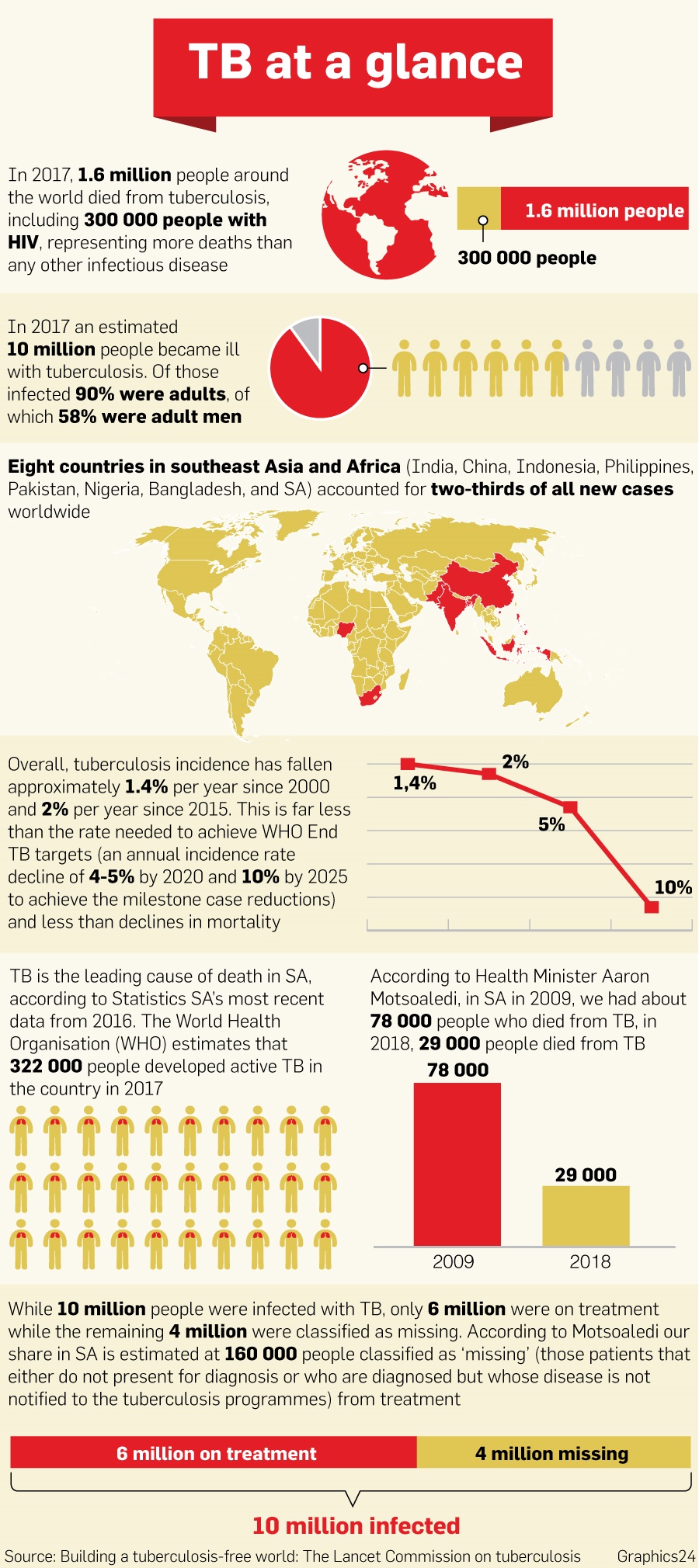
Nutrition
However, it’s vital that patients complete their treatment, so that the TB bacteria are completely killed off in the body. This prevents symptoms from returning and the risk of bacteria becoming drug resistant.
Why is it important to complete the treatment for TB?
Patients with active TB disease should receive at least three drugs as their initial TB treatment. Fewer than three drugs can result in the development of drug resistant TB. If a patient is failing their treatment this means that they are either developing TB symptoms again, or their symptoms are not going away at all.
