Precautions
· If there is suspicion of a patient having trimethoprim/sulfamethazine toxicity, a treatment plan includes the administration of activated charcoal (if ingested), gastric lavage, and supportive intravenous (IV) and oral fluids. More severe treatment measures may consist of hemodialysis and alkalizing the patient's urine.
How do you take sulfamethoxazole trimethoprim?
· Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim combination is an antibiotic. It works by eliminating the bacteria that cause many kinds of infections. This medicine will not work for colds, flu, or other virus infections. This medicine is available only with your doctor's prescription. This product is available in the following dosage forms: Tablet Suspension
What should I do if I miss a dose of trimethoprim?
· high potassium level--nausea, weakness, tingly feeling, chest pain, irregular heartbeats, loss of movement. Common side effects may include: vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain; rash, itching; or. swelling in your tongue. This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects.
How often can you take 200 mg of trimethoprim?
inflammation of the tissue lining the sinuses. pneumonia caused by bacteria. bacterial infection with chronic bronchitis. chronic bronchitis caused by …
Is trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole still a popular antibiotic?
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole for treatment of severe Staphylococcus aureus infections In select infections, TMP/SMX may be a useful alternative to vancomycin for treatment of severe S. aureus infections. Additional randomized studies should be conducted comparing this agent with vancomycin and linezolid.

How long does it take for sulfamethoxazole trimethoprim to work?
Bactrim (sulfamethoxazole / trimethoprim) is absorbed by the body and begins to kill bacteria within 1 to 4 hours after taking your dose. For more common problems like urinary tract infections and ear infections, most people will start to feel relief after a few days.
Is trimethoprim a good antibiotic?
Sometimes trimethoprim is the only suitable antibiotic to treat an infection. In this case the benefit of taking it is likely to outweigh the small risk of harm, but discuss this with your doctor.
How does trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole work?
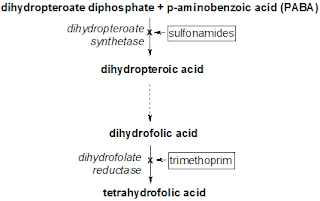
Sulfamethoxazole stops bacteria from making dihydrofolic acid and trimethoprim prevents the formation of tetrahydrofolic acid; both significant steps in the formation of nucleic acids and proteins essential to many bacteria. The combination of sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim kills bacteria.
How many days do you take sulfamethoxazole?
The usual dose is 75 to 100 milligrams (mg) per kilogram of body weight of sulfamethoxazole and 15 to 20 milligrams (mg) per kilogram of body weight of trimethoprim each day, given in equally divided doses every 6 hours for 14 to 21 days.
Why do you take trimethoprim at night?
To prevent an infection: The dose to prevent infection is half a tablet (150mg) at night. If you have frequent urine infections, you will have to take trimethoprim each night for a few months to prevent recurrent infections. Always take your trimethoprim exactly as your doctor has told you.
What is the strongest antibiotic for a UTI?
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, nitrofurantoin, and fosfomycin are the most preferred antibiotics for treating a UTI....Common doses:Amoxicillin/clavulanate: 500 twice a day for 5 to 7 days.Cefdinir: 300 mg twice a day for 5 to 7 days.Cephalexin: 250 mg to 500 mg every 6 hours for 7 days.
Is sulfamethoxazole a strong antibiotic?
Is Sulfamethoxazole a strong antibiotic? Yes, sulfamethoxazole is an antibiotic used for treating bacterial infections such as infections of the urinary tract, prostatitis, and bronchitis.
What foods should I avoid while taking Bactrim?
What drugs and food should I avoid while taking Bactrim (Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim Oral/Injection)? If you use the injection form of this medicine, do not eat or drink anything that contains propylene glycol (an ingredient in many processed foods, soft drinks, and medicines). Dangerous effects could occur.
How does sulfamethoxazole make you feel?
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and loss of appetite may occur. If any of these effects persist or worsen, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly. Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects.
Why do you need to drink a lot of water with antibiotics?
Antibiotics are usually taken with water because taking them together with fruit juices, dairy products or alcohol can affect how the body absorbs some drugs.
What are the side effects of taking trimethoprim?
Side EffectsBlack, tarry stools.blood in urine or stools.bluish fingernails, lips, or skin.changes in facial skin color.difficult breathing or shortness of breath.fever with or without chills.general feeling of discomfort or illness.neck stiffness.More items...•
What are the side effects of sulfamethoxazole trimethoprim?
