If it remains untreated, the infection can affect your brain and spinal cord later in life. Primary syphilis usually breaks out about 3 weeks after exposure but can range from 9 to 30 days after exposure. The chancre will last from 3 to 6 weeks and then will disappear with or without treatment.
Full Answer
What are the first signs of a STD?
Nov 05, 2021 · If you start to exhibit symptoms once again after a successful course of treatment, it is most likely that you have been reinfected since treatment usually does not cannot remove the bacteria. Women typically have a high rate of reinfection and need to be tested once again within 3 to 4 months following the conclusion of treatment.
What are ways to prevent STDs?
Oct 24, 2021 · You should notice an improvement quite quickly after having treatment. Discharge or pain when you urinate should improve within a week. Bleeding between periods or heavier periods should improve by your next period. Pelvic pain and pain in the testicles should start to improve quickly but may take up to two weeks to go away.
Which STD tests should I get?
Oct 31, 2021 · You should notice an improvement quite quickly after having treatment. Discharge or pain when you urinate should improve within a week. Bleeding between periods or heavier periods should improve by your next period. Pelvic pain and pain in the testicles should start to improve quickly but may take up to two weeks to go away.
When do the symptoms of common STDs appear?
Apr 04, 2022 · Your signs or symptoms last longer than 1 week or get worse during treatment. Your signs or symptoms return after treatment. You have pain during sex. You have questions or concerns about your condition or care. Medicines: Antibiotics help treat the infection caused by bacteria. Both you and your sex partner need treatment to prevent chlamydia from spreading. …

How do you know if you have an STD?
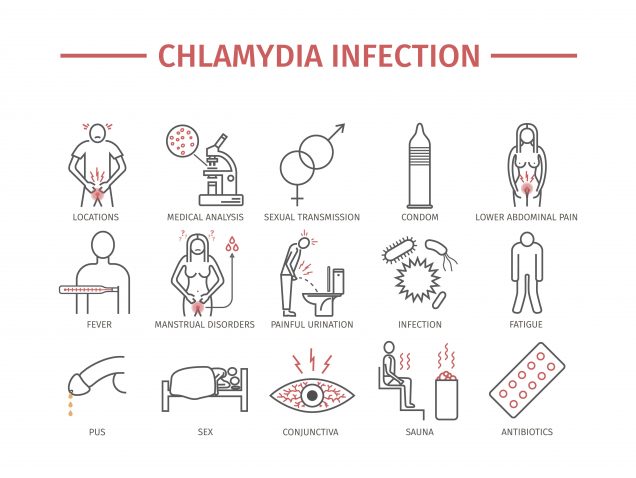
Some symptoms of STDs include: Painful or painless ulcers on the skin of the genitalia of both sexes and in the vagina in women. Fever. Swollen glands.
What is the treatment for STDs?
In the case of gonorrhea and chlamydia, your doctor will usually give an antibiotic injection to treat gonorrhea and oral antibiotics to treat chlamydia.
What to do if you suspect an STD?
Then, your doctor will examine you, focusing on your genital area. He or she also will examine your anal area and in women, do a pelvic exam.
Can syphilis be cured?
In addition, treatment for chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis will avoid potential long-term complications. Viral infections, such as genital warts, genital herpes and HIV cannot be cured. However, they can be treated with medications.
How to test for chlamydia?
To test for chlamydia infections, your doctor will send a sample of fluid from the tip of the penis or cervix. Chlamydia can also be diagnosed with a urine test. Gonorrhea requires a direct sample from the tip of the penis, cervix or rectum. Syphilis and HIV can be confirmed with a blood test.
Can chlamydia cause infertility?
For example, chlamydia may not cause symptoms in all those infected; however, the scarring effect of the bacteria can lead to infertility, especially in women. Second, STDs are seen as threats to public health. With proper identification and treatment, the rates of infection can be reduced.
How to treat genital warts?
Syphilis usually is treated with one or more injections of penicillin. Genital warts can be treated by freezing or by applying topical agents.
How long does it take to get a chlamydia test?
There are several types of tests that can be done to diagnose Chlamydia infection. Test results are usually available in 2 or 3 days, except cultures which require between 5 and 7 days.
How long does it take for azithromycin to go away?
If you are provided treatment of antibiotics that include azithromycin which you take for 24 hours, you will still have to avoid sexual contacts for about a week after taking the tablets. This infection can go away with no treatments as well, but it will take a lot longer.
What is the cause of chlamydia?
