
Full Answer
How does a wastewater treatment plant work?
Treating wastewater is a complex process that involves the use of high-tech and reliable equipment. Lakeside is proud to supply the equipment and purification systems that wastewater treatment plants need to filter, clean, and disinfect water before it is sent back into local waterways.
How is wastewater treated and reused?
Wastewater is now sent to wastewater treatment plants—many of which use the same purification process found in nature to clean water. Most wastewater treatment plants prepare wastewater for reuse in two separate stages: the primary and secondary stage.
What is the primary and secondary treatment of wastewater?
Primary Treatment of Wastewater 1 Primary Treatment of Wastewater The sewage water is first allowed to pass through a primary wastewater treatment plant. ... 2 Secondary Treatment of Wastewater Around 85% of organic matter from sewage is removed during secondary wastewater treatment. ... 3 Tertiary Treatment of Wastewater
How do floatable wastewater treatment systems remove floatable solids?
Floatable solids do so because their weight by volume is less than that of water. Primary wastewater treatments that remove these solids in process containers include primary clarifiers, air-flotation units and cone-shape Imhoff settlers.
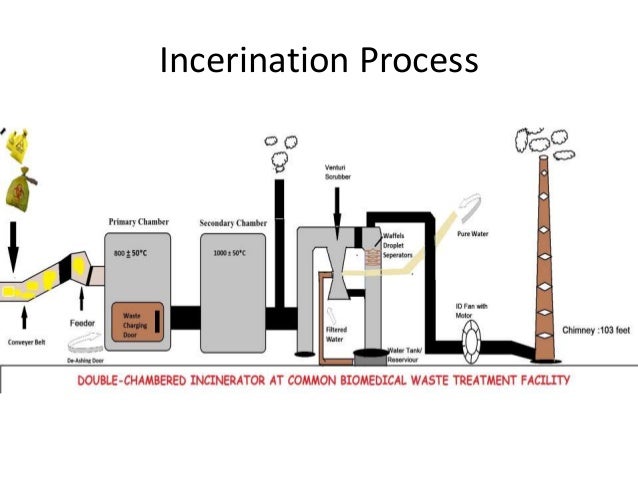
How do you separate solid waste from water?
Several methods are available to separate solids from liquids:Sedimentation (solids settle by gravity).Mechanical separation. Gravity and mechanical separation are the two most common techniques used for this purpose.Evaporation ponds. ... Dehydration. ... Coagulation Flocculation.
How does the wastewater treatment plant work?
There are two basic stages in the treat- ment of wastes, primary and secondary, which are outlined here. In the primary stage, solids are allowed to settle and removed from wastewater. The secondary stage uses biological processes to further purify wastewater. Sometimes, these stages are combined into one operation.
What happens to the solids in wastewater at a wastewater treatment plant?
The process occurs when a wastewater treatment plant is operating properly. Most solids in the wastewater will be removed at the plant, while the water is discharged as effluent to the receiving waters. These solids, or sludge, must be stabilized and reduced in volume before they can be reused or disposed of.
How do sewage treatment plants create solid waste?
solid waste particles: either when flowing water travels through a grate that blocks large solids from passing or when the particles settle out into a settling pond. Two common methods of disposing of solid waste from sewage treatment plants are transporting it to a landfill or spreading it onto agricultural lands.
How do water treatment plants treat water?
Disinfection. After the water has been filtered, water treatment plants may add one or more chemical disinfectants (such as chlorine, chloramine, or chlorine dioxide) to kill any remaining parasites, bacteria, or viruses.
What are the 5 steps of wastewater treatment?
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake. ... Sludge Treatment.
What happens to water after treatment?
What happens to the treated water when it leaves the wastewater treatment plant? The treated wastewater is released into local waterways where it's used again for any number of purposes, such as supplying drinking water, irrigating crops, and sustaining aquatic life.
What happens to sewage water after it is treated?
Once removed, phosphorus, in the form of a phosphate-rich sewage sludge, may be sent to landfill or used as fertilizer in admixture with other digested sewage sludges. In the latter case, the treated sewage sludge is also sometimes referred to as biosolids.
What are the 3 stages of wastewater treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.
What is solid waste treatment plant?
Solid waste treatment plant is a solid waste treatment & disposal facility consisting of different devices and combining with different sorting methods to separate useful resources out from the municipal solid waste.
What are the 4 stages of wastewater treatment?
