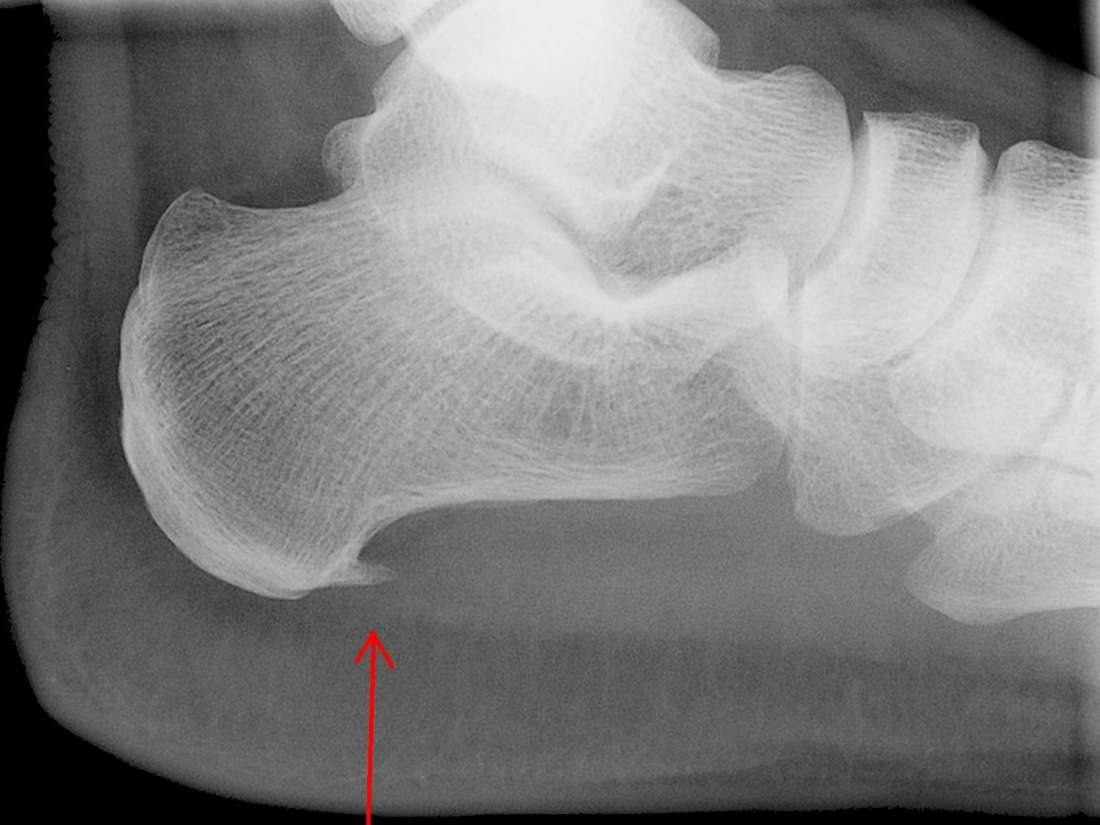
What factors affect functional hemostasis in trauma patients?
Results: A notable impairment of hemostasis arises at a pH < or = 7.1. Similar effects are caused by a BE of -12.5 or less. Similar effects are caused by a BE of -12.5 or less. Thus, in case of severe bleeding, buffering toward physiologic pH values is recommended, especially with massive transfusions of older RBCCs displaying exhausted red ...
What is the difference between reliability and reliability in clinical assessment?
May 25, 2020 · To test the impact and influence of resiliency, we collected data from 25,248 peers that participated in a resiliency assessment. We matched up one peer with another peer in the same workgroup.
What is resilience and does it work?
Background: There is heterogeneity in conceptualizations of resiliency, and there is, to date, no established theoretically driven resiliency assessment measure that aligns with a targeted resiliency intervention. We operationalize resiliency as one's ability to maintain adaptive functioning in response to the ongoing, chronic stress of daily living, and we use a novel …
How can being resilient help you and your peers?
Nov 01, 2012 · Achieving hemostasis (ie, bleeding control) is a critical focus of clinicians working in the surgical setting because uncontrolled surgical bleeding is associated with increased mortality rates and higher costs.1, 2 Failure to achieve hemostasis can unnecessarily prolong the surgical procedure, impair wound healing, increase infection risk, and result in unanticipated …

Why is resilient important?
Resilience is important because it gives people the strength needed to process and overcome hardship. Those lacking resilience get easily overwhelmed, and may turn to unhealthy coping mechanisms. Resilient people tap into their strengths and support systems to overcome challenges and work through problems.Dec 11, 2020
What does resilience mean and how can it help people with trauma?
