
How is Genomics used in oncology?
Jul 01, 2019 · Gene therapy is a type of treatment in which healthy foreign genetic material is inserted into a person’s cells to cure a rare condition or disease [ 25 ]. Instead of only treating symptoms, gene therapy aims to correct the underlying genetic cause of the disease and, thus, serve as a one-shot cure.
Can genomics revolutionize mental health care?
Feb 08, 2022 · How Genomic Cancer Tests Work. Genomic testing looks at the genes in your cancer, to help your doctor make more informed decisions about your disease and match you to the right treatment. These ...
How does gene therapy work?
Gene therapy can be used to modify cells inside or outside the body. When it’s done inside the body, a doctor will inject the vector carrying the gene directly into the part of the body that has ...
What is genomic medicine and precision medicine?
The ways in which genomic medicine is making a difference Personal — each patient has medicines, treatment, and a health care plan tailored to them and their individual needs and... Doctors — access to genomic information helps with diagnosis, managing treatments, and spotting symptoms across a ...
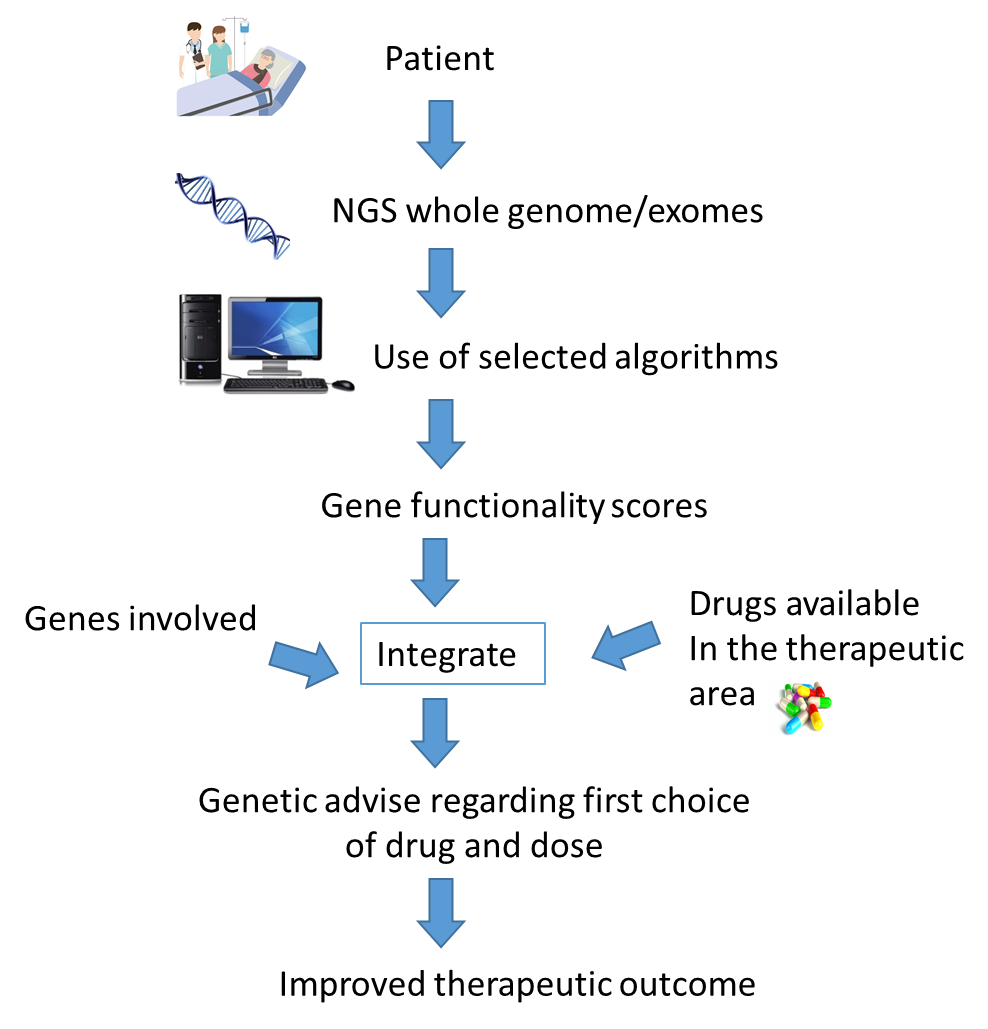
How does genomic medicine work?
