Medication
Mar 11, 2021 · Dermatologists recommend treating impetigo. It can help cure the impetigo and prevent others from getting this highly contagious skin infection. With treatment, impetigo is usually no longer contagious within 24 to 48 hours. Without treatment, impetigo often clears on its own in two to four weeks.
How long does impetigo last without treatment?
There is no over-the-counter (OTC) treatment for impetigo. Controlling and Preventing Impetigo Untreated, impetigo often clears up on its own after a few …
How is impetigo treated and treated?
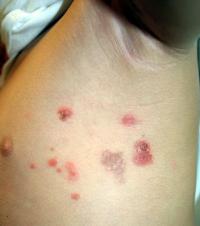
Impetigo starts as a red, itchy sore. As it heals, a crusty, yellow or “honey-colored” scab forms over the sore. In general, impetigo is a mild infection that can occur anywhere on the body. It most often affects exposed skin, such as around the nose and mouth or on the arms or legs.
What is the cost of antibiotics for impetigo?
Jul 16, 2020 · Research has shown that milder cases of impetigo go away faster when they're treated with particular antibiotic creams. It isn't clear whether antiseptic solutions or creams can help. Impetigo is a skin infection that is usually itchy and sometimes painful, and is most common in children. It is caused by bacteria and is highly contagious. Left untreated, it usually clears up …
What is the incubation period of impetigo?
May 07, 2022 · Untreated lesions of nonbullous impetigo may rarely progress to ecthyma, a deep dermal infection, after which subsequent scarring can occur. With appropriate treatment, lesions usually resolve...

How long does it take for impetigo to clear?
With treatment, impetigo is usually no longer contagious within 24 to 48 hours. Without treatment, impetigo often clears on its own in two to four weeks. During this time, there is a greater risk of developing complications. You may see new blisters and sores.
What is the best treatment for impetigo?
An antibiotic usually cures impetigo. Dermatologists often prescribe an antibiotic that you apply to the skin, such as mupirocin or retapamulin. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved retapamulin to treat impetigo in children as young as 9 months old.
Can you use antibiotics on skin with impetigo?
This is called off-label use and is legal. It can also be very helpful. If a dermatologist prescribes an antibiotic you apply to the skin, you would apply it to the skin with impetigo. If you have several outbreaks of impetigo, you may need to apply it inside the nostrils.
Can antibiotics be used to treat impetigo?
If a dermatologist prescribes an antibiotic you apply to the skin, you would apply it to the skin with impetigo. If you have several outbreaks of impetigo, you may need to apply it inside the nostrils. The bacteria that cause impetigo often thrive in the nostrils. Sometimes stronger medicine is necessary.
How to get rid of impetigo on skin?
The following steps are often very helpful: Soak the skin with impetigo in warm water and soap to gently remove dirt and crusts. Apply the antibiotic (or other medicine) as prescribed. Cover the skin with impetigo to help it heal and prevent spreading the infection to others.
How long do you have to stay home from school with impetigo?
Because impetigo is very contagious, a child may need to stay home from school for a few days. If this is necessary, your dermatologist will tell you when your child can return to school.
What antibiotics are prescribed for impetigo?
Dermatologists often prescribe an antibiotic that you apply to the skin, such as mupirocin or retapamulin. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved retapamulin to treat impetigo in children as young as 9 months old. Mupirocin is FDA approved to treat people 12 years of age and older.
How long does it take for impetigo to clear up?
Untreated, impetigo often clears up on its own after a few days or weeks, Smith says. The key is to keep the infected area clean with soap and water and not to scratch it. The downside of not treating impetigo is that some people might develop more lesions that spread to other areas of their body.
What is the best treatment for impetigo?
Impetigo is usually treated with topical or oral antibiotics. If you have multiple lesions or if there is an outbreak, your doctor might prescribe an oral antibiotic. There is no over-the-counter (OTC) treatment for impetigo.
How to spread impetigo?
And you can infect others. “To spread impetigo, you need fairly close contact — not casual contact — with the infected person or the objects they touched,” he says. Avoid spreading impetigo to other people or other parts of your body by: 1 Cleaning the infected areas with soap and water. 2 Loosely covering scabs and sores until they heal. 3 Gently removing crusty scabs. 4 Washing your hands with soap and water after touching infected areas or infected persons.
What causes impetigo on the skin?
What Causes Impetigo. Two types of bacteria found on our skin cause impetigo: Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes (which also causes strep throat). Most of us go about our lives carrying around these bacteria without a problem, Smith says.
Can you get impetigo more than once?
Anyone can get impetigo — and more than once, Smith says. Although impetigo is a year-round disease, it occurs most often during the warm weather months. There are more than 3 million cases of impetigo in the United States every year. “We typically see impetigo with kids 2 to 6 years old, probably because they get more cuts and scrapes ...
Can you touch someone with impetigo?
