
Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: Confusion. Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours.
What are the after effects of ECT treatments?
What are the side effects of ECT?
- Memory loss. Many people experience memory loss after having ECT. Some people find this only lasts for a short time and their memories gradually return as they recover from ECT.
- Immediate side effects. You may experience other side effects immediately after treatment. ...
- Longer-term side effects. Was this page useful? ...
What are the risks of ECT?
Risks of Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
- Memory Loss. Memory loss is the primary side effect associated with ECT treatment. ...
- Concentration and Attention Problems. Some people with have ECT treatments complain of ongoing problems with concentration and attention, much like a person with attention deficit disorder.
- General Confusion. ...
- Other Side Effects. ...
- Other Risks. ...
What are the dangers of ECT?
“ECT (electroconvulsive treatment) damages the brain and mind. In many cases, it results in huge permanent gaps in memory for important life events, educational background, and professional skills. The individual may even lose his or her identity.
How does ECT relieve depression?
Today's ECT is much more refined and gentle — and traditionally is one of the most powerful weapons against particularly deep, persistent and debilitating depressions. However, it is expensive, must be performed in a hospital and requires anesthesia, which turns away some of the people who might benefit from it, Olivas says.
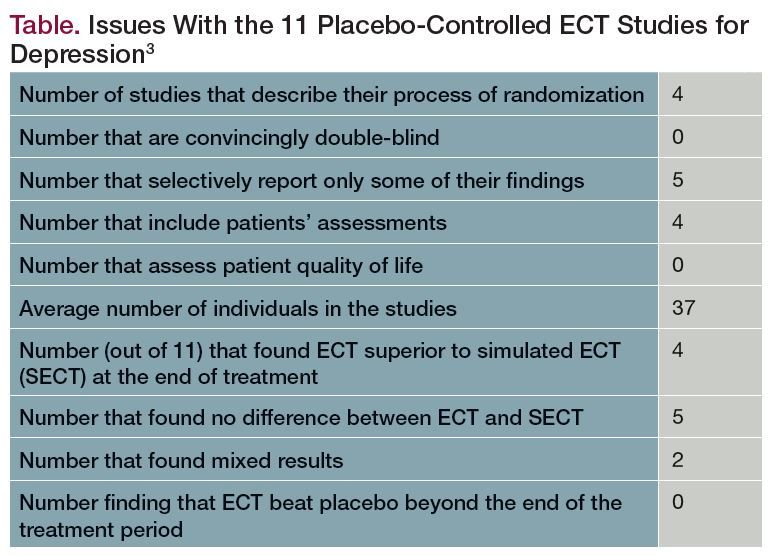
Does ECT damage the brain?
The review of literature and present evidence suggests that ECT has a demonstrable impact on the structure and function of the brain. However, there is a lack of evidence at present to suggest that ECT causes brain damage.
What are the negative side effects of ECT?
What are the risks and side-effects of ECT?loss of memory about the events immediately before and after ECT.heart rhythm disturbances.low blood pressure.headaches.nausea.sore muscles, aching jaw.confusion.
Can ECT cause death?
Conclusion: The ECT-related mortality rate was estimated at 2.1 per 100 000 treatments. In comparison, a recent analysis of the mortality of general anesthesia in relation to surgical procedures reported a mortality rate of 3.4 per 100 000. Our findings document that death caused by ECT is an extremely rare event.
What is the success rate of ECT therapy?
Typically, ECT (whether inpatient or outpatient) is given two to three times a week for a total of six to twelve sessions. Some patients may need more or fewer treatments. These sessions improve depression in 70 to 90 percent of patients, a response rate much higher than that of antidepressant drugs.
When should ECT not be used?
The following strategies should not be used routinely: augmentation of an antidepressant with a benzodiazepine for more than 2 weeks as there is a risk of dependence. augmentation of an antidepressant with buspirone*, carbamazepine*, lamotrigine* or valproate* as there is insufficient evidence for their use.
Can ECT cause brain tumors?
The most common type of tumor was a meningioma, which was present in 16 patients (40%), with arachnoid cysts coming in second place with 11 patients (27.5%). Six patients (15% of the sample) manifested AEs after ECT.
Is shock therapy still used in 2021?
July 19, 2021, at 8:14 a.m. MONDAY, July 19, 2021 (HealthDay News) -- "Shock" therapy often helps lift severe depression, but fear and stigma can deter patients from getting it. Now a large new study is confirming the treatment's safety.
How much memory do you lose with ECT?
