Medication
What Is Type 1 Diabetes? Overview of causes, symptoms, and daily management. Just Diagnosed. The basics of everyday diabetes care for newly diagnosed people. Types of Insulin. Your guide to insulin types and how they work. 4 Ways To Take Insulin. Insulin pens, pumps, and 2 other methods for taking insulin.
Nutrition
This section focuses on the medical management of type 1 diabetes. And as the term “medical management” implies, this management is done with the guidance of your medical provider and medical team. The key principles of medical management are: Regular blood sugar (and ketone) self monitoring as a part of daily living. Taking insulin.
See more
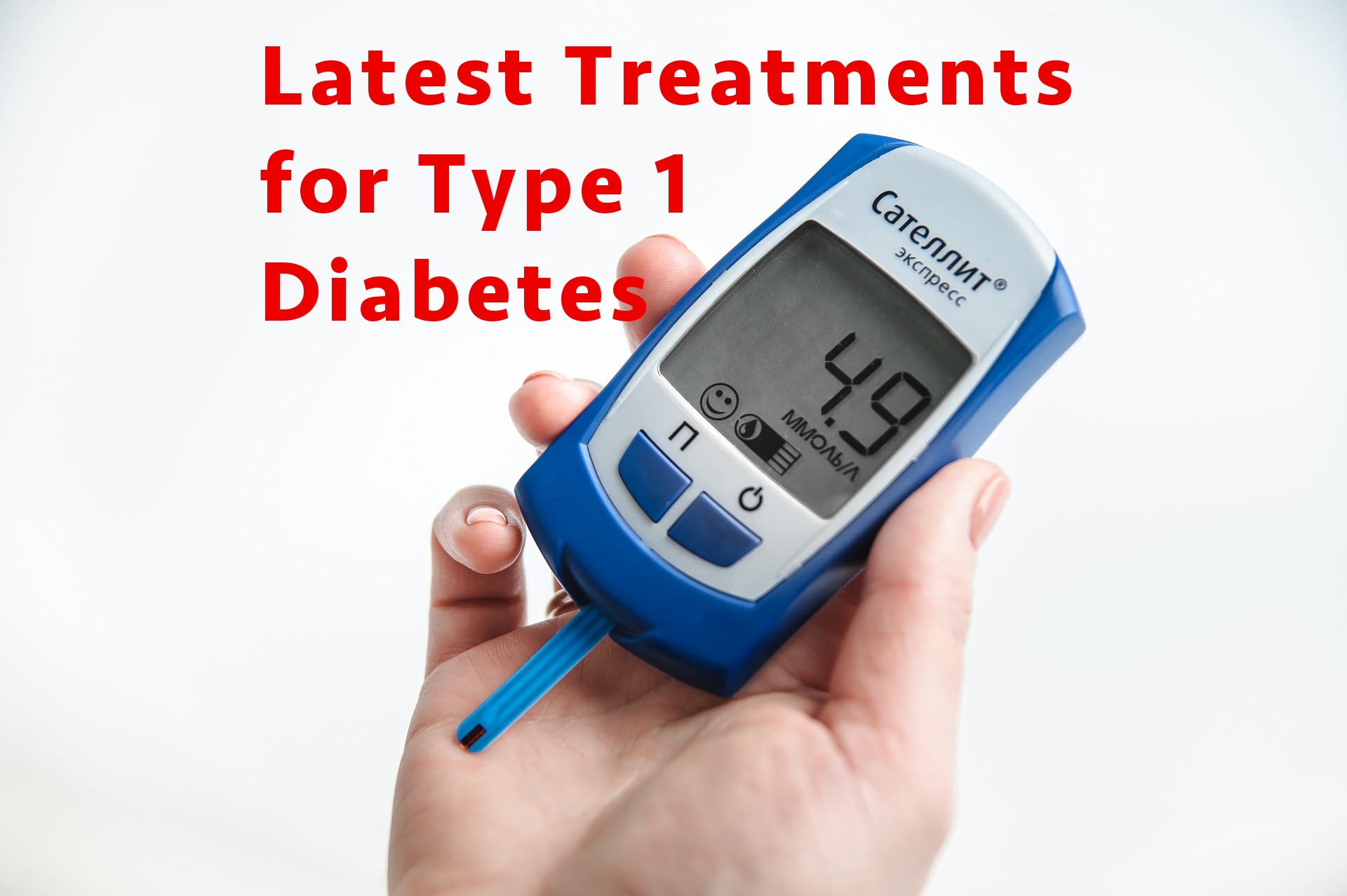
Mar 11, 2022 · If you have type 1 diabetes, you’ll need to take insulin shots (or wear an insulin pump) every day. Insulin is needed to manage your blood sugar levels and give your body energy. You can’t take insulin as a pill. That’s because the acid in your stomach would destroy it before it could get into your bloodstream.
