
Full Answer
How to make oxygen water at home?
The use of oxygen concentrators in the water treatment process helps increase the overall concentration of pure oxygen in the water, expelling impurities and contaminants. OSI's oxygen concentrators are portable and adaptable to your needs.
How do you remove oxygen from water?
There are multiple ways to add oxygen in water treatment based on the need and the existing system design. Regardless of configuration, there is almost certainly an option that would be a fit. Typically, oxygen can be injected directly into the aerobic basin, or in a side-stream and then pumped back into the basin.
How to remove oxygen from water at home?
Feb 25, 2016 · Liquid Oxygen helps biological wastewater treatment plants by increasing their capacity and by helping to settle upset conditions quickly. Upset conditions include times of high Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD); high sludge volume index, also known as bulking; and abnormal production of sulphurous odours. All of these conditions are the results of low dissolved …
How do you make oxygen from water?
This shows that oxygen dissolved in water is only capable of dissolving certain compounds such as ferrous iron. Iron removal constitutes the main use made of oxygen as a chemical oxidant: The higher the pH, the faster the reaction.

Why is oxygen used in water treatment?
In wastewater treatment, aeration is the process used to dissolve air into water. It enables growth of aerobic bacteria on key pollutants such as biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and ammonia during treatment.Oct 3, 2016
What is oxygen in wastewater treatment?
Dissolved oxygen (DO) is added to the aeration basin to enhance the oxidation process by providing oxygen to aerobic microorganisms so they can successfully turn organic wastes into inorganic byproducts. In order to metabolize food and reproduce, each microor- ganism (or bug) must have at least 0.1 to 0.3 mg/L DO.
How does oxygen get into the water?
Oxygen enters water by direct absorption from the atmosphere, which is enhanced by turbulence (see Figure 1). Water also absorbs oxygen released by aquatic plants during photosynthesis.Sep 23, 2021
What are the benefits of mixing oxygen with water?
Oxygenated water is a relatively new functional water product that has oxygen added to it during the canning or bottling process. The added oxygen is claimed to provide health benefits, including aiding exercise recovery, flushing toxins out of the body, and improving alcohol metabolism.Mar 5, 2020
Why is oxygen important in aerobic treatment?
There are several ways that the use of pure oxygen can help to ensure the system operates correctly and has this needed oxygen level with fewer detrimental impacts.
What is the benefit of using pure oxygen?
There are several potential benefits when utilizing pure oxygen to enhance the air system in secondary treatment: Reduction in odors. Improved sludge settling.
How is oxygen stored?
An oxygen system consists of three main parts: 1 The oxygen storage and supply tank, usually called a bulk tank. It is a vessel designed to store cryogenic liquids, including oxygen. Note: Although the oxygen is used as a gas, it is stored in a concentrated form as an extremely cold liquid, approximately -250°F, depending on tank pressure. 2 The oxygen is vaporized in an ambient air vaporizer, which looks like a giant radiator, and then flows to the valve train/control panel. The oxygen flow and pressure are adjusted appropriately depending on the particular system design. 3 Finally, the oxygen is injected. There are several methods of injection. Simple devices such as spargers, diffusers or porous hoses can be used. More complex devices can provide additional mixing energy and typically improve transfer efficiency. These devices can be floating, sit on the bottom of the basin, or even be side stream and will vary based on the applicable criteria (e.g. basin depth and size, quantity of O2 needed, need for mixing, availability of power, and many other factors).
What is the purest environmental aid?
One of the purest environmental aids on the market is oxygen.
How cold is oxygen?
Note: Although the oxygen is used as a gas, it is stored in a concentrated form as an extremely cold liquid, approximately -250°F, depending on tank pressure. The oxygen is vaporized in an ambient air vaporizer, which looks like a giant radiator, and then flows to the valve train/control panel.
Can you add oxygen to water treatment?
There are multiple ways to add oxygen in water treatment based on the need and the existing system design. Regardless of configuration, there is almost certainly an option that would be a fit.
What is secondary wastewater treatment?
Secondary treatment is used to remove dissolved and suspended biological and organic matter, and this works very well in many cases.
How much oxygen is in aeration?
A typical aeration system increases the amount of Oxygen in the system by 10-15% (air has about 21% Oxygen).
How does aeration work in wastewater treatment?
Historically, aeration systems have been used in biological wastewater treatment plants to try to address these issues . A typical aeration system increases the amount of Oxygen in the system by 10-15% (air has about 21% Oxygen). More recently, plants have begun using pure Oxygen transfer systems, which use liquid Oxygen (LOx) and specially designed delivery devices to achieve Oxygen transfer on the order of 70-90%. Other plants have modified their aeration systems to accept Oxygen enrichment, which significantly boosts the Oxygen transfer rate. With either a pure Oxygen transfer system or Oxygen enrichment on an aeration system, plant managers get much finer control over their biomass and tank conditions, and faster response in a crisis.
Application scope
The waste water is usually purified in a traditional sewage treatment plant (WWTP) until it has again a quality that allows the discharge of the water further in the surface water rivers.
Requirements
A basic setup consists of a cryogenic tank for liquid oxygen. This oxygen is then brought in gaseous phase with an atmospheric evaporator and subsequently via a nozzle or ejector into a liquid flow of a dirt carrier.
Why is oxygen important in drinking water?
The presence of oxygen in drinking water is favourable, because it assists protective coating formation on the inside of metal water transport pipes. This requires a concentration of 6-8 mg/L. Oxygen radicals are responsible for derivative diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular illness.
How is oxygen used in the world?