How many drugs does it take to cure tuberculosis (TB)?
If there is resistance then an MDR-TB regimen should be prescribed according to WHO's guidance for the treatment of drug resistant TB. It is often suggested that TB treatment fails because a patient doesn’t take their TB drugs correctly. However there can be a number of different reasons for TB treatment failure.
What is the treatment for drug resistant TB?
Food insecurity should be screened for (and resources provided as needed) at every encounter as the 4-month rifapentine-moxifloxacin regimen should be taken with food. Housing and income insecurity should also be considered to ensure retention in TB care.
What are the treatment options for tuberculosis (TB) due to food insecurity?
How successful is TB treatment?
Reported Tuberculosis in the United States, 2018 Successful therapy completion for TB patients is a major performance indicator for TB programs. Among patients during 2016 who were alive at diagnosis, 87.2% had completed TB treatment successfully.
Does tuberculosis go away after treatment?
After taking TB medicine for several weeks, a doctor will be able to tell TB patients when they are no longer able to spread TB germs to others. Most people with TB disease will need to take TB medicine for at least 6 months to be cured.
Does TB treatment always work?
With the proper treatment, tuberculosis (TB, for short) is almost always curable. Doctors prescribe antibiotics to kill the bacteria that cause it. You'll need to take them for 6 to 9 months. What medications you take and how long you'll have to take them depends on which works to eradicate your TB.
Is tuberculosis can be cured permanently?
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) that most often affect the lungs. Tuberculosis is curable and preventable. TB is spread from person to person through the air.
Does TB shorten your life?
Tuberculosis Life Expectancy Researchers have found that people who have survived active tuberculosis disease through successful treatment may have a lower life expectancy than people with a latent infection, estimating a loss of 3 to 4 years of life.
Can you live a normal life after TB?
While tuberculosis (TB) is a highly contagious disease, it's also very treatable. The best way to avoid complications from the disease is to take medications regularly and complete the full course as prescribed. In the United States, people with TB can live a normal life, both during and after treatment.
Can a person get TB twice?
It is possible to catch TB more than once, if you are unlucky enough to breathe in TB bacteria at another time. Always take new TB symptoms seriously and get them checked out by a doctor. After finishing treatment you might feel like looking at your life with new eyes.
How long can you live with untreated TB?
Left untreated,TB can kill approximately one half of patients within five years and produce significant morbidity (illness) in others. Inadequate therapy for TB can lead to drug-resistant strains of M.
Can I get married after TB treatment?
Finally, treatment of TB requires a 6-month or more course of drug therapy and participants generally considered it preferable to delay marriage until the course has been completed.
Is TB 100 percent curable?
3. There is no cure for TB. This is false; TB is treatable. The most common treatment for a latent TB infection is the antibiotic isoniazid.
What are the 3 stages of tuberculosis?
There are 3 stages of TB—exposure, latent, and active disease. A TB skin test or a TB blood test can diagnose the disease. Treatment exactly as recommended is necessary to cure the disease and prevent its spread to other people.
Can TB come back after 5 years?
The relapse rate differs by a country's incidence and control: 0–27% of TB relapses occur within 2 years after treatment completion and most relapses occur within 5 years; however, some relapses occur 15 years after treatment.
How long do you have to take antibiotics for tuberculosis?
For active tuberculosis, you must take antibiotics for at least six to nine months. The exact drugs and length of treatment depend on your age, overall health, possible drug resistance and where the infection is in your body.
What is the test for TB?
Sputum tests. If your chest X-ray shows signs of tuberculosis, your doctor might take samples of your sputum — the mucus that comes up when you cough. The samples are tested for TB bacteria. Sputum samples can also be used to test for drug-resistant strains of TB.
How long does ethambutol last?
If you have drug-resistant TB, a combination of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones and injectable medications, such as amikacin or capreomycin (Capastat), are generally used for 20 to 30 months. Some types of TB are developing resistance to these medications as well.
