Medication
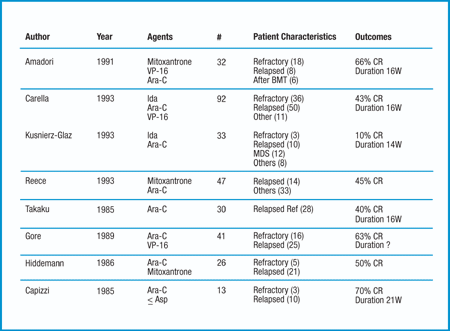
Mar 15, 2016 · But in younger people you are conventionally thinking about intensive chemotherapy, two, three or four cycles, and in people under 65 or 70 who are fit the other decision would be whether a bone marrow or stem cell transplant is required. That’s increasingly used as an important way of maximising the anti-leukemic potential of chemotherapy.
Procedures
Clinical trials of new treatment approaches might also be an option. If AML comes back sooner than 12 months, most doctors will advise a stem cell transplant for younger patients, if possible. Taking part in a clinical trial is another option.
Self-care
Dec 09, 2021 · People older than age 60 don’t typically respond to treatment as well, with about half of them going into remission after induction. Some people who go into remission stay in remission. Still, for...
Nutrition
Mar 04, 2022 · Treatment options for adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, stem cell transplant, and other medications. Get detailed information about the treatment of new and recurrent AML in this expert-reviewed summary. ... a spinal needle (a long, thin needle) is inserted into the lower part of the spinal column to ...
Can acute myeloid leukemia (AML) be cured?
Dec 10, 2021 · How long is chemo for AML? Chemotherapy treatments for AML can be intense. Doctors usually give chemotherapy for AML in two or three phases. Induction chemotherapy is very strong and only given for a week to kill off cancer cells in the blood. Consolidation chemotherapy is given in multiple cycles after the patient has recovered from induction.
What are the treatment phases of AML?
The goal of treatment for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is to put the leukemia into complete remission (the bone marrow and blood cell counts return to normal), ... With consolidation and maintenance, about 8 or 9 out of 10 people with APL stay in long-term remission.
What if AML comes back after treatment?
If this happens, treatment options would be as described in If Acute Myeloid Leukemia Doesn’t Respond or Comes Back After Treatment.. It’s unusual for AML to come back if there are still no signs of the leukemia within a few years after treatment. This can happen, however, especially with the acute promyelocytic (APL) subtype of AML.
What is the treatment for acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL)?
Once you finish treatment, you'll see your doctor every few months for several years. If tests show that your blood and bone marrow are free of AML, you …

How many rounds of chemo is normal for AML?
Most people have 2 rounds of induction chemotherapy. The treatment will be carried out in hospital or in a specialist centre, as you'll need very close medical and nursing supervision. You may be able to go home between treatment rounds.
How long does chemotherapy take AML?
AML chemotherapy usually starts with 1 week of intense treatment. After this, the person may receive a 5-day treatment session every 4 weeks, with the cycle repeating three or four times. Doctors usually recommend a combination of chemotherapy medications rather than a single one.Apr 28, 2021
Can you fully recover from AML?
Most often, acute myeloid leukemia (AML) will go into remission after the initial treatment. But sometimes it doesn't go away completely, or it comes back (relapses) after a period of remission. If this happens, other treatments can be tried, as long as a person is healthy enough for them.Aug 21, 2018
How long are you in the hospital with AML?
Most patients will need to stay in the hospital for 3 to 5 weeks during induction therapy before their blood counts return to normal. Sometimes, 2 rounds of therapy are needed to achieve a CR. Approximately 75% of younger adults with AML and about 50% of patients older than 60 achieve a CR after treatment.
Why is AML so hard to treat?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML): the pervasive aggressor Generally a disease impacting older people, the average age of an AML patient is 68 at the time of diagnosis. Because it's so aggressive, treatment for AML is considered harder on the body, especially for older patients with other health challenges.Apr 19, 2018
Can you beat AML leukemia?
