Definition of settling in wastewater
Wastewater
Wastewater, also written as waste water, is any water that has been adversely affected in quality by anthropogenic influence. Wastewater can originate from a combination of domestic, industrial, commercial or agricultural activities, surface runoff or stormwater, and from sewer inf…
What is settling in water treatment?
In water treatment, settling is an operation that removes suspended particles from the water to be treated. It is a physical process that consists to separate particles of higher density than water from the liquid in which they are found.
What is the process of sewage treatment?
Physical, chemical, and biological processes are used to remove contaminants and produce treated wastewater (or treated effluent) that is safe enough for release into the environment. A by-product of sewage treatment is a semi-solid waste or slurry, called sewage sludge.
How is sewage treated in rural areas?
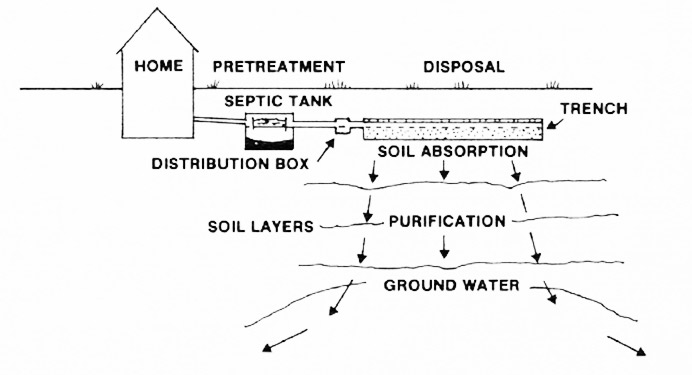
In developing countries and in rural areas with low population densities, sewage is often treated by various on-site sanitation systems and not conveyed in sewers. These systems include septic tanks connected to drain fields, on-site sewage systems (OSS), vermifilter systems and many more.
What is the purpose of a settling tank?
The sewage after bacterial action is then passed on to the next chamber called settling tank. It consists of a set of separating channels with slop slides. The heavier sludge and other sewage particle is separated of the light water; which is then discharged overboard.
How is the settling method used in a water treatment plant?
A sedimentation tank in wastewater treatment removes particles from the water. The accumulated solids, or sludge, form at the bottom of the sedimentation tank and are removed periodically. Coagulants are typically added to the water before sedimentation to aid in the settling process.
What is the function of primary settling?
The objective of primary sedimentation (also known as primary treatment) is the removal of settleable organic solids and floating organic material (called scum) in order to reduce the suspended solids load for downstream treatment processes (Metcalf and Eddy/AECOM, 2014)).
What are the 3 stages of sewage treatment plant?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.
What are the 4 steps of sewage treatment?
4-Step Wastewater Sludge Treatment ProcessStep 1 – Sludge Thickening. The first step in the sewage sludge treatment plan is called thickening. ... Step 2 – Sludge Digestion. After amassing all the solids from the sewage sludge begins the sludge digestion process. ... Step 3 – Dewatering. ... Step 4 – Disposal.
What are the different types of settling?
Different Types Of SettlingDiscrete settling.Flocculent settling.Hindered or zone settling.Compression settling.
What is the difference between primary settling tank and secondary tank?
The main difference is the way each respective treatment is processed. Primary treatment works on sedimentation, where solids separate from the water through several different tanks. In contrast, secondary treatment uses aeration, biofiltration and the interaction of waste throughout its process.
What happens in settling basins?
Settling basins in the field are simple ponds dug downstream of the farm to optimally remove suspended solids effectively, produce clarified effluent, and accumulate and thicken sludge to minimal volume.
What are the main steps used in sewage treatment?
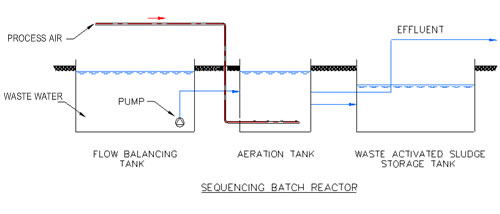
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 6: Filtration. ... Step 7: Disinfection. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake.
What are the methods of sewage treatment?
Majorly, four methods of sewage water treatment are followed – physical, biological, chemical, and sludge water treatment. By following these methods, the wastewater is disinfected from all the sewage materials and converted into treated water that is safe for both human usage and the environment.
What techniques are used for wastewater sludge treatment?
Many sludges are treated using a variety of digestion techniques, the purpose of which is to reduce the amount of organic matter and the number of disease-causing microorganisms present in the solids. The most common treatment options include anaerobic digestion, aerobic digestion, and composting.
What is the first stage in sewage treatment process?
primary sedimentation stageThe first stage in the sewage treatment is the primary sedimentation stage. Sewage including all of the grey and black water from a home flows into a chamber called the primary sedimentation tank and holds waste until it has had enough time for heavy sediment to disperse to the bottom.
How sludge is removed?
Digested sludge is put through large centrifuges that work in the same fashion as a washing machine spin cycle. The spinning centrifuge produces a force that separates the majority of the water from the sludge solid, creating a biosolid substance.
Primary Wastewater Treatment
In the aspect of water resources pollution, primary treatment is a basic necessity for water resource conservation. The concept and function of primary sewage treatment plant (also called POT (Primary Oxygen Treatment)) will be introduced here briefly:
Secondary Wastewater Treatment
The secondary wastewater treatment is a process that separates the organic solids from the wastewater to form effluent, which is treated and safe to release, and solids that can be used as a fertilizer. It is achieved through the following ways:
Tertiary Wastewater Treatment
The tertiary phase includes chemical treatments to stabilize the water for discharge into waterways or reuse within the industry.