Safety: among 7 studies that reported on memory loss, the rate of persistent or permanent memory loss after ECT ranged from 29% to 55%.
What mental illness does ECT treat?
ECT is used to treat:Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat.Treatment-resistant depression, a severe depression that doesn't improve with medications or other treatments.More items...•
Is ECT worth the risk?
Risk Assessment of Electroconvulsive Therapy in Clinical Routine: A 3-Year Analysis of Life-Threatening Events in More Than 3,000 Treatment Sessions. Background: Extensive research has reported that electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can be highly effective in approximately 80% of patients suffering from depression.
What is the failure rate of ECT?
Not only does it work better than medications (according to Weeks, medications have a success rate of 50–60 percent of patients getting better, while ECT succeeds at a rate of 70–90 percent), it works faster. Medications typically take up to eight weeks to show improvement.
Who is a good candidate for ECT?
People who have had ECT before and responded well are good candidates for ECT. Other first-line indications for the procedure include people who are catatonic or suffering from a form of depression known as psychotic depression (depression associated with delusions and hallucinations).
What is the side effect of ECT?
Memory Loss. Memory loss is the primary side effect associated with ECT treatment. Most people experience what’s called retrograde amnesia, which is a loss of memory of events leading up to and including the treatment itself. Some people’s memory loss is longer and greater with ECT. Some have trouble recalling events that occurred during ...
Why should patients with a history of heart problems not undergo ECT treatment?
Patients with a history of heart problems generally should not undergo ECT treatment, because the risk associated with receiving the electrical stimulation is greater. Last medically reviewed on May 17, 2016.
What happens if your doctor fails to do so?
If your doctor fails to do so, that may be a sign they minimize the risks associated with ECT . 1.
How long does confusion last after electroconvulsive therapy?
Many people who undergo the electroconvulsive therapy find that they experience a period of confusion after the procedure has been completed. You may forget why you’re in the hospital, or even what hospital you’re in. For most people, this confusion fades after a few hours, but can last as long as a few days after ...
How long does it take for memory to improve after ECT?
Memory loss generally improves within a few weeks after ECT treatment. As with psychiatric medications, no professional or doctor can tell you for certain what kind of memory loss you will experience, but virtually all patients experience some memory loss. Sometimes the memory loss in some patients is permanent. 2.
Who performs electroconvulsive therapy?
ECT is a medical procedure that can only be performed by a qualified physician or psychiatrist. Because general anesthesia is administered, electroconvulsive therapy carries with it similar risks that any medical procedure using anesthesia does.
Can ECT cause headaches?
4. Other Side Effects. Similar to some psychiatric medications, some people undergoing ECT may experience physical side effects such as nausea, headaches, muscle aches or spasms, and vomiting.
What is ECT used for?
ECT is used to treat: Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. Treatment-resistant depression, a severe depression that doesn't improve with medications or other treatments. Severe mania, a state of intense euphoria, agitation or hyperactivity ...
How often do you get ECT?
In the United States, ECT treatments are generally given two to three times weekly for three to four weeks — for a total of six to 12 treatments. Some doctors use a newer technique called right unilateral ultrabrief pulse electroconvulsive therapy that's done daily on weekdays.
What is ECT in medical terms?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure, done under general anesthesia, in which small electric currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure. ECT seems to cause changes in brain chemistry that can quickly reverse symptoms of certain mental health conditions.
Why is electroconvulsive therapy used?
Why it's done. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. Treatment-resistant depression, ...
How long after ECT can you drive?
However, some people may be advised not to return to work, make important decisions, or drive until one to two weeks after the last ECT in a series, or for at least 24 hours after a single treatment during maintenance therapy.
Can anesthesia cause heart problems?
These generally can be treated with medications. Medical complications. As with any type of medical procedure, especially one that involves anesthesia, there are risks of medical complications. During ECT, heart rate and blood pressure increase, and in rare cases, that can lead to serious heart problems.
Is it safe to take ECT?
Risks. Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: Confusion. Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. You may not know where you are or why you're there. Rarely, confusion may last several days or longer.
Why is ECT controversial?
Kolar writes that “ECT is one of the most controversial treatments in medicine, particularly because of the still unknown mechanism of action and uncertainty about cognitive side effects. ”.
What is ECT therapy?
Photo Credit: Pixabay. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) involves the electrical stimulation of the brain with the intent of inducing seizures.
What is the action mechanism of electroshocks?
The action mechanism of electroshocks is not unknown: intracranial electrocution causes traumatic brain injury, that is the “effectiveness” and the ravages of the treatment. Electroshocks are a simple mutilation, visible after autopsy.
