
As you can see, H. pylori infections can be transmitted from one person to another in a number of ways. There are many combinations of antibiotics and other medications available to eliminate the bacteria while reducing the ulcers. Listed below are some natural remedies that can assist these medications in treating an H. pylori infection.
Full Answer
How to treat H pylori naturally at home without antibiotics?
pylori Treatments
- H. pylori Prevention. ...
- Precautions. If you suspect that you may have a Helicobacter pylori infection, then it is definitely worth getting a H. ...
- Final Thoughts. Helicobacter pylori is a really important health topic since it’s so common all across the globe. ...
How to get rid of H. pylori naturally?
- Add one to two teaspoons of licorice root to a cup of water.
- Bring it to a boil in a saucepan.
- Simmer and strain. Allow it to cool.
- Drink it up.
Can you cure H pylori?
To naturally cure H. Pylori, try drinking about 1 cup (250mL) of cranberry juice a day. Cranberry juice may help prevent bacteria from attaching to your stomach. You can get similar results by adding licorice and probiotics like sauerkraut, kombucha, and yogurt to your diet.
What is the best antibiotic treatment for Helicobacter pylori?
pylori) infection
- Diagnosis. Several tests and procedures are used to determine whether you have an H. pylori infection. ...
- Treatment. H. ...
- Preparing for your appointment. See your primary care doctor if you have signs or symptoms that indicate a complication of H. ...
What is the main cause of H. pylori?
H. pylori bacteria are usually passed from person to person through direct contact with saliva, vomit or stool. H. pylori may also be spread through contaminated food or water.
What foods cause H. pylori?
Some foods may increase the risk of H. pylori infection, and certain dietary habits can trigger stomach lining erosion or otherwise worsen gastritis symptoms....Foods that increase the risk of gastritisred meats.processed meats.foods that are pickled, dried, salted, or smoked.salty foods.fatty foods.alcohol.
Is H. pylori completely curable?
Medications — No single drug cures H. pylori infection. Most treatment regimens involve taking several medications for 14 days. Most of the treatment regimens include a medication called a proton pump inhibitor.
What are symptoms of H. pylori infection?
What are the symptoms of H. pylori infection?Dull or burning pain in your stomach (more often a few hours after eating and at night). ... Unplanned weight loss.Bloating.Nausea and vomiting (bloody vomit).Indigestion (dyspepsia).Burping.Loss of appetite.Dark stools (from blood in your stool).
What will happen if H. pylori goes untreated?
If left untreated, a H. pylori infection can cause gastritis (inflammation of the lining of the stomach). Gastritis can occur suddenly (acute gastritis) or gradually (chronic gastritis).
Does sugar feed H. pylori?
A team of researchers from Sweden, Estonia, and the United States reports in Science that the H. pylori pathogen uses SabA to microscopically 'grab' onto special sugars on stomach cells. Cells bring these sugars to their surfaces to attract immune cells.
What is the fastest way to cure H. pylori?
Doctors typically prescribe a combination of two antibiotics and an acid-reducing drug to treat H. pylori. This is known as triple therapy. If you're resistant to the antibiotics, your doctors may add another medication to your treatment plan.
Can stress cause H. pylori?
Helicobacter pylori infection is a risk factor for development of peptic ulcers, and psychological stress (PS) may have a role in the pathogenesis of this condition. However, no interaction between PS and H. pylori infection (HI) has been established in the development of peptic ulcer, because colonization by H.
Can H. pylori be contagious?
This bacterium is usually not thought to be contagious (able to make others sick). You're unlikely to pass it on to someone else by just direct contact. Usually you get H. Pylori by eating contaminated food or food that is not clean.
How serious is H. pylori?
H. pylori infections can lead to peptic ulcers, but the infection or the ulcer itself can lead to more serious complications. These include: internal bleeding, which can happen when a peptic ulcer breaks through your blood vessel and is associated with iron deficiency anemia.
How long are you contagious with H. pylori?
pylori infection can be spread through kissing, oral sex, and contaminated food or drinking water. If you're taking antibiotics to treat H. pylori, you're still contagious until tests show the infection is gone.
