The crystal lattice structure of the metal may have defects that present a source of plasticity. Heat treatment helps to address these defects. It does so by bringing the metal into the solution of fine particles.
Full Answer
What happens when you heat treat a stone?
This color change may result in the stone being darker, lighter, more intense or of a different color. An example of this is the dissolving of rutile silk inclusions in blue sapphires, which improves both clarity and color. This heat treatment is permanent and irreversible.
What are the clues to heat treatment of gemstones?
The destruction of gas or fluid inclusions or the dissolving of mineral inclusions are clues to heat treatment. For gems that contain rutile needles, the needle margins may become diffuse.
What is heat treatment and how does it work?
Heat treatment is considered to be a natural type of enhancement as it is a continuation of the processes that occur in the earth when the stone was originally formed.
What is an example of heat treatment in jewelry?
An example of this is the dissolving of rutile silk inclusions in blue sapphires, which improves both clarity and color. This heat treatment is permanent and irreversible.

Highlights
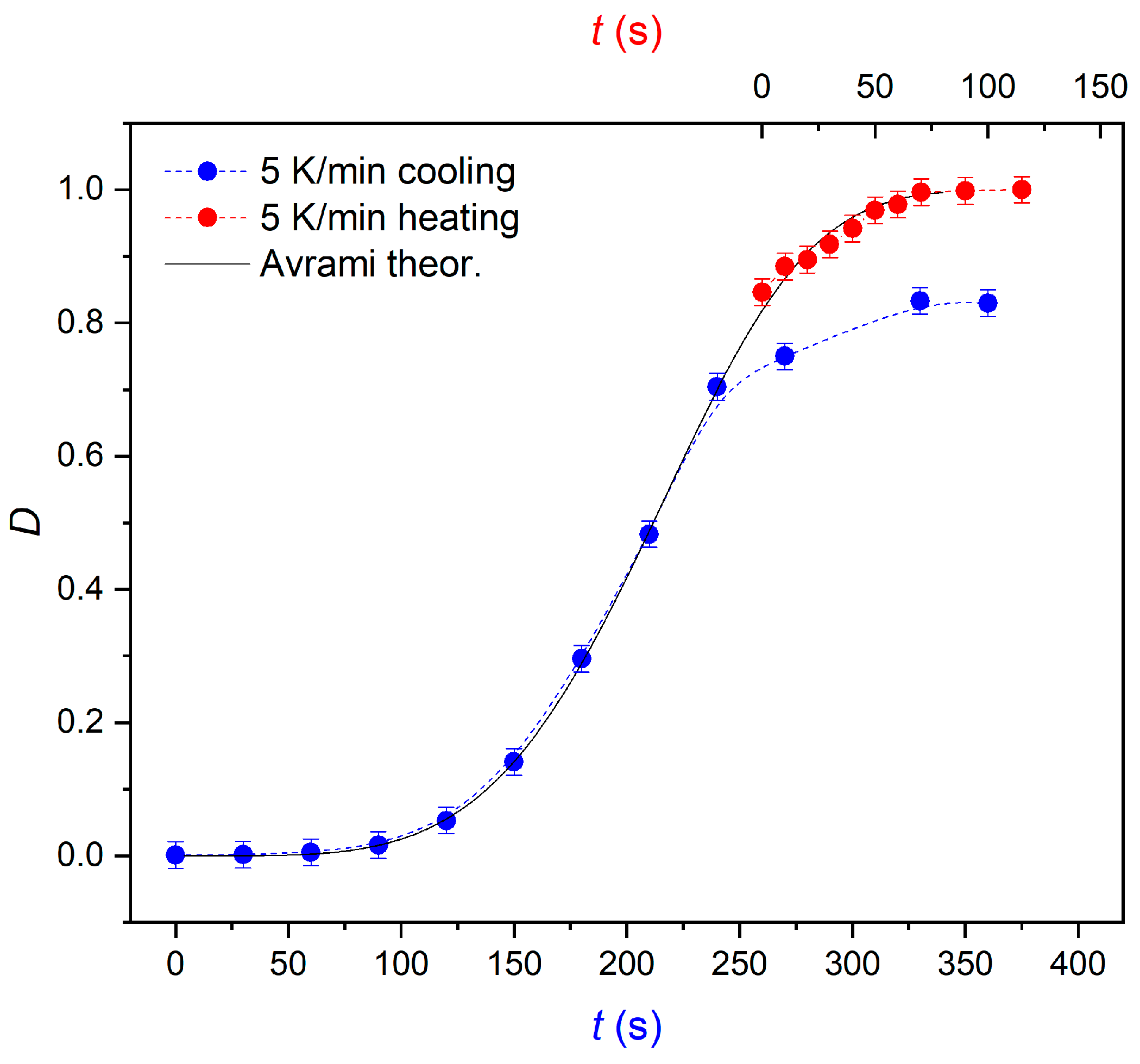
Heat treatment has obvious effect on transformation, structure and hysteresis.