Conclusion
It is essential to select the right technology for a particular application based on the characteristics of the wastewater and the desired results.
What is sewage treatment plant?
A sewage treatment plant is designed to treat and process raw sewage over different steps involving breaking, filtering, settling, controlled aerobic decomposition and chemical treatment. One of the most common things that come in our mind regarding human waste; is to dump it to the sewers and let the government take care of it.
What is chemical sewage treatment?
The preliminary chamber is equipped with coarse and fine mesh of screen as filters to remove large solid particles from getting into the system. In many designs it stay set at the top of the primary chamber with flow measurement device recording and filtering waste water inlet at the same time.
What happens when you discharge sewage in open water?
In the absence of sewage treatment plant when we discharge the waste in open water; the waste starts to attract aerobic bacteria and decompose on its own. Not just it suck up the necessary oxygen from the water but also lead to widespread risks of health epidemic if discharged near port.
How long does it take to remove the smell of chlorine from a water tank?
This is done by adding a 5 % solution of chlorine to kill of bacteria within a period of 30 minutes. Further chemical treatment is done to remove the smell and get rid of the pale colour.
What is the process used to break down sewage into small parts?
The process used to systematically break the sewage into small parts; using biological and chemical method is known as sewage treatment.
How many crews are required to have a sewage treatment plant?
The law requires all ships and water vessels above 4000 Gross tonnage dead weight or carrying more than 15 crew / personal in international waters is required to have dedicated sewage treatment plant or sludge tank to hold sewage for appropriate time.
Why is activated carbon added to sewage?
It get on to absorb all the organic molecules associated with the smell and distinct colour. In many design the activated carbon sets are filled just after the settling chamber; thus allowing waste water to be treated before moved to next chamber.
Where can sewage be treated?
Sewage can be treated close to where the sewage is created , which may be called a "decentralized" system or even an "on-site" system (in septic tanks, biofilters or aerobic treatment systems ). Alternatively, sewage can be collected and transported by a network of pipes and pump stations to a municipal treatment plant.
What is sewage system?
Sewerage (or sewage system) is the infrastructure that conveys sewage or surface runoff ( stormwater, meltwater, rainwater) using sewers. It encompasses components such as receiving drains, manholes, pumping stations, storm overflows, and screening chambers of the combined sewer or sanitary sewer. Sewerage ends at the entry to a sewage treatment plant or at the point of discharge into the environment. It is the system of pipes, chambers, manholes, etc. that conveys the sewage or storm water.
What is wastewater used for?
Physical, chemical, and biological processes are used to remove contaminants and produce treated wastewater (or treated effluent) that is safe enough for release into the environment.
What is municipal wastewater treatment?
Sewage treatment (or domestic wastewater treatment, municipal wastewater treatment) is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage.
How much energy is needed for sewage treatment?
For conventional sewage treatment plants, around 30 percent of the annual operating costs is usually required for energy. The energy requirements vary with type of treatment process as well as wastewater load. For example, constructed wetlands have a lower energy requirement than activated sludge plants, as less energy is required for the aeration step. Sewage treatment plants that produce biogas in their sewage sludge treatment process with anaerobic digestion can produce enough energy to meet most of the energy needs of the sewage treatment plant itself.
What is wastewater treatment plant?
The term "sewage treatment plant" (or "sewage treatment works" in some countries) is nowadays often replaced with the term wastewater treatment plant or wastewater treatment station . Strictly speaking, the latter is a broader term that can also refer to industrial wastewater.
How much of the world's wastewater is treated?
At the global level, an estimated 52% of municipal wastewater is treated. However, wastewater treatment rates are highly unequal for different countries around the world. For example, while high-income countries treat approximately 74% of their municipal wastewater, developing countries treat an average of just 4.2%.
What are the benefits of sedimentation?
Sedimentation of water is one of the most basic processes of purifying water, making it a process that is commonly used and understood throughout the world. It may be used as a preliminary step in some water treatment processes. It provides the following benefits to municipalities that employ it: 1 Fewer chemicals are required for subsequent water treatment. 2 It makes any subsequent process easier. 3 The cost is lower than some other methods. 4 There is less variation in the quality of water that goes through the process.
Why do you add coagulants to water?
Coagulants are typically added to the water before sedimentation to aid in the settling process. After sedimentation, there are often other treatment steps. AOS professionals can discuss sedimentation and other water treatment services that we can provide to enhance the quality of your water.
What are the benefits of water treatment?
It provides the following benefits to municipalities that employ it: Fewer chemicals are required for subsequent water treatment. It makes any subsequent process easier. The cost is lower than some other methods. There is less variation in the quality of water that goes through the process.
How is wastewater treated?
It is done by putting the wastewater into large settlement tanks for the solids to sink to the bottom. The settled solids are called sludge. At the bottom of these circular tanks, large scrappers continuously scrape the floor of the tank and push the sludge towards the center, where it is pumped away for further treatment. The rest of the water is moved to Secondary treatment.
What is the first stage of wastewater treatment?
Screening is the first stage of the wastewater treatment process. Screening removes large objects like diapers, nappies, sanitary items, cotton buds, face wipes, and even broken bottles, bottle tops, plastics, and rags that may block or damage equipment.
Where does liquid waste go?
Wastewater (liquid waste) from flushing the toilet, bathing, washing sinks, and general cleaning goes down the drain and into a pipe, which joins a larger sewer pipe under the road. The sewer pipe goes on to connect to a different sewer pipe that leads to the treatment center.
Why is air pumped into sludge scraping water?
These are called aeration lanes. Air is pumped into the water to encourage bacteria to break down the tiny bits of sludge that escaped the sludge scraping process.