Can acute myeloid leukemia (AML) be cured?
Mar 15, 2016 · A transplant itself will depend on finding a donor, and that is an important and curative approach but it’s quite a complex procedure and that would need to be separately discussed with patients, but that of course would involve another month in hospital and then two or three months recovery. Continue Reading….
How long does it take to die from AML?
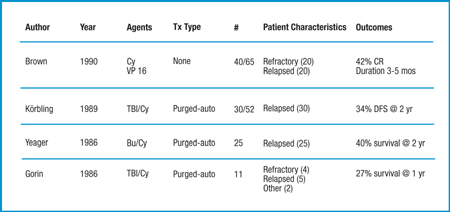
Most often, acute myeloid leukemia (AML) will go into remission after the initial treatment. But sometimes it doesn't go away completely, or it comes back (relapses) after a period of remission. If this happens, other treatments can be tried, as long as a person is healthy enough for them.
What if AML comes back after treatment?
Treatment of AML is usually divided into phases: Induction is the first phase of treatment. It is short and intensive, typically lasting about a week. The goal is to clear the blood of leukemia cells (blasts) and to reduce the number of blasts in the bone marrow to normal.
What are the phases of AML treatment?
Dec 09, 2021 · Acute myeloid leukemia, or AML, is a type of cancer that affects the bone marrow and blood. It’s known by a variety of names, including acute myelogenous leukemia and acute non-lymphocytic leukemia.

How many chemo treatments needed for AML?
Treatment of most patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is typically divided into 2 chemotherapy (chemo) phases: Remission induction (often just called induction)Sep 3, 2020
Can AML be completely cured?
Although AML is a serious disease, it is treatable and often curable with chemotherapy with or without a bone marrow/stem cell transplant (see the Types of Treatment section). It is important to remember that statistics on the survival rates for people with AML are an estimate.
When is AML considered cured?
In adults, treatment results are generally analyzed separately for younger (18-60 y) patients with AML and for older patients (>60 y). With current standard chemotherapy regimens, approximately 40-45% of adults younger than 60 years survive longer than 5 years and are considered cured.
How long does leukemia therapy last?
Treatment often lasts two to three years, although the first months are the most intense. During maintenance phases, children can usually live a relatively normal life and go back to school.Feb 10, 2021
Can you live 20 years with leukemia?
Most people live for about 10 years, but this varies depending on how CLL behaves. People in stages 0 to II may live for 5 to 20 years without treatment. CLL has a very high incidence rate in people older than 60 years.Nov 16, 2021
Can you live a full life after AML?
What are 'Late Effects'? Many people enjoy long and healthy lives after being successfully treated for their blood cancer. Sometimes, however, the treatment can affect a person's health for months or even years after it has finished. Some side effects may not be evident until years after treatment has ceased.Jun 19, 2019
Is AML the worst leukemia?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. It is the most common type of acute leukemia in adults. This type of cancer usually gets worse quickly if it is not treated.Mar 4, 2022
What is the end stages of acute myeloid leukemia?
The majority of AML patients are in a hospital setting at the time of death. Important factors for the location of death include age at diagnosis, disease status, social support and prior induction chemotherapy. Symptoms at the end of life included pain, delirium and bleeding.Dec 3, 2015
Why is AML so hard to treat?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML): the pervasive aggressor Generally a disease impacting older people, the average age of an AML patient is 68 at the time of diagnosis. Because it's so aggressive, treatment for AML is considered harder on the body, especially for older patients with other health challenges.Apr 19, 2018
Can you make a full recovery from leukemia?
As with other types of cancer, there's currently no cure for leukemia. People with leukemia sometimes experience remission, a state after diagnosis and treatment in which the cancer is no longer detected in the body.May 3, 2021
How long is induction therapy for AML?
Most patients will need to stay in the hospital for 3 to 5 weeks during induction therapy before their blood counts return to normal. Sometimes, 2 rounds of therapy are needed to achieve a CR. Approximately 75% of younger adults with AML and about 50% of patients older than 60 achieve a CR after treatment.
How successful is treatment for leukemia?
The cure rates and survival outcomes for patients with ALL have improved over the past few decades. Today, nearly 90 percent of adults diagnosed with ALL achieve a complete remission, which means that leukemia cells can no longer be seen in the bone marrow with a microscope.
For Most Types of Acute Myeloid Leukemia
If acute myeloid leukemia (AML) doesn’t go away with the first treatment, newer drugs or more intensive doses of chemotherapy (chemo) drugs may be...
For Aml With An IDH2 Gene Mutation
If the leukemia cells have an IDH2 gene mutation, one option if the leukemia doesn’t go away or if it comes back later might be treatment with a ta...
For Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
For patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) who don’t respond to initial treatment with chemo plus ATRA or who relapse, arsenic trioxide (...
Why is chemo given in cycles?
For consolidation, chemo is given in cycles, with each period of treatment followed by a rest period to allow the body time to recover.
What is the third phase of chemo?
