How long does HIV kills you?
HIV medicine is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). There is no effective cure for HIV. But with proper medical care, you can control HIV. Most people can get the virus under control within six months. Taking HIV medicine does not prevent transmission of other sexually transmitted diseases. When should I start treatment?
How long can I live if I get HIV?
Mar 29, 2019 · The HIV medications used today have fewer side effects, fewer people experience them, and they are less severe than in the past. Side effects can differ for each type of ART medicine and from person to person. Some side effects can occur once you start a medicine and may only last a few days or weeks.
How long can someone live with HIV for?
Apr 30, 2020 · Population studies proved that AIDS patients who did not take HIV medications survived for roughly three years. Once they developed a dangerous opportunistic illness, life expectancy with AIDS (in the absence of treatment) decreased to one year or less.
How can you tell how long you have had HIV?
These signs and symptoms of acute HIV infection can begin a few days after you are exposed to HIV and usually last for about 14 days. They could last for just a few days, or they could last for several months. You might not realize your illness is acute HIV infection. For one thing, you may not have known that the person

Do you have to take HIV medication for life?
While you may indeed need to take HIV medication for the rest of your life, new treatment options are being developed all the time, and many revolve around long-acting injectables. In a few years, your HIV treatment might require one shot every three months instead of a daily pill.Apr 11, 2018
Can you live a long life with HIV?
During the first period, life expectancy for a 21-year-old with HIV was 38 years, compared to 60 for uninfected peers. By 2014, that gap narrowed dramatically: A 21-year-old with HIV could expect to live to 56, compared to age 65 for uninfected adults, according to the report.Jun 18, 2020
Can HIV come back after treatment?
But if you quit treatment, the virus usually comes back within weeks. That's because pools of HIV are "asleep" in your body. When you stop taking the drugs, this so-called "latent HIV reservoir" wakes up and gives new life to the infection.Apr 12, 2021
Can HIV cured in early stage?
Though there is no cure for HIV, early diagnosis can aid in timely initiation of antiretroviral therapy that can stop the virus from damaging the immune system. An HIV patient who has received timely treatment can live a normal and long life without progressing to late stage HIV.Mar 22, 2020
Is it possible to test negative while your partner is positive?
A: It is quite common for one partner to test positive and the other negative, even if they have been having sex without condoms. Mostly this is explained by luck and the role of other risk factors.Jun 1, 2021
What is HIV treatment?
HIV treatment involves taking medicine that reduces the amount of HIV in your body. HIV medicine is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). There is n...
When should I start treatment?
Start Treatment As Soon As Possible After Diagnosis HIV medicine is recommended for all people with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the vir...
What if I delay treatment?
HIV will continue to harm your immune system. This will put you at higher risk for developing AIDS. Learn more about AIDS and opportunistic infecti...
What are the benefits of taking my HIV medicine every day as prescribed?
Treatment Reduces the Amount of HIV in the Blood The amount of HIV in the blood is called viral load. Taking your HIV medicine as prescribed will h...
Does HIV medicine cause side effects?
HIV medicine can cause side effects in some people. However, not everyone experiences side effects. The most common side effects are Nausea and vom...
Will HIV treatment interfere with my hormone therapy?
There are no known drug interactions between HIV medicine and hormone therapy. Talk to your health care provider if you are worried about taking HI...
What if my treatment is not working?
Your health care provider may change your prescription. A change is not unusual because the same treatment does not affect everyone in the same way.
Sticking to my treatment plan is hard. How can I deal with the challenges?
Tell your health care provider right away if you’re having trouble sticking to your plan. Together you can identify the reasons you’re skipping med...
How long do HIV side effects last?
Some side effects can occur once you start a medicine and may only last a few days or weeks.
What is the treatment for HIV?
HIV treatment involves taking medicines that slow the progression of the virus in your body. HIV is a type of virus called a retrovirus, and the combination of drugs used to treat it is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART is recommended for all people living with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the virus or how healthy they are.
How successful is HIV treatment?
