4-Step Wastewater Sludge Treatment Process
- Sludge Thickening. The first step in the sewage sludge treatment plan is called thickening. ...
- Sludge Digestion. After amassing all the solids from the sewage sludge begins the sludge digestion process. ...
- Dewatering. After retrieving useful gases and other byproducts, the remaining sludge is then dewatered before final disposal.
- Disposal. ...
What happens to sludge from a wastewater treatment facility?
Wastewater then enters the second section or sedimentation tanks. Here, the sludge (the organic portion of the sewage) settles out of the wastewater and is pumped out of the tanks. Some of the water is removed in a step called thickening and then the sludge is processed in large tanks called digesters. 5. Removing scum
What are the disadvantages of a waste water treatment plant?
What Are the Dangers of Living Near a Wastewater Treatment Facility?
- Airborne Hazards. Chemicals from wastewater treatment facilities become airborne when they're air-stripped. ...
- Respiratory and Gastrointestinal Infections. If particles, organisms or pathogens that are air-stripped are inhaled, they go through the bronchial tubes and lungs, are cleared from the lungs, and then swallowed.
- Pests. ...
Does the wastewater treatment plant smell bad?
While wastewater treatment plants do smell, it’s important to reduce those smells for several reasons. First, you don’t want people who live nearby to constantly complain to the town or city about the odors. Second, those odors are linked to harmful gases being released during the treatment process. Odor management helps protect the environment.
What is the purpose of a waste water treatment plant?
- Waste water is collected and flows through plant
- Filtration physical/chemical/biological
- Level of filtration depends on the application process which the water will be reused for
- Clean water is prepared for reuse

What happens to the sludge from wastewater treatment?
Once treated, sewage sludge is then dried and added to a landfill, applied to agricultural cropland as fertilizer, or bagged with other materials and marketed as “biosolid compost” for use in agriculture and landscaping.
How is sludge treated at wastewater treatment plants?
Sewage sludge treatment describes the processes used to manage and dispose of sewage sludge produced during sewage treatment. Sludge is mostly water with lesser amounts of solid material removed from liquid sewage. Primary sludge includes settleable solids removed during primary treatment in primary clarifiers.
Which methods can be used to dispose sludge?
Once treated, sludge can be recycled or disposed of using three main routes: recycling to agriculture (landspreading), incineration or landfilling.
What is sludge How is it removed?
Sludge is mostly water with lesser amounts of solid material removed from liquid sewage. Primary sludge includes settleable solids removed during primary treatment in primary clarifiers. e3radg8 and 8 more users found this answer helpful.
How do you remove sewer sludge?
4-Step Wastewater Sludge Treatment ProcessStep 1 – Sludge Thickening. The first step in the sewage sludge treatment plan is called thickening. ... Step 2 – Sludge Digestion. After amassing all the solids from the sewage sludge begins the sludge digestion process. ... Step 3 – Dewatering. ... Step 4 – Disposal.
What are the two types of sludge disposal?
Like the liquid effluent from the treatment plant, there are two broad methods for the disposal of sludge - (1) disposal in water, and (2) disposal on land. This applies regardless of whether or not the sludge is treated to facilitate or permit the selected method of disposal.
What is the most common method of disposal for sludge created by the softening process?
The most common disposal method for water treatment plant sludge is landfilling.
How is sludge treated in a wastewater treatment plant Class 7?
Sludge is used to produce biogas. Clarified water is then passed through an aerator tank where air is pumped into the water. It helps aerobic bacteria to grow which decompose organic matter like human waste. After several hours, the suspended microbes settle at the bottom of the tank as activated sludge.
How do you remove sludge from water?
There are various options for treating sludge including stabilization, thickening, dewatering, drying, and incineration. The costs for treating sludge and removing sludge from wastewater are roughly the same. Typically a polymer chemical is used for the volume reduction process known as dewatering.
What are the 3 stages of wastewater treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.
What are the steps in wastewater treatment?