Resilience is the ability to adapt to difficult situations. When stress, adversity or trauma strikes, you still experience anger, grief and pain, but you're able to keep functioning — both physically and psychologically.
What are the three components of the resilience process?
Resilience is defined as the ability of a system to maintain key functions and processes in the face of stresses or pressures by resisting to and then recovering or adapting to change. ... Resilience includes three components: 1) resistance; 2) recovery; and 3) transformation.More items...
What is resilience what factors contribute to resilience?
The Main Factors Contributing to Resilience Some of those include having a good support system, maintaining positive relationships, having a good self-image and having a positive attitude. Other factors that contribute to resiliency include: Having the capacity to make realistic plans.
Why is resilience important for trauma?
“In the context of exposure to significant adversity, resilience is both the capacity of individuals to navigate their way to the psychological, social, cultural, and physical resources that sustain their well-being, and their capacity individually and collectively to negotiate for these resources to be provided in ...
How important is it to be prepared and be resilient in disaster?
Individual health and resilience is important for community resilience because healthy, socially connected, prepared people make for stronger communities that are better able to withstand, manage, and recover from disasters.
What are the two most important components to consider when assessing your resilience level?
There are two components of resilience: the ability to absorb or resist the impacts of stresses, such as mass bleaching or storms, and the ability to recover quickly from them.
How do you maintain resilience?
10 Ways to Build Your ResilienceLearn to relax. ... Practice thought awareness. ... Edit your outlook. ... Learn from your mistakes and failures. ... Choose your response. ... Maintain perspective. ... Set yourself some goals. ... Build your self-confidence.More items...
How can you support an individual towards developing positive coping strategies and building resilience?
Different things will work for different people, but these are some ideas you could try:Be kind to yourself. Learning to be kinder to yourself can help with how you feel in different situations. ... Try to find time to relax. ... Develop your interests and hobbies. ... Spend time in nature. ... Look after your physical health.
What can impact resilience?
I discussed the five factors that are important to develop resilience: connection to others, communication, confidence, competence and commitment, and control.
Why is resilience important in healthcare?
Being resilient will help staff to manage stressful situations, protect them from mental ill-health and improve their health and wellbeing. At work, this ensures that they continue to do their job well and deliver high-quality care and support.
How do you demonstrate resilience in an interview?
Interview questions that are designed to assess your resilience include:How do you deal with setbacks?How do you cope with pressure?What has been your biggest failure to date and how did you deal with it?Tell me about a time when you had to deal with a major crisis.More items...
Why is hemostasis important for perioperative nurses?
Achieving hemostasis is a critical focus of clinicians working in the surgical setting, given that uncontrolled surgical bleeding is associated with increased mortality rates and higher costs of care . As principal members of the surgical team, perioperative nurses are in an optimal position to plan and direct care during a bleeding event and throughout a patient's surgical stay. This supplement includes an assessment of the clinical and economic effects of surgical bleeding, a thorough review of available therapies, and a detailed comparison of these products to demonstrate which agents are best suited for a given clinical situation. By understanding the basic science of coagulation and hemostasis and current advances in topical hemostatic agents, including their safety, efficacy, and judicious use, perioperative nurses will be empowered to better assist the surgeon in optimizing patient outcomes.
What is flowable hemostatic agent?
Another important tool for perioperative nurses is flowable hemostatic agents (eg, Surgiflo ®, Floseal ® ). These products include a mechanical gelatin agent plus thrombin that work together to obstruct the flow of blood and convert fibrinogen to fibrin. 14, 15 Although the mechanism of action is similar, Surgiflo is a porcine gelatin available for use with bovine, human pooled plasma, or recombinant thrombin, whereas Floseal includes absorbable bovine gelatin particles combined with pooled human thrombin. 14, 15 Both agents are most effective in cases of localized bleeding and can be applied via a syringe in a downward manner, which allows it to#N#■#N#be administered deep into the wound;#N#■#N#adjust to wound topography;#N#■#N#provide a mechanical barrier; and ultimately,#N#■#N#activate blood clotting. 14, 15#N#The advantage of this is that the surgeon not only can access the top layers of a wound, but also can spread the product to reach irregular surfaces. 15 After approximately three minutes of preparation time, the product takes on a thick consistency, allowing it to stay in place at the bleeding site. The surgeon also may apply pressure directly onto the flowable product using a saline-moistened gauze pad to help keep it in contact with the bleeding surface.15
What is a fibrin sealant?