HIV treatment is most likely to be successful when you know what to expect and are committed to taking your medicines exactly as prescribed. Working with your health care provider to develop a treatment plan will help you learn more about HIV and manage it effectively.
Is HIV treatment a prevention?
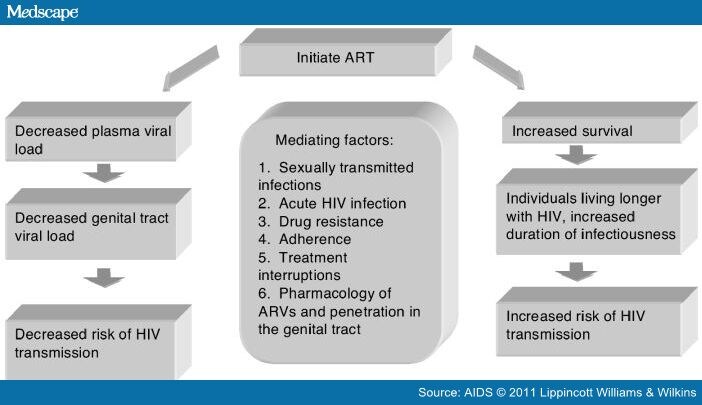
There is also a major prevention benefit. People living with HIV who take HIV medication daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partners. This is called treatment as prevention.
What happens if your CD4 is low?
If your CD4 cell count falls below a certain level, you are at risk of getting an opportunistic infection. These are infections that don’t normally affect people with healthy immune systems but that can infect people with immune systems weakened by HIV infection.
How soon can you start ART for HIV?
Treatment guidelines from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recommend that a person living with HIV begin ART as soon as possible after diagnosis. Starting ART slows the progression of HIV and can keep you healthy for many years.
Can HIV cause drug resistance?
Drug resistance can be a cause of treatment failure for people living with HIV. As HIV multiplies in the body, it sometimes mutates (changes form) and produces variations of itself. Variations of HIV that develop while a person is taking ART can lead to drug-resistant strains of HIV. With drug resistance, HIV medicines that previously controlled ...
How to determine life expectancy?
When looking at both static and dynamic risk factors, we can begin to identify where an individual can gain or lose life-years without even knowing it. Among them: 1 A person's CD4 count at the start of treatment remains one of the strongest indicators of life expectancy. The life expectancy between those whose CD4 count is less than 200 at the start of treatment is 8 years less than those whose count is over 200 at the same time. 2 2 Smokers with HIV lose more life-years to smoking than to HIV. In fact, the risk of death from smoking is twice as high among smokers with HIV , and can trim as much as 10 years a person's lifespan irrespective of HIV. 6 3 Race and longevity are integrally linked to HIV. According to a 2012 study, the mortality rate among HIV-positive Blacks was 13% higher than the rate for Whites and 47% higher than the rate for Hispanic populations. 7 4 Injecting drug users suffer losses, both in terms of HIV-and non-HIV-related illnesses. The strongest contributing factors were poor adherence and hepatitis C co-infection. All told, mortality rates are nearly twice as high for HIV-positive injecting drug users than HIV-positive non-injecting drug users. 8
Who is James Myhre?
James Myhre is an American journalist and HIV educator. Latesha Elopre, MD, is a board-certified internist specializing in HIV. She is an assistant professor of infectious diseases at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. It is natural to wonder how long you could live if you have HIV.
Can HIV patients live longer?
By and large, the outlook is extremely positive. With advances in antiretroviral therapy, people with HIV can today expect to live longer and healthier than ever If treatment is started early and taken daily as directed. 1 . A 20-year-old started on HIV therapy can expect to live into his or her early 70s, according to research from ...
Does HIV affect longevity?
From an individual perspective, longevity is subject to numerous factors that can either increase or decrease life expectancy in a person with HIV.
Is HIV a long term concern?
Moreover, HIV is really only part of the long-term concern. Even for those able to maintain an undetectable viral load, the risk of non-HIV-associated diseases, like cancer and heart disease, is far greater than in the general population and can occur anywhere from 10 to 15 years earlier. 4 .