Causes. Chlamydia is an infection caused by a bacterium called Chlamydia trachomatis. It`s transmitted through vaginal, anal or oral sexual contact with an infected partner. A pregnant woman transmits the infection to the newborn during birth.
Can chlamydia be transmitted to a baby?
Chlamydia can also infect the rectum, eye surface and eyelids. An infected mother can transmit the infection to her baby during childbirth. Between 50% and 70% of infants are born from infected mothers. They acquire the infection in the eyes, rectum, vagina and the back of the throat.
Can chlamydia cause long term damage?
This disease doesn`t cause long-term damage if treated accordingly before complication occur. However, it may cause various complications if left untreated. Treatment is recommended: People who received positive Chlamydia test results. Sexual partners in the last 60 days, even if they don`t show any symptoms.
Can chlamydia spread to other parts of the body?
Still, with no treatment Chlamydia will spread to other body parts. The more times you get infected with it, the more like it is for you to experience complications. In men – this condition may lead to an infection of the testicles and maybe even infertility.
Can PID cause ectopic pregnancy?
In women – this medical condition may spread to other important body organs leading to PID. In turn, this may lead to long-term damages, such as ectopic pregnancy, pelvic pain, infertility and blocked fallopian tubes. In both man and women – More rarely, this infection may lead to joint inflammation.
Why does my STD return?
Reinfection: The most common reason an std returns is because someone re-infected you. Your same partner or a new partner. If you have gonorrhea and chlamydia, a ... Read More
How long does it take for a doctor to answer a question?
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers — it's anonymous and free! Doctors typically provide answers within 24 hours.
Can you take antibiotics for a girlfriend?
No, needs Meds: Antibiotics are the only way to cure this infection, no alternative treatments are available. It is highly unlikely your girlfriend is allergic to all ... Read More
Does chlamydia enter the blood?
Don't count on it: Chlamydia is an infectious disease that does not enter your blood and or ever stimulate the immune system to give immunity.It is more like strep throa ... Read More

What Are Sexually Transmitted Diseases?
- Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections that are spread from person to person through sexual contact, including oral sex, anal sex and the sharing of sex toys. These diseases can be passed through any contact between the genitals of one person and the genitals, anus, mouth or eyes of another person. There are many different STDs, but the most common ones i…
Symptoms
- Symptoms vary depending on the type of infection, although some people who become infected with an STD may not develop symptoms at all. Some symptoms of STDs include: 1. Painful or painless ulcers on the skin of the genitalia of both sexes and in the vagina in women 2. Fever 3. Swollen glands 4. Abdominal pain 5. Discharge from the penis 6. Rectal discharge 7. Vaginal dis…
Diagnosis
- If your doctor suspects that you may be infected with an STD, he or she will ask how many sexual partners you have had and if any of them have had an STD. Then, your doctor will examine you, focusing on your genital area. He or she also will examine your anal area and in women, do a pelvic exam. In addition, your doctor may swab the tip of the penis in men, take a sample of any …
Expected Duration
- How long STDs last depends on the specific type of infection. In some cases, although symptoms may go away without treatment, the patient is still infected and can pass the STD to a partner during unprotected sexual activity. In patients with trichomoniasis, chlamydia, or gonorrhea, treatment with antibiotics can dramatically shorten the duration of symptoms. In addition, treat…
Prevention
- You can help to prevent STDs by: 1. Not having sex 2. Having sex only with one uninfected person 3. Consistently using male latex condoms during sexual activity Remember, although condoms can help reduce your exposure to STDs, they are not foolproof. People who are diagnosed with an STD may be contacted by their local health department so that their sex partners can be evaluat…
Treatment
- The treatment of STDs depends on the infection. In the case of gonorrhea and chlamydia, your doctor will usually give an antibiotic injection to treat gonorrhea and oral antibiotics to treat chlamydia. Genital herpes is a lifelong infection with no cure. However, the blistering skin sores won't last as long if you treat genital herpes with an oral antiviral medication as soon as sympto…
When to Call A Professional
- Call your doctor immediately if you find a sore in your genital area or if you notice an abnormal discharge from your urethra or vagina. You should also call your doctor if your sex partner has had an STD, even if you have no symptoms.
Prognosis
- Most STDs respond well to treatment. However, many patients develop repeat episodes of STDs because their sex partners are not treated or because they continue to be exposed to STDs through unprotected sex. To help avoid getting the same disease again, sex partners usually need treatment as well. Genital herpes cannot be cured, because the virus remains dormant in nerves …
Further Information
- Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances. Medical Disclaimer