According to the American Cancer Society (ACS), around 90 percent of people with an AML type known as acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) will go into remission after “induction” (first round) of chemo. For most other types of AML, the remission rate is around 67 percent.
Can you live a normal life after AML?
What are 'Late Effects'? Many people enjoy long and healthy lives after being successfully treated for their blood cancer. Sometimes, however, the treatment can affect a person's health for months or even years after it has finished. Some side effects may not be evident until years after treatment has ceased.Jun 19, 2019
Can you live a full life after AML?
The average age at diagnosis in the U.S. is 66 years old (3). Approximately 60 to 70% of adult patients (aged 18-65 years) will achieve complete remission (CR), with 50-70% of first CR patients relapsing within 3 years. Approximately 22.6% of adult AML patients survive to five years (3).
What are the odds of beating AML?
Approximately 60% to 70% of adults with AML can be expected to attain CR status after appropriate induction therapy. More than 25% of adults with AML (about 45% of those who attain CR) can be expected to survive 3 or more years and may be cured.Mar 16, 2022
How long can you live with AML without treatment?
Overall survival for AML Without treatment, survival is usually measured in days to weeks. With current treatment regimens, 65%–70% of people with AML reach a complete remission (which means that leukemia cells cannot be seen in the bone marrow) after induction therapy.
How aggressive is AML leukemia?
AML is an aggressive type of cancer that can develop rapidly, so treatment usually needs to begin soon after a diagnosis is confirmed. Chemotherapy is the main treatment for AML. It's used to kill as many leukaemia cells in your body as possible and reduce the risk of the condition coming back (relapsing).
Is leukemia a death sentence?
Today, however, thanks to many advances in treatment and drug therapy, people with leukemia- and especially children- have a better chance of recovery. "Leukemia isn't an automatic death sentence," said Dr. George Selby, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center.Apr 29, 1991
For Most Types of Acute Myeloid Leukemia
If acute myeloid leukemia (AML) doesn’t go away with the first treatment, newer drugs or more intensive doses of chemotherapy (chemo) drugs may be...
For Aml With An IDH2 Gene Mutation
If the leukemia cells have an IDH2 gene mutation, one option if the leukemia doesn’t go away or if it comes back later might be treatment with a ta...
For Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
For patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) who don’t respond to initial treatment with chemo plus ATRA or who relapse, arsenic trioxide (...
What is the treatment for AML?
For AML with a mutation in the IDH1 or IDH2 gene. If the leukemia cells have an IDH1 or IDH2 gene mutation, one option if the leukemia doesn’t go away or if it comes back later might be treatment with a targeted drug called an IDH inhibitor, such as ivosidenib (Tibsovo) for AML with an IDH1 mutation, or enasidenib ...
How long does it take for ATRA to relapse?
For patients whose initial treatment was with the non-chemo drugs all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and arsenic trioxide (ATO) and who relapse early (usually within about 6 months), treatment will most likely be with some of the same chemo drugs used to treat other types of AML.
How to tell if you have leukemia?
Other common symptoms from leukemia are low blood counts and fatigue. Medicines or blood transfusions may be needed to help correct these problems. Nausea and loss of appetite can be treated with medicines and high-calorie food supplements. Infections that occur may be treated with antibiotics.
What is supportive care for leukemia?
Supportive treatment for leukemia that won't go away. If further treatment or a clinical trial is not an option, the focus of treatment may shift to controlling symptoms caused by the leukemia, rather than trying to cure it. This is called palliative treatment or supportive care.
What is the best treatment for a swollen ear?
Treatments that may be helpful include radiation therapy and appropriate pain-relieving medicines. If medicines such as aspirin and ibuprofen don’t help with the pain, stronger opioid medicines such as morphine are likely to be helpful.
Can you get AML with chemotherapy?