Oxygen is also applied commercially. For industrial purposes the element is extracted from air by about 100 million tons annually. Of the total amount, 55% is applied in steel production, 25% is applied in chemical industries, and the remainder is applied in hospitals, for starting missiles, and for slicing metal.
Why is oxygen important?
Dissolved oxygen is an important determinant for stability of waters and survival of water organisms. Micro organisms may decompose organic substances in water by means of oxygen. Oxygen application per unit of time is indicated by BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand).
What is the most abundant element on Earth?
Oxygenis the most abundant element on earth. Oxygen exists as O2and O3(ozone), and is present in a number of compounds including water molecules. It can be found dissolved in water as O2molecules. Consequently, the oxygen content of seawater is 85.7%.
What is the reaction of acid and water?
Under normal conditions acid in water reacts with HCO3-, forming CO2. The oxygen atom is very reactive and forms oxides with virtually all other elements, with the exception of helium, neon, argonand krypton. There are also a large amounts of compounds that react with water. Solubility of oxygen and oxygen compounds.
How much oxygen is in the human body?
The total oxygen concentration in the human body is about 60% of the total body weight. This value may vary strongly, because it is mainly present in water molecules. As was explained earlier for other organisms, humans absorb oxygen through lungs which is than transferred to various organs through the blood.
What are some examples of toxic compounds?
Oxygen atoms can be found in a number of toxic organic and inorganic compounds. Toxic compounds are for example hyper oxides and peroxides. Some substances are toxic under low oxygen conditions in water, because breathing of organisms increases and consequently substances are absorbed more rapidly.
What is the oxidation process in water?
In order to further improve chemical oxidation processes, so-called advanced oxidation processes have now been developed with the ability of generating high oxidation performances in the case of organic pollutants found in water. They share the principle whereby they are capable of generating a more powerful and less selective secondary oxidant in the reaction medium by activating an available primary oxidant. In most cases, the reactive species formed will be the hydroxyl radical whose standard oxidising reduction potential reaches 2.8V at 25°C.
What is the name of the compound that contains oxygen?
Paracetic acid is also called peroxyacetic acid or ethanoperoxoic acid and, like hydrogen peroxide, belongs to the group of peroxide compounds identified by the presence of two adjacent atoms of oxygen (-O-O-, "peroxy" group). Its chemical formula is written CH 3 COOOH.
What happens when chlorine dissolves in water?
The dissolution of chlorine in water thus leads to the formation of hypochlorous acid and hypochlorite anions in varying proportions depending on pH and on the temperature of the medium.
Is chlorination harmful to water?
From inorganic pollution, chlorination can create compounds regarded as deleterious and subject to regulations (chloramines, bromate ion). The presence of these secondary products in chlorinated water mainly depends on the medium’s pH, on the amount of chlorine used and on the reaction time.
Is chlorine dioxide soluble in water?
Chlorine dioxide is extremely soluble in water. Its solubility depends on temperature and pressure. Its dissolution in water at a neutral pH results in a mixture of chlorous and chloric acids. In a base medium, chlorine dioxide undergoes dismutation into chlorite and chlorate ions.
Is ozone soluble in water?
Properties of ozone. Ozone is not very soluble in water. Ozone solubility decreases as temperature rises or as the concentration of ozone in the gas diminishes (see section characteristic constants of gases ).
Why is ozone important to the stratosphere?
Ozone is a gas that is present naturally in the stratosphere as the result of the action of ultraviolet radiation emitted by the sun on oxygen molecules. Thus, it provides protection against harmful UV radiation.
Ozone
The overall cost of producing ozone is decreased drastically if oxygen is used as feed gas. OXYMAT already cooperates with many different ozone producers worldwide – and we have great expertise in designing units to work with ozone generators.
Drinking water treatment
Modern fresh-water plants are closed to avoid the water getting in contact with air and thereby decrease the risk of contamination by air-pollution or similar. In closed systems 95% pure oxygen is mixed into the water at a level of 7 ppm per litre, giving the perfect oxyanion of the water.
Waste water treatment
Treatment and cleaning of waste water is a complex process, in which oxygen plays an important role. OXYMAT offers oxygen generators for bio filters and as feed gas for ozone generators. Similar to ozone generators the bio filters need pure oxygen to become as efficient as possible.
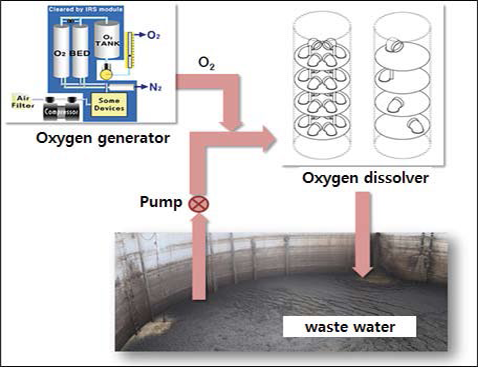
Synthesis
Reactions
- A basic setup consists of a cryogenic tank for liquid oxygen. This oxygen is then brought in gaseous phase with an atmospheric evaporator and subsequently via a nozzle or ejector into a liquid flow of a dirt carrier. IJsfabriek Strombeek possesses besides the necessary oxygenthe different techniques that can be used to inject this in the waste wate...
Mechanism
Chemistry
Properties
Habitat
Applications
Other uses
Significance
Introduction
Safety
Toxicity
- Dissolved oxygen is an important determinant for stability of waters and survival of water organisms. Micro organisms may decompose organic substances in water by means of oxygen. Oxygen application per unit of time is indicated by BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand). Organic pollutants may negatively influence water organisms, because they decrease B...
Environment
Function
Effects
Definition