
The treatment of depression associated with alcohol or substance abuse has shown high resistance and therapy failure [ 10 ]. Moreover, a subset of patients may even suffer from worsened depression symptoms. Accordingly, some studies evaluated the combination of pharmacological treatment with psychotherapy in this patient population [ 11 ].
Does alcohol cause or cure depression?
Alcohol use issues can cause or worsen symptoms of depression. At the same time, people with depression may attempt to self-medicate with alcohol. Treating both will help ease symptoms of both.
What is the link between alcohol and depression?
“Depression and alcohol abuse are usually linked, because we take sedatives to fight chemical depression, which only makes the situation worse.” The more alcohol you drink, the more severe your symptoms.
Can alcohol cause serious depression?
This molecule have depressive effect in brain as it is lipid soluble also. As a summary, yes alcohol cause and increase depressive symptoms and signs. There is typically a deeper root cause to depression that often causes drinking. Drinking can lead to consequences that cause depression.
Is alcohol good against depression?
Some students who struggle with depression may turn to alcohol for relief. But drinking is deceptive at first, your mood seems to improve, and you think you’re starting to feel better. However, alcohol can trigger and worsen depression symptoms and lead to permanent devastating consequences.
/alveoli-56b36ca35f9b58def9c99cc0.jpg)
What does alcohol do to a depressed person?
Alcohol can lower serotonin and norepinephrine levels, which help regulate mood. Lower levels of these chemicals can make a depressed person more depressed. Alcohol temporarily cuts off the effects of stress hormones. This can exaggerate your depression symptoms because it depresses the brain and nervous system.
Can alcohol be used to treat depression?
Alcohol may be a form of self-medication for people with depression. The “burst” of energy from alcohol can be a welcome relief against some symptoms. For example, alcohol may temporarily reduce anxiety and lower inhibitions.
Why is alcohol not an effective way to relieve depression?
Drinking can heighten the symptoms of depression, which can have life-threatening implications. This is because alcohol impacts the same areas of the brain that help regulate mood. Drinking can alter the brain's chemical levels, which can trigger the symptoms of a mental health illness, such as depression.
What's the best antidepressant for an alcoholic?
The antidepressants nefazodone, desipramine, and imipramine were found to have the most robust effects on decreasing depressive symptoms.
Does alcohol affect depression and anxiety?
Regular, heavy drinking interferes with chemicals in the brain that are vital for good mental health. So while we might feel relaxed after a drink, in the long run alcohol has an impact on mental health and can contribute to feelings of depression and anxiety, and make stress harder to deal with.
How does alcohol affect serotonin?
Serotonin plays an important role in mediating alcohol's effects on the brain. Alcohol exposure alters several aspects of serotonergic signal transmission in the brain. For example, alcohol modulates the serotonin levels in the synapses and modifies the activities of specific serotonin receptor proteins.
Is alcohol a depressant or antidepressant?
Alcohol is classified as a Central Nervous System Depressant, meaning that it slows down brain functioning and neural activity.
Is alcohol a stress reliever?
Alcohol consumption can reduce the magnitude of an organism's response to stress. This reduction is called stress-response dampening (SRD) (Levenson et al. 1980). Researchers can measure alcohol's SRD effects in various ways.
How to understand how alcoholism and depression play off of each other?
To understand how alcoholism and depression play off of each other, one must understand what the mood disorder is. Perhaps the best way to understand this disorder is to look at its symptoms.
Why do people drink alcohol to relax?
Because alcohol does make us feel more relaxed after a drink or two , the logic used to justify self-medicating with it seems solid to those trying to escape depression.
What is the best treatment for depressive disorder?
Antidepressant medications: these alter the chemistry of the brain to right imbalances that contribute to the depressive disorder. Cognitive behavioral therapy: a type of therapy which helps patients address the dysfunctional thoughts and actions that fuel their disorders.
What are the causes of alcoholism?
The other half of that risk can be contributed to the environment, social factors, and the presence of other disorders which can push an individual towards using alcohol—such as pain disorders and mood disorders.
What are the symptoms of mood disorder?
Feelings of guilt, worthlessness, and helplessness. Pessimism and hopelessness. Anxiety. Feelings of emptiness. Restlessness. Aches and pains. Suicidal thoughts or attempts. Reading through these symptoms, it is clear this mood disorder is not easy to live with, which is why so many people seek treatment.
