
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help you manage your diabetes. It may also improve your critical health numbers, including weight, blood sugar, blood pressure and blood cholesterol. Managing weight Being overweight or obese make it hard to manage Type 2 diabetes.
Full Answer
How does diabetes affect lifestyle?
Change in eating habits, increasing weight and decreased physical activity are major factors leading to increased incidence of type 2 diabetes. Obesity is the most important modifiable risk factor. Smoking is an independent risk factor for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diet and exercise are primary therapeutic options for its management.
How to reverse diabetes naturally?
Jan 02, 2021 · Lifestyle modifications for diabetes include 1. Diet plan: What you eat directly affects the blood glucose level. People with diabetes should have a proper diet plan to control blood glucose levels. Consultation with a dietitian is …
What is it like to live with diabetes?
Clinicians are also researching changes in lifestyle activities that could help maintain blood pressure and healthy blood sugar levels in persons with diabetes, with such lifestyle changes including increased daily exercise and a well-balanced diet that has no sugars, reduced fats, and fresh fruits and vegetables.
What is diabetes and how can I manage it?
Healthy dietary changes based on the current recommendations and the Mediterranean dietary pattern can be recommended for the long-term prevention of diabetes. There is limited or insufficient data to show that prevention of T2D by lifestyle changes results in a lower risk of cardiovascular and microvascular complications.
Why is lifestyle modification important for diabetes?
An active lifestyle helps you control your diabetes by bringing down your blood sugar. It also lowers your chances of getting heart disease. Plus, it can help you lose extra pounds and ease stress.
How effective are lifestyle changes in controlling diabetes?
Lifestyle changes can delay or prevent the development of type 2 diabetes in patients with obesity and impaired glucose tolerance. The risks improve with weight loss and increased physical activity. A decrease of 7% to 10% or more from baseline weight can have a significant effect.
What lifestyle modifications might help to lower the risk of developing diabetes?
AdvertisementLose extra weight. Losing weight reduces the risk of diabetes. ... Be more physically active. There are many benefits to regular physical activity. ... Eat healthy plant foods. Plants provide vitamins, minerals and carbohydrates in your diet. ... Eat healthy fats. ... Skip fad diets and make healthier choices.Jun 25, 2021
What are some of the lifestyle changes for diabetes?
What to do:Talk to your doctor about an exercise plan. Ask your doctor about what type of exercise is appropriate for you. ... Keep an exercise schedule. ... Know your numbers. ... Check your blood sugar level. ... Stay hydrated. ... Be prepared. ... Adjust your diabetes treatment plan as needed.
What effect does lifestyle intervention have on the incidence of diabetes ie reduction of diabetes based on results from large randomized studies?
Randomized controlled trials have shown that lifestyle interventions focused on physical activity, healthy diets, and weight loss can reduce diabetes risk by 58% in people with IGT. Evidence also shows that lifestyle changes may help mitigate the effects of genes on diabetes risk.
Can lifestyle changes reverse diabetes?
Although there's no cure for type 2 diabetes, studies show it's possible for some people to reverse it. Through diet changes and weight loss, you may be able to reach and hold normal blood sugar levels without medication. This doesn't mean you're completely cured. Type 2 diabetes is an ongoing disease.Dec 6, 2020
How can diet and exercise prevent diabetes?
Diet and exercise Weight loss resulting from healthy eating and increased physical activity enables muscle cells to use insulin and glucose more efficiently, thus lowering diabetes risk. Lack of exercise can cause muscle cells to lose their sensitivity to insulin, which controls levels of sugar in the blood.
How does exercise help type 2 diabetes?
How Exercise Improves Insulin Health. Exercise helps manage prediabetes and type 2 diabetes by lowering blood glucose levels and improving insulin sensitivity throughout the body.Sep 15, 2020
Why is diet plus exercise so important in preventing and managing diabetes?
If you have diabetes, being active makes your body more sensitive to insulin (the hormone that allows cells in your body to use blood sugar for energy), which helps manage your diabetes. Physical activity also helps control blood sugar levels and lowers your risk of heart disease and nerve damage.
What is lifestyle modification?
Lifestyle modification involves altering long-term habits, typically of eating or physical activity, and maintaining the new behaviour for months or years. Lifestyle modification can be used to treat a range of diseases, including obesity.
What are the benefits of aerobic exercise?
Benefits of it include reduction of cardiovascular risk factors, weight loss, improvement of well-being, and glucose control. Moderate to a high amount of aerobic activity lowers cardiovascular and overall mortality risks in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Why do diabetics lose sensation in their feet?
