How long can you have chlamydia before transmitting it?
· Persons with chlamydia should abstain from sexual activity for 7 days after single dose antibiotics or until completion of a 7-day course of antibiotics, to prevent spreading the infection to partners. It is important to take all of the medication prescribed to cure chlamydia. Medication for chlamydia should not be shared with anyone.
How long does it take to be cured of chlamydia?
Most likely you wouldn't have been contagious must past a few days, but even the most conservative recommendations is 7 days, so you were fine. Had your gf been tested and treated? If you had sex with her prior to being diagnosed, she needs to be treated as well. Aj
How long after treatment does Chlamydia go away?
· Persons with chlamydia should abstain from sexual activity for 7 days after single dose antibiotics or until completion of a 7-day course of antibiotics, to prevent spreading the …
Can a doctor tell how long you have had chlamydia?
To minimize disease transmission to sex partners, persons treated for chlamydia should be instructed to abstain from sexual intercourse for 7 days after single-dose therapy or until …

How long can you transmit chlamydia after treatment?
Chlamydia Treatment and Care Persons with chlamydia should abstain from sexual activity for 7 days after single dose antibiotics or until completion of a 7-day course of antibiotics, to prevent spreading the infection to partners.
Why do I have to wait 7 days after chlamydia treatment?
If you're being treated for chlamydia, it's important to avoid sex until 7 days after finishing your medicine. This gives your body time to clear up the infection completely to make sure it doesn't get passed on to anyone.
Can you still transmit chlamydia A week after taking medication?
When can I have sex again? Don't have sex if you're being treated for chlamydia or if you're experiencing symptoms. After taking the one-day antibiotic treatment, wait a week before having sex to prevent spreading chlamydia to a partner.
How do I know if my chlamydia is gone?
If you take the treatment according to the instructions, you won't usually need a test to check the chlamydia has gone. If you're aged under 25, you should be offered a repeat test 3 months after finishing the treatment. This is because you're at a higher risk of getting chlamydia again.
How long after azithromycin is chlamydia gone?
It takes about one week for azithromycin to completely cure a chlamydial infection, and in some cases it can take up to two weeks for the infection to clear. If you are sexually active during this time, you can pass the infection to your partner(s), even if you have no symptoms.
Can I reinfect myself with chlamydia?
Thankfully, it's also curable. But new research suggests that for some people, curing chlamydia doesn't prevent reinfection, even if they're not exposed to it again. Apparently the disease can live inside your gut, and reinfect you out of the blue.
How long do chlamydia antibodies stay in blood?
Conclusions: Chlamydia antibody detection decreases with time since infection and this is most apparent in the first 6 months. In women who have had more than one infection, antibody remained detectable longer for all tests, but this was more marked for the pgp3 ELISA and MIF assay.
Do you have to tell future partners about chlamydia?
No. Since chlamydia is transmitted only through sexual contact, exclusion is not necessary. Who Do I Need to Tell About My Infection? You should tell your current sexual partners and all sexual partners that you have had in the last three months so they can be tested and treated for chlamydia.
Why do you have to wait 3 months to retest for chlamydia?
Retesting a few months after diagnosis and treatment of chlamydia can detect repeat infection for earlier treatment to prevent complications and further transmission. Retesting is not the same as a test-of-cure (TOC). Retesting for reinfection of chlamydia is done routinely.
Can you get reinfected with chlamydia while on antibiotics?
If your partner did not get treated They eliminate the existing chlamydia infection, but antibiotics don't make you immune to the disease. That means that you can get reinfected by a sexual partner who has chlamydia.
What are the chances of chlamydia treatment not working?
Background. Three recent prospective studies have suggested that the 1 g dose of azithromycin for Chlamydia trachomatis (Ct) was less effective than expected, reporting a wide range of treatment failure rates (5.8%–22.6%).
How do you know if you have chlamydia?
For men, symptoms of Chlamydia may include pain in testicles or swelling in testicles, burning sensation while peeing, etc. Chlamydia is common in women and men below the age of 25.
Is chlamydia contagious?
As contagious as Chlamydia is, the average person might not feel the symptoms until much later when the infection has taken place. Some of the symptoms a person having Chlamydia might face can include an increase in the vaginal discharge from normal days, they can also experience pain or a burning sensation during sex, ...
Can chlamydia cause infertility?