How does genomics work?
What is genomic treatment?
What are the 4 steps of gene therapy?
- STEP 1: CONSULTATION (may include multiple visits over time) Discuss risks and benefits of different treatment options, which may include gene therapy. ...
- STEP 2: PREPARATION. Will include all cell collection for ex vivo gene therapy treatments. ...
- STEP 3: TREATMENT. May be an inpatient procedure. ...
- STEP 4: RECOVERY/FOLLOW-UP.
How is genome sequencing done?
What do genomes look like?
Is genomic testing accurate?
The accuracy of genetic tests to detect mutated genes varies, depending on the condition being tested for and whether or not the gene mutation was previously identified in a family member. Even if you don't have the mutated gene, that doesn't necessarily mean you'll never get the disease.Apr 14, 2020
How long does genomic testing take?
How successful is gene therapy?
What are the 5 steps of gene therapy?
- 1Creating a working gene.
- 2Building a therapeutic vector.
- 3Determining eligibility.
- 4Delivering the working gene.
- 5Monitoring safety and efficacy.
What are the two types of gene therapy?
- Somatic gene therapy: transfer of a section of DNA to any cell of the body that doesn't produce sperm or eggs. ...
- Germline gene therapy: transfer of a section of DNA to cells that produce eggs or sperm.
What are the disadvantages of gene therapy?
- Expensive. Gene therapy can be extremely pricey, making it inaccessible for some people. ...
- Experimental. Gene therapy is relatively new and there's still a lot about it that we don't know. ...
- Potentially dangerous. ...
- Ethical issues. ...
- May cause infection.
How does gene therapy work?
Gene therapy can be used to modify cells inside or outside the body. When it’s done inside the body, a doctor will inject the vector carrying the gene directly into the part of the body that has defective cells. In gene therapy that is used to modify cells outside of the body, blood, bone marrow, or another tissue can be taken from a patient, ...
How many gene therapy products have been approved?
Now this research on gene therapy is finally paying off. Since August 2017, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved three gene therapy products, the first of their kind.
What can scientists do to help the body?
They can replace a gene that causes a medical problem with one that doesn’t, add genes to help the body to fight or treat disease, or turn off genes that are causing problems. In order to insert new genes directly into cells, ...
What are the functions of genes in the body?
Within our cells there are thousands of genes that provide the information for the production of specific proteins and enzymes that make muscles, bones, and blood, which in turn support most of our body’s functions, such as digestion, making energy, and growing .
What is the vehicle used to insert new genes into cells?
In order to insert new genes directly into cells, scientists use a vehicle called a “vector” which is genetically engineered to deliver the gene. Viruses, for example, have a natural ability to deliver genetic material into cells, and therefore, can be used as vectors.
Can a defective gene make you sick?
The genes in your body’s cells play an important role in your health — indeed, a defective gene or genes can make you sick. Recognizing this, scientists have been working for decades on ways to modify genes or replace faulty genes with healthy ones to treat, cure or prevent a disease or medical condition. Now this research on gene therapy is ...
Can gene therapy be used in humans?
Before a company can market a gene therapy product for use in humans, the gene therapy product has to be tested for safety and effectiveness so that FDA scientists can consider whether the risks of the therapy are acceptable in light of the benefits.
How does genomic medicine make a difference?
The ways in which genomic medicine is making a difference. This greater understanding of the links between biology and disease brings benefits on several levels. Personal — each patient has medicines, treatment, and a health care plan tailored to them and their individual needs and risks. As an example, take the treatment of colorectal cancers.
What is genomic medicine?
Genomic medicine is the study of our genes (DNA) and their interaction with our health. Genomics investigates how a person’s biological information can be used to improve their clinical care and health outcomes (eg through effective diagnosis and personalised treatment.
How does epigenetics work?
The emerging field of epigenetics takes this idea one step further. It's based on the concept that each gene has its own chemical tag that tells the gene how to act. It is possible to turn the gene off (make it dormant) or turn it on (make it active) according to its chemical tag. In this way, the genetic code remains the same but the way in which it is expressed changes. 8
Why do doctors use genomic information?