Fibrin sealants—which have separate US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approvals as a topical hemostat, sealant, and adhesive—provide higher concentrations of fibrinogen and thrombin than those that occur naturally in blood, thereby allowing for clot formation . 15 Fibrin sealants—namely Tisseel™, Evicel ®, and Vitagel™—are effective for both local and diffuse bleeding and can be applied using either a syringe for local bleeding or spray with a gas-driven device for diffuse-bleeding areas. 14, 15 These agents are more effective when applied to a relatively dry surface area. They may also be used to treat active bleeding with an absorbable gelatin sponge, however, to allow the surgeon to put pressure on the bleeding site. 15
Is bioglue a sealant?
Albumin and glutaraldehyde ( BioGlue), discussed earlier as a sealant, is also FDA approved to be used as an adhesive during a ortic dissection for attachment of the intimal and adventitial layers of the aorta.41 The characteristics of this product (eg, ease of preparation and use, safety concerns) are the same when this product is used as a sealant or as an adhesive. 15
What are sealants used for?
14, 15 These agents, often used in conjunction with topical hemostats, enhance the surgical armamentarium and offer an additional strategy for reducing bleeding and transfusions. Similar to hemostats, sealants also differ with regard to safety, efficacy, usability, and cost ( Table 3 ), 15 all of which perioperative nurses should familiarize themselves with to best assist the surgical team.
Is NACCME accredited?
This activity has been planned and implemented by North American Center for Continuing Medical Education, LLC (NACCME) and Horizon CME for the advancement of patient care. NACCME is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME), the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education (ACPE), and the American Nurses Credentialing Center (ANCC) to provide continuing education for the health care team.
What is bioglue used for?
15 BioGlue can be used as either a sealant or an adhesive to achieve hemostasis. When used as a sealant, albumin and glutaraldehyde provides a strong tissue bond to seal large blood vessel anastomoses. 15 Preparation is relatively quick and use is moderately easy because this agent is available prepackaged in applicator syringes. It should be applied sparingly, however, to avoid unintended tissue contact. 15 Clinical trial data suggest that BioGlue may be a viable alternative to standard vascular repair, with a large multicenter study reporting significantly higher rates of hemostasis with BioGlue compared with standard care (81% versus 57%, respectively; P < .003). 41 Major adverse events with BioGlue include the potential for tissue necrosis, nerve injury, adhesive embolism, limitation of aortic growth, and pseudoaneurysm, as well as the risk of toxicity from glutaraldehyde. 14, 15, 41
How does a mental health professional assess a client?
For a mental health professional to be able to effectively help treat a client and know that the treatment selected worked (or is working), he/she first must engage in the clinical assessment of the client, or collecting information and drawing conclusions through the use of observation, psychological tests, neurological tests, and interviews to determine the person’s problem and the presenting symptoms. This collection of information involves learning about the client’s skills, abilities, personality characteristics, cognitive and emotional functioning, the social context in terms of environmental stressors that are faced, and cultural factors particular to them such as their language or ethnicity. Clinical assessment is not just conducted at the beginning of the process of seeking help but throughout the process. Why is that?
What are the three critical concepts of assessment?
The assessment process involves three critical concepts – reliability, validity, and standardization . Actually, these three are important to science in general. First, we want the assessment to be reliable or consistent. Outside of clinical assessment, when our car has an issue and we take it to the mechanic, we want to make sure that what one mechanic says is wrong with our car is the same as what another says, or even two others. If not, the measurement tools they use to assess cars are flawed. The same is true of a patient who is suffering from a mental disorder. If one mental health professional says the person suffers from major depressive disorder and another says the issue is borderline personality disorder, then there is an issue with the assessment tool being used (in this case, the DSM and more on that in a bit). Ensuring that two different raters are consistent in their assessment of patients is called interrater reliability. Another type of reliability occurs when a person takes a test one day, and then the same test on another day. We would expect the person’s answers to be consistent, which is called test-retest reliability. For example, let’s say the person takes the MMPI on Tuesday and then the same test on Friday. Unless something miraculous or tragic happened over the two days in between tests, the scores on the MMPI should be nearly identical to one another. What does identical mean? The score at test and the score at retest are correlated with one another. If the test is reliable, the correlation should be very high (remember, a correlation goes from -1.00 to +1.00, and positive means as one score goes up, so does the other, so the correlation for the two tests should be high on the positive side).
What is module 3 of the DSM-5?
Module 3 covers the issues of clinical assessment, diagnosis, and treatment. We will define assessment and then describe key issues such as reliability, validity, standardization, and specific methods that are used. In terms of clinical diagnosis, we will discuss the two main classification systems used around the world – the DSM-5 and ICD-10. Finally, we discuss the reasons why people may seek treatment and what to expect when doing so.