The Wastewater Treatment ProcessStage One — Bar Screening. ... Stage Two — Screening. ... Stage Three — Primary Clarifier. ... Stage Four — Aeration. ... Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier. ... Stage Six — Chlorination (Disinfection) ... Stage Seven — Water Analysis & Testing. ... Stage Eight — Effluent Disposal.
Why is raw sludge better for dewatering?
Raw sludge is more amenable to dewatering by vacuum filtration because the coarse solids are rendered fine during digestion. Hence filtration of raw primary or mixture of primary and secondary sludges permits slightly better yields, lower chemical requirement and lower cake moisture contents than filtration of digested sludges.
Where can sludge be disposed of?
The sludge may be disposed of in an abandoned mine/quarry. This method may be adopted only for sludges that have been stabilized so that no decomposition or nuisance conditions will result. Thus this method can be safely adopted for digested sludge, clean grit and incinerator residue.
What is sludge digestion?
Sludge digestion is a biological process in which the organic matter present in the sludge is decomposed by micro-organisms and is thus stabilized. It is accomplished in sludge-digestion tanks or digesters, which are usually closed cylindrical tanks. The principal purposes of sludge digestion are to reduce its putrescibility or offensive odour, pathogenic contents and to improve it dewatering characteristics.
Why is sludge conditioned?
Sludge is conditioned mainly to improve its dewatering characteristics. Prior conditioning of sludge before application of dewatering methods renders it more amenable to dewatering.
What is the purpose of centrifugal thickening?
Centrifugation or centrifugal thickening employs centrifuges which cause settling of sludge particles under the influence of centrifugal forces . Centrifuges are used both to thicken and to dewater sludges. Their application in thickening is normally limited to waste activated sludge.
How is flotation thickening used?
Floatation thickening is used mainly for thickening or concentrating light biological sludges such as waste activated sludges which have a density very close to that of water and are thus readily buoyed to the surface.
Why do we heat dry sludge?
The purpose of heat drying is to reduce further the moisture content and volume as well as weight of the dewatered sludge, so that it can be used after drying without causing offensive odours or risk to public health, or it can be incinerated efficiently. Several methods such as sludge drying under controlled heat, flash drying, rotary kiln, multiple hearth furnaces, etc., have been used in combination with incineration devices.
What is the process of dewatering sludge?
Other processes used to dewater sludge include filter presses, belt filter presses, centrifuges, and vacuum filters.
Where to dispose of sedimentation sludge?
Many options exist for disposal of sedimentation sludge such as disposal in streams, lagoons and landfills. In the past, sludge and backwash water was typically released into streams and other bodies of water. However, this practice is becoming much less common and is now well regulated. Most of the other alternatives require transporting sludge ...
What is the concentration of alum sludge?
The solids in the sludge are mainly flocs, excess coagulant, such as alum. Alum sludge has a solids concentration of only about 1 % when automatically removed from the basin, or about 2% if manually removed. Many options exist for disposal of sedimentation sludge such as disposal in streams, lagoons and landfills.
What type of sedimentation basin is used for sand?
The most common use of type I or discrete settling is plain sedimentation basins, which are generally adopted prior to slow sand filter to remove sand, gravel and other discrete particles from raw water sources such as river supply and to reduce the turbidity level to less than 40 NTU.
Is sludge transported away from treatment plant?
Most of the other alternatives require transporting sludge away from the treatment plant. Sludge is typically dried before it is trucked away since the greater volume of wet sludge makes it much more expensive to transport. This drying process is known as dewatering ...
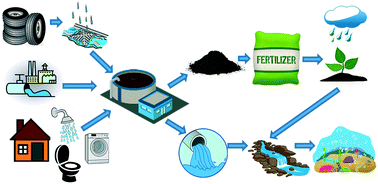
What Is Wastewater Sludge?
Wastewater sludge is a semisolid waste or residue byproduct of wastewater treatment. This product contains organic and inorganic materials, plant nutrients, organic chemicals and pathogens, making proper sludge management in water treatment essential to minimize negative environmental impacts.