Four common ways to treat wastewater include physical water treatment, biological water treatment, chemical treatment, and sludge treatment. Let us learn about these processes in detail. In this stage, physical methods are used for cleaning the wastewater.
What is the difference between water treatment and wastewater treatment?
While water treatment plants are used to clean and purify water, wastewater treatment plants are used to clean and purify wastewater.
What are the stages of wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment plants oversee three main stages: primary, secondary, and tertiary. However, some pollutants require advanced treatment, such as the quaternary, which involves fine filtration or oxidation processes to lower emergent pollutants dissemination.
How do ponds treat wastewater?
Algae relies on energy from the sun, inorganic compounds, and carbon (IV) oxid e released into the water by bacteria to grow. Through photosynthesis, algae release the oxygen required by aerobic bacteria. Sometimes, experts introduce mechanical aerators to provide more oxygen.
What is biofiltration in aquaculture?
Biofiltration is a standard method in greywater recycling, wastewater treatment, and aquaculture, as it helps raise the water quality while lowering water replacement. Biological filters eliminate contaminants through biodegrading natural components, filtering suspended solids, and absorbing micro-pollutants. Biofiltration processes are typically aerobic, so the microorganisms need oxygen for metabolism.
What is the purpose of tertiary treatment?
Its primary purpose is to increase the water quality to meet industrial and domestic standards or the specific safe discharge requirements while also removing nitrates and phosphates. For municipal wastewater treatment, this stage also involves eliminating pathogens, making the water safe to drink. The tertiary treatment process is usually performed using substances such as sand and activated carbon.
How long does aeration last?
Aeration is a timely process that can last for 30 hours and is equally instrumental, as it involves combining wastewater with a microorgan ism solution. Aeration gives the bacteria oxygen to stabilize and treats the wastewater by biodegrading the organic substance containing carbon to create carbon (IV) oxide and water. Without sufficient oxygen, breakdown has to occur under slow and odorous septic conditions, resulting in an incomplete transformation of pollutants.=
How is wastewater drained to the WWTP?
1. Firstly, wastewater is drained to the WWTP by gravity through the main sewer system of the size of a car. Having such size, objects you could hardly imagine reach the WWTPs, ranging from mattresses, fridges, tree branches to wallets disposed of by thieves in order to get rid of the evidence. 2.
What is wastewater in agriculture?
What is wastewater? It is used water originating from domestic, industrial, agricultural, and medical or transport activities. Used water becomes wastewater upon the change of its quality, composition and/or temperature. However, wastewater does not include water released from ponds or reservoirs for fish farming.
How long does it take for sludge to dry out?
9. Sludge, digested and dewatered to the optimal degree, is finally disposed of at the dump. In about a month, sludge is adequately dried out and ripe. If it complies with agricultural standards, it can be reused for fertilisation of industrial crops.
What is wastewater water?
Wastewater can be divided into two major groups: Sewage water is all wastewater used in domestic dwellings (e. g. originating from toilets, showers or sinks). Industrial wastewater originates from production, industrial and commercial activities, and has a different chemical composition to sewage water.
What is the first stage of wastewater treatment?
The first mechanical stage is called preliminary treatment or rather pre-treatment. Water flows through gravel chamber for settling out the grit from water. Afterwards, gravel is disposed of at the dump. Water further reaches the bar screens used to remove large objects from the wastewater.
What is the purpose of bar screens in wastewater treatment?
Water further reaches the bar screens used to remove large objects from the wastewater. At first come the coarse screens and then the fine screens which remove smaller objects such as matches, cigarette butts or undigested foods. 3. After the removal of large objects, grit is to be removed from the wastewater.
What is secondary treatment?
The secondary treatment, also called biological stage, is based on natural processes. WWTPs use bacteria which consume the contaminants, in particular biodegradable organics, carbon and phosphorus. Dead bacteria and organic residues subsequently transform into sludge. 6.
How Does a Waste Water Treatment Plant Work?
A waste water treatment plant cleans sewage and water so that they can be returned to the environment. These plants remove solids and pollutants, break down organic matter and restore the oxygen content of treated water. They achieve these results through four sets of operations: preliminary, primary, secondary and sludge treatments.
Pretreatment Phase
Waste water plants remove the ‘easy pickings’ during the pretreatment phase. A set of bar screens rakes away large items such as tree limbs, garbage, leaves, cans, rags, plastic bottles, diapers and other waste materials.
