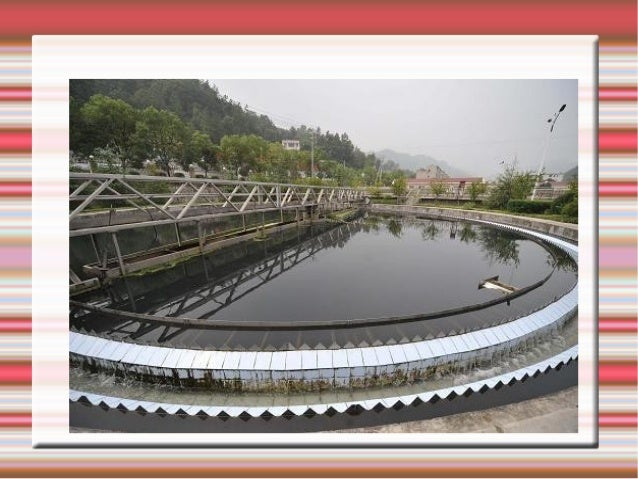
How Does a Wastewater Treatment Plant Work?
- Pre-treatment Phase. The pre-treatment phase that occurs at a wastewater treatment plant is designed to get rid of the larger and easier to remove items from the water.
- Primary Treatment Phase. Once the pre-treatment phase concludes, the primary treatment phase can begin. ...
- Secondary Treatment Phase. ...
- Sludge Treatment Phase. ...
What are the main steps in sewage treatment?
Jan 16, 2020 · Very modern sewage treatment plants have additional treatment stages for further phosphorus elimination or the killing of pathogens. Bacterial flakes and sludge are processed into gas in digestion towers and in many cases are used to supply the sewage plant with energy.
How to purify wastewater using just plants?
Mar 20, 2019 · A sewage treatment plant is designed to treat and process raw sewage over different steps involving breaking, filtering, settling, controlled aerobic decomposition and chemical treatment. One of the most common things that come in our mind regarding human waste; is to dump it to the sewers and let the government take care of it.
How much does a sewage treatment plant cost?
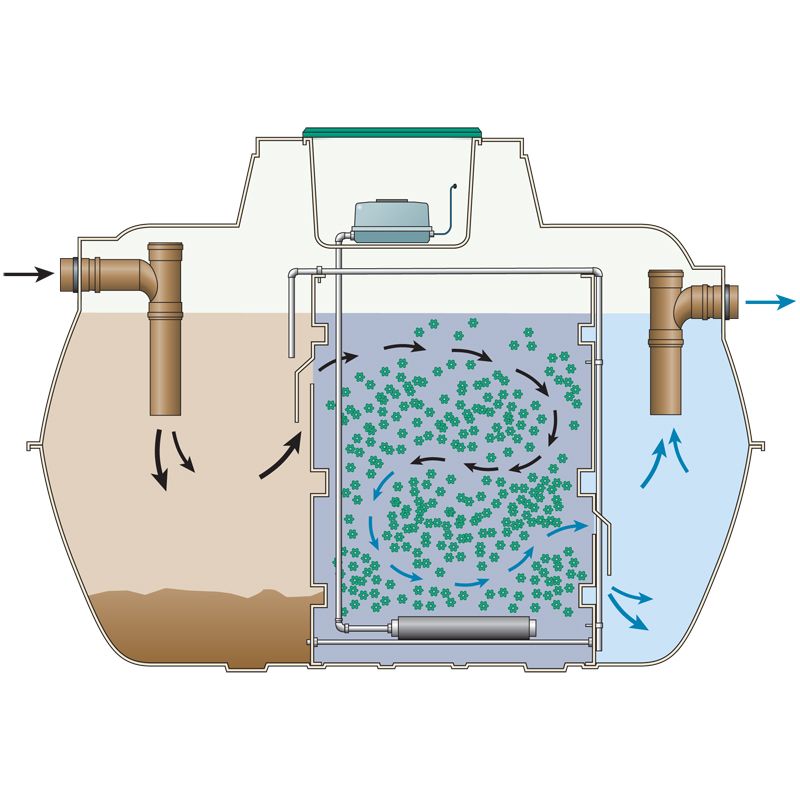
Jan 24, 2018 · Using bacteria to treat wastewater. A sewage treatment plant is a treatment system that uses naturally occurring bacteria to treat wastewater. The proves can be broken down into 4 key areas, all of which occur in an underground tank: 1. Settlement. When wastewater first arrives at the treatment plant it enters an initial settlement zone.