A third phase called maintenance (or post-consolidation) involves giving a low dose of chemo for months or years after consolidation is finished. This is often used to treat acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), but it is not usually used for other types of AML. Most chemo drugs used to treat AML are given into a vein in the arm (IV), ...
What is the best medication for AML?
6-thioguanine (6-TG) Hydroxyurea. Corticosteroid drugs, such as prednisone or dexamethasone. Methotrexate (MTX) 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) Azacitidine. Decitabine. For more on how chemo is used to treat AML, see Typical Treatment of Most Types of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML), Except APL.
What is chemo for AML?
Chemotherapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Chemotherapy (chemo) is the use of anti-cancer drugs that are injected into a vein, under the skin, or into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), or drugs that are taken by mouth to destroy or control cancer cells . Except when given into the CSF, these drugs enter the bloodstream and reach all areas ...
How long does AML treatment last?
Treatment of AML is usually divided into phases: Induction is the first phase of treatment. It is short and intensive, typically lasting about a week. The goal is to clear the blood of leukemia cells (blasts) and to reduce the number of blasts in the bone marrow to normal.
Where is chemo given?
Most chemo drugs used to treat AML are given into a vein in the arm (IV), although some can be injected under the skin or taken by mouth as pills. If there are signs that the leukemia has reached the brain or spinal cord (which is not common with AML), chemo might also be given into the CSF (known as intrathecal chemo ).
What are the drugs that help prevent viral and fungal infections?
Drugs known as growth factors, such as filgrastim (Neupogen), pegfilgrastim (Neulasta), and sargramostim (Leukine), are sometimes given to increase the white blood cell counts after chemo, to help lower the chance of infection.
How long does it take for AML to go away?
Some people who go into remission stay in remission. Still, for many, AML can return over time. The five-year overall survival rate for AML is 27.4 percent. Trusted Source. , according to the National Cancer Institute (NCI).
What is the prognosis for AML?
The outlook and prognosis for AML varies widely. Doctors consider many factors when giving someone a prognosis, such as the person’s age or type of AML. Much of it is based on the outcomes and analysis of blood tests, imaging studies, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examinations, and bone marrow biopsies.
What is AML in medical terms?
What is acute myeloid leukemia (AML)? Acute myeloid leukemia, or AML, is a type of cancer that affects the bone marrow and blood. It’s known by a variety of names, including acute myelogenous leukemia and acute non-lymphocytic leukemia. AML is the second most common leukemia type in adults. Doctors call AML “ acute ” because ...
Why is AML called acute?
Doctors call AML “ acute ” because the condition can progress rapidly. The term “ leukemia ” refers to cancers of the bone marrow and blood cells. The word myeloid, or myelogenous, refers to the cell type it affects. Myeloid cells are precursors to other blood cells.
How many people go into remission after chemo?
Around 90 percent of people with an AML type known as acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) will go into remission after “induction” (first round) of chemo. This is according to the American Cancer Society (ACS). For most other types of AML, the remission rate is around 67 percent.
What are some examples of AML?
Some cell mutation types are known to be more responsive to treatments. Examples include mutated CEBPA and inv (16) CBFB-MYH11 cells. Some cell mutations can be very treatment-resistant.
What does AML mean?
Regardless of prognosis, an AML diagnosis can create emotions of fear, anxiety, and uncertainty. You may be unsure where to turn or seek support. A cancer diagnosis presents the opportunity for you to grow nearer to those closest to you and evaluate how you can live a life you enjoy.
What to do if you have AML?
A lab will check for certain gene changes and other substances that are found in AML cells. If your cancer does return, your doctor may put you on more chemo or other types of cancer drugs. Another option is to have a stem cell transplant. Once you finish treatment, you'll see your doctor every few months for several years.
What is the second phase of AML?
You'll now go into the second phase of AML treatment, which is called post-remission or consolidation therapy.
How to know if you are in remission?
How do you know you're in remission? Your doctor will tell you that you're in "complete remission" when: 1 There are no signs of leukemia cells, called blasts, in your bone marrow. 2 You don't have symptoms of AML. 3 Your blood count -- which measures the number of blood cells -- is back to normal.
What happens if you go into remission after a cancer treatment?
When cancer returns after treatment, it's called a relapse. During these visits, your doctor may take a sample of your blood or bone marrow. A lab will check for certain gene changes and other substances that are found in AML cells.
How to heal from chemo?
Eat well. Your body needs a good mix of nutrition to heal. Try to put veggies, fruits, lean protein, whole grains, and low-fat dairy in your diet. If your stomach is upset because you're getting chemo, eat smaller meals every 2 to 3 hours instead of three big meals. Get extra rest.
Can you stop treatment for AML?
It's a sign your cancer is under control. Yet it doesn't mean that you're cured or you can stop treatment completely. With AML, some cancer cells can be left behind even when you're in remission. That's why you'll get treated until all signs of your AML are gone.
Can leukemia be detected in bone marrow?
There are no signs of leukemia cells, called blasts, in your bone marrow. You don't have symptoms of AML. Your blood count -- which measures the number of blood cells -- is back to normal.
What are the different types of leukemia?
