Explore
Symptoms
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Chronic bronchitis
- Frequent chest colds
- Less tolerance for exercise than usual
- Year-round allergies
- Bronchiectasis (inflammation of the lungs)
What are the symptoms of alpha 1?
Signs and symptoms of alpha-gal syndrome may include:
- Hives, itching, or itchy, scaly skin (eczema)
- Swelling of the lips, face, tongue and throat, or other body parts
- Wheezing or shortness of breath
- A runny nose
- Stomach pain, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting
- Sneezing
- Headaches
- A severe, potentially deadly allergic reaction that restricts breathing (anaphylaxis)
What are the symptoms of alpha - 1 disease?
a charity that supports families suffering from Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency. Alpha-1 is a genetic condition that affects the lungs and liver but despite one in nine Australians having at least one affected gene, awareness is minimal. It's something Mark ...
What is alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency?
One of the functions of TIMP-3 is to inhibit a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17 (ADAM17). The only TIMP that inhibits ADAM17 is TIMP-3. ADAM17 causes the production and release of tissue necrosis factor alpha (TNFα). A patient was treated with ...
What is one alpha medication?

What can be done for alpha-1 deficiency?
There is no cure for AAT deficiency, but there are treatments to slow the lung damage it causes. You may need a lifelong treatment called augmentation therapy. This treatment raises the levels of the AAT protein in your lungs, using ATT protein taken from the blood of donors. This helps slow down lung damage.
Can you treat alpha-1 antitrypsin?
Although there's no cure for AAT deficiency, you can raise the amount of AAT protein in your blood, which protects you against more lung damage. Doctors call this augmentation therapy. You may also have this treatment if you get emphysema. Augmentation therapy is also called replacement therapy.
How long can you live with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency?
Many people with Alpha-1, especially those who do not smoke, do not develop serious complications. They have a normal life expectancy. Other people may develop more serious conditions as a result of the disorder.
How do you get tested for alpha-1?
The best way to diagnose alpha-1 is a test that looks at your DNA (genetic information.) Your doctor will take a blood sample. Lab workers will check your sample for the faulty genes that cause alpha-1. Another blood test measures how much of the alpha-1 protein is in your body.
Does liver transplant cure alpha-1?
Severe infant liver failure in Alpha-1 is always treated with liver transplantation, which cures the disease by replacing the failing liver with a normal donor liver that has normal Alpha-1 genes. A successful liver transplant leads to normal blood and lung levels of normal alpha-1 antitrypsin protein.
Who treats alpha1?
This page can help. Clinical Resource Centers (CRCs) are located throughout North America and specialize in patient care, education and research for those with Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1). Some centers treat lung disease and others liver disease.
What is the life expectancy of alpha-1?
How does Alpha-1 lung disease affect my life expectancy? People who continue to smoke and have Alpha-1 lung disease, have an average life expectance of about 60 years of age.
What are the signs of alpha-1?
Shortness of breath. Excessive cough with phlegm/sputum production. Wheezing. Decrease in exercise capacity and a persistent low energy state or tiredness.
Is alpha-1 an autoimmune disease?
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease affecting many young people worldwide.
Is alpha-1 the same as COPD?
Alpha-1 is often first diagnosed as asthma or smoking-related Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). COPD includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Alpha-1 is the most common genetic risk factor for COPD. About 3 percent of all people diagnosed with COPD may have undetected Alpha-1.
Who should get tested for alpha-1?
If you have one or more of the following risk factors, you should be tested for Alpha-1:A family history of Alpha-1. ... One of these conditions: COPD, emphysema, chronic bronchitis or bronchiectasis.Unexplained liver disease.A family history of lung or liver disease.The skin disease panniculitis.
Does alpha-1 cause tiredness?
Numerous studies confirm that some AATD-affected individuals have low quality of life, more comorbidities, and a higher mortality rate than the usual population. Dyspnea and fatigue are the most common clinical manifestations.
What is the treatment for alpha 1?
Treatment. The specific therapy for the treatment of Alpha-1-related lung disease is augmentation therapy – also called replacement therapy. Augmentation therapy is the use of alpha-1 antitrypsin protein (AAT) from the blood plasma of healthy human donors to augment (increase) the alpha-1 levels circulating in the blood and lungs ...
What is the Alpha 1 booklet?
This information is based on AlphaNet’s booklet, Augmentation Therapy, The Specific Therapy for Alpha-1 Lung Disease. The booklet is part of the Skinny Little Reference Guide series, extracted from AlphaNet’s Big Fat Reference Guide to Alpha-1. These resources are available on AlphaNet’s website, www.alphanet.org. The Alpha-1 Foundation is grateful to AlphaNet for its generous help.