Can you self medicate by drinking?
There are numerous ways people self-medicate, including taking drugs, gorging on food, and even shopping sprees. But for many, alcohol holds more appeal than other ways of trying to escape their disorder, which is even more worrisome when speaking about underage drinking.
Can delirium tremens be caused by alcoholism?
In other words, it is unknown if someone without prior mood disorder or a predisposition to depressive disorders will develop the disorder as a result of alcoholism or just suffer post alcohol depression. In some cases, severe symptoms of delirium tremens can develop.
What are the factors that affect depression?
This includes your physical health, such as having a serious illness like cancer, diabetes, or heart disease, as well as your levels of neurotransmitters (brain chemicals), which can become imbalanced and influence depression. Stress, major life changes, and exposure to trauma.
What are the causes of depressive symptoms?
Taking certain medications. Some of the side effects of medications can cause or contribute to depressive symptoms. Low socioeconomic status.
How long does it take to get diagnosed with major depressive disorder?
Major depressive disorder. This causes severe symptoms that must be present for at least 2 weeks to receive the diagnosis. Symptoms affect your ability to work, sleep, eat, study, and function. Persistent depressive disorder, also known as dysthymia.
How long does postpartum depression last?
This causes less severe symptoms than major depression, but symptoms tend to last longer (at least 2 years in most cases). Postpartum depression, also known as perinatal depression. This is a type of major depression that can occur to women during pregnancy or after they give birth. Seasonal affective disorder.
What are the risk factors for depression?
These risk factors include: 1,2,3,4,5. Genetics and heritability. Genes are not destiny, but a family history of depression is considered a risk factor.
Can antidepressants be abused?
These medications can help to modify a person’s brain chemistry in order to stabilize moods. Antidepressants are generally not considered addictive, and they are unlikely to be abused. This is especially helpful when treating a person with concurrent depression and alcoholism, as those with substance use disorders are more apt to attempt to abuse medications.
Can depression cause alcoholism?
While depression can put a person at greater risk to develop an alcohol problem, the inverse is even more common. According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), depression can arise and increase during a battle with alcoholism. This increase in depression can then lead to more drinking, thus perpetuating this cycle from the other angle.
Why do people use the word "depressed"?
And often, people may use the word “depressed” as a way to verbalize how they are feeling. In the case of individuals who are diagnosed with depression, these low moods and feelings of sadness are often much more severe and occur for longer periods of time. 1 Depressive disorders can affect a person’s ability to function in many areas ...
How do you know if you are depressed?
While many people may feel down or sad from time to time, a depression diagnosis would mean experiencing the below symptoms for at least two weeks. 1 The signs and symptoms of depression include: 2,6 1 Feelings of hopelessness. 2 Sad moods lasting most of the day/week. 3 Frequent crying spells. 4 Loss of appetite, or greatly increased appetite. 5 Inability to sleep, or excessive sleeping. 6 Feelings of worthlessness and guilt. 7 Suicidal thoughts. 8 Irritability. 9 Loss of interests in hobbies and other activities. 10 Inability to fulfill roles in life, such as parenting or working. 11 Extreme fatigue. 12 Inability to concentrate or make decisions. 13 Moving very slowly or unable to do things at a normal pace.
What is the term for depression that lasts more than 2 years?
A person may suffer from: 2. Persistent depressive disorder: Depression lasting more than 2 years. Peripartum depression: Depression occurring during or after pregnancy, impairing a woman’s ability to care for her child.
How long does a depressive episode last?
3. Persistent depressive disorder: Depression lasting more than 2 years.
How long does it take to feel down?
While many people may feel down or sad from time to time, a depression diagnosis would mean experiencing the below symptoms for at least two weeks. 1 The signs and symptoms of depression include: 2,6. Feelings of hopelessness. Sad moods lasting most of the day/week. Frequent crying spells.
What are the symptoms of a sad mood?
Sad moods lasting most of the day/week. Frequent crying spells. Loss of appetite, or greatly increased appetite. Inability to sleep, or excessive sleeping. Feelings of worthlessness and guilt. Suicidal thoughts. Irritability. Loss of interests in hobbies and other activities.
Which comes first, AUD or depression?