Types of Wastewater Sludge
The type of sludge produced depends upon the source and its use. The four types of sludge are:
Why Sludge Removal Is Necessary
Wastewater sludge contains many dangerous pathogens that must be properly removed to preserve the water quality. Before wastewater can undergo sludge removal, it must be treated to reduce the sludge volume and stabilize the organic materials.
How to Prepare Sludge for Removal
During the preparation process for removing wastewater, waterborne contaminants separate into a concentrated stream. There is often too much of this sludge line wastewater to dispose of it directly, so it requires additional processes to prepare for proper sludge treatment and disposal.
The Sludge Thickening and Dewatering Process
Sludge thickening and dewatering is critical to minimize water waste and turn the sludge back into a useable product. Failure to thicken the sludge will create excess waste and increase its potential to reenter the water system and cause pollution.
Dewatering Process
The dewatering process is essential for waste minimization and separates sludge into solids and liquids. Before the dewatering process begins, the sludge must undergo a conditioning treatment with mineral chemicals such as iron salt and lime. After this treatment, the sludge thickens and is then dewatered for disposal.
How to Dispose of Wastewater Sludge
What constitutes proper wastewater sludge removal equipment will depend on government regulations such as the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act, plant location and the sludge’s characteristics. Sludge disposal methods include:
How to manage sewage sludge in treatment plants?
It requires a large area of land. Therefore, this method is used mainly in rural areas and not used in urban areas. Composting is one of the other ways to manage sewage sludge in treatment plants. In this method, dewatering is done which is followed by mixing the mostly solid sludge with high carbon organic material.
What is sludge treatment?
There are now strong biological solutions that help in wastewater and sludge treatment.
Why is wastewater treatment important?
Treatment is important because sludge emanates toxic gases and it can act as a health hazard. There are several treatment methods used to treat sewage sludge.
What is sewage sludge?
Sludge or sewage sludge can be defined as the residue or the by-product which is left after the wastewater treatment processes are carried out in the wastewater treatment plants. The solid, semi-solid, and slurry residue is a combination of various components like organic and inorganic materials, plant nutrients, chemicals, ...
What is the primary treatment of wastewater?
The primary treatment of wastewater plants involves various processes like filtering of solid particles like wood, paper, plastic, vegetable matter, etc. Also, oil and grease are removed during this process. Gravity sedimentation, flotation processes, chemical precipitation, sedimentation leads to the generation of primary sludge which is settled ...
What is wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment plants collect a large amount of domestic waste, industrial waste, agricultural waste, and waste from commercial spaces and provide treatment. This involves primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment of wastewater which uses physical, biological, and chemical means to purify the wastewater.
What is the process of sludge?
In the aerobic process, the sludge is supplied with oxygen which produces carbon dioxide. The biological processes ably reduce sludge volume, eliminates pathogens, and even makes it easy to dry the sludge. It converts organic sludge into liquids and gases.
Why is it important to treat sludge?
Therefore, it is extremely important to properly treat such sludge in order to minimize its environmental repercussions.
How does sewage sludge digest?
After amassing all the solids from the sewage sludge begins the sludge digestion process. This is a biological process in which the organic solids present in the sludge are decomposed into stable substances. This process also helps reduce the total mass of solids, while destroying any present pathogens to enable easy dewatering. The sludge digestion process is a two-phase process. In the first stage, the dry solid sludge is heated and mixed in a closed tank to enable anaerobic digestion by acid-forming bacteria. These bacteria hydrolyze the large molecules of proteins and lipids present in the sludge and break them down into smaller water-soluble molecules, which they then ferment into various fatty acids. The sludge then flows into the second tank where it is converted by other bacteria to produce a mixture of carbon dioxide (CO 2) and methane, after which the methane is collected and reused to power the digestion tank and generate power (depending on the quantity retrieved).
How much water is in dewatered sludge?
In most cases, dewatered sludge usually contains a significant amount of water, as much as 70 percent, in spite of its solidified state. Therefore, it is important to dry and dewater the sludge beforehand.