What are the FDA approved products for augmentation therapy?
The five approved products are Prolastin-C® and Prolastin-C Liquid® from Grifols, Aralast NP™ from Take da, Zemaira® from CSL Behring and Glassia® from Kamada Ltd. A product named Trypsone® from Grifols is available in Spain. Prolastin has been marketed since 1988 and has an excellent safety record. Aralast NP and Zemaira were introduced to the marketplace in 2003 and Glassia was introduced in 2010. Each was approved by demonstrating that they were comparable to Prolastin in their safety and in augmenting blood and lung alpha-1 levels.
Why do Alphas need to be tested for IgA?
Alphas who are about to start augmentation therapy should be tested for IgA deficiency, because giving repeated infusions of a plasma-derived product can lead to severe allergic reactions in people who are IgA-deficient. This is due to the small amount of IgA protein contained in each vial of augmentation therapy.
Can you give augmentation therapy to someone with emphysema?
Augmentation therapy should be given to individuals with documented emphysema and severe Alpha-1 (defined as individuals with two abnormal alpha-1 genes). There has been some controversy, however, about giving augmentation therapy to anyone whose lung disease is very mild or very severe. In some research studies conducted since the introduction ...
Can Alphas have allergies?
Some Alphas have symptoms that seem like mild allergic reactions: rash or hives, itching, tightness in the chest, dyspnea, and/or wheezing. Many of them can continue receiving augmentation therapy if they take an antihistamine, such as Benadryl, before their infusions. Rarely, side effects are severe enough to cause an Alpha to stop augmentation therapy entirely.
What is the Alpha 1 Foundation?
The Alpha-1 Foundation has information about a nationwide network of affiliated support groups for alpha-1 patients and families.
What to do if you have no symptoms?
If you have no symptoms, you may be advised to return for regular follow-ups. You should restrict alcohol consumption, get regular exercise and control your weight. You should get a flu shot every year and ask your doctor about getting a pneumonia vaccine.
What is the treatment for COPD?
Your treatment may include prescribed inhaled medications to control symptoms of COPD , referral to a pulmonary rehabilitation program, oxygen therapy, and antibiotics and inhaled corticosteroids to control symptoms of flare-ups, infections or exacerbations if needed.
How to help people with lung disease?
Communicate regularly with your doctors about changes in your breathing and general health. The Lung Association recommends patients and caregivers join our Living with Lung Disease Support Community or attend Better Breathers Club meetings to connect with others facing this disease. You can also call the Lung Association's Lung Helpline at 1-800-LUNGUSA to talk to a trained respiratory professional who can help answer your questions and connect you with additional support
Can AAT affect long term survival?
AAT deficiency may or may not affect your long-term survival. If you are diagnosed with AAT deficiency, your doctor may or may not suggest treatment based on the results of other testing and the severity of your symptoms. Patients who are diagnosed with AAT deficiency before symptoms occur usually have better outcomes than those who are diagnosed ...
How does Alpha 1 help?
Other people may develop more serious conditions as a result of the disorder. Getting the right treatment for diseases caused by Alpha-1 can help you live a longer, healthier life. Treatment can also ease symptoms to improve your quality of life.
Why do doctors diagnose alpha 1?
Doctors often first diagnose people with Alpha-1 as having asthma, because the disorders share many symptoms, especially shortness of breath. If you don’t respond to asthma treatment, your doctor may order several tests to diagnose Alpha-1.
What is the Alpha 1 gene?
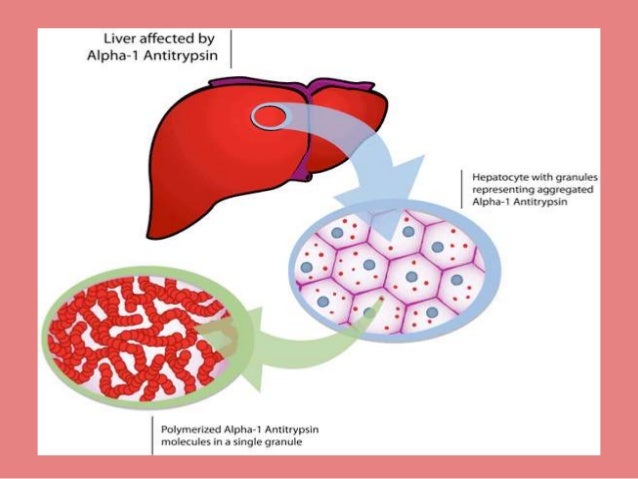
Alpha-1 is a rare genetic (inherited) disorder in which people have low levels of AAT in their bloodstream. This disorder can increase your risk of developing lung and liver diseases, including emphysema (damaged air sacs in the lungs) and cirrhosis (liver scarring). The low level of AAT means that lungs are not protected, and the liver is injured by the build-up of the protein there.