Primary Treatment
After pretreatment, the waste water collects in primary clarifiers, which are large basins and sedimentation tanks. Gravity allows smaller particles to settle out. Mechanically driven scrapers collect solid matter and direct it to hoppers connected to the sludge treatment equipment.
Secondary Treatment
In the next phase, plants aerate and agitate the waste water in secondary basins, adding beneficial microorganisms to break down organic matter into sludge. Plants employ a number of alternative strategies to break down sludge. For example, plants can culture a mass of microbes and pass the waste material over the biofilm.
Sludge Treatment
The final phase is to treat the remaining water and biosolids, or sludge. Gravity separates organic waste from heavier grit, which can be deposited in a landfill. The remaining primary sludge passes to a thickener, where it is centrifuged and fed to digesting tanks containing anaerobic bacteria.
What is wastewater treatment?
admin-seo. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), wastewater treatment is one of the most common forms of pollution control in the U.S. Lakeside Equipment Corporation is proud to supply equipment and systems that are used across the country at wastewater treatment plants, which are facilities that clean wastewater ...
How does wastewater enter the primary stage of treatment?
Sewage enters the primary stage of treatment as soon as it arrives at a wastewater treatment facility. First, it is sent through a screen that is designed to remove large pieces of debris that could damage Lakeside equipment used elsewhere in the facility. Some facilities have multiple screens in place to remove objects and materials ...
How does wastewater get into an aeration tank?
The wastewater enters an aeration tank, where it is mixed with sludge. Air is then pumped into the aeration tank to facilitate the growth of bacteria and other small organisms within the sludge. The bacteria and other microorganisms break down the organic matter in the water into harmless byproducts.
What happens when wastewater is pumped into a sedimentation tank?
The wastewater slowly flows through a sedimentation tank, and as it flows, the solids that remain in the water start to drift towards the bottom of the tank. This is the final step in the primary stage of the wastewater treatment process. At this point, the majority of the solids have been removed from the water.
What is the secondary stage of wastewater treatment?
The secondary stage of the treatment process is designed to remove up to 85% of organic matter that remains in the wastewater. There are a number of different ways to achieve this goal, but many facilities use either the trickling filter or activated sludge process.
What is grit in sewage?
After passing through the screen, the sewage water moves into the grit chamber. Grit can include sand, gravel, eggshells, or any other type of solid material that makes it through the screening process.
Can bacteria keep up with sewage?
But, the bacteria and other organisms could not keep up with the increase in population and production of sewage. Wastewater is now sent to wastewater treatment plants—many of which use the same purification process found in nature to clean water. Most wastewater treatment plants prepare wastewater for reuse in two separate stages: ...
What happens when wastewater enters a settling tank?
Short circuits: As wastewater enters the settling tank, it should be evenly dispersed through the entire cross-section of the tank. It should flow at the same velocity in all areas toward the discharge end. If velocity is greater in some sections than others, short-circuiting may occur.
What is a solid in wastewater?
Solids —including those suspended, settle-able or floatable — are non-liquid or fluid substances separated from clarified wastewater in primary treatment . Solids —including those suspended, settle-able or floatable — are non-liquid or fluid substances separated from clarified wastewater in primary treatment.
Why are floatable solids used in wastewater treatment?
Floatable solids do so because their weight by volume is less than that of water. Primary wastewater treatments that remove these solids in process containers include primary clarifiers, air-flotation units and cone-shape Imhoff settlers. While effective solids separation supersedes control of pH and flow or other factors, ...
What is suspended solid?
Suspended solids are those small, solid particles that remain so in water, as a colloid, or due to the motion of the water. Settle-able solid s are particles that will settle within a reasonable length of time assuming little movement. The weight by volume of settle-able solids is greater than water. Floatable solids do so because their weight by ...
What is the purpose of flotation thickening?
The objective of flotation thickening is to separate solids from the liquid phase by matching air bubbles to particles of suspended solids. Four general methods of flotation are common, as follows:
What are the factors that affect the settling rate of water?
Most common include temperature variation, short circuits, detention time, weir-overflow rate, surface-loading rate and solids loading. Three of these factors are discussed below. 1. Temperature: In general, as water temperature increases, the settling rate of particles increases; as temperature decreases, so does the settling rate.
Can air be dissolved in primary or secondary effluent?