What test is used to test for tuberculosis?
The most commonly used diagnostic tool for tuberculosis is a skin test, though blood tests are becoming more commonplace. A small amount of a substance called tuberculin is injected just ...
Can a TB test be wrong?
Results can be wrong. The TB skin test isn't perfect. Sometimes, it suggests that people have TB when they don't. It can also indicate that people don't have TB when they do. You can have a false-positive result if you've been vaccinated recently with the bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine.
Can TB drugs cause liver damage?
Serious side effects of TB drugs aren't common but can be dangerous when they do occur. All tuberculosis medications can be toxic to your liver. When taking these medications, call your doctor immediately if you have any of the following:
Is TB a serious disease?
TB is a serious disease, and can be fatal if not treated properly. It is important to remember that all medications have risks and benefits. Learn more from CDC’s Dear Colleague letter. Not everyone infected with TB bacteria becomes sick. As a result, two TB-related conditions exist: latent TB infection and TB disease.
Can rifampin be used for TB?
Treatment. impurities in rifampin and rifapentine, two important anti-tuberculosis (TB) medications. People with TB disease or latent TB infection taking rifampin or rifapentine should continue taking their current medication, and should talk with their healthcare provider about any concerns.
How long does TB treatment last?
For new patients with presumed drug susceptible pulmonary TB, the World Health Organisation (WHO) recommends that they should have six months of treatment. This consists of a two month intensive phase followed by a four month continuation phase.
What are the best drugs for TB?
The drugs that a patient should take depends on whether the patient has ever had TB treatment before. If the patient has never had treatment before then it can be assumed that the bacteria in the patient's body will respond, and be sensitive to all the TB drugs. So the patient can then be given the following drugs: 1 Isoniazid 2 Rifampicin 3 Pyyrazinamide 4 & Ethambutol.
Why does TB treatment fail?
It is often suggested that TB treatment fails because a patient doesn’t take their TB drugs correctly. However there can be a number of different reasons for TB treatment failure. It is certainly true that if a patient doesn’t take their TB drugs properly that this can lead to the development of drug resistant TB.
What is the responsibility of a doctor for TB?
A patient must take their drugs properly. But it is also the responsibility of the doctor to make sure that the patient has the correct drugs. The doctor must also explain to the patient how to take the drugs correctly. In many countries there are "alternative" medicines available.
How many drugs are there for TB?
There are more than twenty drugs available for TB treatment. Which ones have to be taken depends on the circumstances of the patient. If you are having TB treatment (sometimes known as antitubercular treatment or ATT), then this should always be supervised by an experienced doctor or other health person.
What happens if you take only one or two TB drugs?
If only one or two TB drugs are taken then only some of the bacteria may be killed. They may then become resistant to the TB drugs which then don't work. If the person becomes sick again then different TB drugs called second line drugs may be needed.
How often should I take isoniazid?
Isoniazid. plus rifampicin. for the continuation treatment phase. It is recommended that patients take the TB drugs every day for six months. Taking the drugs three times a week used to be considered satisfactory but is no longer recommended by the WHO. It is essential that all the recommended TB drugs are taken.
How long does it take to cure TB?
TB treatment takes at least six months, patients need to take many tablets each day and side effects are common. This can be very difficult for people to manage, but it’s crucial that they take their treatment as prescribed and complete the course, to ensure they are completely cured and prevent them developing drug-resistant TB.
What is drug resistant TB?
Drug-resistant TB requires a longer course of treatment, with different combinations of drugs that can have more side effects. A patient will be tested to find out the exact course of treatment that should work for them.
Can TB go away?
With any medication, it is possible to experience side effects. Most are nothing to worry about and will go away. The TB nurse or doctor should advise patients of these before they start treatment.
Can latent TB be treated?
Most cases of latent TB are not considered for treatment, as 90% of people with latent TB do not go on to become ill with active TB. Treatment is recommended for people whose immune systems are weaker as they are more likely to go on to develop an active infection. This includes children and people living with HIV.