If AML doesn’t go away completely with induction treatment, sometimes a second, similar course of chemotherapy (chemo), often called reinduction, can be tried. If this isn't helpful, treatment with other chemo drugs or more intensive doses of chemo may be tried, if the person can tolerate them. A stem cell transplant may be an option for some people, as it can allow higher doses of chemo to be used. Clinical trials of new treatment approaches may also be an option.
Does AML go away?
Most often, acute myeloid leukemia (AML) will go into remission after the initial treatment. But sometimes it doesn't go away completely, or it comes back (relapses) after a period of remission. If this happens, other treatments can be tried, as long as a person is healthy enough for them.
How long does it take for AML to go away?
Some people who go into remission stay in remission. Still, for many, AML can return over time. The five-year overall survival rate for AML is 27.4 percent. Trusted Source. , according to the National Cancer Institute (NCI).
What is the treatment for AML?
Most people with AML receive chemotherapy treatments. These medications rapidly kill dividing cells, such as cancer cells. Chemotherapy can lead to remission, which means a person doesn’t have symptoms of the disease and their blood cell counts are in a normal range.
Why is AML called acute?
Doctors call AML “ acute ” because the condition can progress rapidly. The term “ leukemia ” refers to cancers of the bone marrow and blood cells. The word myeloid, or myelogenous, refers to the cell type it affects. Myeloid cells are precursors to other blood cells.
What is AML in medical terms?
What is acute myeloid leukemia (AML)? Acute myeloid leukemia, or AML, is a type of cancer that affects the bone marrow and blood. It’s known by a variety of names, including acute myelogenous leukemia and acute non-lymphocytic leukemia. AML is the second most common leukemia type in adults. Doctors call AML “ acute ” because ...
How many people go into remission after chemo?
Around 90 percent of people with an AML type known as acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) will go into remission after “induction” (first round) of chemo. This is according to the American Cancer Society (ACS). For most other types of AML, the remission rate is around 67 percent.
What is the prognosis for AML?
The outlook and prognosis for AML varies widely. Doctors consider many factors when giving someone a prognosis, such as the person’s age or type of AML. Much of it is based on the outcomes and analysis of blood tests, imaging studies, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examinations, and bone marrow biopsies.
How old do you have to be to get AML?
Doctors know that survival rates for those diagnosed with AML are more promising for people who are under the age of 60. This could be for a number of reasons. Some people older than the age of 60 may have chronic conditions or may not be in good health.
How old do you have to be to get chemo?
How intense the treatment is can depend on a person’s age and health. Doctors often give the most intensive chemo to people under the age of 60, but some older patients in good health may benefit from similar or slightly less intensive treatment.
What is cytarabine ara C?
Cytarabine (ara-C) An anthracycline drug such as daunorubicin (daunomycin) or idarubicin. This is sometimes called a 7 + 3 regimen, because it consists of getting cytarabine continuously for 7 days, along with short infusions of an anthracycline on each of the first 3 days.
Can leukemia be lower with chemo?
Some people with AML have very high numbers of leukemia cells in their blood when they are first diagnosed, which can cause problems with normal blood circulation. This is called leukostasis. Chemo can take a few days to lower the number of leukemia cells in the blood. In the meantime, leukapheresis (sometimes just called pheresis) might be used before chemo.
Can radiation therapy be used for leukemia?
Radiation therapy might be used as well. Patients typically need to stay in the hospital during induction (and possibly for some time afterward). Induction destroys most of the normal bone marrow cells as well as the leukemia cells, so most patients develop dangerously low blood counts, and may be very ill.
Can older people tolerate intensive consolidation?
Older patients or those in poor health may not be able to tolerate intensive consolidation treatment. Often, giving them more intensive therapy raises the risk of serious side effects (including treatment-related death) without providing much more of a benefit. These patients may be treated with:
Can AML be treated with chemo?
The acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) subtype of AML is treated differently. Treatment for AML usually needs to start as quickly as possible after it is diagnosed because it can progress very quickly. Sometimes another type of treatment needs to be started even before the chemo has had a chance to work.
What is the difference between AML and AML?
Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets. Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. This type of cancer usually gets worse quickly if it is not treated.
