Medication
How long does it take for folliculitis to heal? Mild folliculitis usually heals on its own in about 2 weeks . You can take care of yourself at home with: A warm compress. This may ease itching and help healing. How do you get rid of bumps after laser hair removal? If the small red bumps are causing you any discomfort, apply a cold compress to ...
Procedures
Types of deep folliculitis include:
- Sycosis barbae: This is when the whole follicle gets infected after shaving. ...
- Gram-negative folliculitis: This type is caused by the use of long-term antibiotics to treat acne. ...
- Boils and carbuncles: A boil (a red bump that can be tender or painful) happens when a hair follicle is seriously infected. ...
Self-care
What are the best home remedies for carpal folliculitis?
- Practice good hygiene. Wash the affected area two to three times a day with oatmeal, aloe vera, or mild antibacterial soap.
- Wear loose clothing. ...
- Avoid or modify shaving. ...
- Use a moist compress. ...
- Use antibacterial topical medications. ...
- Use anti-itch creams or NSAIDs. ...
- Use over-the-counter antihistamines. ...
Nutrition
While there is no cure for folliculitis, prevention can be relatively simple. All it takes is a few changes in some simple routines to protect your skin. Hot and damp skin is much more susceptible to hair follicle damage. Keeping the skin cool, clean and able to breathe can help protect hair follicles.
How long does folliculitis take to heal?
What is folliculitis and how is it treated?
What is the best antibiotic for folliculitis?
Is there a permanent cure for folliculitis?
How to get rid of a scab?
How to stop infection from spreading?
How to get rid of itchy skin?
How to treat folliculitis?
How to diagnose folliculitis?
What is the best treatment for folliculitis?
What to do if you have a skin condition?
See more
About this website

How do you get rid of folliculitis?
Apply antibiotic creams Over-the-counter antibiotic creams, gels, and ointments may help clear up a small patch of folliculitis. Look for antibiotic creams that are put on cuts and scrapes. Apply the cream with a new, clean cotton swab. Avoid using too much antibiotic cream and use it only where needed.
What is the best medicine for folliculitis?
Oral isotretinoin is the most effective treatment for gram-negative folliculitis caused by certain types of bacteria. It is also the go-to treatment for the most severe and resistant cases of scalp folliculitis called folliculitis decalvans.
How long does it take to treat folliculitis?
Mild folliculitis usually heals on its own in about 2 weeks. You can take care of yourself at home with: A warm compress. This may ease itching and help healing.
What is the fastest way to cure folliculitis?
The following approaches may help relieve discomfort, speed healing and prevent an infection from spreading:Apply a warm, moist washcloth or compress. ... Apply over-the-counter antibiotics. ... Apply soothing lotions. ... Clean the affected skin. ... Protect the skin.
What soap is good for folliculitis?
Antibacterial soap: Use antibacterial bar soaps such as Dial® or Cetaphil®. Use skin washes that contain benzoyl peroxide. If these bumps are bothersome or painful.
What foods to avoid if you have folliculitis?
Brooks also advises avoiding diets high in carbs and sugars or with a high glycemic index, which can cause fluctuations in your glucose levels. “Rising glucose levels increase hormones in your skin, leading to oil production, which can cause folliculitis [inflammation of hair follicles],” he says.
Is folliculitis fungal or bacterial?
Folliculitis is most often caused by an infection of hair follicles with Staphylococcus aureus (staph) bacteria. Folliculitis may also be caused by viruses, fungi and even an inflammation from ingrown hairs.
Can folliculitis be cured?
Most cases of folliculitis are completely curable. There are very uncommon, long-standing cases of folliculitis that may not be curable. Often these more resistant cases may be controlled with proper treatment and medication. Folliculitis sometimes clears completely by itself without treatment.
Folliculitis Home Treatment: 12 Remedies to Consider
Folliculitis can sometimes be serious. You may need medical treatment like prescription antibiotics, steroid medication, and in rare cases, even surgery.
How to Treat Folliculitis Over the Counter | Healthfully
When hair follicles become red, itchy and infected, folliculitis is the probable cause 1. Folliculitis can result from shaving, friction between the skin and clothing, excessive sweating or infected cuts or wounds 1. Superficial folliculitis, a condition in which the staph bacteria infects the hair follicles, often can be treated with over-the-counter products and remedies 1.
What Is the Best Antibiotic for Foliculitis? | New Health Advisor
When choosing the best antibiotic for folliculitis, you first need to know the cause of your infection. There're many antibiotics and home remedies that can help.