What does it mean if you test positive for H. pylori?
A positive H. pylori stool antigen, breath test, or biopsy indicates that your signs and symptoms are likely caused by a peptic ulcer due to these bacteria. Treatment with a combination of antibiotics and other medications will be prescribed to kill the bacteria and stop the pain and the ulceration.
Is boiled egg good for H. pylori?
pylori eradication therapy. High consumption of fish and egg appears to be negatively associated with successful Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy in H. pylori‒positive patients with gastritis and/or duodenal ulcers, a recent study has found.
How do you fight H. pylori?
H. pylori infections typically require triple therapy with two antibiotics and a proton pump inhibitor. Antibiotics can cause side effects. Using natural treatments might be helpful in preventing these side effects, protecting the stomach, helping the body to better fight infection, and promoting overall good health.
Does Fasting get rid of H. pylori?
fermentum and carrageenan against the pathogen, it is undetectable at 1.5 or 2.5 h, respectively, allowing to conclude that the administration of the probiotic under fasting (harsher acid environment) provides a better anti-H. pylori effect that administering it associated with the diet.
Is probiotics good for H. pylori?
Studies published to date suggest that probiotics can have dual role in fighting against H. pylori infection. They diminish the frequency of gastrointestinal adverse events caused by antibiotic therapy and increase the eradication rate.
How to treat H pylori pain?
Eating or taking antacid drugs may relieve this pain. If you have this type of pain or a strong pain that doesn’t seem to go away, you should visit your doctor. A number of other symptoms may be associated with H. pylori infection, including: excessive burping. feeling bloated.
How many rounds of treatment for H pylori?
pylori infection, your outlook will depend on the disease, how soon it’s diagnosed, and how it’s treated. You may need to take more than one round of treatment to kill the H. pylori bacteria.
Why does H. pylori cause ulcers?
This makes the stomach cells more vulnerable to the harsh acids. Stomach acid and H. pylori together irritate the stomach lining and may cause ulcers in your stomach or duodenum , which is the first part of your small intestine.
What causes peptic ulcers?
It’s now understood that peptic ulcers are caused by this type of bacteria, rather than stress or eating foods high in acid. About 10 percent of people infected with H. pylori develop a peptic ulcer, according to the Mayo Clinic.
What is the infection of the stomach?
What is an H. pylori infection? H. pylori is a common type of bacteria that grows in the digestive tract and has a tendency to attack the stomach lining. It infects the stomachs of roughly 60 percent.
What is the H in the stomach?
The “H” in the name is short for Helicobacter. “Helico” means spiral, which indicates that the bacteria are spiral shaped. H. pylori often infect your stomach during childhood.
Why do you need a stool sample?
A stool sample may be needed to check for signs of H. pylori in your feces. Your doctor will give you a container to take home with you to catch and store a sample of your stool. Once you return the container to your healthcare provider, they will send the sample to a laboratory for analysis.
How does H pylori spread?
H. pylori bacteria may be passed from person to person through direct contact with saliva, vomit or fecal matter. H. pylori may also be spread through contaminated food or water.
What are the risk factors for H. pylori?
Risk factors for H. pylori infection are related to living conditions in your childhood, such as: Living in crowded conditions. You have a greater risk of H. pylori infection if you live in a home with many other people. Living without a reliable supply of clean water.
What is the cause of peptic ulcers?
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection occurs when H. pylori bacteria infect your stomach. This usually happens during childhood. A common cause of peptic ulcers, H. pylori infection may be present in more than half the people in the world. Most people don't realize they have H. pylori infection, because they never get sick from it.
What causes inflammation in the stomach?
Inflammation of the stomach lining. H. pylori infection can irritate your stomach, causing inflammation (gastritis).
Where does a duodenal ulcer develop?
A duodenal ulcer is a peptic ulcer that develops in the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). An esophageal ulcer occurs in the lower part of your esophagus. Complications associated with H. pylori infection include: Ulcers. H. pylori can damage the protective lining of your stomach and small intestine.
Can you live with someone with H pylori?
Living with someone who has an H. pylori infection. If someone you live with has H. pylori infection, you're more likely to also have H. pylori infection.