When was the DSM 5 published?
3.2.2.1. A brief history of the DSM. The DSM-5 was published in 2013 and took the place of the DSM IV-TR (TR means Text Revision; published in 2000), but the history of the DSM goes back to 1944 when the American Psychiatric Association published a predecessor of the DSM which was a “statistical classification of institutionalized mental patients” and “…was designed to improve communication about the types of patients cared for in these hospitals” (APA, 2013, p. 6). The DSM evolved through four major editions after World War II into a diagnostic classification system to be used psychiatrists and physicians, but also other mental health professionals. The Herculean task of revising the DSM began in 1999 when the APA embarked upon an evaluation of the strengths and weaknesses of the DSM in coordination with the World Health Organization (WHO) Division of Mental Health, the World Psychiatric Association, and the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH). This collaboration resulted in the publication of a monograph in 2002 called A Research Agenda for DSM-V. From 2003 to 2008, the APA, WHO, NIMH, the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), and the National Institute on Alcoholism and Alcohol Abuse (NIAAA) convened 13 international DSM-5 research planning conferences “to review the world literature in specific diagnostic areas to prepare for revisions in developing both DSM-5 and the International Classification of Disease, 11th Revision (ICD-11)” (APA, 2013).
When was the DSM revised?
The Herculean task of revising the DSM began in 1999 when the APA embarked upon an evaluation of the strengths and weaknesses of the DSM in coordination with the World Health Organization (WHO) Division of Mental Health, the World Psychiatric Association, and the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH).
What are the limitations of an interview?
The limitation of the interview is that it lacks reliability, especially in the case of the unstructured interview. 3.1.3.3. Psychological tests and inventories. Psychological tests assess the client’s personality, social skills, cognitive abilities, emotions, behavioral responses, or interests.
What is the purpose of a CT scan?
Finally, computed tomography or the CT scan involves taking X-rays of the brain at different angles and is used to diagnose brain damage caused by head injuries or brain tumors. 3.1.3.5. Physical examination.
Abstract
Hemostasis assessment in a preoperative setting is used to avoid bleeding complications. The most common assays for detecting coagulation factor deficiencies are prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), and thrombin time (TT).
Keywords
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
About this chapter
Sucker C., Zotz R.B. (2015) Hemostasis Assessment and Evaluation. In: Marcucci C., Schoettker P. (eds) Perioperative Hemostasis. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-55004-1_5
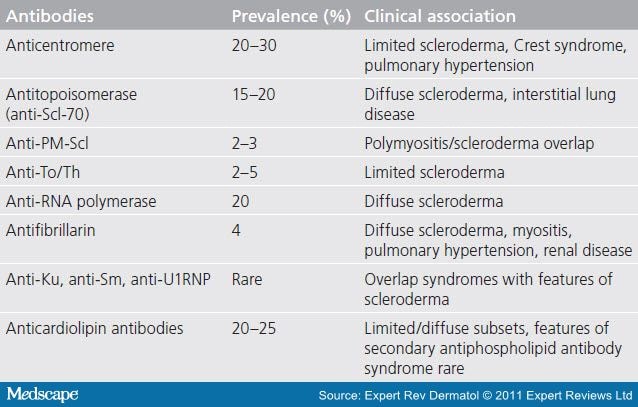
Detection
Physical/Cyber Protection and Resilience
- Water systems are considered one of the nation’s critical infrastructures. It is assumed that no physical or software protection can prevent all attacks. So this critical infrastructure requires increased protection and the ability of utilities to detect, respond to, and recover from physical and cyberattacks. Water system operators can lose their ...
Related Links
- EPA's Water Security Testbed
- EPA’s Water Security Test Bed (WSTB) video EXIT
- Public Health Security and Bioterrorism Preparedness and Response Act (Bioterrorism Act of 2002)Exit
- WaterISACExit
Related Products
- Sensor Studies
- Cyber Security
- Blast Vulnerability Assessment Tool – Water Information Sharing and Analysis Center (WaterISAC) Portal EXIT
- Threat Ensemble Vulnerability Assessment (TEVA) Sensor Placement Optimization (TEVA-S…
- Sensor Studies
- Cyber Security
- Blast Vulnerability Assessment Tool – Water Information Sharing and Analysis Center (WaterISAC) Portal EXIT
- Threat Ensemble Vulnerability Assessment (TEVA) Sensor Placement Optimization (TEVA-SPOT)