What are the factors that affect life expectancy?
Gains and Losses in Life Years. Factors that influence life expectancy are either static (fix ed) or dynamic (able to change over time). Static factors, like race or sexual orientation, influence life expectancy because they are ones people are often unable to escape.
Can statistics predict infection?
It is important to remember that statistics are not a prognosis. They cannot predict what will happen during the course of an infection. They can only suggest what you steps you can take to minimize the risk of illness based on the factors you, as an individual, can readily change.
How to prevent foodborne illness?
Because HIV and AIDS compromise the immune system’s defenses, patients are more susceptible to foodborne illnesses. Stick to these basic rules for safeguarding your health: 1 Avoid raw eggs, meats, fish, and other seafood. 2 Use a separate cutting board for meat. 3 Wash all fruits and vegetables thoroughly. 4 Clean cutting boards, utensils, and your hands with warm soapy water after coming into contact with raw meat and other ingredients. 5 Avoid drinking water or any products prepared with water from natural, unfiltered sources (e.g., lakes, ponds, rivers, etc.). Switch to bottled or filtered tap water at home. 6 Boil water before drinking or cooking with it to kill waterborne bacteria. 7 When traveling abroad, steer clear of local drinking water and ice, as well as unpasteurized beverages.
How long can a person with HIV live?
Recent research shows that a young person with HIV or AIDS could potentially live almost as long as anyone else in the general population. But this is only the case if they have routine access to health care and respond well to modern antiretroviral treatments (ARTs). So a 20-year-old who starts on ARTs today, for example, might eventually live to be 67.
Is eating right good for HIV?
While eating right is beneficial to everyone, it’s absolutely essential for HIV and AIDS patients , regardless of what stage they’re in. The drugs prescribed to combat the virus often upset the digestive system, causing additional issues, such as:
How long can a person with HIV live without treatment?
Population studies proved that AIDS patients who did not take HIV medications survived for roughly three years. Once they developed a dangerous opportunistic illness, life expectancy with AIDS (in the absence of treatment) decreased to one year or less.
How to treat HIV and AIDS?
Beginning a treatment regimen is the first step in creating a positive care plan and should include strategies for protecting your immune system. Since numerous ART options exist to manage the virus, consult your health care provider about tailoring a drug plan to your unique symptoms.
How to maintain long term physical and mental health?
Exercise is a great way to maintain long-term physical and mental health, while also upping strength, endurance, and fitness. An HIV or AIDS diagnosis will not affect your ability to engage in these activities. Ask your health care provider about how to stay fit and make workouts a part of your daily routine. 6. Practicing safe sex.
How to help someone with depression?
Socializing with friends, reading, listening to music, and engaging in your favorite hobbies helps battle depression and the loss of brain function. Don’t be afraid to try something different, which might offer a chance to forge new relationships and serve as a source of personal enjoyment.
What is a swollen lymph node?
Swollen lymph nodes (glands that protect from infections; they can be felt when swollen in the armpits, groin and neck) In the acute stage, the virus multiplies rapidly and spreads throughout the body. HIV targets and destroys the CD4 cells (the infection-fighting cells of the immune system); in this stage of HIV infection, ...
How long does HIV last?
In the case of an untreated HIV infection, the overall mortality rate is more than 90%. The average time from infection to death is eight to ten years. This may; however, vary from person to person. Many factors affect survival:
Does HIV increase over time?
With the increasing use of antiretroviral therapy (ART) and the introduction of better antiviral regimens, survival with HIV infection has increased over time. The survival, however, is not yet equivalent to that in uninfected individuals.
What is the final stage of HIV?
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome ( AIDS) is the final and most severe stage of HIV. In this stage, HIV reduces CD4 cell counts to very low levels (less than 200 units), which severely damages the immune system.
How long does it take for HIV to progress?
If ART is not given, a chronic HIV infection usually advances to AIDS in 10 years or longer. In some people, however, it may advance faster. If ART is administered, the person may stay in this stage for several decades.
What is an opportunistic infection?
