The general criteria for receiving the COVID-19 antibody treatment are:
- People who are 65 years of age or older.
- Those who have a body mass index (BMI) of 35 or higher.
- People who have chronic kidney disease, diabetes, immunosuppressive disease, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, or a chronic respiratory disease ...
- Those who are currently receiving immunosuppressive treatment.
- People with conditions that are not being addressed by clinical trials.
- Are high risk** for developing severe COVID-19 AND.
- Have a positive COVID-19 test and have not yet been admitted to the hospital AND.
- Are 12 years of age or older (and at least 88 pounds)
Who qualifies for monoclonal antibody treatment?
· Anyone who is pregnant, or aged 65 or older, qualifies for monoclonal antibody treatment by way of being "high risk." As does anyone who is overweight, which is classified in this instance as...
How do you know if you qualify for covid-19 antibody treatment?
· Individuals qualify for monoclonal antibody treatment if: they have tested positive for COVID-19, and; it has been 10 days or less since symptoms first started, and; they have other health conditions that put them at higher risk. Monoclonal antibody treatment is most effective when given early—and the sooner it is given, the better.
How do I make an appointment for monoclonal antibody treatment?
If you test positive for COVID-19 and have mild to moderate symptoms, these treatments can help fight the disease and keep you out of the hospital. This treatment involves an infusion of monoclonal antibodies (specifically bamlanivimab, or casirivimab and imdevimab) to treat COVID-19. Health care providers can only give the infusions in certain settings.
Do you need to quarantine after monoclonal antibody therapy?
A visit with a UCHealth provider is required in order to determine if you qualify for monoclonal antibody or antiviral therapy. Please note that any UCHealth Urgent Care location can evaluate you in order to determine if you qualify. If a provider …
What are the conditions that are not being addressed by clinical trials?
· Monoclonal antibody infusions were granted emergency use authorization by the FDA and are recommended for adults and pediatric patients (12 or older) who meet one of the following criteria: 65 years old or older Have a BMI of more than 25 kg/m2, or if age 12-17, have BMI above the 85th percentile for their age and gender based on CDC growth charts
What is the FDA's drug program?
· Monoclonal antibodies are man-made proteins that act like human antibodies in the immune system which help fight off infections. This specific treatment is for people in the early stages of COVID-19 with mild-to-moderate symptoms. Here is the criteria for treatment according to the FDA: All people age 65 and older

What is a monoclonal antibody for COVID-19?
Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-produced molecules that act as substitute antibodies that can restore, enhance or mimic the immune system's attack on cells. Monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 may block the virus that causes COVID-19 from attaching to human cells, making it more difficult for the virus to reproduce and cause harm. Monoclonal antibodies may also neutralize a virus.
How can you get antibody tests for COVID-19 in the United States?
Antibody tests for COVID-19 are available through healthcare providers and laboratories. Check with your healthcare provider to see if they offer antibody tests and whether you should get one.
How long do COVID-19 antibodies last?
At this time, it is unknown for how long antibodies persist following infection and if the presence of antibodies confers protective immunity.
What is the difference between monoclonal antibodies and the COVID-19 vaccine?
COVID-19 vaccines help stimulate and prepare a person's immune system to respond if they are exposed to the virus. However, monoclonal antibodies boost the immune system only after a person is already sick, speeding up their immune response to prevent COVID-19 from getting worse.
What is the COVID-19 antibody test?
COVID-19 antibody tests can help identify people who may have been infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus or have recovered from a COVID-19 infection.
Would COVID-19 antibody test be positive after vaccine?
Be aware that if you have a positive test result on a SARS-CoV-2 antibody test, it is possible you were previously infected with SARS-CoV-2. A COVID-19 vaccination may also cause a positive antibody test result for some but not all antibody tests.
Can you get COVID-19 if you already had it and have antibodies?
It is important to remember that some people with antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 may become infected after vaccination (vaccine breakthrough infection) or after recovering from a past infection (reinfected).
How long does it take for antibodies to develop after exposure to COVID-19?
It can take days to weeks after an infection for your body to make antibodies.
Do people produce COVID-19 antibodies after infection?
Most people who've recovered from COVID-19 do make antibodies against the virus.
Should you still get the COVID-19 vaccine if you were treated with monoclonal antibodies?