Is ECT effective?
He writes, “There is no doubt that ECT is effective and life-saving for a selected population of patients. However, a good balance of sustained benefits and possible risks or serious cognitive side effects is not always reached.”.
Is electroconvulsive therapy safe?
Proponents of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) claim that it is safe and effective and that the side effects are short-lived. However, a new review, published in the journal Evidence-Based Mental Health, reports on the likelihood of permanent cognitive impairment and permanent memory loss after ECT.
Is memory improved by ECT?
For instance, the consent forms provided by the licensing body, the American Psychiatric Association (APA), state that “Most patients report that memory is actually improved by ECT.”. But researchers say that statement “is contradicted by all service-user research” as well as many findings in the research literature.
Does ECT help memory loss?
In recent years, doctors have attempted to mitigate the possibility of memory loss and cognitive impairment by modifying the ECT technique (for instance, stimulating only one side of the brain at a time). However, these findings indicate that the treatment still carries considerable risk.
What are the risks of ECT?
It is a result of various complications of ECT such as reactions to anesthesia, cardiovascular complications, pulmonary complications, or stroke. Potential mitigating factors include those proposed for each of these key risks. Dental and oral trauma including dental fractures, dislocations, lacerations, and prosthetic damage are uncommon ...
What are the complications of ECT?
Pain and discomfort are common but generally mild to moderate complications of ECT. They are typically treated with the use of as-needed analgesic medication. Physical trauma associated with ECT, they include fractures and soft tissue injury.
What are the mitigating factors for ECT?
Potential mitigating factors include appropriate pre-ECT assessment of pulmonary function, pre- ECT tests such as chest x-ray and pulmonary function test, and appropriate monitoring and clinical management before, during, and after the procedure. Skin burns are uncommon and typically mild complications of ECT.
How long after ECT do you have anterograde memory deficits?
While anterograde memory deficits may resolve in the days to weeks after ECT, autobiographical memory deficits may be more persistent.
What are the most common causes of ECT?
They most commonly include arrhythmias and/or ischemia. Cardiovascular complications are one of the most frequent causes of morbidity and mortality associated with ECT. Potential mitigating factors for cardiovascular complications include pre-ECT assessment which may include blood pressure assessment, pre-ECT electrocardiogram, ...
What are the potential mitigating factors for status epilepticus?
Potential mitigating factors include an appropriate pre-ECT neurological assessment as well as EEG monitoring during the procedure and the availability of rapid treatment of prolonged seizures should they occur.
How long does cognitive dysfunction last after ECT?
Memory dysfunction in general largely resolves in the days to weeks after the completion of a course of ECT.
What is ECT treatment?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is an effective treatment commonly used for depression and other major psychiatric disorders. We discuss potential adverse effects (AEs) associated with ECT and strategies for their prevention and management. Common acute AEs include headache, nausea, ...
What is ECT therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is an effective treatment commonly used for depression and other major psychiatric disorders. We discuss potential adverse effects (AEs) associated with ECT and strategies for their prevention and management. Common acute AEs include headache, nausea, myalgia, and confusion; these are self-limiting ...

Overview
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure, done under general anesthesia, in which small electric currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure. ECT seems to cause changes in brain chemistry that can quickly reverse symptoms of certain mental health conditions. ECT often works when other treatments are unsuccessful and when the full course o…
Why It's Done
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: 1. Severe depression,particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. 2. Treatment-resistant depression,a severe depression that doesn't improve with medications o…
Risks
- Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: 1. Confusion.Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. You may not know where you are or why you're there. Rarely, confusion may last several days or longer. Confusion is generally more noticeable in older adults....
How You Prepare
- Before having your first ECT treatment, you'll need a full evaluation, which usually includes: 1. Medical history 2. Complete physical exam 3. Psychiatric assessment 4. Basic blood tests 5. Electrocardiogram (ECG) to check your heart health 6. Discussion of the risks of anesthesia These exams help make sure that ECT is safe for you.
What You Can Expect
- The ECT procedure takes about five to 10 minutes, with added time for preparation and recovery. ECT can be done while you're hospitalized or as an outpatient procedure.
Results
- Many people begin to notice an improvement in their symptoms after about six treatments with electroconvulsive therapy. Full improvement may take longer, though ECT may not work for everyone. Response to antidepressant medications, in comparison, can take several weeks or more. No one knows for certain how ECT helps treat severe depression and other mental illness…