Abstract
In this study, the effect of heat treatment on crystal structure, martensitic transformation, thermodynamic behavior and magnetic properties of polycrystalline Mn 53 Ni 25 Ga 22 ferromagnetic shape memory alloy was systematically investigated.
Effect of Heat Treatment on Crystal Structure and Wear Performance of Carbon-Carbon Composites
Center for Advanced Friction Studies. Southern Illinois University, Carbondale. IL
Summary
The processing temperature of a carbon–carbon (C/C) composite controls the extent of graphitization and crystal size. Often times the processing temperatures in industrial furnaces with graphite hot zones are not known with great accuracy because of the changes in emissivity with increasing temperature.
Why is heat treatment important?
It is very important manufacturing process that can not only help the manufacturing process but can also improve the product, its performance, and its characteristics in many ways. By Heat Treatment process, Example: The plain carbon steel. The following changes may be achieved: The hardness of Steel may be increased or decreased.
What is recrystallization in steel?
This causes complete recrystallization in steel to form New grain structure. This will release the internal stresses previously the strip in the steel and improve the machinability.
What are the changes in steel?
The following changes may be achieved: The hardness of Steel may be increased or decreased. Internal stresses that are set up due to cold or hot working may be relieved. The machinability of Steel may be enhanced. The mechanical properties like tensile strength the Talati shock resistance toughness etc may be improved.
What is nitriding used for?
Nitriding is generally employed to Steel parts which are moving like engine parts such a cylinder, crankshaft, etc. 6. Cyaniding: Cyaniding is also a surface hardening process in which the heated parts to be surface hardened are immersed in a bath of molten sodium or potassium cyanide.
What is the purpose of hardening steel?
Hardening is carried to accomplish the following: To reduce the grain size. Obtain maximum hardness.
What is annealing in metal?
Annealing is carried out for accomplishing one or more of the following: Softening of a metal or alloy. This may be done due to improving machinability. Relieving internal residual stresses caused by the various manufacturing process. Refining the grain size of the metal or alloy.
What is normalizing steel?
Normalizing is a heat treatment process similar to annealing in which the Steel is heated to about 50 degree Celsius above the upper critical temperature followed by air cooling. This results in a softer state which will be lesser soft than that produced by annealing.
What does heat do to gemstones?
High heat, such as that from a charcoal fire, can make a bland looking gemstone change its color into something spectacular.
What happens to a stone when it is heated?
During treatment, the stone is heated to very high temperatures (approximately 1600 Celsius) causing inclusions, chemical elements, and other impurities to reform themselves and change the color of the stone. This color change may result in the stone being darker, lighter, more intense or of a different color.
What gemstones are heat treated?
A methyst, citrine, ametrine, aquamarine, tourmaline, topaz, light green tourmaline, sapphire, ruby, tanzanite, and blue zircon are gemstones that are typically color-enhanced by heat treatment.
Why are my rubies glassy?
On rubies, inclusions may be found that are glassy in appearance. These are caused by borax-based substances that are used in the heat treatment process. I t is usually more difficult to find out if a stone has not been treated than if it has. Unadulterated stones can be harder to verify.
What stone is more commonly heated?
Here is a full list of the more commonly heated stones and how heat treatment enhances them. Amethyst - lightens the color and will change the color of pale amethyst to "yellow" that will be sold as citrine. Aquamarine - removes the greenish undertones that are common in this stone to produce a more blue stone.
Can gemologists see the inner workings of a stone?
However, there are some clues that can help. For example, gemologists can examine the inner workings of the stone and study the inclusions for signs of heat treatment. For example, if the stone has been treated, tiny inclusions such as small crystals will melt during the heat treatment process.