How old do you have to be to know if you have Alpha 1?
You might never know you have the disorder. People who have symptoms usually notice them between ages 20 and 50. People with lung diseases caused by Alpha-1 have symptoms like those caused by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Shortness of breath especially with exertion, is most common.
What is the purpose of Alpha-1 antitrypsin?
This protein protects your lungs and other organs from the harmful effects of irritants and infections.
What causes Alpha-1?
Mutations (changes) in the gene that produces the AAT protein cause Alpha-1. In people with the most common abnormal type of Alpha-1 (called ZZ type), AAT proteins are misshapen.
What are the symptoms of Alpha 1?
Signs and symptoms of liver diseases caused by Alpha-1 may include: Easy bruising. Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes). Swelling in the belly or legs from fluid. Vomiting blood.
How often do you get AAT replacement therapy?
You get a new supply of AAT protein that comes from the blood of healthy human donors. You get the treatment once a week. The replacement alpha-1 gets into your body through an IV.
How to diagnose AAT deficiency?
You need to get blood tests to confirm your diagnosis. These tests check to see if you have the broken genes that cause AAT deficiency. They also look to see how much of the protein you have in your bloodstream.
What causes AAT to be low?
The broken genes you get from your parents cause you to have a low level of AAT protein in your blood. It can build up in the liver instead of going into your bloodstream. That buildup in your liver causes liver disease. The shortage of AAT protein in your bloodstream leads to lung disease. Tests for AAT Deficiency.
Why does AAT cause hardening?
It causes hardening of the skin along with painful lumps or patches. Causes of AAT Deficiency. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency runs in families. If you have it, you got it from faulty genes that both your parents passed down to you. Some people get the genes but don't have any symptoms.
Why do we need AAT?
You need AAT to protect your lungs. Without it, infections and other irritants, like tobacco smoke, break down parts of your lung even faster. If you have AAT deficiency, you might not have breathing symptoms until you're in your 20s or 30s.
Can you raise AAT protein?
Although there’s no cure for AAT deficiency, you can raise the amount of AAT protein in your blood, which protects you against more lung damage. Doctors call this augmentation therapy. You may also have this treatment if you get emphysema. Augmentation therapy is also called replacement therapy.
Is AAT deficiency severe?
AAT deficiency is different for everyone. Some people have severe problems. Others may have few or no symptoms.
What is Alpha 1 Antitrypsin?
About Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is an inherited condition that causes low levels of, or no, alpha-1 antitrypsin in the blood.
How many copies of Alpha-1 antitrypsin are there?
Most people have two normal copies of the alpha-1 antitrypsin gene. Individuals with AATD have one normal copy and one damaged copy, or they have two damaged copies. Most individuals who have one normal gene can produce enough alpha-1 antitripsin to live healthy lives, especially if they do not smoke.
What are the symptoms of AATD?
In affected adults, the first symptoms of AATD are shortness of breath with mild activity, reduced ability to exercise and wheezing. These symptoms usually appear between the ages of 20 and 40. Other signs and symptoms can include repeated respiratory infections, fatigue, rapid heartbeat upon standing, vision problems and unintentional weight loss.
What is the purpose of AAT?
AAT protects the lungs so they can work normally . Without enough AAT, the lungs can be damaged, and this damage may make breathing difficult. Everyone has two copies of the gene for AAT and receives one copy of the gene from each parent. Most people have two normal copies of the alpha-1 antitrypsin gene.
Is there a cure for alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency?
Treatment of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) is based on a person's symptoms. There is currently no cure. The major goal of AATD management is preventing or slowing the progression of lung disease. Treatments include bronchodilators and prompt treatment with antibiotics for upper respiratory tract infections.
Which gene is the most common allele of the Alpha-1 gene?
The M gene is the most common allele of the alpha-1 gene. It produces normal levels of the alpha-1 antitrypsin protein.
Is AATD inherited?
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) is inherited in families in an autosomal codominant pattern. Codominant inheritance means that two different variants of the gene (alleles) may be expressed, and both versions contribute to the genetic trait.
Who should be tested for Alpha 1?
The Clinical Practice Guidelines recommend that people with any of the following conditions/criteria should be tested for Alpha-1: Parents, siblings, children and extended family members of people who are identified with an abnormal alpha-1 gene should be provided genetic counseling and offered testing for Alpha-1.
What is Alpha 1?
The Medical and Scientific Advisory Committee of the Alpha-1 Foundation has released clinical recommendations designed to guide doctors on how to properly diagnose and treat Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) in adults.
What is the most widely available and least expensive specific test for Alpha-1?
The most widely available and least expensive specific test for Alpha-1 is the AAT serum level.