Because impetigo spreads by skin-to-skin contact, there often are small outbreaks within a family or a classroom, Smith says. Avoid touching objects that someone with impetigo has used, such as utensils, towels, sheets, clothing and toys.
What are the two types of bacteria that cause impetigo?
Two types of bacteria found on our skin cause impetigo: Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes (which also causes strep throat). Most of us go about our lives carrying around these bacteria without a problem, Smith says.
What is the best treatment for impetigo?
Antibiotics Treat Impetigo. Impetigo is treated with antibiotics that are either rubbed onto the sores (topical antibiotics) or taken by mouth (oral antibiotics). A doctor might recommend a topical ointment, such as mupirocin or retapamulin, for only a few sores. Oral antibiotics can be used when there are more sores.
How to keep impetigo from spreading?
These items should not be shared with anyone else. After they have been washed, these items are safe for others to use. The best way to keep from getting or spreading group A strep is to wash your hands often .
What is impetigo in Spanish?
Español (Spanish) minus. Related Pages. Impetigo (im-peh-TIE-go) is a bacterial infection of the skin that is more common in young children than other ages . Doctors use antibiotics to treat impetigo and prevent rare, but serious long-term health problems. Antibiotics can also help protect others from getting sick.
What is impetigo in children?
Related Pages. Impetigo (im-peh-TIE-go) is a bacterial infection of the skin that is more common in young children than other ages. Doctors use antibiotics to treat impetigo and prevent rare, but serious long-term health problems. Antibiotics can also help protect others from getting sick.
Why do doctors prescribe antibiotics for impetigo?
Doctors use antibiotics to treat impetigo and prevent rare, but serious long-term health problems. Antibiotics can also help protect others from getting sick.
What is impetigo on the body?
As it heals, a crusty, yellow or “honey-colored” scab forms over the sore. In general, impetigo is a mild infection that can occur anywhere on the body. It most often affects exposed skin, such as around the nose and mouth or on the arms or legs.
Where does impetigo occur?
In general, impetigo is a mild infection that can occur anywhere on the body. It most often affects exposed skin, such as around the nose and mouth or on the arms or legs. Symptoms include red, itchy sores that break open and leak a clear fluid or pus for a few days.
How long does it take for impetigo to develop?
The incubation period of impetigo, from colonization of the skin to development of the characteristic lesions, is about 10 days. 1 It is important to note not everyone who becomes colonized will go on to develop impetigo.
How to prevent impetigo?
The spread of impetigo can be prevented by covering lesions, treating with antibiotics, and practicing good hand hygiene. Clothing, linens, and towels used by an infected person should be washed every day and not shared with others in the household.
Is impetigo a contagious infection?
Impetigo. Impetigo is a superficial bacterial skin infection that is highly contagious. Impetigo can be caused by Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphylococcus aureus. This page focuses on infections caused by S. pyogenes, which are also called group A Streptococcus or group A strep.
What is Impetigo caused by?
Impetigo can be caused by Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphylococcus aureus. This page focuses on infections caused by S. pyogenes, which are also called group A Streptococcus or group A strep.
How is streptococcal impetigo spread?
Streptococcal impetigo is most commonly spread through direct contact with other people with impetigo. People with impetigo are much more likely to transmit the bacteria than asymptomatic carriers. Crowding, such as found in schools and daycare centers, increases the risk of disease spread from person to person.
Can impetigo be transmitted?
People with impetigo are much more likely to transmit the bacteria than asymptomatic carriers. Crowding, such as found in schools and daycare centers, increases the risk of disease spread from person to person. Lesions can be spread (by fingers and clothing) to other parts of the body.
What age group is most likely to get impetigo?
Risk Factors. Impetigo can occur in people of all ages, but it is most common among children 2 through 5 years of age. Scabies infections and activities that result in cutaneous cuts or abrasions (e.g., sports such as wrestling and football) increase the risk of impetigo.
How to prevent impetigo?
Other tips to avoid impetigo include: Keep hands clean: Wash hands regularly. Use alcohol-based sanitizer if you don’t have soap and water. Practice good hygiene: Clip your (and your child’s) fingernails regularly to avoid scratching.
Can antibiotics help with impetigo?
Antibiotics can treat impetigo. A provider may prescribe topical antibiotics to put on the skin. Your child may need to take oral antibiotics (a liquid or pill) if the condition covers a large area of skin or multiple body parts. Examples of antibiotic treatments include:
How old do you have to be to get impetigo?
Impetigo usually happens to children between ages 2 and 6. Older children and adults can also get it. You may also be at higher risk if you: Live in a tropical climate, with hot, humid summers and mild winters. Have a scabies infection.
Can you get impetigo from a cut?
When you get a cut, bite or scratch that opens the skin, bacteria can enter and cause an impetigo infection. But impetigo can infect the skin even if it’s not broken or punctured. Impetigo happens more often in warmer months when children are outside more. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
What is bullous impetigo?