Can you test for H pylori?
In areas of the world where H. pylori infection and its complications are common, doctors sometimes test healthy people for H. pyl ori. Whether there is a benefit to testing for H. pylori infection when you have no signs or symptoms of infection is controversial among doctors.
Why do we do a H pylori test?
pylori infection. This test is done to investigate symptoms that may be caused by other conditions such as gastric ulcer or gastritis that may be due to H. pylori. The test may be repeated after treatment depending on what is found at the first endoscopy or if symptoms persist after H. pylori treatment.
How many antibiotics are given for H pylori?
H. pylori infections are usually treated with at least two different antibiotics at once, to help prevent the bacteria from developing a resistance to one particular antibiotic. Your doctor also will prescribe or recommend an acid-suppressing drug, to help your stomach lining heal.
What is the most common test for H pylori?
Stool tests. The most common stool test to detect H. pylori is called a stool antigen test that looks for foreign proteins (antigens) associated with H. pylori infection in your stool. Antibiotics, acid-suppressing drugs known as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol) can interfere with the accuracy of these tests.
How long do you have to stop taking PPI before a blood test?
If you are taking a PPI, your doctor will ask you to stop taking the PPI medications for one or two weeks before the test. This test isn't always recommended solely to diagnose an H. pylori infection because it's more invasive than a breath or stool test.
How long after treatment for H pylori can you get tested?
Your doctor may recommend that you undergo testing for H. pylori at least four weeks after your treatment. If the tests show the treatment was unsuccessful, you may undergo another round of treatment with a different combination of antibiotic medications.
How long after antibiotics can you test stool?
If you were previously diagnosed with and treated for H. pylori, your doctor will generally wait at least four weeks after you complete your antibiotic treatment to test your stool. If you are taking a PPI, your doctor will ask you to stop taking PPI medications for one or two weeks before the test.
What are some examples of PPIs?
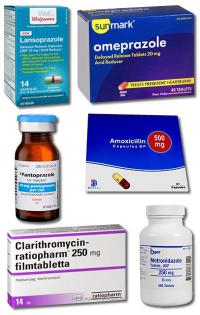
Some examples of PPIs are omeprazole (Prilosec), esomeprazole (Nexium), lansoprazole (Prevacid) and pantoprazole (Protonix).
How do you get H pylori?
You can get H. pylori from food, water, or utensils. It’s more common in countries or communities that lack clean water or good sewage systems. You can also pick up the bacteria through contact with the saliva or other body fluids of infected people. Many people get H. pylori during childhood, but adults can get it, too.
What medicine can kill H pylori?
Bismuth subsalicylate, which may also help kill H. pylori along with your antibiotics. Medicines that block the chemical histamine, which prompts your stomach to make more acid. These are cimetidine ( Tagamet ), famotidine (Fluxid, Pepcid ), nizatidine ( Axid ), or ranitidine ( Zantac ).
Why do I get ulcers on my stomach?
For decades, doctors thought people got ulcers from stress, spicy foods, smoking, or other lifestyle habits. But when scientists discovered H. pylori in 1982, they found that the germs were the cause of most stomach ulcers.
What is the name of the bacteria that live in the stomach?
Helicobacter pylori ( H. pylori) is a type of bacteria. These germs can enter your body and live in your digestive tract. After many years, they can cause sores, called ulcers, in the lining of your stomach or the upper part of your small intestine. For some people, an infection can lead to stomach cancer.
How long does it take for a sore to heal from H pylori?
If you have ulcers caused by H. pylori, you’ll need treatment to kill the germs, heal your stomach lining, and keep the sores from coming back. It usually takes 1 to 2 weeks of treatment to get better. Your doctor will probably tell you to take a few different types of drugs.
How to test for H. pylori?
Urea breath test. You’ll drink a special liquid that has a substance called urea. Then you’ll breathe into a bag, which your doctor will send to a lab for testing. If you have H. pylori, the bacteria will change the urea in your body into carbon dioxide, and lab tests will show that your breath has higher than normal levels of the gas.