Air also can be dissolved in primary or secondary effluent, thus avoiding solids recycling in the dissolved air flotation (DAF) unit. Mixing the retention tank contents should also be used to increase air put into solution.
What is wastewater treatment?
A wastewater treatment plant treats sewage water from various sources and makes it reusable. It comprises several processes that address specific needs for wastewater treatment. The treatment system treats the sewage from domestic use, rainwater, runoff, and other pollutants that go down the street gutters. The sewage also includes water ...
How much organic matter is removed from sewage?
Around 85% of organic matter from sewage is removed during secondary wastewater treatment. The process involves forcefully mixing the wastewater with bacteria and oxygen, bacteria digest organic matter with the help of oxygen. These processes are performed by the trickling filter and activated sludge tank.
What happens when you remove grit from a sedimentation tank?
Once the settled grit is removed, the wastewater is passed to the sedimentation tanks, settling tanks , or clarifiers. This step removes organic and inorganic matter and suspended solids. By properly adjusting the water flow in the sedimentation tank, the suspended particles start to sink to the bottom and form a solid mass.
How does sewage water work?
The sewage water is first allowed to pass through a primary wastewater treatment plant. At this stage, the treatment uses screens and settling tanks to remove most of the floating materials from the wastewater. Solid materials account for around 35% of the wastewater. Hence, removing the solid waste at the primary stage makes ...
What is the mass of wastewater called?
The solid mass is called raw primary biosolids or sludge. Scum is formed on the top of the wastewater and is skimmed off from the top. The primary treatment process removes around 90% of suspended solids, 55% of fecal coliforms, and 50% of biological oxygen demand (BOD).
What is tertiary treatment?
This treatment is employed when the water from the secondary treatment has an undesirable amount of dissolved substances like metals, color, nutrients, and organic chemicals. Several physical, chemical, and biological treatment processes are performed for tertiary treatment.
How is wastewater drained?
Waste water is drained through pipe systems and thus enters the public sewerage system . Here we differentiate between two types of drainage. In the combined sewer system, domestic and commercial wastewater is fed into a sewer together with rainwater that accumulates on sealed surfaces (e.g. streets and roofs).
What is the process of removing nutrient from wastewater?
In the actual clarifier, bacteria and fungi have the task of metabolising organic components in the wastewater into its individual parts. This process is called Biological nutrient removal. Oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor areas provide optimal conditions for breaking down all carbon and phosphate compounds and urea from the urine.
How does a separate sewer system work?
The separate sewer system divides the media. Dirty water is fed into one sewer, surface water into another. Because of the low dirt load, the collected surface water is usually discharged into neighbouring waters (lakes or rivers). The wastewater and the combined sewer both end up at the treatment plant. Of course, in the case of combined sewer ...
What is the process of cleaning a toilet called?
Rakes filter everything that is not permeable as solid matter in the wastewater. This can be toilet paper, wet wipes, but also a toothbrush or other things that do not belong in a toilet. This process is called pretreatment.
Where does wastewater end up in a combined sewer system?
The wastewater and the combined sewer both end up at the treatment plant. Of course, in the case of combined sewer systems, the sewage treatment plant has more work to do, as all the surface water has to be cleaned as well.
What happens to clarified water?
In the end, the clarified water is returned to the natural water cycle, usually lakes or streams. Very modern sewage treatment plants have additional treatment stages for further phosphorus elimination or the killing of pathogens.

Pre-Treatment Phase
- http://www.instagram.com/p/CBuVtZ1DbHv/ The pre-treatment phase that occurs at a wastewater treatment plant is designed to get rid of the larger and easier to remove items from the water. These items can include everything from tree branches and cans to plastic bottles an…
Primary Treatment Phase
- http://www.instagram.com/p/B-WWIQHlkY8/ Once the pre-treatment phase concludes, the primary treatment phase can begin. The wastewater will be collected in sedimentation tanks and large basins at this point, which is done to allow contaminants to sink to the bottom of the water. Once the smaller particles in the water have settled, scrapers are used to collect the solids and send t…
Secondary Treatment Phase
- http://www.instagram.com/p/B_ZLcJVhNJD/ This is a very important phase of the wastewater treatment process that involves the agitation and aeration of the water within secondary basins. It’s at this point in the process that microorganisms are added to the water in order to break down any organic matterinto sludge that can be more readily discarded. Certain plants will grow a sub…