How do plants give off waste?
The Sewage Treatment Plant process is similar to the way that a Septic Tank works but mechanical components provide additional processes to help break down solids to produce a cleaner, more environmentally friendly effluent. Wastewater and sewage, usually from a number of properties, are fed into the primary settlement tank where solids and liquids separate and …
Where does human waste go after a sewage treatment plant?
The treated wastewater is released into local waterways where it's used again for any number of purposes, such as supplying drinking water, irrigating crops, and sustaining aquatic life.
What do sewage plants do with poop?
The wastewater flows through bar screens to remove trash and debris, then slowly moves through a grit tank where sand and heavy particles settle and are removed. During primary treatment, water moves on to sedimenta- tion tanks where it's undis- turbed for a few hours.
What are the 3 stages of sewage treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
What are the 4 steps of sewage treatment?
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake. ... Sludge Treatment.
What does ghost poop mean?
The scholars at Urban Dictionary defined ghost poops as “The single most satisfying bowel movement that man is capable of.” Generally speaking, a ghost poop means you experience the relief of a bowel movement without seeing any evidence of it, whether inside the toilet bowl or when you wipe your butt.Dec 15, 2021
Does poop float in a septic tank?
When the waste water from your toilet, shower, sinks and washing machine leave your house, it's combined. When it hits the septic tank, however, it begins to separate. The heaviest particulate matter in the waste, called sludge, sinks to the bottom.
How many types of sewage treatment plants are there?
4 Types of Sewage Treatment Plants.Aug 7, 2018
What are the methods of sewage treatment?
Majorly, four methods of sewage water treatment are followed – physical, biological, chemical, and sludge water treatment. By following these methods, the wastewater is disinfected from all the sewage materials and converted into treated water that is safe for both human usage and the environment.
What happens to solids in a sewage treatment plant?
At the POTW, the sewage passes through a series of treatment steps that use physical, biological, and chemical processes to remove nutrients and solids, break down organic materials, and destroy pathogens (disease-causing organisms) in the water.Sep 15, 2010
What happens in screening and grit removal?
The wastewater passes through a screen to remove rags and large debris. The screening system washes and dewaters the debris before discharging it into a garbage can.
What techniques are used for wastewater sludge treatment?
Sludge stabilization is a treatment technique applied to biological sludge to reduce its odor-causing or toxic properties. This treatment often reduces the amount of solids as a side effect. Anaerobic and aerobic digestion, lime treatment, chlorine oxidation, heat treatment, and composting fall into this category.
How we can remove sludge from wastewater treatment plant?
There are various options for treating sludge including stabilization, thickening, dewatering, drying, and incineration. The costs for treating sludge and removing sludge from wastewater are roughly the same. Typically a polymer chemical is used for the volume reduction process known as dewatering.Sep 24, 2014
What is sewage treatment plant?
A sewage treatment plant is designed to treat and process raw sewage over different steps involving breaking, filtering, settling, controlled aerobic decomposition and chemical treatment. One of the most common things that come in our mind regarding human waste; is to dump it to the sewers and let the government take care of it.
What is chemical sewage treatment?
The preliminary chamber is equipped with coarse and fine mesh of screen as filters to remove large solid particles from getting into the system. In many designs it stay set at the top of the primary chamber with flow measurement device recording and filtering waste water inlet at the same time.
Why is activated carbon added to sewage?