What is the best treatment for Type 1 diabetes?
People who have type 1 diabetes must take insulin as part of their treatment. Because their bodies can't make insulin anymore, they need to get the right amount to keep their blood sugar levels in a healthy range. The only way to get insulin into the body now is by injection with a needle or with an insulin pump.
How I cured my type 1 diabetes?
Feb 17, 2021 · As an adjunct to meal-time insulin, the injectable amylin analogue pramlintide is approved only in the USA for the treatment of type 1 and type 2 diabetes alike . In type 1 diabetes, pramlintide has been shown to improve postprandial glucose levels to some extent . Its clinical use has been limited, arguably because of the modest efficacy alongside the occurrence of …
How dangerous is diabetes type 1?
Mar 10, 2022 · Treatment Treatment for type 1 diabetes includes: Taking insulin Monitoring blood sugar Eating healthy foods Exercising regularly You'll work closely with your child's diabetes treatment team — health care provider, certified diabetes care and education specialist, and registered dietitian.
How you can cope with Type 1 diabetes?
Nov 20, 2017 · Insulin therapy itself is the basis in treatment of type 1 diabetes. Recent years have brought multiple solutions in the implementation of the treatment. New types of insulin, modern glycaemia monitoring, and insulin administration techniques revolutionized the capabilities of contemporary insulin therapy.
See more

How can type 1 diabetes be treated or cured?
What is the first treatment for type 1 diabetes?
Can a Type 1 diabetic go away?
Which is worse type 1 or 2 diabetes?
Can type 1 diabetes be treated without insulin?
Can you live a normal life with type 1 diabetes?
What are the warning signs of diabetes type 1?
- Increased thirst.
- Frequent urination.
- Bed-wetting in children who previously didn't wet the bed during the night.
- Extreme hunger.
- Unintended weight loss.
- Irritability and other mood changes.
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Blurred vision.
Which type of diabetes is worse?
Overview
With type 1 diabetes, your pancreas loses the ability to make enough insulin, a hormone that helps the body absorb blood sugar, or glucose, and convert it to energy. When this happens, the sugar builds up in your blood.
Insulin
If your body is no longer producing enough insulin, you’ll need to take insulin every day to help regulate your blood sugar. Because glucose levels can fluctuate, people with type 1 diabetes usually need to check their blood sugar throughout the day to determine how much insulin they need to take.
Metformin
Metformin is an oral medication that is often prescribed to people with type 2 diabetes to help them control their glucose levels. This medication does not increase insulin in the body. Instead, it lowers glucose production, and also helps insulin work more effectively.
Medications
Your doctor might prescribe other medications, such as blood pressure medication, cholesterol-lowering medications, or aspirin. These medications don’t treat the diabetes itself, but help reduce the risk of other health problems that can be related to diabetes, such as hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and kidney problems.
Artificial Pancreas
An artificial pancreas is a medical device that mimics the work of a real pancreas by monitoring your blood sugar levels and releasing insulin automatically. Instead of checking your glucose levels and injecting yourself throughout the day, you wear a sensor under your skin, a continuous glucose monitor, and an insulin pump.
Islet Cell Transplantation
Islet cell transplantation is a procedure that takes healthy insulin-producing cells from a donor pancreas, and transplants them into a person with type 1 diabetes.
Pancreas Transplant
In some cases, doctors can take a healthy transplant from a deceased donor, and transplant it into the body of someone with type 1 diabetes. While this procedure can restore the body’s natural insulin production, it’s also risky, because the medications you have to take to prevent your body from rejecting the pancreas can have serious side effects.
How to manage diabetes?
This section focuses on the medical management of type 1 diabetes. And as the term “medical management” implies, this management is done with the guidance of your medical provider and medical team. The key principles of medical management are: 1 Regular blood sugar (and ketone) self monitoring as a part of daily living 2 Taking insulin 3 Problem solving how and when to make adjustments in your food and insulin doses to prevent high or low blood sugars 4 Understanding complications and how to screen for, prevent and treat them
What are the principles of medical management?
The key principles of medical management are: Regular blood sugar (and ketone) self monitoring as a part of daily living. Taking insulin. Problem solving how and when to make adjustments in your food and insulin doses to prevent high or low blood sugars.
What is blood sugar monitoring?
Blood sugar & ketone monitoring: The tool that tells you whether your treatment is successful. Medications: Includes insulin, amylin analogs and use of the insulin pump. Self-management solutions: How to analyze what is causing you to have low blood sugars and/or high blood sugars. Complications:
Can a person with diabetes live a long life?