Overview
Folliculitis is a common skin condition that’s often caused by an infected or inflamed hair follicle. It can look similar to acne and be uncomfortable or itchy. Folliculitis often has a psychosocial impact because of its appearance.
Symptoms and Causes
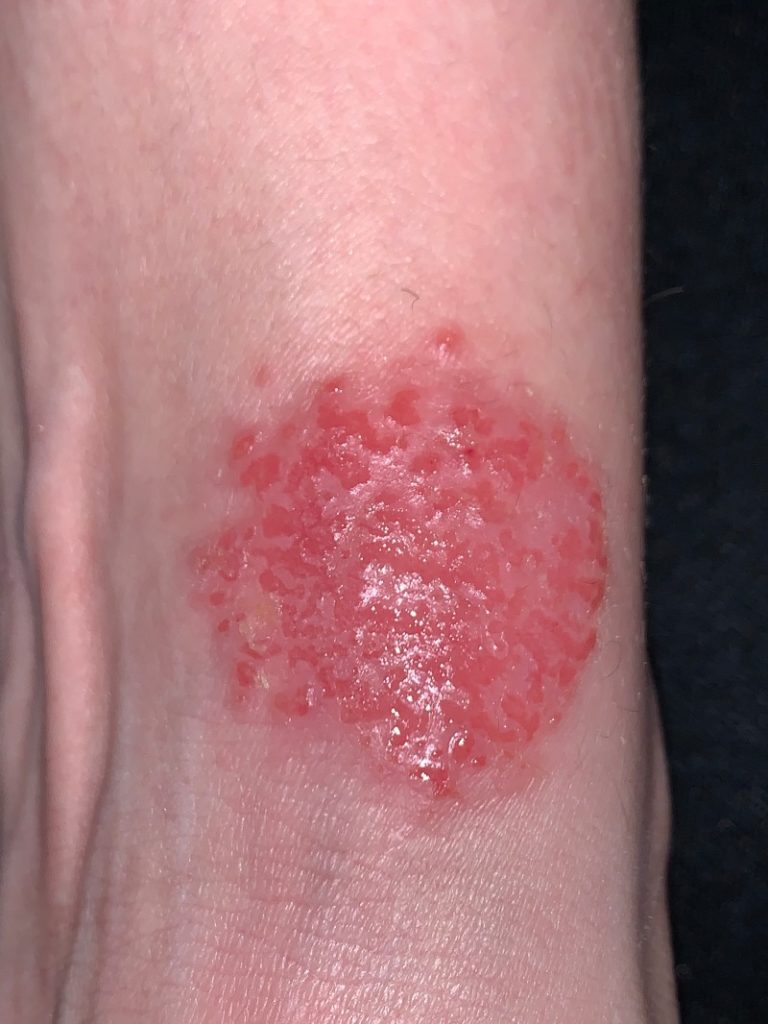
In most cases, the main symptom of folliculitis is red bumps that look like pimples on your skin. These could also look like they’re white-filled bumps or they could be filled with pus (pustules). Folliculitis can feel itchy and uncomfortable. Many people feel the need to scratch when they have folliculitis.
Diagnosis and Tests
Folliculitis is usually diagnosed during a physical exam with your healthcare provider. This can be done during an appointment and in most cases, you do not need to see a skincare specialist. Your primary care physician is usually able to diagnose folliculitis and provide a treatment plan.
Management and Treatment
Treatment options for folliculitis depend on the type of folliculitis you have and it’s severity. Certain types may need more aggressive types of care, while others may go away with little to no treatment. If your folliculitis is mild, it can sometimes be treated at home. There are several ways you can care for your irritated skin, including:
Prevention
In many cases, you can work to prevent folliculitis or manage it by changing your lifestyle habits. Folliculitis infections usually involve bacteria and yeast entering your hair follicles. By changing some parts of your normal self-care routine, you can limit the amount of infectious material in your hair follicles.
Living With
Even though many cases of folliculitis can be cared for at home and go away after a short period of time, do not hesitate to call your healthcare provider if you are concerned. In most cases, a quick exam by your provider will tell you if you need treatment for folliculitis or if it will go away on its own.
How to apply folliculitis pack?
For the vinegar pack, mix 1 tablespoon of vinegar and ½ cup of water together. Dip cotton balls into the mixture. Apply to affected areas for 20 minutes, twice a day.
What is folliculitis skin?