More commonBlack, tarry stools.blistering, peeling, or loosening of the skin.changes in skin color.chest pain or tightness.cough or hoarseness.general feeling of tiredness or weakness.headache.itching, skin rash.More items...•
What is sulfamethoxazole trimethoprim?
1. How it works. Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim is a fixed combination medicine containing two antibiotics - sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. Sulfamethoxazole stops bacteria from making dihydrofolic acid and trimethoprim prevents the formation of tetrahydrofolic acid; both significant steps in the formation of nucleic acids ...
What is the difference between sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim?
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim belongs to the class of medicines known as antibiotics. The sulfamethoxazole component belongs to the class of medicines known as sulfonamides, and the trimethoprim component belongs to the class of medicines known as folic acid inhibitors. 2. Upsides.
How long does sulfamethoxazole stay in your system?
The antibacterial effects of sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim persist for at least 12 hours. 7. Interactions. Medicines that interact with sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim may either decrease its effect, affect how long it works for, increase side effects, or have less of an effect when taken with sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim.
What is sulfamethoxazole used for?
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim is a combination antibiotic used to treat infections such as those affecting the ear, urinary tract, lungs, or gastrointestinal tract.
What medications interact with sulfamethoxazole?
Common medications that may interact with sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim include: anticonvulsants such as phenytoin. antidepressants, such as amitriptyline, amoxapine, and desipramine. cyclosporine. digoxin. anticoagulants ( blood thinners), such as war farin. blood pressure medications, such as captopril or enalapril.
Does sulfamethoxazole cause diarrhea?
Like other antibiotics, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim can change the natural balance of bacteria present in your gut and may cause severe and persistent diarrhea, associated with a bacteria called Clostridium difficile.
Is sulfamethoxazole good for kidney disease?
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim is an effective combination antibiotic; however, it may not be suitable for those with kidney or liver disease or folate deficiency. The risk of side effects may be higher in the elderly.
Dosing
The dose of this medicine will be different for different patients. Follow your doctor's orders or the directions on the label. The following information includes only the average doses of this medicine. If your dose is different, do not change it unless your doctor tells you to do so.
Missed Dose
If you miss a dose of this medicine, take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular dosing schedule. Do not double doses.
Storage
Store the medicine in a closed container at room temperature, away from heat, moisture, and direct light. Keep from freezing.
What is sulfamethoxazole used for?
Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim combination is used to treat infections including urinary tract infections, middle ear infections (otitis media), bronchitis, traveler's diarrhea, and shigellosis (bacillary dysentery). This medicine is also used to prevent or treat Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia or Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), a very serious kind of pneumonia. This type of pneumonia occurs more commonly in patients whose immune systems are not working normally, including cancer patients, transplant patients, and patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS).
Does sulfamethoxazole work for colds?
Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim combination is an antibiotic. It works by eliminating the bacteria that cause many kinds of infections. This medicine will not work for colds, flu, or other virus infections. This medicine is available only with your doctor's prescription.
What is the purpose of trimethoprim?
Trimethoprim is an antibiotic that is used to treat bladder or kidney infections, or ear infections caused by certain bacteria.
What are the side effects of trimethoprim?
Trimethoprim side effects. Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction: hives; difficult breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. Call your doctor at once if you have: severe stomach pain, diarrhea that is watery or bloody (even if it occurs months after your last dose);
Is it safe to breastfeed with trimethoprim?
Trimethoprim can interfere with your body's ability to metabolize folic acid, a form of vitamin B important in the development of the unborn baby's brain and spinal cord. It may not be safe to breastfeed while using this medicine. Ask your doctor about any risk.
Can trimethoprim be used for viral infections?
This medicine will not treat a viral infection such as the flu or a common cold. This medicine can affect the results of certain medical tests. Tell any doctor who treats you that you are taking trimethoprim. Store at room temperature away from moisture, heat, and light.
Can you take trimethoprim if you have anemia?
You should not use trimethoprim if you have anemia caused by a folate ( folic acid) deficiency.
What is trimethoprim used for?
Trimethoprim is a prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of bacterial infections. Trimethoprim may be used alone or with other medications.
How to report a side effect of trimethoprim?
For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How is trimethoprim excreted?
