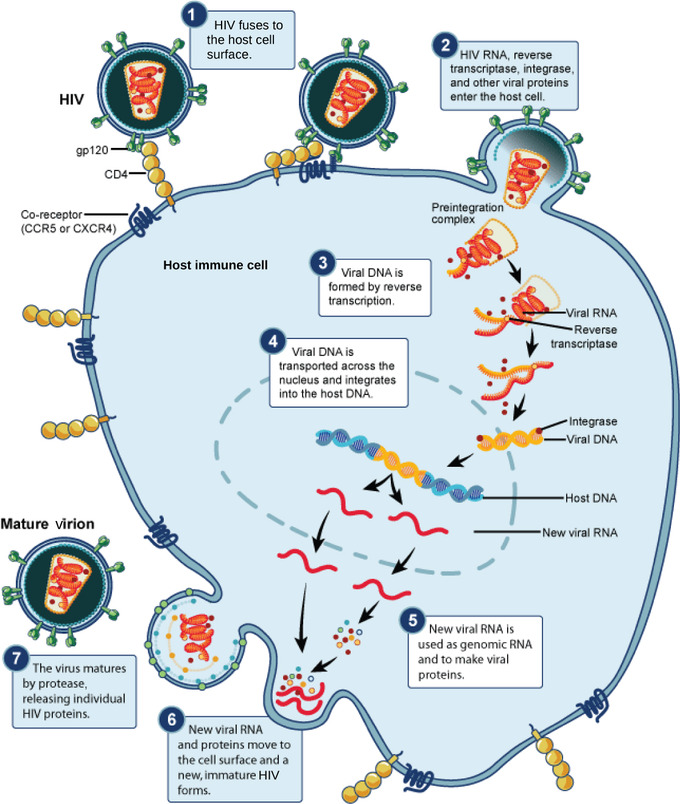
When the HIV virus enters a healthy cell, it attempts to make copies of itself. It does this by using an enzyme called reverse transcriptase. The NRTIs work because they block that enzyme. Without reverse transcriptase, HIV can't make new virus copies of itself.
What are reverse transcriptase inhibitors?
Jan 07, 2022 · The second virus is hepatitis B. Reverse transcriptase inhibitors have also been used for post-exposure prophylaxis when concern exists for potential patient infection with HIV. Lastly, reverse transcriptase inhibitors are being used to decrease the spread of HIV from mother to child during pregnancy and labor and delivery. The drug of choice for HIV treatment of the …
How do reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) work in pediatric HIV infection?
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors NNRTIs are drugs that selectively target the HIV-1 RT enzyme. NNRTIs have been shown to interact with a non-substrate-binding site on HIV-1 RT to affect the HIV DNA polymerization step [21]. NNRTIs include delavirdine, EFV, etravirine, nevirapine and rilpivirine (RPV).
What is antiretroviral therapy for HIV?
Feb 04, 2007 · This animation shows how a medication called AZT, which is a reverse transcriptase inhibitor, can be used to treat HIV/AIDS. In order to complete its life cycle, HIV uses an enzyme called reverse transcriptase to convert its viral RNA to DNA. The animation illustrates how the drug azidothymidine, or AZT (also known as zidovudine or Retrovir), blocks the …
Is tyr188leu a good design feature for HIV-1 reverse transcriptase?
Introduction: While considerable advances have been made in the development of antiretroviral agents, there is still work to be done. Reverse transcriptase inhibitors are important drugs for the treatment of HIV, and considerable research is currently ongoing to develop new agents and to modify currently existing agents.

Which of the following is a reverse transcriptase inhibitor used in the treatment of HIV?
Doravirine (MK-1439), also called Pifeltro, is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor developed by Merck & Co. for use in the treatment of HIV/AIDS. In August 2018, the FDA approved doravirine.
What is reverse transcriptase and what is its importance in the management of HIV infection?
HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT) contributes to the development of resistance to all anti-AIDS drugs by introducing mutations into the viral genome. At the molecular level, mutations in RT result in resistance to RT inhibitors.Apr 19, 2013
Why is reverse transcriptase important in medicine?
Reverse Transcriptase (RT) is essential for HIV replication because the viral RNA genome on its own is highly susceptible to degradation by intracellular RNases. RT rapidly makes a much more nuclease-resistant double-stranded DNA copy of the RNA template that later integrates to form the proviral DNA.
How does a reverse inhibitor work?
Rev is the name of an HIV protein that helps to transport HIV's genetic information within an infected immune cell. HIV uses the Rev protein to replicate and produce new virus. Rev inhibitors are drugs that interfere with the Rev protein's activity to prevent HIV from multiplying in the body.
What is the treatment for HIV?
Treatment with nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) is one way to help stop the virus from replicating and control HIV infection. Here’s what NRTIs are, how they work, and the side effects they can cause.
How does HIV spread?
HIV attacks cells within the body’s immune system. To spread, the virus needs to enter these cells and make copies of itself. The copies are then released from these cells and infect other cells.
What are the side effects of lipodystrophy?
lipodystrophy (abnormal distribution of body fat) nervous system effects, including anxiety, confusion, depression, or dizziness. lactic acidosis. Although these side effects aren’t common, it’s important to know that they can occur and to discuss them with a healthcare provider.
How do NRTIs work?
To treat HIV, NRTIs work by blocking an enzyme HIV needs to make copies of itself. Normally, HIV enters certain cells in the body that are part of the immune system.
Is the risk of side effects higher if you have a medical history?
The risk of side effects may be higher depending on a person’s medical history and lifestyle. According to the NIH, the risk of some negative side effects may be higher if the person:
What is a reverse transcriptase inhibitor?
Reverse-transcriptase inhibitors ( RTIs) are a class of antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV infection or AIDS, and in some cases hepatitis B. RTIs inhibit activity of reverse transcriptase, a viral DNA polymerase that is required for replication of HIV and other retroviruses .
What is the function of reverse transcriptase?
When HIV infects a cell, reverse transcriptase copies the viral single stranded RNA genome into a double-stranded viral DNA. The viral DNA is then integrated into the host chromosomal DNA, which then allows host cellular processes, such as transcription and translation, to reproduce the virus. RTIs block reverse transcriptase's enzymatic function ...
What is doravirine used for?
Doravirine (MK-1439), also called Pifeltro, is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor developed by Merck & Co. for use in the treatment of HIV/AIDS. In August 2018, the FDA approved doravirine. It is also used in a combination tablet as doravirine/lamivudine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (Delstrigo).
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat HIV-1?
Nucleoside reverse transcriptase translocation inhibitor (NRTTIs) This is a new class of antivirals, MK-8591 or Islatravir being the first agent of this group. Islatravir was developed by Merck & Co.. It is orally available, long acting antiviral, being tested as ART against HIV-1.
What is the function of RTIs?
RTIs block reverse transcriptase's enzymatic function and prevent completion of synthesis of the double-stranded viral DNA, thus preventing HIV from multiplying. A similar process occurs with other types of viruses. The hepatitis B virus, for example, carries its genetic material in the form of DNA, and employs an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase ...
Is entecavir a drug?
Entecavir, also called ETV, is a guanosine analog used for hepatitis B under the trade name Baraclude. It is not approved for HIV treatment. Truvada, made of emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, is used to treat and prevent HIV. It is approved for HIV prevention in the US and manufactured by Gilead.
What is a narti?
Nucleoside analog reverse-transcriptase inhibitors (NARTIs or NRTIs) compose the first class of antiretroviral drugs developed. In order to be incorporated into the viral DNA, NRTIs must be activated in the cell by the addition of three phosphate groups to their deoxyribose moiety, to form NRTI triphosphates. This phosphorylation step is carried out by cellular kinase enzymes. NRTIs can induce mitochondrial impairment that leads to a number of adverse events, including symptomatic lactic acidosis.