Natural Home Remedies. Precautions. Folliculitis is a common skin disorder where the hair follicles become inflamed and sometimes infected. Dermatological conditions that also fall in the folliculitis category include hot tub rash, barber’s itch and razor burn.
What is the bacteria that causes itchy bumps on the skin?
Bacterial Folliculitis. Very common. It’s marked by itchy, white pus-filled bumps often caused by the S. aureus bacteria. The staph bacteria live on the skin all of the time, but generally only cause a problem when entering the body through a cut, scrape or a wound.
What are the symptoms of folliculitis?
The most common symptoms of folliculitis are the appearance of clusters of red bumps or white pus-filled bumps that resemble pimples. Intense itching and soreness is common. There are two groups of folliculitis — superficial folliculitis and deep folliculitis, each including several types with different root causes.
How long does it take for folliculitis to heal?
While many cases of folliculitis will resolve within a week or two with good hygiene and self-management, if you have a severe case or your folliculitis often reoccurs, a visit to your physician is warranted.
Why does folliculitis come on so quickly?
Eruptions that come on quickly are often due to Staphylococcus aurea bacteria, while chronic or recurring folliculitis may be due to co-occurring medical conditions that make you more susceptible to infection. The infection can spread, leading to a more widespread problem, so proper treatment is necessary. ( 3)
How to get rid of pimples and bumps?
( 13) Apply witch hazel with a sterile cotton pad on and around the bumps and pimples.
How to prevent foliculitis from spreading?
To prevent the infection from spreading, avoid scratching or shaving the area, clean the affected area regularly, and use topical antiseptics like benzoyl peroxide.
What is the best treatment for folliculitis?
Over-the-counter topical antimicrobial washes and medications are often the first-line medical treatment for folliculitis, whether it’s treated at home or under the care of a healthcare provider. A daily regimen of benzoyl peroxide washes are usually enough to effectively treat folliculitis or prevent its recurrence.
What antibiotics are used for bacterial folliculitis?
If the condition does not respond to topical antibiotics, oral antibiotics such as cephalexin, ampicillin, or ciprofloxacin will be used depending on the type of bacteria causing the infection.
How long does folliculitis last?
Diabetes, the use of makeup, waxing, and a compromised immune system are also risk factors. If folliculitis spreads, grows worse, or persists for more than two weeks, it’s time to see a healthcare provider. Frequently, all that’s required is a history and a physical examination to diagnose folliculitis.
How long does it take for folliculitis to go away?
Most cases of folliculitis go undiagnosed. The condition is benign, often mistaken for acne, and usually resolves in a few days to a couple of weeks. People who shave frequently, wear tight clothes, carry excess weight, or use hot tubs or pools are more vulnerable to the condition.
What is the swelling of the hair follicles?
Folliculitis is a swelling of the hair follicles, the tiny pouches in the skin from which hair grows. There are many causes of folliculitis including infection, irritation, blockage, or injury. Any place on the body that has hair is vulnerable to folliculitis, which means everywhere except the palms and the soles.
Why do my follicles get red?
Follicles fill up with white blood cells and become swollen, red, and pus-filled. Exposing the affected area to ultraviolet light slows down the immune system and reduces both the swelling and pustules.
Use a Decongesting Cleanser
Before heading to a professional, stop by your local pharmacy for some at-home treatments. It turns out there are plenty of cost-efficient ways to tackle folliculitis without digging deep into your wallet. Dr. Zalka recommends using a cleanser that prevents pores from becoming clogged or inflamed.
Dig Deep With a Chemical Exfoliant
Sometimes it pays off to dig a little deeper. Exfoliating will help get rid of dead skin cells, which can help clear any ongoing outbreaks.
Try Body Spray Treatments for Convenient Application
If you’re on the go, there are also effective body sprays that allow easy application for difficult areas to reach that may reduce acne breakouts anywhere on the body.
Take a Break From Shaving and Waxing
If the problem you’re seeing persists, consider giving that area a break from shaving and/or waxing for a bit. Shaving and waxing can easily "open up" your breakout, exposing the whitehead and causing the spread of bacteria to other areas where you shave with the same razor head—thus leading to more breakouts. 4
Wear Loose-Fitting Clothing
It’s important to be mindful of your clothing choices when you’re dealing with a folliculitis outbreak. Try to avoid tight clothing for a while, which can cause friction or rubbing that further inflames your breakouts.