What is Alpha 1 Foundation?
The Alpha-1 Foundation offers a confidential opportunity to be tested for Alpha-1 through the Alpha-1 Coded Testing (ACT) Study. This research study is through the Alpha-1 Foundation and examines people’s thoughts and feelings about the risks and benefits associated with learning genetic information. Testing through the ACT Study is free and ...
Why is Alpha 1 protein level testing not recommended?
For family testing, alpha-1-protein-level testing alone is not recommended because it does not fully characterize the risk of disease from Alpha-1
What is the clinical practice guidelines for COPD?
The Clinical Practice Guidelines, based on the latest evidence and six years of work, recommend best practices on testing for Alpha-1, Alpha-1 lung and liver disease, and when augmentation therapy should be prescribed, among other recommendations. The guidelines, published in the Journal of the COPD Foundation in July 2016, ...
How to contact Alpha 1 Genetic Counseling?
For information on the Alpha-1 Foundation Genetic Counseling Program, call (877) 228-7321 ext. 326 or click here.
What is Alpha 1 testing?
In response to concerns surrounding testing, privacy and the benefit of an early diagnosis, the Alpha-1 Foundation developed a free and confidential opportunity for testing. This is a research study called the Alpha-1 Coded Testing (ACT) Study.
How many genes are in Alpha 1?
For each trait a person inherits, there are usually two genes; one gene comes from each parent. People with Alpha-1 have received two abnormal alpha-1 antitrypsin genes. One of these abnormal genes came from their mother and one from their father. . "What is Alpha-1?".
Why is AAT low in the blood?
The low level of AAT in the blood occurs because the AAT is abnormal and cannot be released from the liver at the normal rate. This leads to a build-up of abnormal AAT in the liver that can cause liver disease and a decrease of AAT in the blood that can lead to lung disease. Symptoms related to the lung:
What is the function of AAT?
The main function of AAT is to protect the lungs from inflammation caused by infection and inhaled irritants such as tobacco smoke. The low level of AAT in the blood occurs because the AAT is abnormal and cannot be released from the liver at the normal rate.
Can you get alpha 1 from a blood test?
Alpha-1 can lead to lung destruction and is often first diagnosed as asthma or smoking-related Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Alpha-1 cannot be diagnosed by symptoms or by a medical examination alone; you need to get a simple, reliable blood test to know for sure.
Is Alpha 1 healthy?
People with Alpha-1 may remain healthy throughout their lives. Early diagnosis and avoiding risk factors, such as cigarette smoking, can help prevent Alpha-1 from causing disease.
Can Alpha 1 cause liver damage?
Alpha-1 can also lead to liver disease. The most serious liver diseases are cirrhosis and liver cancer.
How to test for Alpha 1?
Testing for Alpha-1 is simple, quick and highly accurate. Testing can be conducted on a blood sample (blood draw or finger stick test). Consult with your health insurance provider to determine if your plan covers the cost of this test.
Why is alpha 1 not recommended?
For family testing, alpha-1-protein-level testing alone is not recommended because it does not fully characterize the risk of disease from Alpha-1. For family testing or diagnostic testing of people who have symptoms, genotyping is recommended for at least the S and Z alleles.
What is Alpha 1 Foundation?
The Alpha-1 Foundation encourages testing for Alpha-1 among those at high risk for this genetic disorder. Early diagnosis can help an Alpha consider different lifestyles, professions or other personal decisions that could maintain or improve their health.
Why is Alpha 1 delayed?
Many people at risk for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency delay being tested due to concerns about privacy of test results. The Alpha-1 Foundation offers a confidential opportunity to be tested for Alpha-1 through the Alpha-1 Coded Testing (ACT) Study.
Can you get Alpha 1 tested by a doctor?
Free Confidential Testing. Alpha-1 cannot be diagnosed by symptoms or by a medical examination alone; you need to get a blood test to know for sure.
What is the test for Alpha-1?
There are three types of simple laboratory tests for Alpha-1. First, you can test for the amount of AAT protein in the blood. This is often called a serum level.
What is the normal AAT level for Alpha 1?
In general, individuals with severe Alpha-1 deficiencies tend to have an AAT level of less than 50 mg/dL. The national testing laboratories use the μM system, and the low end of the normal range is approximately 28 μM in this system. Individuals with a level less than 11 μM are considered to have severe deficiency of AAT.
How high is AAT in blood?
The normal range of AAT in the blood can be as high as 400 mg/dL or 4 grams in each quart of blood. The level can be measured using one of a variety of techniques but, most commonly, antibodies against AAT are used to quantify the amount of AAT in the serum. The results are expressed either in mg/dL (milligrams per 100 cc of blood) or in μM (micromoles).