Due to diabetic neuropathy, people with diabetes lose sensation in the foot that may result in unnoticed injury, and ulceration. The high glucose level in diabetes leads to non-healing of the wound, so foot care is very important. ADA recommends the use of specialized therapeutic footwear for high-risk patients with diabetes.
Does smoking increase blood pressure?
The use of tobacco and e-cigarette should be avoided. Alcohol stimulates the appetite so that you will eat a lot. Ultimately, it will affect your glucose control and increase blood pressure .
Does obesity cause diabetes?
Obesity is known to cause insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. So for reducing the risk of developing diabetes and better blood glucose control, weight loss is recommended.
How to prevent diabetes 2?
Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes by Diet and Lifestyle Modification Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes by Diet and Lifestyle Modification Type 2 diabetes is a common metabolic disorder that results in high levels of blood sugar. This medical condition occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin, it becomes resistant to insulins effects, or both. Having a sedentary lifestyle or being obese are some of the factors that can cause T2D . In case you change your lifestyle and adopt a healthy diet and exercise routine, you can reduce the chances of developing this metabolic disorder. T2D is the most common form of diabetes mellitus and affects 95% of diabetic people. Type 1 diabetes is the less common form of diabetes that affects only 5% of people with diabetes. Unlike type 2 diabetes, type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented through diet or lifestyle changes; however, it can be managed through insulin therapy. The signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes usually develop slowly over time. In fact, you can haveT2Dwithout showing any warning signs. Typically, people watch out for the following signs and symptoms of T2D: If you have any of these symptoms, it is important you visit your doctor for a medical check up. They will be able to identify the root cause of your symptoms. If type 2 diabetes is suspected, they can advise you of the best lifestyle changes and diet program. Considering the long-term health consequences that come with poorly managed type 2 diabetes, the best option is to prevent this chronic condition in the first place. Research shows that up to 90% of T2D prevention happens through lifestyle and diet modification. T2D can be prevented when the warning signs are detected early on. In case you are diagnosed with prediabetes , your doctor can help you make the necessar Continue reading >>
What is the most common type of diabetes?
T2D is the most common form of diabetes mellitus and affects 95% of diabetic people. Type 1 diabetes is the less common form of diabetes that affects only 5% of people with diabetes. Unlike type 2 diabetes, type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented through diet or lifestyle changes; however, it can be managed through insulin therapy.
How many people in the world have diabetes?
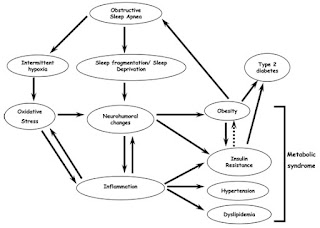
Diabetes, a global escalating public health problem, primarily because of the increasing prevalence, is estimated to affect 285 million individuals worldwide [1] (Approximately 90% have type 2 diabetes mellitus) and causes hundreds of billions of dollars of economic damage each year. Global estimates for the year 2030 predict a further growth of almost 50%. [2] In 2000, it is estimated that 2.8% of world's population had diabetes mellitus and that by 2030 this number will be 4.4% of the world's population. According to WHO [2] the 'top' three countries in terms of the number of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) individuals with diabetes are India (31.7 million in 2000; 79.4 million in 2030), China (20.8 million in 2000; 42.3 million in 2030) and the US (17.7 million in 2000; 30.3 million in 2030). This increase is a warning sign for Indian health care system to be vigilant for adequate diabetes mellitus management. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a complex and pleomorphic metabolic disorder, characterized by defects in insulin secretion and insulin action which lead to hyperglycemia. [3] With the onset of this chronic condition and the associated co-morbidities (hypertension, abdominal obesity, dyslipidemia and insulin resistance; together termed as metabolic syndrome), a life-long reduction in quality of life and premature mortality due to micro and macro-vascular complications can be expected. [4] Genetic background and environment factors are likely to be important in determining susceptibility to associated micro and macro-vascular complications, but exposure of tissues to chronic hyperglycemia is the main initiating factor. Thus, the primary therapeutic goal is to reduce plasma hyperglycemia. For many years, it is generally accepted that exercise is a cornerstone of dia Continue reading >>
How to control diabetes?