Bullous impetigo is a rare type of impetigo. It has larger blisters that don’t break open as easily. It often appears on the neck, torso, armpits or groin. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
What causes impetigo in the body?
The main cause of impetigo is a bacterial infection. The bacteria usually enters the skin through a cut, scrape, rash or insect bite. Most of the time, the cause is the Staphylococcus aureus (“staph” bacteria). Sometimes, group A Streptococcus bacteria can cause it. This type of bacteria also leads to strep throat and fever.
What does it mean when your child has impetigo?
If you or your child has impetigo caused by staph bacteria, you may notice: Reddish skin surrounding red blisters, full of liquid or pus that eventually looks cloudy. Blisters that burst easily and leak. Raw, shiny areas that scab over with a yellow/brown crust.
How long does it take for impetigo to clear up?
Treatment can help the impetigo clear up within 10 days and limit the chances of it spreading. (2) “If you’re having it present for a couple of days, you should see a provider about the infection, and it should be appropriately treated,” Oza says.
How long does it take for an antibiotic to treat impetigo?
Oza says he’d likely prescribe one for 7 to 10 days, though you’ll probably see results much sooner.
Can you treat impetigo with topical treatment?
For mild cases of impetigo, your doctor may recommend topical treatment . Alamy. Impetigo is a bacterial infection that occurs most often in young children ages 2 to 5. ( 1) “Kids get it by being around each other, kind of rubbing up against each other,” says Suzanne Friedler, MD, a board-certified fellow of the American Academy ...
What age does impetigo occur?
Impetigo is a bacterial infection that occurs most often in young children ages 2 to 5. ( 1) “Kids get it by being around each other, kind of rubbing up against each other,” says Suzanne Friedler, MD, a board-certified fellow of the American Academy of Dermatology and a clinical instructor at Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York City.
Can you catch impetigo from your child?
Impetigo is contagious and is passed through direct physical contact. ( 2) But just because your child touches another child with impetigo doesn’t mean he ...
Can you get impetigo from a bug bite?
But if the skin is compromised in some way, whether through a scrape or a bug bite or an eczema flare-up, the risk of developing impetigo increases.
Can impetigo be treated?
The good news is that both types of impetigo are easily treated. The key is to treat it early. “You have an infection on your skin and if you don’t treat it, it can continue to worsen,” Oza says. “It’s something that you want to take care of.".
How long does it take for bullous impetigo to heal?
aureus, results in large, flaccid bullae and is more likely to affect intertriginous areas. Both types usually resolve within two to three weeks without scarring, and complications are rare, with the most serious being poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis.
Is impetigo a self-limited condition?
Impetigo is usually a self-limited condition , and although rare, complications can occur. These include cellulitis (nonbullous form), septicemia, osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, lymphangitis, lymphadenitis, guttate psoriasis, staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, and acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis, with poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis being the most serious. 14 The number of possible causes, incidence, and clinical severity of acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis have decreased, because the causative organism of impetigo has shifted from S. pyogenes to S. aureus. 13 Most cases of poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis in the United States are associated with pharyngitis. The strains of S. pyogenes implicated in impetigo are thought to have minimal nephritogenic potential. 13 There are no data to indicate that antibiotic treatment of impetigo has any effect on preventing the development of acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis, which can occur in up to 5% of patients with nonbullous impetigo. 1, 11, 15, 16 Rheumatic fever does not appear to be a complication of impetigo. 16
What is impetigo contagiosa?
Impetigo is the most common bacterial skin infection in children two to five years of age. There are two principal types: nonbullous (70% of cases) and bullous (30% of cases). Nonbullous impetigo, or impetigo contagiosa, is caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes, ...
What is impetigo in children?
References. Impetigo is the most common bacterial skin infection in children two to five years of age. There are two principal types: nonbullous (70% of cases) and bullous (30% of cases). Nonbullous impetigo, or impetigo contagiosa, is caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes, and is characterized by honey-colored crusts on ...
What causes nonbullous impetigo?
Nonbullous impetigo, or impetigo contagiosa, is caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes, and is characterized by honey-colored crusts on the face and extremities. Impetigo primarily affects the skin or secondarily infects insect bites, eczema, or herpetic lesions.
Why is penicillin not used for impetigo?
Oral penicillin should not be used for impetigo because it is less effective than other antibiotics. Oral erythromycin and macrolides should not be used to treat impetigo because of emerging drug resistance. There is insufficient evidence to recommend topical disinfectants for the treatment of impetigo.
Can macrolides be used for impetigo?
B. 8, 12. Oral erythromycin and macrolides should not be used to treat impetigo because of emerging drug resistance. B. 8, 12. There is insufficient evidence to recommend topical disinfectants for the treatment of impetigo.