Try a Benzoyl Peroxide Wash
Benzoyl peroxide cleansers daily in the shower are very effective, as they kill pathogenic bacteria and remove dead skin cells. 5
Consider Laser Hair Removal
If you’ve had some success with any of these treatments, a dermatologist may suggest a hair removal laser course to prevent further folliculitis. The hair follicle is the root of the problem, and the follicles affected can be removed by laser in some circumstances.
What are the two types of folliculitis?
Types of Folliculitis. There are two primary types of folliculitis. Superficial folliculitis is when only part of the follicle is damaged, while deep folliculitis is when the whole follicle is damaged. Bacterial folliculitis: The most common form, this type causes itchy white bumps filled with pus.
What causes red bumps after shaving?
Sycosis barbae: This is when the whole follicle gets infected after shaving. It causes large red pus-filled bumps and can lead to scarring in some cases. Gram-negative folliculitis: This type is caused by the use of long-term antibiotics to treat acne.
Why do I have bumps on my face after shaving?
Razor bumps (pseudofolliculitis barbae): This type is caused by ingrown hairs linked to shaving or a bikini wax. You’ll have dark bumps, or keloids, on your face or neck after shaving or in your groin area after a wax. Pityrosporum folliculitis: This type happens along with a yeast infection. It causes red, itchy, pus-filled pimples ...
How do you know if you have folliculitis?
You may have: Groups of small red bumps like pimples, some with white heads on them. Blisters that break open, ooze, and become crusty. Large areas of red, swollen skin that may leak pus.
What causes pimples on the back of the neck?
Pityrosporum folliculitis: This type happens along with a yeast infection. It causes red, itchy, pus-filled pimples that show up on your upper body, mostly on your back and chest, but you can also have them on your neck, shoulders, arms and face. Types of deep folliculitis include:
What to do if folliculitis doesn't work?
If these self-care treatments don’t work, your doctor may give you: Antibiotic cream if the folliculitis is caused by bacteria (pills for very severe cases only) Antifungal creams, shampoos, or pills if it’s caused by fungus. Steroid cream to help reduce swelling. Folliculitis Prevention.
How to reduce swelling from folliculitis?
Steroid cream to help reduce swelling. Folliculitis Prevention. To lower your chances of getting folliculitis, your best bet is to stop shaving for at least 3 months, but for a lot of people that won’t do. You might want to try an electric razor or hair removal products (depilatories) or other ways to remove hair.
What are the symptoms of a follicle?
Folliculitis signs and symptoms include: Clusters of small red bumps or white-headed pimples that develop around hair follicles. Pus-filled blisters that break open and crust over.
What causes folliculitis in hair?
Causes. Folliculitis is most often caused by an infection of hair follicles with Staphylococcus aureus (staph) bacteria. Folliculitis may also be caused by viruses, fungi and even an inflammation from ingrown hairs.
What is the name of the infection that affects the upper part of the hair follicle?
Folliculitis. When hair follicles are damaged, they may be invaded by viruses, bacteria and fungi, leading to infections such as folliculitis. Superficial folliculitis affects the upper part of the hair follicle and the skin directly next to the follicle.
Why does my hot tub have a red bump?
Hot tub folliculitis causes red, round, itchy bumps that may later develop into small pus-filled blisters. The rash is likely to be worse in areas where your swimsuit holds contaminated water against your skin.
What does it look like when you have a pimple on your hair?
At first it may look like small red bumps or white-headed pimples around hair follicles — the tiny pockets from which each hair grows. The infection can spread and turn into nonhealing, crusty sores. The condition isn't life-threatening, but it can be itchy, sore and embarrassing. Severe infections can cause permanent hair loss and scarring.
What causes hair follicles to become inflamed?
Folliculitis is a common skin condition in which hair follicles become inflamed. It's usually caused by a bacterial or fungal infection.
How to prevent folliculitis from coming back?
You can try to prevent folliculitis from coming back with these tips: Avoid tight clothes. It helps to reduce friction between your skin and clothing. Dry out your rubber gloves between uses. If you wear rubber gloves regularly, after each use turn them inside out, rinse with soap and water, and dry thoroughly.
What is folliculitis in hair?
Takeaway. Folliculitis is an infection or irritation in the hair follicles. Follicles are tiny openings or pockets in the skin where each hair grows from. This common skin condition is usually caused by a bacterial or fungal infection. Most cases of folliculitis are mild.
How to treat folliculitis on hands?
You can use antibiotic ointment or anti-itching lotion first. Wash the area and your hands with warm soapy water. Cut a clean cotton cloth into strips or use gauze bandages — the type used to dress cuts.
How to help eczema rash?