Eat healthy. This is crucial when you have diabetes, because what you eat affects your blood sugar. No foods are strictly off-limits. Focus on eating only as much as your body needs. Get plenty of vegetables, fruits, and whole grains. Choose nonfat dairy and lean meats . Limit foods that are high in sugar and fat. Remember that carbohydrates turn into sugar, so watch your carb intake. Try to keep it about the same from meal to meal. This is even more important if you take insulin or drugs to control your blood sugars. 2. Exercise. If you're not active now, it’s time to start. You don't have to join a gym and do cross-training. Just walk, ride a bike, or play active video games. Your goal should be 30 minutes of activity that makes you sweat and breathe a little harder most days of the week. An active lifestyle helps you control your diabetes by bringing down your blood sugar. It also lowers your chances of getting heart disease. Plus, it can help you lose extra pounds and ease stress. 3. Get checkups. See your doctor at least twice a year. Diabetes raises your odds of heart disease. So learn your numbers: cholesterol, blood pressure, and A1c (average blood sugar over 3 months). Get a full eye exam every year. Visit a foot doctor to check for problems like foot ulcers and nerve damage. 4. Manage stress. When you're stressed, your blood sugar levels go up. And when you're anxious, you may not manage your diabetes well. You may forget to exercise, eat right, or take your medicines. Find ways to relieve stress -- through deep breathing, yoga, or hobbies that relax you. 5. Stop smoking. Diabetes makes you more likely to have health problems like heart disease Continue reading >>
What is type 2 diabetes?
TYPE 2 DIABETES OVERVIEW Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition, but people with diabetes can lead a full life while keeping their diabetes under control. Lifestyle modifications (changes in day-to-day habits) are an essential component of any diabetes management plan.
What are the lifestyle changes for diabetics?
Home / Resources / Articles / Nutrition and Lifestyle Modifications for Diabetes Patients Nutrition and Lifestyle Modifications for Diabetes Patients Lifestyle change is the new trend for managing a patients diabetes, according to research. It is well established that diabetes mellitus (DM) is a progressive metabolic disorder, characterized by hallmark signs such as hyperglycemia, which is due to a deficiency of the hormone insulin. Besides glucose control, which is essential for patients who have DM, there is a strong need for patients to maintain a healthy and balanced life in order to avoid any complications. There are essentially seven key self-preservation behaviors in patients with diabetes that predict healthy outcomes, namely: eating well, being physically active, monitoring blood sugar regularly, compliance and adherence to the medications prescribed, good problem-solving skills, healthy coping skills and risk-reduction behaviors. All seven of these behaviors have proven to show a positive correlation with good glycemic control, reduction of complications and improvement in quality of life. Individuals with diabetes have been shown to make a drastic impact on the advancement and development of their disease by partaking in their own care. Despite this fact, when looking at a longer-term change in individuals, compliance and adherence to these activities is incredibly low. In a new study published in US Endocrinology, researchers examined the effectiveness of nutrition and lifestyle modifications in improving diabetes outcomes. One of their essential focuses was on the ABCs of diabetes management: A1c, blood pressure and cholesterol. Maintaining an A1c level of about 7%, keeping your blood pressure <140/90mmHg, and maintaining LDL at <100mg/dL (with no cardiova Continue reading >>
What are secondary objectives?
Secondary objectives are: Assess whether the prescription of a DASH-type diet and encouragement for physical activity through use of pedo Continue reading >>. The lifestyle changes that can cut type 2 diabetes risk. Regular, early lifestyle changes key to reducing type 2 diabetes & cardiovascular disease.
What is the AHA's goal for 2020?
The Strategic Plan from the AHA for 2020, articulated the goal “by 2020 to improve the cardiovascular health of all Americans by 20%, while reducing deaths from CVD and stroke by 20%.”3To achieve these goals the AHA outlined a series of steps, many of which depend on lifestyle modalities.
How does daily activity affect cardiovascular disease?
Daily habits and actions powerfully affect the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), in general, and coronary heart disease, in particular. Regular physical activity, sound nutrition, weight management, and not smoking cigarettes have all been demonstrated to significantly reduce the risk of CVD. In 2 large cohort studies a reduction of risk ...
What are the best ways to reduce CVD risk?
Increased physical activity, proper nutrition, weight management, avoidance of tobacco, and stress reduction are all key modalities that both lower the risk of CVD and enhance quality of life.
What is the look ahead trial?
The large, National Institutes of Health–funded Look AHEAD (Action for Health and Diabetes) Trial showed that individuals who lost 7% of body weight significantly lowered all cardiovascular risk factors, except for LDL cholesterol levels.41However , the rate of cardiovascular events was not reduced during the trial.
Why use BMI?
Use BMI as a first step in establishing criteria to judge potential health risk. Counsel patients that lifestyle changes can produce modest and sustained weight loss and achieve meaningful health benefits, while greater weight loss produces greater benefits.
What are the best diets for CVD?