Excretion of trimethoprim (trimethoprim (trimethoprim tablet) tablet) is primarily by the kidneys through glomerular filtration and tubular secretion. Urine concentrations of trimethoprim (trimethoprim (trimethoprim tablet) tablet) are considerably higher than are the concentrations in the blood.
What test is performed to determine the susceptibility of the bacteria to trimethoprim?
Cultures and susceptibility tests should be performed to determine the susceptibility of the bacteria to trimethoprim (trimethoprim (trimethoprim tablet) tablet) . Therapy may be initiated prior to obtaining the results of these tests.
What are the side effects of taking trimethoprim?
The adverse effects encountered most often with trimethoprim (trimethoprim (trimethoprim tablet) tablet) were rash and pruritus.
Where is trimethoprim metabolized?
Ten to twenty percent of trimethoprim (trimethoprim (trimethoprim tablet) tablet) is metabolized, primarily in the liver; the remainder is excreted unchanged in the urine. The principal metabolites of trimethoprim (trimethoprim (trimethoprim tablet) tablet) are the 1- and 3-oxides and the 3'- and 4'-hydroxy derivatives. The free form is considered to be the therapeutically active form. Approximately 44% of trimethoprim (trimethoprim (trimethoprim tablet) tablet) is bound to plasma proteins.
Does trimethoprim interfere with methotrexate?
Trimethoprim (trimethoprim (trimethoprim tablet) tablet) can interfere with a serum methotre xate assay as determined by the Competitive Binding Protein Technique (CBPA) when a bacterial dihydrofolate reductase is used as the binding protein. No interference occurs, however, if methotrexate is measured by a radioimmunoassay (RIA). The presence of trimethoprim (trimethoprim (trimethoprim tablet) tablet) may also interfere with the Jaffé alkaline picrate reaction assay for creatinine resulting in over estimations of about 10% in the range of normal values.
How to take sulfamethoxazole trimethoprim?
How to use sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim oral. Take this medication by mouth, as directed by your doctor, with a full glass of water (8 ounces / 240 milliliters). If stomach upset occurs, take with food or milk. Drink plenty of fluids while taking this medication to lower the unlikely risk of kidney stones forming, ...
What is sulfamethoxazole used for?
It is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections (such as middle ear, urine, respiratory, and intestinal infections).
Where to report side effects?
You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch. In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345. Precautions.
Can you stop taking blood thinners without your doctor's approval?
Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval. Some products that may interact with this drug include: " blood thinners " (such as warfarin ), dofetilide, methenamine, methotrexate. This product may interfere with certain laboratory tests, possibly causing false test results.
What are the side effects of trimethoprim?
Immune-mediated idiosyncratic reactions are often associated with a reactive metabolite, leading to drug-specific antibodies or T-lymphocyte activation. Simple exanthems and fixed drug eruptions are some of the most common adverse effects of trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole, occurring in about 3% of hospital inpatients taking the drug.54Less common is a classic drug hypersensitivity syndrome manifesting with a triad of fever, exanthem and varying degrees of internal organ involvement. Typical manifestations vary in presentation and severity. They include hematologic abnormalities (most commonly lymphopenia or lymphocytosis, but occasionally eosinophilia), cholestatic or hepatocellular hepatitis (which may progress to fulminant hepatic failure), renal dysfunction (including acute interstitial nephritis),11–15Stevens–Johnson syndrome and potentially life-threatening toxic epidermal necrolysis.16If there has been no previous exposure to trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole, these reactions typically begin after at least four or five days of therapy but may occur after several weeks of prolonged therapy. Importantly, the presence of fever can mislead clinicians by suggesting an unresolved infection, thereby delaying discontinuation of trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole.
How long does it take for neurologic symptoms to resolve after discontinuation of trimethoprim?
Other rare adverse neurologic effects include delirium and milder effects such as tremor,5which typically occurs in the first week of therapy, and gait disturbances.5,6In general, neurologic symptoms occur within days of continuous treatment and resolve following discontinuation of trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole.
Does trimethoprim cause aseptic meningitis?
Trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole readily crosses the blood–brain barrier40and is associated with various adverse neurologic events, all of which have been described only in case reports. Numerous instances of aseptic meningitis (involving high doses of trimethoprim alone or trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole) have been reported, many of them involving patients with pre-existing autoimmune disease or HIV infection.4The mechanism of toxicity is not well defined, but an immunologic process is suggested.4Clinically, drug-induced meningitis is indistinguishable from other causes of aseptic meningitis, and the diagnosis is suggested by negative results of microbiologic testing, temporal association with drug initiation, prompt improvement following discontinuation of the offending drug and the absence of another identifiable cause.