People with type 1 diabetes (T 1D) can live long, happy lives with proper care and disease management. Advancements in medication types and delivery methods give people the freedom to choose which treatment options work best with their particular circumstance. T1D prognoses can be greatly improved with a combination of treatments and lifestyle choices.
How is Type 1 diabetes managed?
Type 1 diabetes is managed through use of a variety of insulins. People with T1D must work closely with their medical team to find the right insulin treatment for their condition. Further information about the types of insulin and their effects are available on our insulin page.
What is the drug used to treat diabetes?
Metformin. Combined with insulin, diet and exercise, type 2 diabetes (T2D) drug metformin is sometimes prescribed to people with T1D to help treat their diabetes. Metformin helps control the body’s blood-sugar levels and how the liver processes sugar.
Is pramlintide a hormone?
Used in conjunction with insulin, pramlintide is often prescribed after other medications prove not as effective as needed. It acts as a hormone to help the body better control blood sugar.
Can aspirin be used with insulin?
Medications for high blood pressure and high cholesterol as well as aspirin can be prescribed with insulin to help the overall health and treatment of diabetes. Since people with diabetes have an increased chance of cardiovascular disease, these drugs are used in combination with other diabetes medications.
What is the purpose of blood sugar monitoring?
Monitoring lets a person know when insulin may be needed to correct high blood sugar or when carbohydrates may be needed to correct low blood sugar. Monitoring blood sugar can be done using traditional blood-sugar meters or continuous glucose monitors (CGMs).
How to get diabetes educator?
Whether you just got diagnosed with type 1 diabetes or have had it for some time, meeting with a diabetes educator is a great way to get support and guidance, including how to: 1 Develop and stick to a healthy eating and activity plan 2 Test your blood sugar and keep a record of the results 3 Recognize the signs of high or low blood sugar and what to do about it 4 Give yourself insulin by syringe, pen, or pump 5 Monitor your feet, skin, and eyes to catch problems early 6 Buy diabetes supplies and store them properly 7 Manage stress and deal with daily diabetes care
Is high blood sugar a sign of diabetes?
High blood sugar is damaging to the body and causes many of the symptoms and complica tions of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes (previously called insulin-dependent or juvenile diabetes) is usually diagnosed in children, teens, and young adults, but it can develop at any age. Type 1 diabetes is less common than type 2 —approximately 5-10% ...
What is the cause of type 1 diabetes?
What Causes Type 1 Diabetes? Type 1 diabetes is thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction (the body attacks itself by mistake) that destroys the cells in the pancreas that make insulin, called beta cells. This process can go on for months or years before any symptoms appear.
How does Type 1 diabetes happen?
Type 1 diabetes is thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction (the body attacks itself by mistake) that destroys the cells in the pancreas that make insulin, called beta cells. This process can go on for months or years before any symptoms appear. Some people have certain genes (traits passed on from parent to child) ...
Does diet cause diabetes?
Being exposed to a trigger in the environment, such as a virus, is also thought to play a part in developing type 1 diabetes. Diet and lifestyle habits don’t cause type 1 diabetes.
How long does it take for diabetes to show symptoms?
Type 1 diabetes symptoms can develop in just a few weeks or months. Once symptoms appear, they can be severe. Some type 1 diabetes symptoms are similar to symptoms of other health conditions.
How long does it take for diabetes to develop?
Type 1 diabetes symptoms can develop in just a few weeks or months. Once symptoms appear, they can be severe. Some type 1 diabetes symptoms are similar to symptoms of other health conditions. Don’t guess—if you think you could have type 1 diabetes, see your doctor right away to get your blood sugar tested. Untreated diabetes can lead ...
How to treat high blood sugar?
High blood sugar levels can make people with type 1 diabetes feel sick, so their treatment plan involves keeping their blood sugar levels within a healthy range, while making sure they grow and develop normally. To do that, people with type 1 diabetes need to: 1 take insulin as prescribed 2 eat a healthy, balanced diet with accurate carbohydrate counts 3 check blood sugar levels as prescribed 4 get regular physical activity
What is the first thing to understand when it comes to treating diabetes?
The first thing to understand when it comes to treating diabetes is your blood glucose level, which is the amount of glucose in the blood. Glucose is a sugar that comes from the foods we eat and also is formed and stored inside the body.
Can type 1 diabetes cause high blood glucose?
People with type 1 diabetes can no longer produce insulin. This means that glucose stays in the bloodstream and doesn't get into the cells, causing blood glucose levels to go too high.
Can diabetes make you sick?
