do smaller cancers. Tissue margins with signs of breast cancer. After breast tissue is removed, the margins of the tissue are examined for signs of cancer cells.
Can breast cancer be removed with surgery?
Breast cancers that can't be removed with surgery. Inflammatory breast cancer, an aggressive type of cancer that spreads to the lymph channels of the skin covering the breast. This type of cancer is typically treated with chemotherapy before a mastectomy, followed by radiation, to decrease the chance of recurrence.
What is the procedure to remove breast cancer?
Internal radiation (brachytherapy). After you have surgery to remove the cancer, your doctor temporarily places a radiation-delivery device in your breast in the area where the cancer once was. A radioactive source is placed into the device for short periods of time over the course of your treatment.
What is the best treatment for breast cancer after lumpectomy?
It’s important to follow the treatment plan prescribed by your health care provider in terms of: Timing. Dose. Frequency. Completing radiation therapy . Radiation therapy after lumpectomy lowers the risk of breast cancer recurrence and may increase the chances of survival [ 4 ]. It’s usually recommended after lumpectomy.
What is the goal of radiation therapy?
The goal of radiation therapy is to kill any cancer that might be left in the breast or nearby lymph nodes after surgery. Radiation therapy is an option for many women who have: Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS, non-invasive breast cancer) Early breast cancer. Radiation therapy is standard treatment for most women who have:
What is DCIS radiation?
Radiation therapy and DCIS. Radiation therapy is often given to women who are treated with lumpectomy (also called breast-conserving surgery) for DCIS. In rare cases, radiation therapy is given to women treated with mastectomy for DCIS. Learn more about treatment for DCIS.
Where are lymph nodes located in breast cancer?
These can include the lymph nodes in the underarm area (axillary nodes), around the collarbone or near the breastbone (internal mammary nodes). Going Through Radiation Therapy. Radiation therapy is carefully planned and precisely given. Your treatment is tailored to your breast cancer and your body.
Can radiation therapy cause breast cancer?
Radiation therapy can cause harm to normal tissue during and after treatment in people who have certain inherited gene mutations. In some women at higher risk of breast cancer recurrence, radiation therapy may still be used. Past radiation therapy to the same breast or to the same side of the chest.
What are the side effects of radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy has some short-term side effects (such as skin tenderness) and for some women, long-term side effects (such as lymphedema ). Learn more about possible side effects of radiation therapy.
Can breast implants be removed?
In these cases, the implant may need to be removed. Radiation therapy and breast reconstruction with implants.

Overview
Why It's Done
- Radiation therapy kills cancer cells. It's often used after surgery to reduce the risk that the cancer will come back. It can also be used to provide relief from pain and other symptoms of advanced breast cancer.
Risks
- Side effects from radiation therapy differ significantly depending on the type of treatment and which tissues are treated. Side effects tend to be most significant toward the end of your radiation treatment. After your sessions are complete, it may be several days or weeks before side effects clear up. Common side effects during treatment may include: 1. Mild to moderate fatigu…
How You Prepare
- Before your radiation treatments, you'll meet with your radiation therapy team, which may include: 1. A radiation oncologist,a doctor who specializes in treating cancer with radiation. Your radiation oncologist determines the appropriate therapy for you, follows your progress and adjusts your treatment, if necessary. 2. A radiation oncology medical physicist and a dosimetrist,who make c…
What You Can Expect
- Radiation therapy usually begins three to eight weeks after surgery unless chemotherapy is planned. When chemotherapy is planned, radiation usually starts three to four weeks after chemotherapy is finished. You will likely have radiation therapy as an outpatient at a hospital or other treatment facility. A common treatment schedule (course) historically has included one ra…
Results
- After you complete radiation therapy, your radiation oncologist or other medical professionals will schedule follow-up visits to monitor your progress, look for late side effects and check for signs of cancer recurrence. Make a list of questions you want to ask members of your care team. After your radiation therapy is completed, tell your medical professional if you experience: 1. Persiste…
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiesof tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.