What happens if you breathe in H. pylori?
pylori, the bacteria will change the urea in your body into carbon dioxide, and lab tests will show that your breath has higher than normal levels of the gas. To look more closely at your ulcers, your doctor may use:
When do most people develop H. pylori?
Most people who develop an H. pylori infection do so during childhood.
How long does H pylori last?
If it goes untreated, H. pylori can last a lifetime, and in most instances, it causes only minimal damage. Many people with the infection don’t have symptoms and never experience any health problems as a result.
What is the name of the bacteria that causes stomach infections?
Helicobacter pylori ( H. pylori) is a type of bacteria that can cause an infection in your stomach.
What is a blood draw for H pylori?
A blood draw may be done to look for H. pylori antibodies in your body. Although blood tests are easy to perform, they’re often not as accurate as other diagnostic approaches.
What are the best medications to reduce stomach acid?
They include Prilosec (omeprazole), Nexium (esomeprazole), Prevacid (lansoprazole), and Protonix (pantoprazole). Histamine (H2) blockers target a substance in your body called histamine, which can trigger stomach acid production. Pepcid (famotidine) and Zantac (ranitidine) are two commonly used H2 blockers.
How do you know if you have H pylori?
Signs and Symptoms of H. Pylori. Most people with H. pylori don’t feel sick, but when symptoms do occur, they include the following: Nausea . Stomachache or burning in the stomach. Abdominal pain that’s worse when your stomach is empty. Burping.
What can a stool sample detect?
A stool sample can help doctors detect proteins that are associated with H. pylori. You’ll need to stop taking medicines such as proton pump inhibitors, antibiotics, or bismuth subsalicylate before having this test.
What is the best treatment for H. pylori?
These are the some of the best, scientifically-backed treatments to naturally fight this bacterial infection: 1. Probiotics . Since H. pylor i is an unwanted or “bad bacteria” in the gut, it makes total sense that probiotics (the “good bacteria”) can help to naturally fight this type of infection.
What Is H. pylori?
So, exactly what is H. pylori? Helicobacter pylori ( H. pylori) is a spiral shaped bacteria. It causes chronic inflammation and infection in the stomach and duodenum (the first part of the small intestine immediately beyond the stomach). This type of bacteria is often called “ulcer bacteria” because it creates a cytotoxin (vacuolating cytotoxin A or Vac-A) that can precipitate an ulcer forming somewhere in the digestive system. ( 4)
How long has Helicobacter pylori been around?
It’s a type of bacteria known as Helicobacter pylori ( H. pylori) and it’s been around for at least two hundred thousand years. And, it’s actually not uncommon for a person to have this bacteria living inside of them for an entire lifetime and not even know it! ( 1)
What is the most successful pathogen in human history?
Do you know what’s been called “the most successful pathogen in human history?” It’s a type of bacteria known as Helicobacter pylori ( H. pylori) and it’s been around for at least two hundred thousand years. And, it’s actually not uncommon for a person to have this bacteria living inside of them for an entire lifetime and not even know it! ( 1)
How many people have helicobacter pylori?
In developing countries, the numbers are even worse, with up to 80 percent of adults and 10 percent of children likely having a H. pylori infection.
What is the name of the strain of probiotics that fights H pylori?
Lactobacillus fermentum , Lactobacillus casei and Lactobacillus brevis are three specifics strains of probiotics that have been highlighted in scientific research for their ability to fight H. pylori bacteria. ( 16, 17, 18)
How do you know if you have H pylori?
Signs & Symptoms. As I said, the majority of people with an H. pylori infection won’t even have a clue that they have it because they have zero symptoms. Other times, the infection will show itself in occasional H. pylori symptoms like: ( 8) Bloating. Belching.
What are the alternatives to eradication of H. pylori?
Alternative treatments have been proposed for the eradication of H. pylori. Some of them including novel antibiotics or classical ones in different combinations; these treatments are being used in the regular clinical practice as novel and more effective treatments.
What is H. pyloriis associated with?