What is the purpose of wastewater treatment?
Mainly many sludges are treated using a variety of digestion techniques, the purpose of which is to reduce the bulk amount of organic matter and the number of disease-causing microorganisms present in the solids. Wastewater Treatment Plant like etp, zld stp plant etc are very good solutions for wastewater.
How is sewage treated?
While sewage sludge is usually treated using a standard plan of action , it is extremely important to factor in aspects like the origin of the sewage, the treatment process used to reduce the sewage to sludge, as well as the possible byproducts that can be retrieved from it for further use before choosing a sludge treatment plan.
What is the first step in sewage treatment?
The first step in the sewage sludge treatment plan is called thickening. In this step, the sewage sludge is thickened in a gravity thickener to reduce its overall volume, thus enabling the easy handling of the sludge.
What is the process of sludge digestion?
The sludge digestion process is a two-phase process. In the first stage, the dry solid sludge is heated and mixed in a closed tank to enable anaerobic digestion by acid-forming bacteria.
Aerobic and anaerobic sludge treatment
As you certainly know, both aerobic and anaerobic sludge treatment employs microorganisms and bacteria. Anaerobic bacteria convert organic matter into biogas, reducing the volume of sludge by up to 50%.
Solar drying
Solar drying requires sufficient space since the partially dewatered sludge is transported to a drying hall where it is tipped into large beds and left to dry for several days.
Vacuum filtration
Imagine a drum filled with sludge. Valves and pipes are so arranged that, as the drum rotates, a vacuum is applied, drawing out water from the solid mixture.
Sludge fields
Sludge fields are the simplest, yet the least effective method of dewatering. Why?
Drying and incineration
Unlike drying halls or sludge fields, it is much easier to dry the sludge using hot gas. The sludge is heated to a temperature at which the water is immediately removed from the solids.
How much sewage sludge does Pennsylvania produce?
This means that Pennsylvania's POTWs generate approximately 300,000 tons of sewage sludge (dry weight basis) each year.
How are sludge solids concentrated?
Sludge solids are concentrated either by settling due to gravity or by introducing air, which causes sludge solids to float.
What is biosolids in sewage?
The term "biosolids" also helps to distinguish sewage sludge from industrial sludge by emphasizing that the former is produced by a biological process.
What is biosolids in wastewater treatment?
The industry defines biosolids as sewage sludge that has undergone sufficient treatment for stabilization and pathogen reduction, and that is of sufficiently high quality to be land applied. The term is intended to distinguish high-quality, treated sewage sludge from raw sewage sludge and from sewage sludge that contains large quantities of environmental pollutants. The term "biosolids" also helps to distinguish sewage sludge from industrial sludge by emphasizing that the former is produced by a biological process. The term has been criticized by some as an attempt to disguise the real nature of sewage sludge, thereby making land application of this material less objectionable to the general public. Although "biosolids" undoubtedly does not conjure up the same negative images as does "sewage sludge" or simply "sludge," it is a legitimate and functional term when correctly used to make the distinction described above. In this document, "sewage sludge" will be used to refer to wastewater treatment solids generally, and "biosolids" will be used to refer specifically to material that is suitable for land application.
How long does it take for a sludge to increase pH?
Sufficient alkaline material, most commonly lime (CaO), is added to the sludge to increase its pH to at least 12 for 2 hours. The pH must remain above 11.5 for an additional 22 hours.
How long does sludge stay in the air?
One of the most widely used methods for sludge treatment. Sludge is held in the absence of air for 15 to 60 days at temperatures of 68 to 131°F. Anaerobic bacteria feed on the sludge, producing methane and carbon dioxide. In some treatment plants, the methane is collected and burned to maintain the treatment temperature.
What is municipal sewage?
Municipal wastewater, or sewage, refers to water that has been used in urban and suburban area homes or businesses for washing, bathing, and flushing toilets. Municipal wastewater also may include water from industrial sources.