What is the subtype of AML?
Most AML subtypes are based on how mature (developed) the cancer cells are at the time of diagnosis and how different they are from normal cells. Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) is a subtype of AML that occurs when parts of two genes stick together.
What is the extent of cancer?
In adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the subtype of AML and whether the leukemia has spread outside the blood and bone marrow are used instead of the stage to plan treatment.
What is radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. External radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body to send radiation toward the cancer. Total-body irradiation sends radiation toward the whole body. It is a type of external radiation that may be used to prepare the body for a stem cell transplant when the leukemia has recurred.
What is the name of the drug that kills leukemia cells?
Arsenic trioxide and all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) are anticancer drugs that kill leukemia cells, stop the leukemia cells from dividing, or help the leukemia cells mature into white blood cells. These drugs are used in the treatment of a subtype of AML called acute promyelocytic leukemia.
What is the treatment for acute myeloid leukemia?
Treatment of adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) during the remission phase depends on the subtype of AML and may include the following: Combination chemotherapy. High-dose chemotherapy, with or without radiation therapy, and stem cell transplant using the patient's stem cells . High-dose chemotherapy and stem cell transplant using donor stem ...
What is PDQ cancer?
This PDQ cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of adult acute myeloid leukemia. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
What is the goal of AML treatment?
The goal of treatment for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is to put the leukemia into complete remission (the bone marrow and blood cell counts return to normal), preferably a complete molecular remission (no signs of leukemia in the bone marrow, even using sensitive lab tests), and to keep it that way.
How many people with AML go into remission?
For most types of AML. About 2 out of 3 people with AML who get standard induction chemotherapy (chemo) go into remission. This usually means the bone marrow contains fewer than 5% blast cells, the blood cell counts return to within normal limits, and there are no signs or symptoms of the disease. The actual chance of remission depends ...
How to plan for cancer treatment?
Talk with your doctor about developing a survivorship care plan for you. This plan might include: 1 A suggested schedule for follow-up exams and tests 2 A schedule for other tests you might need in the future, such as early detection (screening) tests for other types of cancer, or tests to look for long-term health effects from your tumor or its treatment 3 A list of possible late- or long-term side effects from your treatment, including what to watch for and when you should contact your doctor 4 Diet and physical activity suggestions
Is it normal to feel depressed after leukemia?
Some amount of feeling depressed, anxious, or worried is normal when leukemia is part of your life. Some people are affected more than others. But everyone can benefit from help and support from other people, whether friends and family, religious groups, support groups, professional counselors, or others.
Is it important to have insurance after cancer treatment?
Even after treatment, it’s very important to have health insurance. Tests and doctor visits cost a lot, and even though no one wants to think of their cancer coming back, this could happen.
Can leukemia come back after treatment?
You may be relieved to finish treatment, but find it hard not to worry about the leukemia coming back. (When leukemia comes back after treatment, it is called a relapse or recurrence.) This is a very common concern in people who have had leukemia. For other people, the leukemia may never go away completely.
What is the second phase of AML?
You'll now go into the second phase of AML treatment, which is called post-remission or consolidation therapy.
How to know if you are in remission?
How do you know you're in remission? Your doctor will tell you that you're in "complete remission" when: 1 There are no signs of leukemia cells, called blasts, in your bone marrow. 2 You don't have symptoms of AML. 3 Your blood count -- which measures the number of blood cells -- is back to normal.
How to heal from chemo?
Eat well. Your body needs a good mix of nutrition to heal. Try to put veggies, fruits, lean protein, whole grains, and low-fat dairy in your diet. If your stomach is upset because you're getting chemo, eat smaller meals every 2 to 3 hours instead of three big meals. Get extra rest.
Can leukemia be detected in bone marrow?
There are no signs of leukemia cells, called blasts, in your bone marrow. You don't have symptoms of AML. Your blood count -- which measures the number of blood cells -- is back to normal.
Treating Leukostasis
Induction
Consolidation
Treating Frail Or Older Adults