H. pyloriis associated with the development of gastrointestinal disorders as chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer, and gastric adenocarcinoma (Kuipers 1997). H. pyloriis also involved in the development of other extra-gastric disorders such as mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma (MALT), idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, vitamin B12deficiency, and iron deficiency (Kuipers 1997). Eradication of H. pyloricould help in the management of these H. pylori-associated disorders.
How many people are infected by Helicobacter pylori?
Helicobacter pyloriis a common bacteria infecting about half of world’s population, with higher prevalence in developing countries, where H. pyloricould infect up to 80% of the population (Moayyedi and Hunt 2004), than in developed ones.
What is a probiotic?
Probiotics are defined as living microbial species that can include anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative mechanisms that may improve bowel microecology and general health (Lu et al. 2016). Probiotics are live microorganisms, which when administered in adequate amounts confer a health benefit on the host.
How high is the prevalence of H. pyloriresistance to clarithromycin?
In a recent systematic review, the global incidence of primary H. pyloriresistance to clarithromycin has been reported to be as high as 17.2%, showing an increase worldwide (Kuipers 1997). The prevalence of H. pyloriresistance to clarithromycin varies among different countries, such as 10.6 to 25% in North America, 16% in Japan, and 1.7 to 23.4% in Europe (Elitsur et al. 2006; Horiki et al. 2012; Koletzko et al. 2006). This disparity in resistance rates seems to be correlated to the national level of macrolide consumption and different policies for antibiotic consumption in different countries (Agudo et al. 2010a, b), for example, 49% of clarithromycin resistance has been reported in some Spanish areas, but only 1% in the Netherlands, reflecting a stricter Northern European policy for antibiotic use than in Southern European countries (Seck et al. 2013). New macrolides were marketed in Europe at the beginning of the 90’s; patients were exposed to macrolides in order to treat respiratory infections with antibiotics of this group. Additional aspects such as geographic features, virulence factors of H. pyloristrains, or some host aspects [age, place of birth] could contribute to the significant variation in the prevalence of antibiotic resistance (Van Doorn et al. 2000).
What should be taken into account before establishing a treatment plan for the patient to avoid repeated treatments?
Information about local resistant to antibiotics should be taken into account before establishing a treatment plan for the patient to avoid repeated treatments. Several expositions to antibiotic treatments could result in more side effects and a decrease in the percentage of antibiotic resistance.
What is the present article on H. pylorieradication?
The present article is a revision of H. pylorieradication treatment, focusing on emerging approaches to avoid the treatment failure, using new therapies with antimicrobials or with probiotics.

Overview
Symptoms
- Most people with H. pylori infection will never have any signs or symptoms. It's not clear why many people don't have symptoms. But some people may be born with more resistance to the harmful effects of H. pylori. When signs or symptoms do occur with H. pyloriinfection, they are typically related to gastritis or a peptic ulcer and may include: 1. An ache or burning pain in your …
Causes
- H. pylori infection occurs when H. pylori bacteria infect your stomach. H. pylori bacteria are usually passed from person to person through direct contact with saliva, vomit or stool. H. pylori may also be spread through contaminated food or water. The exact way H. pyloribacteria causes gastritis or a peptic ulcer in some people is still unknown.
Risk Factors
- People often get H. pylori infection during childhood. Risk factors for H. pyloriinfection are related to living conditions in childhood, such as: 1. Living in crowded conditions. Living in a home with many other people can increase your risk of H. pyloriinfection. 2. Living without a reliable supply of clean water. Having a reliable supply of clean, running water helps reduce the risk of H. pylori…
Complications
- Complications associated with H. pyloriinfection include: 1. Ulcers. H. pylori can damage the protective lining of the stomach and small intestine. This can allow stomach acid to create an open sore (ulcer). About 10% of people with H. pyloriwill develop an ulcer. 2. Inflammation of the stomach lining. H. pyloriinfection can affect the stomach, causing irritation and swelling (gastriti…
Prevention
- In areas of the world where H. pylori infection and its complications are common, health care providers sometimes test healthy people for H. pylori. Whether there is a benefit to testing for H. pyloriinfection when you have no signs or symptoms of infection is controversial among experts. If you're concerned about H. pylori infection or you think you may have a high risk of stomach ca…