Doctors — access to genomic information helps with diagnosis, managing treatments, and spotting symptoms across a wider cohort of patients. There have been a few cases where cerebral palsy diagnosis has been re-evaluated in the light of genetic testing, revealing a new diagnosis and, as a result, a new, effective treatment plan. 2.
What does genetic makeup show?
To assess risk — someone's genetic makeup can show their susceptibility to suffer certain illnesses, like heart disease, stroke, and cancer. Perhaps they're likely to have high cholesterol levels or to suffer problems with their veins.
Is genomic medicine evolving?
The broad area known as genomic medicine is evolving — the study of genetic mutation pathways and their variations is particularly exciting. But what does this mean for people on a practical level? As discussed earlier, there are some hereditary diseases that are difficult to diagnose simply because of the wide range of genes involved.
Can you have a genetic test for a disease?
Scientists and doctors have been studying genes and hereditary conditions (those handed down from parent to child) for many years. These days, it's possible for someone to have a genetic test for a number of illnesses. A blood sample is taken and closely examined for abnormal chromosomes, but because so much information is stored on the DNA, scientists only tend to look for particular disorders.
What is gene therapy?
Learn more. Gene therapy is designed to introduce genetic material into cells to compensate for abnormal genes or to make a beneficial protein. If a mutated gene causes a necessary protein to be faulty or missing, gene therapy may be able to introduce a normal copy of the gene to restore the function of the protein.
What happens if a gene is delivered by a vector?
If the treatment is successful, the new gene delivered by the vector will make a functioning protein. Researchers must overcome many technical challenges before gene therapy will be a practical approach to treating disease. For example, scientists must find better ways to deliver genes and target them to particular cells.
How is a vector given?
The vector can be injected or given intravenously (by IV) directly into a specific tissue in the body, where it is taken up by individual cells . Alternately, a sample of the patient's cells can be removed and exposed to the vector in a laboratory setting. The cells containing the vector are then returned to the patient. If the treatment is successful, the new gene delivered by the vector will make a functioning protein.
Where is the genetics home reference?
Genetics Home Reference has merged with MedlinePlus. Genetics Home Reference content now can be found in the "Genetics" section of MedlinePlus. Learn more
Where is the Genetic Science Learning Center?
The Genetic Science Learning Center at the University of Utah provides information about various technical aspects of gene therapy in Gene Delivery: Tools of the Trade. They also discuss other approaches to gene therapy and offer a related learning activity called Space Doctor.
Why are viruses used as vectors?
Certain viruses are often used as vectors because they can deliver the new gene by infecting the cell. The viruses are modified so they can't cause disease when used in people. Some types of virus, such as retroviruses, integrate their genetic material (including the new gene) into a chromosome in the human cell.
What is genomic medicine?
Genomic medicine is an emerging medical discipline that involves using genomic information about an individual as part of their clinical care ( e.g. for diagnostic or therapeutic decision-making) and the health outcomes and policy implications of that clinical use. Already, genomic medicine is making an impact in the fields of oncology, ...
What is the division of genomics?
Within NHGRI, the Division of Genomics and Society includes two branches that focus on engagement of the public, healthcare providers and policy makers in genomics topics: Education and Community Involvement Branch (ECIB) and Policy and Program Analysis Branch (PPAB).
Why is the Human Genome Project important?
The nation's investment in the Human Genome Project (HGP) was grounded in the expectation that knowledge generated as a result of that extraordinary research effort would be used to advance our understanding of biology and disease and to improve health.
How long does it take to translate a new research finding into clinical practice?
It has often been estimated that it takes, on average, 17 years to translate a novel research finding into routine clinical practice. This time lag is due to a combination of factors, including the need to validate research findings, the fact that clinical trials are complex and take time to conduct and then analyze, and because disseminating information and educating healthcare workers about a new advance is not an overnight process.
Is genomic medicine a subset of precision medicine?
Genomic medicine, as defined above, can be considered a subset of precision medicine. The translation of new discoveries to use in patient care takes many years. Genomic medicine is beginning to fuel new approaches in certain medical specialties.
Is oncology a genomics?
Oncology, in particular, is at the leading edge of incorporating genomics, as diagnostics for genetic and genomic markers are increasingly included in cancer screening, and to guide tailored treatment strategies. Background.