Even though the symptoms of Chlamydia do not seem that harmful, it is only because the infection should not spread in the body. If spread in the body, Chlamydia can harm the uterus and the fallopian tubes in women, which can lead to serious consequences in the future like damage to the reproductive system, infertility, etc. In men, it does not usually cause bigger health problems but it can spread to the tube which carries the sperm, which can sometimes result in infertility.
Chlamydia Is Common But Many People Dont Realize They Have It
About 1.7 million chlamydia infections were reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 2017, but the real number is likely higher because chlamydia is considered an underreported infection.
What Is The Treatment For Chlamydia
Chlamydia can be easily cured with antibiotics. HIV-positive persons with chlamydia should receive the same treatment as those who are HIV-negative.
When Will The Signs And Symptoms Go Away
You should notice an improvement quite quickly after having treatment.
Letting Partners Know You Have Chlamydia
Sexual partners may be infected too. If you have chlamydia, anyone you have had sex with from the last 6 months needs to be informed, tested and treated.
When To See A Doctor
If a person has symptoms of chlamydia after testing and treatment or thinks that they have come into contact with chlamydia again, they should see their doctor.
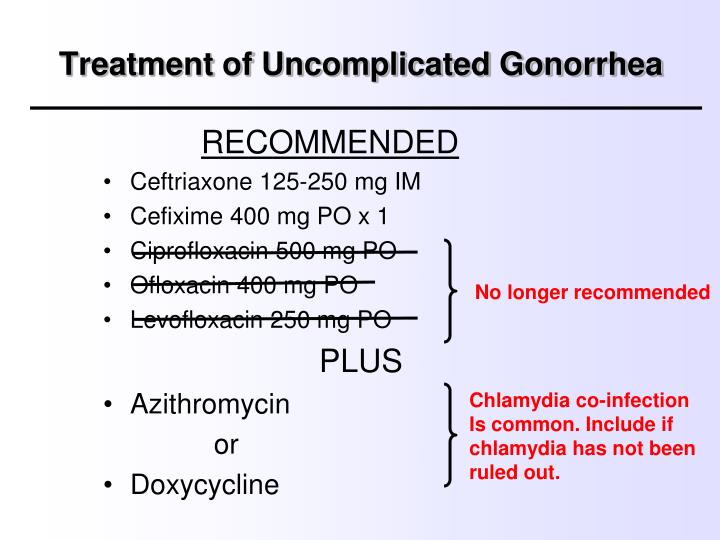
What Antibiotic Kills Gonorrhea
The most common treatment is a single antibiotic injection of ceftriaxone and a single dose of oral azithromycin, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention treatment guidelines. Currently, there are no at-home treatments to cure gonorrhea. It is strongly advised that you get care from a doctor.
Can I Still Have Chlamydia After Treatment
I also received after sale communication from the doctor. If you have a partner with chlamydia. Use a new condom each time can i still have chlamydia after treatment have sex. Sex after Chlamydia treatment can only be safe if the conditions mentioned above are met by both the infected and the sex partner.
When should a chlamydial etiology be considered?
A chlamydial etiology should be considered for all infants aged ≤30 days who experience conjunctivitis, especially if the mother has a history of chlamydial infection. These infants should receive evaluation and age-appropriate care and treatment.
Where to collect chlamydial specimens?
Specimens for chlamydial testing should be collected from the nasopharynx. Tissue culture is the definitive standard diagnostic test for chlamydial pneumonia. Nonculture tests (e.g., DFA and NAAT) can be used. DFA is the only nonculture FDA-cleared test for detecting C. trachomatis from nasopharyngeal specimens; however, DFA of nasopharyngeal specimens has a lower sensitivity and specificity than culture. NAATs are not cleared by FDA for detecting chlamydia from nasopharyngeal specimens, and clinical laboratories should verify the procedure according to CLIA regulations ( 553 ). Tracheal aspirates and lung biopsy specimens, if collected, should be tested for C. trachomatis.
Can azithromycin be used for neonatal chlamydia?
Although data regarding use of azithromycin for treating neonatal chlamydial infection are limited, available data demonstrate that a short therapy course might be effective ( 834 ). Topical antibiotic therapy alone is inadequate for treating ophthalmia neonatorum caused by chlamydia and is unnecessary when systemic treatment is administered.