High blood sugar levels can make people with type 1 diabetes feel sick, so their treatment plan involves keeping their blood sugar levels within a healthy range, while making sure they grow and develop normally. To do that, people with type 1 diabetes need to: take insulin as prescribed.
How to treat type 1 diabetes?
To do that, people with type 1 diabetes need to: take insulin as prescribed. eat a healthy, balanced diet with accurate carbohydrate counts. check blood sugar levels as prescribed. get regular physical activity. Following the treatment plan can help a person stay healthy, but it's not a cure for diabetes.
How to cure diabetes?
eat a healthy, balanced diet with accurate carbohydrate counts. check blood sugar levels as prescribed. get regular physical activity. Following the treatment plan can help a person stay healthy, but it's not a cure for diabetes. Right now, there's no cure for diabetes, so people with type 1 diabetes will need treatment for the rest ...
Can you take insulin if you have type 1 diabetes?
Take Insulin as Prescribed. People who have type 1 diabetes must take insulin as part of their treatment. Because their bodies can't make insulin anymore, they need to get the right amount to keep their blood sugar levels in a healthy range.
Is type 1 diabetes asymptomatic?
In its early stage (Stage 1), type 1 diabetes is usually asymptomatic; however, the development of autoimmunity is often detectable in early life, with circulating autoantibodies targeting insulin or other proteins, such as GAD65, insulinoma-associated protein 2 (IA2) or zinc transporter 8 (ZNT8) [5].
Does metformin help with diabetes?
However, partly because of its ameliorating effect on insulin resistance, metformin has been somewhat promising in managing the disease, especially in children and adolescents, as well as in obese people with type 1 diabetes, with studies indicating reduced insulin requirements and body weight reduction [73–75].
What is GLP-1 in diabetes?
GLP-1 is a hormone of the incretin system that is secreted upon food intake. A marked uptake has been seen in the use of GLP-1 RAs in type 2 diabetes due to their pleiotropic glucose-dependent effects that improve glycaemic control and reduce body weight [90].
What is the HLA region of chromosome 6?
Type 1 diabetes is a polygenic disorder, in which susceptibility loci or genetic variation contributes to disease risk. The HLA region on chromosome 6 is the main susceptibility locus and, in recent years, many other loci across the genome have been associated with an increasing risk of the disease [8].
Is verapamil a calcium channel blocker?
Verapamil is a common calcium-channel blocker used for decades as an anti-hypertensive agent. In mouse models of type 1 diabetes, verapamil promoted survival of functional beta cells via a mechanism that involves reduced expression of the cellular redox regulator thioredoxin-interacting protein [102].
How to treat diabetes in children?
Treatment for type 1 diabetes includes: Taking insulin. Carbohydrate counting. Frequent blood sugar monitoring.
How to help a diabetic child with diabetes?
Encourage your child to get at least 60 minutes of physical activity daily or, better yet, exercise with your child. Make physical activity part of your child's daily routine.
Does diabetes cause depression?
People with diabetes have an increased risk of depression, anxiety and diabetes-related distress. That's why some diabetes specialists regularly include a social worker or psychologist as part of their diabetes care team. If you notice that your child or adolescent is persistently sad or pessimistic, or experiences dramatic changes in sleeping habits, weight, friends or school performance, have your child screened for depression.
Can a child live a normal life with diabetes?
If you and your child work with your child's doctor and do your best to manage your child's diabetes, your child will likely live a long and normal life.
How often does a CGM monitor blood sugar?
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices measure your blood sugar every few minutes using a temporary or implanted sensor inserted under the skin. Some devices show your blood sugar reading at all times on a receiver or your smartphone or smartwatch, while others require that you check your blood sugar by running the receiver over the sensor.
What is the best way to deliver insulin?
There are several options for insulin delivery, including: Fine needle and syringe. This looks like a shot you might get in a doctor's office, but with a much thinner needle. Insulin pen with fine needle. This device looks like an ink pen, except the cartridge is filled with insulin. An insulin pump.
What is an insulin pump?
An insulin pump. This is a small device worn on the outside of your body that you program to deliver specific amounts of insulin throughout the day and when you eat.

Prognosis
Administration
Medical uses
Treatment
Side effects
Diagnosis
Example
- Used in conjunction with insulin, pramlintide is often prescribed after other medications prove not as effective as needed. It acts as a hormone to help the body better control blood sugar.
Diet
- Medications for high blood pressure and high cholesterol as well as aspirin can be prescribed with insulin to help the overall health and treatment of diabetes. Since people with diabetes have an increased chance of cardiovascular disease, these drugs are used in combination with other diabetes medications. Treatment for T1D includes monitoring and lifestyle choices in addition t…