It can be difficult to know which one comes first—AUD or depression, but research has shown that regardless of the order, both issues are among the most prevalent psychiatric disorders and co-occur often. 5 Studies have also indicated that this dual diagnosis, or comorbidity, is associated with greater severity and a worse prognosis for both disorders. 5
How long does it take for alcohol to cause depressive symptoms?
Alcohol-induced depressive disorder refers to a depressive-like syndrome (characterized by depressed mood or anhedonia) that occurs only during and shortly after alcohol intoxication or withdrawal, remits after 3 to 4 weeks of alcohol abstinence, and is associated with significant distress and impairment.
Why is alcohol withdrawal so difficult to diagnose?
Diagnosis is particularly challenging because of overlapping symptoms, such as the depressant effects of alcohol, and because of features that are common to both alcohol withdrawal and depressive disorders, such as insomnia and psychomotor agitation.
What are the different types of depressive disorders?
Depressive disorders are complex and heterogeneous syndromes. These disorders are characterized by disrupted mood (e.g., low, numb, or irritable), along with an array of cognitive (e.g., feelings of worthlessness and difficulty concentrating) and physical (e.g., fatigue and lack of energy) symptoms. The DSM-5 includes seven distinct disorders under the category of depressive disorders, including major depressive disorder, persistent depressive disorder (dysthymia), premenstrual dysphoric disorder, substance/medication-induced depressive disorder, disruptive mood dysregulation disorder, other specified depressive disorder, and unspecified depressive disorder. 6 This review focuses on major depressive disorder, dysthymia, and substance-induced depressive disorder, which are the depressive disorders that have been studied most often in both the general population and among people with AUD.
How long does it take to show signs of major depressive disorder?
Major depressive disorder is characterized by the presence of five or more symptoms that are present for at least 2 weeks. One of these symptoms must include depressed mood or anhedonia (significant loss of interest or pleasure in activities).
Is dysthymia a depressive disorder?
Dysthymia is more chronic than major depressive disorder, yet it is typically a milder disorder, characterized by at least 2 years of depressed mood and at least two additional symptoms, including dysfunction in appetite, sleep, energy, self-esteem, concentration, or decision-making, and feelings of hopelessness.
Is alcohol use disorder a psychiatric disorder?
Alcohol use disorder ( AUD) and depressive disorders are among the most prevalent psychiatric disorders and co-occur more often than expected by chance. The aim of this review is to characterize the prevalence, course, and treatment of co-occurring AUD and depressive disorders. Studies have indicated that the co-occurrence ...
Does AUD precede depressive disorder?
These studies have yielded mixed evidence. Some studies indicate that depressive disorders typically precede the onset of AUD, 21 others suggest that AUD generally precedes depressive disorders, 22 and still others report that the order of onset varies by gender (with women more likely to have earlier onset of depression than men). 17
How do you know if you have an alcohol use disorder?
According to the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM–5), these are some signs and symptoms that could reveal an alcohol use disorder: Your drinking is interfering with home, school, or work. You’ve stopped engaging in activities that are important to you.
What to do if you are susceptible to alcoholism?
If you believe you’re susceptible of experiencing alcohol addiction or depression, you may want to speak with a mental health professional, such as a social worker, counselor, or therapist, about these concerns and how best to prevent or cope with these disorders.
What is the difference between depression and depressive disorder?
Having difficulty concentrating. Major depressive disorder involves persistent and prolonged symptoms, but depression, in general, takes on many different forms. Depressive symptoms can result from life stressors, mental health conditions, medical conditions, and other factors.
What are the factors that affect PTSD?
Those factors include: Genetics, including a family history of depression or substance misuse. History of trauma or abuse, or PTSD, which may result from child abuse, sexual assault, combat, etc. Underlying mental health conditions. Environmental factors, including exposures to violence, trauma, assault, abuse, etc.
How do you know if you are depressed?
Some common signs and symptoms of depression, according to the DSM-5 Manual, include: 1 Feeling sad, empty, or hopeless 2 Losing interest in activities you once enjoyed 3 Experiencing a significant change in weight or decrease in appetite 4 Having trouble sleeping, experiencing fatigue, or sleeping too much 5 Experiencing thoughts of death or suicidal thoughts 6 Having difficulty concentrating
Is alcohol dependence a depressive disorder?