Can neonates have chlamydia?
Neonates born to mothers for whom pre natal chlamydia screening has been confirmed and the results are negative are not at high risk for infection.
Is doxycycline effective for urogenital chlamydia?
Available evidence supports that doxycycline is efficacious for C. trachomatis infections of urogenital, rectal, and oropha ryngeal sites. Although azithromycin maintains high efficacy for urogenital C. trachomatis infection among women, concern exists regarding effectiveness of azithromycin for concomitant rectal C. trachomatis infection, which can occur commonly among women and cannot be predicted by reported sexual activity. Inadequately treated rectal C. trachomatis infection among women who have urogenital chlamydia can increase the risk for transmission and place women at risk for repeat urogenital C. trachomatis infection through autoinoculation from the anorectal site ( 816 ). Doxycycline is also available in a delayed-release 200-mg tablet formulation, which requires once-daily dosing for 7 days and is as effective as doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 7 days for treating urogenital C. trachomatis infection in men and women. It is more costly but also has lower frequency of gastrointestinal side effects ( 817 ). Levofloxacin is an effective treatment alternative but is more expensive. Erythromycin is no longer recommended because of the frequency of gastrointestinal side effects, which can result in nonadherence. When nonadherence to doxycycline regimen is a substantial concern, azithromycin 1 g regimen is an alternative treatment option but might require posttreatment evaluation and testing because it has demonstrated lower treatment efficacy among persons with rectal infection.
Can C. trachomatis be transmitted to genital sites?
Although the clinical significance of oropharyngeal C. trachomatis infection is unclear and routine oropharyngeal screening is not recommended, oropharyngeal C. trachomatis can be sexually transmitted to genital sites ( 211, 814 ); therefore, if C. trachomatis is identified from an oropharyngeal specimen while screening for pharyngeal gonorrhea, it should be treated. Evidence is limited regarding the efficacy of antimicrobial regimens for oropharyngeal chlamydia; however, a recently published observational study indicates doxycycline might be more efficacious than azithromycin for oropharyngeal chlamydia ( 815 ).
How to diagnose C. trachomatis?
For women, C. trachomatis urogenital infection can be diagnosed by vaginal or cervical swabs or first-void urine. For men, C. trachomatis urethral infection can be diagnosed by testing first-void urine or a urethral swab. NAATs are the most sensitive tests for these specimens and are the recommended test for detecting C. trachomatis infection ( 553 ). NAATs that are FDA cleared for use with vaginal swab specimens can be collected by a clinician or patient in a clinical setting. Patient-collected vaginal swab specimens are equivalent in sensitivity and specificity to those collected by a clinician using NAATs ( 792, 793 ), and this screening strategy is highly acceptable among women ( 794, 795 ). Optimal urogenital specimen types for chlamydia screening by using NAAT include first-catch urine (for men) and vaginal swabs (for women) ( 553 ). Recent studies have demonstrated that among men, NAAT performance on self-collected meatal swabs is comparable to patient-collected urine or provider-collected urethral swabs ( 796 – 798 ). Patient collection of a meatal swab for C. trachomatis testing might be a reasonable approach for men who are either unable to provide urine or prefer to collect their own meatal swab over providing urine. Previous evidence indicates that the liquid-based cytology specimens collected for Pap smears might be acceptable specimens for NAAT, although test sensitivity using these specimens might be lower than that associated with use of cervical or vaginal swab specimens ( 799 ); regardless, certain NAATs have been cleared by FDA for use on liquid-based cytology specimens.
Why is chlamydia considered a silent infection?
Chlamydia is known as a ‘silent’ infection because most infected people are asymptomatic and lack abnormal physical examination findings. Estimates of the proportion of chlamydia-infected people who develop symptoms vary by setting and study methodology; two published studies that incorporated modeling techniques to address limitations of point prevalence surveys estimated that only about 10% of men and 5-30% of women with laboratory-confirmed chlamydial infection develop symptoms. 21.22 The incubation period of chlamydia is poorly defined. However, given the relatively slow replication cycle of the organism, symptoms may not appear until several weeks after exposure in those persons who develop symptoms.
What is chlamydia trachomatis?
What is chlamydia? Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by infection with Chlamydia trachomatis. It can cause cervicitis in women and urethritis and proctitis in both men and women. Chlamydial infections in women can lead to serious consequences including pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), tubal factor infertility, ...