What should a clinic decide on TB treatment?
Clinicians should choose the appropriate treatment regimen based on drug susceptibility results of the presumed source case (if known), coexisting medical conditions (e.g., HIV. ), and potential for drug-drug interactions. Consultation with a TB expert is advised if the known source of TB infection has drug-resistant TB.
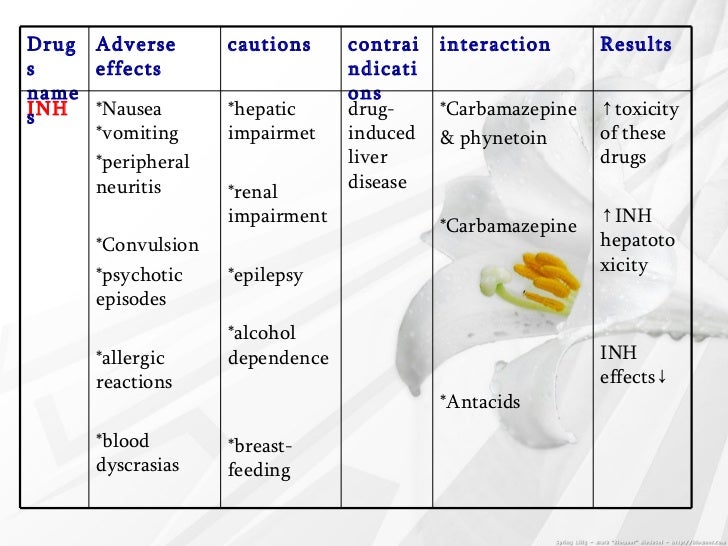
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat TB?
Isoniazid (INH) Rifapentine (RPT) Rifampin (RIF) These medications are used on their own or in combination, as shown in the table below. CDC and the National Tuberculosis Controllers Association (NTCA) preferentially recommend short-course, rifamycin-based, 3- or 4-month latent TB infection treatment regimens over 6- or 9-month isoniazid ...
Is 6H or 9H better for TB?
Although effective, 6H and 9H have higher toxicity risk and lower treatment completion rates than most short-term treatment regimens. All treatment must be modified if the patient is a contact of an individual with drug-resistant TB disease.
How many drugs are needed for TB?
TB infection is treated with one or two drugs, whereas TB disease initially requires four drugs.
What is the CDC's role in TB?
However, because prevention of TB has major public health implications, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommend testing populations that are at increased risk for TB infection and treating those for whom TB disease has been ruled out.
What is LTBI in healthcare?
Latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) is the presence of M. tuberculosis organisms (tubercle bacilli) without symptoms or radiographic or bacteriologic evidence of TB disease. Approximately 90-95% of those infected are able to mount an immune response that halts the progression from LTBI to TB disease. However, because prevention of TB has major public health implications, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommend testing populations that are at increased risk for TB infection and treating those for whom TB disease has been ruled out. Health care providers must communicate the risks and benefits of treatment to their patients and encourage adherence and treatment completion.
How is acceptance of LTBI influenced?
A patient’s acceptance of LTBI treatment is often influenced by the initial approach of the health care provider. When discussing the risks and benefits of treatment it is important to explain that
Background
What findings led to the interim guidance for the 4-month rifapentine-moxifloxacin regimen?
Sputum Samples
What specimens are acceptable for baseline molecular susceptibility testing?
Drug Susceptibility Testing
Is baseline molecular drug susceptibility testing for rapid identification of mutations associated with resistance to at least rifapentine, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and fluoroquinolones advisable?
Baseline Patient Evaluations
What levels of blood potassium, calcium, or magnesium would disqualify a patient for treatment?
Patient Considerations
What factors should be considered for patients with obesity when using the 4-month rifapentine-moxifloxacin regimen?
Drug Information
What are potential drug-drug interactions of antiretroviral (ARV) drugs in people living with HIV with the 4-month rifapentine-moxifloxacin regimen?