Alcohol Use Disorder and Depression. Many studies have found that alcohol dependence is closely linked to depression. 4 When it comes to diagnosing an alcohol use disorder and a major depressive disorder, it’s important to address them simultaneously, as they can significantly impact your recovery.
Is alcohol a socially acceptable drug?
Alcohol may be a socially acceptable drug, but it’s still a drug. Alcohol abuse and dependence are both considered an alcohol use disorder, with studies finding that alcohol dependence is more closely tied to the persistence of depressive disorders. 3
Introduction
- Psychiatric disorders, such as anxiety and mood disorders, commonly co-occur with alcohol use disorder (AUD). Depressive disorders are the most common psychiatric disorders among people with AUD.1 The co-occurrence of these disorders is associated with greater severity and worse prognosis than either disorder alone,2,3 including a heightened risk for suicidal behavior.4This r…
Overview of Depressive Disorders
- Depressive disorders are complex and heterogeneous syndromes. These disorders are characterized by disrupted mood (e.g., low, numb, or irritable), along with an array of cognitive (e.g., feelings of worthlessness and difficulty concentrating) and physical (e.g., fatigue and lack of energy) symptoms. The DSM-5 includes seven distinct disorders under the category of depressi…
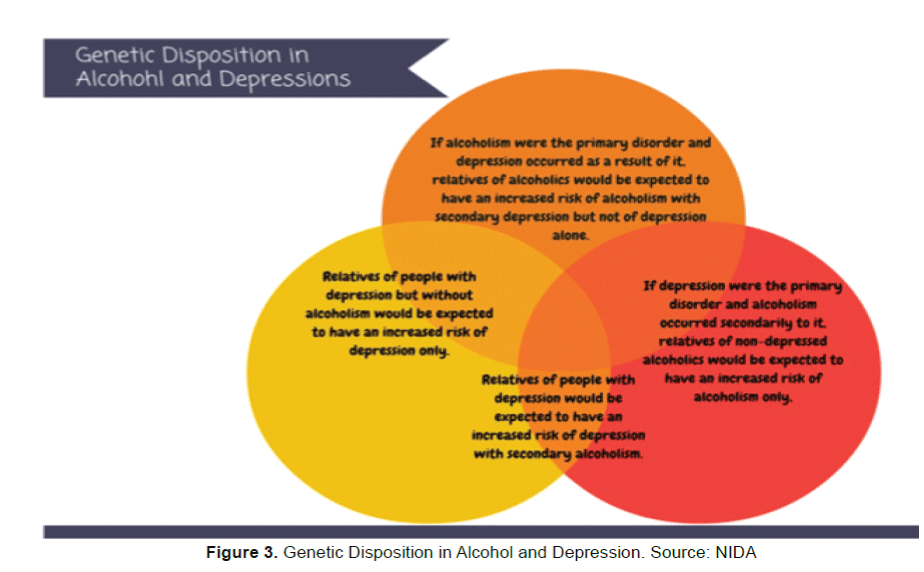
Pathways to Co-Occurrence
- Several potential developmental pathways have been proposed to explain the high rate of co-occurring AUD and depressive disorders, including: (1) depressive disorders increase risk for AUD, (2) AUD increases risk for depressive disorders, and (3) both conditions share pathophysiology or have common risk factors. Although evidence supports all three...
Treatment of Co-Occurring AUD and Depressive Disorders
- Many randomized trials have investigated treatments for co-occurring AUD and depressive disorders. In this section, trials that used medication and psychotherapy treatments are discussed, as are the effects of those treatments on depressive symptoms and AUD symptoms.
Future Research Directions
- Research has substantially improved understanding of the etiology, course, and treatment of co-occurring AUD and depressive disorders. However, significant gaps remain in our understanding of these two disorders, and these gaps present important opportunities for future research. More knowledge about optimal treatments for co-occurring AUD and depressive disorders is needed. …
Conclusion
- People with AUD have a heightened risk for depressive disorders, which are the most common co-occurring psychiatric disorders for this population. AUD and depressive disorders appear to share some behavioral, genetic, and environmental risk factors, yet these shared risks remain poorly understood. Diagnosis and treatment of the commonly co-occurring AUD and depressive disord…