Opportunistic infections are infections and infection-related cancers that occur more frequently or are more severe in people with weakened immune systems than in people with healthy immune systems. Once a person progresses to AIDS, they have a high viral load and can transmit HIV to others very easily. In the absence of treatment, people ...
What is the role of CD4 T cells in HIV?
HIV targets white blood cells called CD4 T cells that help protect the body from infection. By killing these cells, HIV progressively weakens the body’s defenses against infection and illness, leading to complications that can be fatal — unless a person receives ...
How long does it take for HIV to spread?
At this time, it can easily transmit to others — through blood, semen and preseminal fluids, rectal fluid, vaginal fluid, and breast milk. Within 2–4 weeks.
Can antiretroviral therapy be used to treat HIV?
Antiretroviral therapy can prevent HIV from progressing, especially when a person starts taking it early. People with HIV who receive this treatment can live long, healthy lives, with life expectancies comparable to those of people without HIV. This article looks at the timeline of HIV symptoms, the stages of the infection, and the outlook.
What is PEP for HIV?
For anyone who may have been exposed to HIV, it is important to talk to a healthcare provider for advice and ask them about preventive therapy called post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) Trusted Source. . People at risk of exposure to HIV can take pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) Trusted Source.
How long does HIV last?
This may last for several days or weeks. Not everyone experiences these symptoms, however. If a person does not undergo testing, it is possible for HIV to progress without any indication that it is in the body. The flu-like symptoms of a stage 1 HIV infection may include: a fever. muscle or joint pain.
What are the symptoms of seroconversion?
a sore throat. swollen glands. nausea or vomiting. These symptoms are collectively known as a seroconversion illness. They represent the body’s natural response to an infection as it attempts to kill off the virus. However, the human body cannot completely remove this virus once it is present.
How does antiretroviral therapy help?
Antiretroviral therapy keeps the immune system healthy and reduces the risk of transmitting the virus to virtually zero. The sooner a person receives a diagnosis, the sooner they can begin treatment. Early treatment can improve the person’s outlook and lower the risk of the virus passing on to others.
How to avoid HIV?
Abstinence, or not having sex, is the only type of protection that works every time. But if you are having sex, you can lower your risk if you: Use a condomevery time you have sex.
Can you get HIV from breast milk?
To spread HIV, the fluids either have to go straight into your bloodstream (like from a needle) or touch mucous membranes -- areas like the inside of your mouth, vagina, or rectum. You can’t get HIV by sitting on a toilet seat or sharing dishes with an infected person.
Can HIV live in water?
Tiny amounts of HIV have been found in saliva, poop, sweat, and tears. But research shows it poses little risk. The virus can’t survive in water, so you don’t have to worry about swimmingpools or hot tubs. One study found HIV can live in used needles for over a month if the temperature and conditions are just right.

What The Current Research Says
Factors That Reduce Life Expectancy
- Despite these advances, there are factors that can increase or decrease the life expectancy of people with HIV. These range from things we can control (such as taking our pills every day) to things we can't (such as race or poverty). These factors not only influence not only how a person responds to treatment but whether they are able to access treatment in the first place.5 Becaus…
Losses in Life Years
- There is not always a straight line between how certain risk factors increase or decrease the life expectancy of someone with HIV. This is because people tend to have overlapping risk factors. Take, for example, Black men who have sex with men (MSM). The combination of racism, poverty, homophobia, and stigma—as well as the biological vulnerabilities to HIV—places Black MSM in t…
Summary
- Studies show that people living with HIV today can expect to live a near-normal life expectancy if treatment is started early and taken every day as prescribed. Even so, there are things that can undermine a person's ability to do so. This includes factors likes poverty, stigma, racism, and homophobia that can stand in a person's way of accessing consistent care and treatment. Othe…
A Word from Verywell
- As encouraging as the statistics are, it doesn't mean you have less to worry about when it comes to HIV. In the end, the choices you make will determine how well you respond to treatment and influence your individual risk of both HIV- and non-HIV-related illnesses. Ultimately, HIV is about more than just pills. You need to also take of your general health by eating a healthy diet, exercis…