When was trimethoprim introduced?
Introduced in 1968 , trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole remains a popular antibiotic because of its low cost, effectiveness and familiarity among clinicians. It is the most frequently prescribed antibiotic for urinary tract infections in Canada.1Other indications include treatment of infections caused by Pneumocystis jiroveci, Toxoplasma gondii, Stenotrophomonas maltophiliaand community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. In addition, among patients with depressed CD4 counts from infection with HIV, the use of low-dose trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole for prophylaxis against P. jiroveciand T. gondiiis associated with decreased mortality caused by opportunistic infections.2With up to 4000 prescriptions for trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole dispensed each week in Ontario,3this drug is used by hundreds of thousands of Canadians each year.
Can trimethoprim cause blood dyscrasia?
Several uncommon but potentially serious blood dyscrasias have been reported following the use of trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole. The incidence of severe hematologic toxicity is unknown, but estimates range up to 1.7–5.5/100 000 prescriptions.9,10Several mechanisms have been implicated and described in case reports (Table 2). Generation of antibodies to the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex on platelets can cause immune thrombocytopenia, which is typically observed within the first week of treatment and is generally reversible on discontinuation of the drug.47–49
Does trimethoprim cause leukopenia?
Although uncommon at therapeutic doses, the inhibition of folate metabolism by trimethoprim can cause dose-related leukopenia and megaloblastosis, both of which are responsive to folinic acid.41,42Periodic monitoring of the complete blood count may be advisable in patients receiving a high dose of trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole for extended periods.
How It Works
This medication is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections. It is also used to treat a certain type of pneumonia (pneumocystis pneumonia) in patients with a weakened immune system.
May Treat: Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia · Gastroenteritis due to Shigella · E. coli urinary tract infection · Enterobacter cloacae urinary tract infection · Haemophilus influenzae acute otitis media and more
Brand Names: Bactrim · Septra · Sulfatrim · Bactrim DS · Septra DS and more
Drug Class: Antibacterial Folate Antagonist - Other Combinations
Availability: Prescription sometimes needed
Pregnancy: Consult your doctor. This medication may be harmful to an unborn child.
Lactation: Does not adversely affect lactation
Upsides
Downsides
Bottom Line
Tips
Response and Effectiveness
- Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim is a combination antibiotic used to treat infections such as those affecting the ear, urinary tract, lungs, or gastrointestinal tract.
- Active against a wide range of susceptible strains of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species, Enterobacter species, Haemoph...
- Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim is a combination antibiotic used to treat infections such as those affecting the ear, urinary tract, lungs, or gastrointestinal tract.
- Active against a wide range of susceptible strains of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species, Enterobacter species, Haemoph...
- Effective concentrations of both sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim are reached in the gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, lungs, mouth, middle ear, and vagina. Both antibiotics also cross the pl...
- Bacterial resistance is less likely to develop with the combination of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim than if either ingredient (sulfamethoxazole or trimethoprim) is taken alone.
Interactions
- If you are between the ages of 18 and 60, take no other medication or have no other medical conditions, side effects you are more likely to experience include: 1. Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, mouth or tongue inflammation, weight loss, flatulence, rash, and itchy skin. 2. May not be suitable for some people including those with kidney or liver disease, folate deficiency (th…
References
- Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim is an effective combination antibiotic; however, it may not be suitable for those with kidney or liver disease or folate deficiency. The risk of side effects may be higher in the elderly.
Further Information
- May be taken with or without food. Swallow tablets with a big glass of water.
- Take only as directed by your doctor and do not share with anyone else as misuse can encourage the development of drug-resistant bacteria and reduce the effectiveness of sulfamethoxazole/trimethopr...
- Discontinue and seek urgent medical advice if a skin rash develops.
- May be taken with or without food. Swallow tablets with a big glass of water.
- Take only as directed by your doctor and do not share with anyone else as misuse can encourage the development of drug-resistant bacteria and reduce the effectiveness of sulfamethoxazole/trimethopr...
- Discontinue and seek urgent medical advice if a skin rash develops.
- Complete the full course as prescribed (unless instructed not to do so by your doctor) to reduce the risk of resistant bacteria developing.