Dietary guidance, over the past 20 years, has moved from specific foods and nutrients to a primary emphasis on dietary patterns. The following dietary patterns have all been recommended to lower the risk of CVD: 1 US healthy eating pattern 2 Low-fat diets 3 Mediterranean diet 4 DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet 5 Vegetarian diet 6 Plant-based diets
Is diabetes a risk factor for CVD?
Diabetes is a recognized and significant risk factor for CVD.53CVD is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality among individuals with diabetes. Lifestyle therapies, including proper nutrition and regular physical activity, are key therapeutic modalities to reduce the risk of CVD in individuals with diabetes.
What is the recommended daily limit for cholesterol?
An ideal limit is less than 1,500 mg per day for most adults.) Lean meats. (round, sirloin, chuck and loin) Cholesterol. Patients with abnormal cholesterol levels, particularly those with Type 2 diabetes or at risk for heart failure, should be cautious in consuming foods rich in cholesterol. Fruits and vegetables.
How to manage Type 2 diabetes?
Managing weight. Being overweight or obese make it hard to manage Type 2 diabetes. It also increases the risk for high blood cholesterol and high blood pressure — risk factors for cardiovascular disease , which is the leading cause of death for people with diabetes. Two ways to help manage weight are to eat healthy and be more physically active. ...
How to get rid of stress?
Diminish energy level. Interrupt sleep. Trigger various unhealthy responses, including overeating, drinking too much alcohol, smoking, procrastinating and not sleeping enough. We can't get rid of stress, but we can deal with it in a healthy way.
What to do when your kitchen isn't convenient?
With a little forethought, you can properly nourish your body wherever life takes you. Remember these tips for eating on the go: Bring a healthy lunch and snacks to eat throughout the day.
How to prevent diabetes?
Eating healthy. Making healthy food choices, including controlling portion sizes and reading food labels, is key to maintaining the right weight and preventing or managing diabetes. With prediabetes or diabetes, you have additional issues with food. For example, it’s important to limit simple carbohydrates that are in foods such as table sugar, ...
How to track blood sugar?
Keep a food and blood glucose log. By writing down what you eat, when you eat and how it affects your glucose levels, you can track how foods affect your body. Check your blood sugar 1 hour to 1.5 hours after eating to see how your body reacts to various foods.
How often should I eat non-fried fish?
Non-fried fish at least twice per week, especially those high in omega-3 fatty acids. (such as salmon, lake trout, mackerel and herring) Fatty and processed meats. (such as fatty beef and pork, salami and hot dogs) Chicken or turkey. (white meat without skin) Sodium.
Why are Hispanics at higher risk for diabetes?
Why the greater risk for type 2 diabetes and its complications? These factors can play a part: 1 Genetics: Hispanics/Latinos have genes that increase their chance of developing type 2 diabetes. Diabetes is very complicated, though, and the connection isn’t completely clear. 2 Food: In some Hispanic/Latino cultures, foods can be high in fat and calories. Also, family celebrations may involve social pressure to overeat, and turning down food could be seen as impolite. 3 Weight/activity: Hispanics/Latinos have higher rates of obesity and tend to be less physically active than non-Hispanic whites. And some see overweight as a sign of health instead of as a health problem.
How many minutes a day do you need to do a lifestyle change?
That’s just 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week. In the lifestyle change program, you’ll work with a trained coach and share experiences with others who have the same goals and challenges. Some classes welcome other adult family members to attend along with you for support.
How much chance of developing type 2 diabetes?
Over their lifetime, US adults overall have a 40% chance of developing type 2 diabetes. But if you’re a Hispanic/Latino American adult, your chance is more than 50%, and you’re likely to develop it at a younger age. Diabetes complications also hit harder: Hispanics/Latinos have higher rates of kidney failure. external icon.
How to manage blood sugar levels?
If you have diabetes, you need to make choices and take action every day to manage your blood sugar levels. That includes eating healthy food, being physically active most days, taking medicine if needed, and getting regular checkups.
What is DSMES good for?
DSMES has many benefits, from helping improve blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels to enhancing quality of life. Help could also be as close as the dinner table. Hispanic/Latino people are known for their strong family connections, and for sharing meals together at home.
Which group is more likely to develop prediabetes?
People of certain racial and ethnic groups are more likely to develop prediabetes and type 2 diabetes, including African Americans, Hispanic/Latino Americans, and Asian Americans. Learn why Hispanic/Latino risk is higher, and some ways to prevent type 2 diabetes or manage diabetes if you already have it. Hispanic/Latino Americans make up ...
Is it possible to have type 2 diabetes if you are Puerto Rican?
For example, if your heritage is Puerto Rican, you’re about twice as likely to have type 2 diabetes as someone whose background is South American.