How do non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors work?
Both nucleoside and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors work at the same stage of the viral replication cycle, when the viral RNA converts itself into DNA using reverse transcriptase enzyme. The nucleoside transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), have a nucleoside that is structurally similar to the T-cell DNA’s nucleoside.
What is the treatment for HIV?
Antiretroviral therapy is a treatment regimen for HIV infection, with a combination of three or more drug classes that stop virus replication in different ways. An NNRTI drug is usually one of the drugs used in the combination when antiretroviral therapy is first initiated after diagnosis of HIV infection.
What are the effects of central nervous system?
Central nervous system effects such as#N#Sleepiness#N#Vivid dreams#N#Confusion#N#Visual hallucinations#N#Suicidal thoughts (higher risk in patients with psychiatric history or on psychoactive medications) 1 Sleepiness 2 Vivid dreams 3 Confusion 4 Visual hallucinations 5 Suicidal thoughts (higher risk in patients with psychiatric history or on psychoactive medications)
What is the cause of HIV?
HIV infection is caused by a virus that infects and weakens the human immune system. HIV specifically targets the T-cell, which is a type of lymphocyte that develops in the thymus gland and is an integral part of the immune system. The virus enters the T-cell and uses its cell machinery to replicate itself, destroying the host cell in the process.
What is NNRTI in HIV?
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) are one of the classes of drugs that form part of the antiretroviral therapy (ART) for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. An NNRTI drug may be part of a cocktail of ART drugs that each target HIV at different points in its replication cycle to help lower the level of virus in the body and prevent HIV from causing AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). AIDS may lead to death from secondary infections after immune system collapse.
What enzyme converts RNA into DNA?
The virus releases and uses a special enzyme known as reverse transcriptase to convert its RNA into DNA that can enter the nucleus. The NNRTI drug binds to the reverse transcriptase enzyme, altering its structure and inhibiting its function in the transcription of RNA into DNA.
Can HIV be cured?
The virus enters the T-cell and uses its cell machinery to replicate itself, destroying the host cell in the process. Untreated HIV can progress to acquired immune deficiency syndrome ( AIDS ), a late stage of HIV infection when the body’s immunity is so compromised it cannot fight infections effectively. HIV infection has no cure, and the patient ...
What is the purpose of protease inhibitors?
Protease inhibitors may be one class of drugs included in the ART cocktail for HIV to prevent its progression into AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome ), which may cause death from secondary infection or cancer after the collapse of the immune system.
What is the cause of HIV?
HIV infection is caused by a virus that attacks the human immune system. HIV targets and enters an immune cell known as T-cell, and uses its cell machinery to create more HIV viral copies, which disperse to infect other T-cells.
What happens when the immune system becomes impaired?
Uncontrolled HIV infection in its later stages results in acquired immune deficiency syndrome ( AIDS ), when the immune system becomes highly impaired and loses its ability to fight infections effectively.
When were protease inhibitors first used?
Protease inhibitors were first introduced in 1995 and are effective for both HIV -1 and HIV -2 infections. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) form the backbone of the three-drug ART regimen, and protease inhibitors are often an additional drug class included in the regimen, to improve the chances of controlling the viral growth.
Can ART cure HIV?
There is no cure for HIV infection, but ART can effectively manage HIV as a chronic disease. Protease inhibitors have a low incidence of drug resistance in treatment-naive patients (patients undergoing treatment for the first time). Drug resistance tests are performed before ART is initiated, but protease inhibitor -based ART regimens are often ...
Can HIV mutate?
Formation of new infectious virus particles is then prevented or inhibited. HIV may eventually mutate and develop resistance to the drugs. Many second-generation protease inhibitors continue to be effective until multiple mutations take place.
Can you take Prezista with food?
Darunavir (Prezista) Available as tablets to be taken with food along with booster drugs such as ritonavir or cobicistat. Approved for antiretroviral treatment-naive patients or treatment-experienced patients without darunavir -resistance mutations.