There are four common types of leukemia which include: Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL): In this type of leukemia, immature lymphoid cells grow rapidly in the blood. It is the most common type of leukemia in children and rarely affects adults. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML):
What is asparlas mknl?
Asparlas (calaspargase pegol - mknl) Asparlas (calaspargase pegol - mknl) is an asparagine specific enzyme indicated as a component of a multi-agent chemotherapeutic regimen for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in pediatric and young adult patients age 1 month to 21 years.
What is Onureg used for?
Onureg is a prescription medicine used for continued treatment of adults with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who had a first complete remission (CR) following intensive induction chemotherapy with or without recovery of your blood cell counts , and who are not able to complete intensive curative therapy.
How long do children live with leukemia?
More than four out of five children live at least 5 years. The prognosis for adults is not as good.
What is the disease of the bone marrow?
Leukemia is a cancer of the white blood cells of the bone marrow. Patients with leukemia have an over-production of a particular blood cell type in the body, the white blood cells (cells that fight infection, and provide immunity).
What is the name of the cancer that affects the white blood cells?
Leukemia is a group of cancers of the blood affecting the white blood cells. White blood cells are the infection-fighting cells of the body. In leukemia , white blood cell production becomes abnormal in the bone marrow. The abnormal white blood cells divide uncontrollably and eventually outnumber the healthy white blood cells.
How long does it take for cancer to go into remission?
About 80 percent who go into remission will do so within 1 month of therapy . In some people, however, the disease will return, lowering the cure rate. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): On average, people with this cancer survive 9 years, although some have lived for decades, cancer always comes back at some point.
What is the disease of the elderly called?
Acute Myeloid Leukemia, or AML, is a rapidly progressing disease specific to elderly people. AML attacks the DNA of red blood cells while they are forming in the bone marrow. The body is then unable to produce enough red blood cells and platelets to sustain life. Early symptoms of AML are also symptoms of aging. Early symptoms include lethargy, bruising easily and shortness of breath. A person with later stage AML will experience unexplained internal and external bleeding. A bone marrow biopsy will confirm the diagnosis of AML.
What is the treatment for AML?
Treatment options for AML include chemotherapy and bone marrow stem-cell transplant. Elderly people are more likely to experience chemotherapy toxicity, which is harder to live with than AML. Chemotherapy toxicity can be fatal in and of itself.
How long does it take for AML to die?
The final stage of AML is, unfortunately, death. The Merck Manual online states that most patients die within a few weeks to a few months after diagnosis. Elderly AML patients often die suddenly from internal bleeding. Other patients survive for a while with frequent blood transfusions.
What are the symptoms of internal bleeding?
Symptoms of a lethal, internal bleeding include shivers, confusion, loss of consciousness and death. Signs that death is imminent are the same as with any other disease. Loss of appetite is the first signal that the AML patient may be dying.
What can hospice do to help a dying patient?
Hospice volunteers and nurses can help the dying patient maintain dignity during the process of death. The final stage of AML is, unfortunately, death. Some patients and families choose to treat just the pain, so the patient may be comfortable during the final moments of life.
How do you know if you are dying from AML?
Signs that death is imminent are the same as with any other disease. Loss of appetite is the first signal that the AML patient may be dying. A person who is dying will sleep more often than not. AML patients in their final stages experience labored breathing. Each breath may be quite audible.
What happens when a patient does not have an advanced directive?
When the patient does not have an advanced directive, the family needs to determine which measures the doctors should take to sustain life. Some patients and families choose to treat just the pain, so the patient may be comfortable during the final moments of life.
Is azacitidine a frontline treatment?
Azacitidine is recommended front-line treatment for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who are not candidates for intensive treatment regimens, and was recently granted approval in the European Union for treatment of adult AML. Reviewed here is azacitidine experience in AML, including: mechanistic and pharmacokinetic data;
Is azacitidine good for myeloid leukemia?
Azacitidine is recommended front-line treatment for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who are not candidates for intensive treatment regimens, and was recently granted approval in the European Union for treatment of adult AML. Reviewed here is azacitidine experience in AML, including: ….
Complete Remission
This means that there are no signs of leukemia after treatment. Blood counts have returned to normal and there are fewer than 5% immature leukemia cells (blasts) in the bone marrow.
Complete Remission with Incomplete Hematologic Recovery
This means that all of the criteria for complete remission are achieved except that the absolute neutrophil count (ANC) is <1000 cells/μL or the platelet count is <100,000/μL in the blood.
Minimal Residual Disease (MRD)
MRD refers to the small number of cancer cells that remain in the body after treatment. The number of remaining cells may be so small that they do not cause any physical signs or symptoms and often cannot even be detected through traditional methods, such as viewing cells under a microscope.
Relapsed (Recurrent) AML
This means that the AML has returned after a period of remission. Blood counts may be abnormal again. A discussion about treatment options to try to get the AML back into remission may be warranted at this time.
Refractory AML
This means that the AML has not gone away and has not responded to 2 cycles of chemotherapy. Patients who are progressing while on therapy are considered "refractory" to their treatment.