It get on to absorb all the organic molecules associated with the smell and distinct colour. In many design the activated carbon sets are filled just after the settling chamber; thus allowing waste water to be treated before moved to next chamber.
How long does it take for chlorine to kill bacteria?
This is done by adding a 5 % solution of chlorine to kill of bacteria within a period of 30 minutes. Further chemical treatment is done to remove the smell and get rid of the pale colour. The treated water is then either discharged to the sea, to shore facilities or used in toilets for flushing.
Where is raw water stored?
The raw waste water originating from toilet, wash basins and bathrooms; with a concentration of 0.1% solid waste by weight is stored in the primary chamber. The sewage is fed into the chamber with special macerator pumps that reduce human waste to slurry using blending and grinding techniques.
How does activated carbon work?
In many design the activated carbon sets are filled just after the settling chamber; thus allowing waste water to be treated before moved to next chamber. This is achieved by the process called adsorption. Many a times they not just used to remove odor and color; but also unwanted bi-product of biological treatment.
Where does waste water go after biological treatment?
The waste water after biological treatment went to the settling chamber where the heavier solid particles settles down by effect of gravity. To further support the process and nullify effects of flow of sewage; the waste water is inserted into the chamber from chamber and exit from top to the next chamber.
What is a sewage treatment plant?
A sewage treatment plant is designed to take wastewater from a building (wastewater is defined as water from showers, baths, toilets, washing machines, dishwashers and sinks) and treat it to take out contaminants that are harmful to the environment.
What happens to water after settlement?
Following the settlement stage, cleaned water is then free from solids and has undergone a massive reduction in Ammonia and contaminants and can be discharged into a stream or river.
Why is large surface area important?
The large surface area is important as it allows lots of room for bacteria to colonise. An Example this style of treatment is the Tricel NOVA. With this style of sewage treatment, water flows through the filter material, therefore the “food” comes to the bacteria.
What is active sludge?
Active sludge. Active sludge (or activated sludge) treatment plants do not have filter material, instead, bacteria is encouraged to grow freely in the water. Waste (food) is introduced to the chamber and gets mixed with the bacteria. The bacteria bind to the food and begin feeding upon it.
Do active sludge systems work?
However, active sludge systems have less of an ability to block if items such as wet wipes get through the system, and there is some suggestion that bacteria can last slightly longer with no food when growing on filter material.
Do bacteria need food?
Bacteria also need food, this comes from the waste in the sewage water. If the environment is right (i.e., lots of oxygen and food) the microscopic bacteria will thrive and feed upon the contaminants.Bacteria can live freely in the water or grow on filter material; this is why you see some systems that have filter material, and some without. 3.
What is the first stage of wastewater treatment?
The first mechanical stage is called preliminary treatment or rather pre-treatment. Water flows through gravel chamber for settling out the grit from water. Afterwards, gravel is disposed of at the dump. Water further reaches the bar screens used to remove large objects from the wastewater.
What is wastewater in agriculture?
What is wastewater? It is used water originating from domestic, industrial, agricultural, and medical or transport activities. Used water becomes wastewater upon the change of its quality, composition and/or temperature. However, wastewater does not include water released from ponds or reservoirs for fish farming.
What is wastewater water?
Wastewater can be divided into two major groups: Sewage water is all wastewater used in domestic dwellings (e. g. originating from toilets, showers or sinks). Industrial wastewater originates from production, industrial and commercial activities, and has a different chemical composition to sewage water.
How long does it take for sludge to dry out?
9. Sludge, digested and dewatered to the optimal degree, is finally disposed of at the dump. In about a month, sludge is adequately dried out and ripe. If it complies with agricultural standards, it can be reused for fertilisation of industrial crops.
What is secondary treatment?
The secondary treatment, also called biological stage, is based on natural processes. WWTPs use bacteria which consume the contaminants, in particular biodegradable organics, carbon and phosphorus. Dead bacteria and organic residues subsequently transform into sludge. 6.