If you were treated for COVID-19 with monoclonal antibodies or convalescent plasma, there is no need to delay getting a COVID-19 vaccine.
What is a monoclonal antibody?
Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-produced molecules that act as substitute antibodies that can restore, enhance or mimic the immune system's attack on cells.
How many types of monoclonal antibody COVID-19 treatments are there in the US?
In the United States, there are three anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody treatments with FDA Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the treatment of COVID-19: bamlanivimab plus etesevimab, casirivimab plus imdevimab,, and sotrovimab.
Who Qualifies For COVID Antibody Treatment?
Monoclonal antibody treatment can protect people who are at high risk of developing a serious illness from COVID-19.
Locating Sites For COVID-19 Antibody Treatments
Updated 1/12/21 . Locating Sites For COVID-19 Antibody Treatments . Use these resources to identify sites of care administering COVID-19 antibody therapies.
ARE YOU ELIGIBLE FOR MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY TREATMENT?
All age eligible unvaccinated patients who qualify and receive monoclonal antibody therapy should be advised to receive the COVID-19 vaccine 90 days after the monoclonal antibody administration.
What is the purpose of monoclonal antibody therapy?
The goal of this therapy is to help prevent hospitalizations, reduce viral loads and lessen symptom severity.
What are monoclonal antibodies?
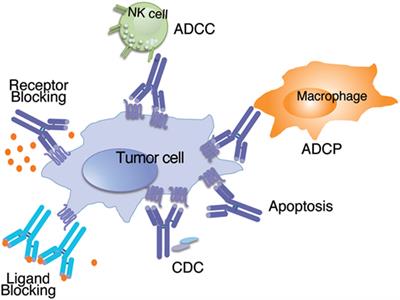
However, monoclonal antibodies are mass-produced in a laboratory and are designed to recognize a specific component of this virus — the spike protein on its outer shell .
What antibodies interfere with the virus?
By targeting the spike protein, these specific antibodies interfere with the virus' ability to attach and gain entry into human cells. The two monoclonal antibody therapies currently available are the bamlanivimab and a combination of the casirivimab and imdevimab.
How long should you wait to get a second shot?
If you already received the first dose of vaccine before monoclonal antibody therapy, current CDC guidelines recommend you wait 90 days before receiving the second dose. Categories: Tips to Live By. Tags: Coronavirus, Infectious Disease.
What are monoclonal antibodies?
Our bodies naturally make antibodies to fight infections. However, if you haven’t received the COVID-19 vaccine or had a previous COVID-19 infection, your body will not have antibodies designed to recognize a new virus like SARS-CoV-2.
How does monoclonal antibody therapy help?
Monoclonal antibody therapy is a way of treating COVID-19 for people who have tested positive, have had mild symptoms for seven days or less, and are at high risk for developing more serious symptoms.
Who is eligible for monoclonal antibody therapy?
Given that COVID-19 vaccination provides strong protection against severe disease and need for hospitalization, monoclonal antibody therapy is an option for certain high-risk patients with COVID-19.
What is the function of antibodies?
Antibodies are proteins that exist in our bodies as part of our immune system to recognize and defend against harmful viruses and bacteria. Monoclonal antibodies are made in a laboratory and designed to target a specific virus or bacteria.
What antibody is used to block the virus?
Monoclonal antibodies against COVID-19 attach to the virus to block it from entering human cells. The monoclonal antibody protein also “marks” the virus to be broken down by the immune system and cleared from the body.
Can monoclonal antibodies cause nausea?
Most people tolerate monoclonal antibody infusions very well. Some people may experience infusion-related side effects, such as nausea and dizziness, that are short-lived and go away on their own. As with any medication, there is the potential for mild or more severe allergic reactions, which are uncommon.
What are the conditions that are not being addressed by clinical trials?
People who have chronic kidney disease, diabetes, immunosuppressive disease, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, or a chronic respiratory disease like COPD. Those who are currently receiving immunosuppressive treatment. People with conditions that are not being addressed by clinical trials. Generally, the treatment is not recommended ...
What is the FDA's drug program?
Since late last year, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has been approving drugs that are specifically tailored to fighting the virus. These are known as COVID-19 antibody treatments and if you meet certain criteria, you could be next in line.