What is the best specimen for genital chlamydia?
Vaginal swabs , either patient- or clinician-collected, are the optimal specimen to screen for genital chlamydia using NAATs in women; urine is the specimen of choice for men, and is an effective alternative specimen type for women. 43 Self-collected vaginal swab specimens perform at least as well as other approved specimens using NAATs. 44 In addition, patients may prefer self-collected vaginal swabs or urine-based screening to the more invasive endocervical or urethral swab specimens. 45 Adolescent girls may be particularly good candidates for self-collected vaginal swab- or urine-based screening because pelvic exams are not indicated if they are asymptomatic.
What is the most sensitive test for chlamydia?
There are a number of diagnostic tests for chlamydia, including nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), cell culture, and others. NAATs are the most sensitive tests, and can be performed on easily obtainable specimens such as vaginal swabs (either clinician- or patient-collected) or urine. 43.
Does chlamydia increase chances of HIV?
Untreated chlamydia may increase a person’s chances of acquiring or transmitting HIV – the virus that causes AIDS. 36
Can chlamydia cause long term damage?
However, chlamydial infections can lead to serious health problems with both short- and long-term consequences.
Can chlamydia be found in the throat?
29. While chlamydia can also be found in the throats of women and men having oral sex with an infected partner, it is typically asymptomatic and not thought to be an important cause of pharyngitis. 26.
Who Is At Risk For Chlamydia
Any sexually active person can be infected with chlamydia. It is a very common STD, especially among young people. 3 It is estimated that 1 in 20 sexually active young women aged 14-24 years has chlamydia. 5
Home Remedies For Chlamydia Symptoms
You may still experience painful or uncomfortable symptoms while youre taking chlamydia antibiotics.
How Common Is Chlamydia
CDC estimates that there were four million chlamydial infections in 2018. 3 Chlamydia is also the most frequently reported bacterial sexually transmitted infection in the United States. 4 However, a large number of cases are not reported because most people with chlamydia are asymptomatic and do not seek testing.
How Is Chlamydia Diagnosed And Treated
If you have chlamydia symptoms or had intercourse with someone without protection, you should inform your doctor about testing or take a home chlamydia test.
Chlamydia Can Sometimes Go Away On Its Own
Some diseases and infections can go away on their own, so its not surprising that people wonder: does chlamydia go away on its own? The truth is, it sometimes does. In about 20% of people who have no symptoms, chlamydia may resolve spontaneously without treatment.
How Can Chlamydia Be Prevented
Latex male condoms, when used consistently and correctly, can reduce the risk of getting or giving chlamydia. 53 The surest way to avoid chlamydia is to abstain from vaginal, anal, and oral sex, or to be in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested and is known to be uninfected.
How Long Can You Have Chlamydia Without Knowing
If youve had intercourse with an infected man or woman, chlamydia symptoms may appear between 1 3 weeks after contact.
What Can You Do To Relieve Your Symptoms
No home remedy for chlamydia can replace antibiotics. Chlamydia is a bacterial infection, so you need to take antibiotics to cure it.
What Does A Chlamydia Test Involve
If you have a vulva, you may be asked to take a swab around the inside of your vagina yourself.
How To Cope With Side Effects
headaches make sure you rest and drink plenty of fluids. Everyday painkillers, such as paracetamol and ibuprofen, are safe to take with doxycycline.
What Is The Treatment For Chlamydia
Chlamydia can be easily cured with antibiotics. HIV-positive persons with chlamydia should receive the same treatment as those who are HIV-negative.
Can Chlamydia Be Cured
Yes, chlamydia can be cured with the right treatment. It is important that you take all of the medication your doctor prescribes to cure your infection. When taken properly it will stop the infection and could decrease your chances of having complications later on. You should not share medication for chlamydia with anyone.
Is Azithromycin Better Than Doxycycline At Curing Chlamydia
STD guidelines still favor azithromycin over doxycycline for the treatment of chlamydia. This is because of the following reasons:
Does Azithromycin Cure Chlamydia
Cure rates of 97% were reported in an analysis of 12 randomized clinical trials that investigated the use of azithromycin 1 gram for the treatment of chlamydia. That means for every 100 people with chlamydia who take azithromycin, 97 will be cured and 3 will not be cured.