Is genomic medicine advancing?
Genomic medicine is advancing at a rapid pace. View this list of interesting developments in clinical implementation, pharmacogenomics, oncology, and more.
What is advanced genomic testing?
Advanced genomic testing is designed to help identify the DNA alterations that may be driving the growth of a specific tumor. Information about genomic mutations that are unique to your individual cancer may help doctors identify treatments designed to target those mutations.
What diseases are linked to genomics?
Researchers have used the discoveries to link dozens of diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease and inherited colon cancer, to specific genes. In recent years, researchers have taken the advancements one step further, with genomic tests of the cancer itself.
What does an oncologist do?
Your oncologist will explain the results to you and any indications for new treatment options, and together you will formulate a treatment plan targeted to your individual situation.
How many genes are in a human cell?
Researchers mapped the entire human genetic code, discovering that every human cell is packed with an estimated 20,000 to 30,000 genes. This marked a dramatic shift in the understanding of cancer and other diseases.
Is genomic testing right for you?
Whether genomic testing is right for you is a decision you make with your medical team based on your individual situation.
Is genomic testing appropriate for cancer patients?
Precision cancer care is an evolving science, and advanced genomic testing is not appropriate for every patient. Even when the test is recommended, it may not produce results that lead directly to a treatment plan. The analyses may help doctors consider more precise therapies in many cases, but not all mutations can be matched with known treatment ...
What is the idea behind genomics?
The idea behind the study of cancer genomics is that, if we can understand what has gone wrong genetically to cause a particular cancer, then treatments can be developed to combat the DNA errors that are at fault. Essentially, we would treat the genetic errors, rather than using treatments like radiation and chemotherapy that broadly affect an entire region of the body, including healthy tissue and cells.
How is cancer genomics measured?
Gene expression, or activity, can be measured by the abundance of different RNA. RNA is a molecule that is present in all living cells and is essential for the coding, decoding, ...
Why are biomarkers important?
Cancer biomarkers are useful in predicting how the cancer will progress and, consequently, your prognosis. Biomarkers are also currently being studied as a means of identifying which treatment a specific patient’s cancer is likely to respond to.
What is the totality of genetic changes within an individual's genome called?
The totality of genetic changes within an individual’s genome are called somatic changes . These somatic changes and the resulting genetic abnormalities are believed to account for 95% of all cancer cases. So, understanding and being able to repair or eradicate these errors becomes key to successfully treating cancer.
Why is precision medicine important for cancer?
Because they are treating only the cancer-causing genetic changes or molecular activities, such treatments are much less toxic to patients than traditional treatments like chemotherapy or radiation. Precision medicine is a high-priority focus area for head and neck cancer researchers.
What is cancer in biology?
#N#Cancer is a disease that occurs when the DNA of normal cells is changed or damaged, causing uncontrolled growth of affected cells. As such, a tumor is best understood as an overgrowth of cells. Typically, cells are programmed to serve their function and to avoid development of tumors. Normal cell behaviors—such as changing or differentiating, stopping growth, dying or self-destruction when damaged—protect against tumor formation. Unfortunately, damaged DNA can cause mistakes in these instructions, so that the cells no longer behave as they should. When this happens, cancer can develop.
Why do cancer cells have different DNA?
Because cancer cells have genetic alterations, they carry a different version of your DNA than healthy cells do. DNA is a molecule that is found in every cell of an organism (a person, animal, plant, etc.) and carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of that organism.
Why are vectors used in gene therapy?
The most common gene therapy vectors are viruses because they can recognize certain cells and carry genetic material into the cells' genes. Researchers are trying to take advantage of this unique capability. They:
What is the role of a missing or defective gene in cancer?
Researchers hope that replacing missing or defective genes can help treat certain diseases. For example, a common tumor suppressor gene called p53 normally prevents tumor growth in your body. Several types of cancer have been linked to a missing or inactive p53 gene.
Why do some cells become diseased?
In cancer, some cells become diseased because certain genes have been permanently turned off. Using gene therapy, mutated genes that cause disease could be turned off so that they no longer promote disease, or healthy genes that help prevent disease could be turned on so that they can inhibit the disease. Other cells may be missing certain genes.