Try wet wraps. Wet wrap therapy is a way to help ease skin itching and irritation. Dermatologists recommend this at-home therapy for people who have eczema and other skin rashes. It can also be used to help reduce folliculitis symptoms like itchiness. Not scratching itchy skin can help speed up healing.
How to dilute essential oil?
Dilute the essential oil by adding a few drops to a carrier oil or a moisturizing cream. Essential oils are powerful, so using them directly or too much can irritate your skin. Essential oils that may help treat skin infections like folliculitis include: cinnamon oil.
What does it look like when you have folliculitis?
The hair follicle may get inflamed and appear red and bumpy. It may look like a small pink or red rash on the skin. Mild folliculitis may cause signs and symptoms like: itchiness.
How to get rid of folliculitis?
1. Do a soap wash. Clean the area with warm water and soap twice a day. Dry off with a clean towel and avoid sharing your towel with anyone.
How to help with soreness and swelling?
A warm, moist compress can help soothe soreness, swelling, and pain. Use a new or sterilized washcloth. Boil a soft cotton cloth or launder it in warm water and soap to make sure it’s clean .
How to prevent irritant folliculitis?
To prevent reoccurring irritant folliculitis, use a gentle hair removal method, such as a lady's electric razor. Avoid soap and apply plenty of shaving gel, if using a blade shaver.
What causes folliculitis in adults?
Yeasts. The most common yeast to cause a folliculitis is Pityrosporum ovale, also known as Malassezia. Malassezia folliculitis (pityrosporum folliculitis) is an itchy acne-like condition usually affecting the upper trunk of a young adult.
What is the term for a red spot on the back of your hair?
Folliculitis means an inflamed hair follicle due to any cause. The result is a tender red spot, often with a surface pustule. Folliculitis may be superficial or deep. It can affect anywhere there are hairs, including chest, back, buttocks, arms, and legs. Acne and its variants are also types of folliculitis.
Why do you take a swab from a pustule?
Folliculitis due to infection. Swabs should be taken from the pustules for cytology and culture in the laboratory to determine if folliculitis is due to an infection.
Why does my pool have folliculitis?
Spa pool folliculitis is due to infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which thrives in warm water. Gram-negative folliculitis is a pustular facial eruption also due to infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa or other similar organisms. When it appears, it usually follows tetracycline treatment of acne but is quite rare.
What is eosinophilic folliculitis?
Eosinophilic folliculitis is a specific type of folliculitis that may arise in some immune-suppressed individuals such as those infected by human immunodeficiency virus ( HIV) or those who have cancer.
What is the parasitic infection of the face?
Parasitic infection. Folliculitis on the face or scalp of older or immunosuppressed adults may be due to colonisation by hair follicle mites (demodex). This is known as demodicosis. The human infestation, scabies, often provokes folliculitis, as well as non-follicular papules, vesicles and pustules.
How to get rid of a scab?
Gently wash the infected skin twice a day with antibacterial soap. Use a clean washcloth and towel each time and don't share your towels or washcloths. Use hot, soapy water to wash these items . And wash clothing that has touched the affected area.
How to stop infection from spreading?
The following approaches may help relieve discomfort, speed healing and prevent an infection from spreading: Apply a warm, moist washcloth or compress. Do this several times a day to relieve discomfort and help the area drain, if needed.
How to get rid of itchy skin?
Moisten the compress with a saltwater solution (1 teaspoon of table salt in 2 cups of water). Apply over-the-counter antibiotics. Try various nonprescription infection-fighting gels, creams and washes. Apply soothing lotions. Try relieving itchy skin with a soothing lotion or an over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream.
How to treat folliculitis?
Options include medications and interventions such as laser hair removal. Even if treatment helps, the infection may come back.
How to diagnose folliculitis?
Diagnosis. Your doctor is likely to diagnose folliculitis by looking at your skin and reviewing your medical history. He or she may use a technique for microscopic examination of the skin (dermoscopy). If initial treatments don't clear up your infection, your doctor may use a swab to take a sample of your infected skin or hair.
What is the best treatment for folliculitis?
Creams or pills to control infection. For mild infections, your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic cream, lotion or gel. Oral antibiotics aren't routinely used for folliculitis. But for a severe or recurrent infection, your doctor may prescribe them.
What to do if you have a skin condition?
List any symptoms you're experiencing, including those that seem unrelated to your skin condition. List key personal information, including any major stresses or recent life changes. List all medications, vitamins and supplements you're taking. List questions to ask your doctor.
