What are some medical uses of isotopes?
- Chromium-51 which is Used in research in red blood cell survival studies.
- Cobalt-57 Used as a tracer to diagnose pernicious anemia.
- Cobalt-60 Used to sterilize surgical instruments.
- Copper-67 When injected with monoclonal antibodies into a cancer patient, helps the antibodies bind to and destroy the tumor.
- Gallium-67 Used in medical diagnosis.
What are some applications of radioactive isotopes?
Questions
- Define tracer and give an example of how tracers work.
- Name two isotopes that have been used as tracers.
- Explain how radioactive dating works.
- Name two isotopes that have been used in radioactive dating.
- The current disintegration rate for carbon-14 is 14.0 Bq. ...
- A small asteroid crashes to Earth. ...
- What is a positive aspect of the irradiation of food?
What are the harmful effects of radioactive isotopes?
You should not be afraid of radiation too much if you know a few things:
- Alpha particles - heavy but do not go over 20 cm. So if you don’t have an isotope close to you - you are totally safe.
- Beta radiation - electrons. Blocked by any objects. Held by cloth and skin a lot. They go through, but lose a lot of energy.
- Gamma is rare and mostly man-made.
How can isotopes be used in medicine?
- Disease prevention and health promotion research (cancer, heart disease, obesity, osteoporosis, etc.)
- Energy metabolism in humans and animals
- Tracer techniques to determine nutrition requirements

How can radioactive substances be used for medical treatment?
Nuclear medicine procedures help detect and treat diseases by using a small amount of radioactive material, called a radiopharmaceutical. Some radiopharmaceuticals are used with imaging equipment to detect diseases. Radiopharmaceuticals can also be placed inside the body near a cancerous tumor to shrink or destroy it.
How are radioactive isotopes used in medicine explain giving examples?
Radioactive isotopes have many useful applications. In medicine, for example, cobalt-60 is extensively employed as a radiation source to arrest the development of cancer. Other radioactive isotopes are used as tracers for diagnostic purposes as well as in research on metabolic processes.
How are radioactive elements used in medical diagnosis?
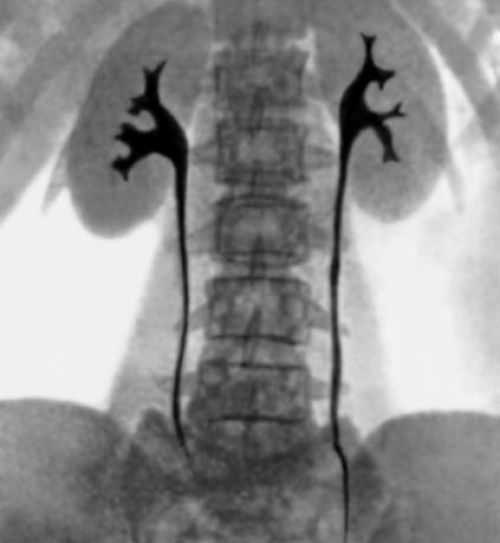
Nuclear medicine diagnosis, nuclear imaging. Radioisotopes are an essential part of medical diagnostic procedures. In combination with imaging devices which register the gamma rays emitted from within, they can be used for imaging to study the dynamic processes taking place in various parts of the body.
What are the medical uses of isotopes?
Medical isotopes are used by medical professionals to diagnose and treat health conditions such as heart disease and cancer. The production of medical isotopes is achieved by using two overarching technologies: nuclear reactors, and particle accelerators (linear accelerators, cyclotrons).
What is radioisotopes used for in medicine?
(Updated April 2021) Nuclear medicine uses radiation to provide diagnostic information about the functioning of a person's specific organs, or to treat them. Diagnostic procedures using radioisotopes are now routine.
What is the most common radioisotope used in nuclear medicine?
The most common radioisotope used in diagnosis is technetium-99 (Tc-99), with some 40 million procedures per year, accounting for about 80% of all nuclear medicine procedures and 85% of diagnostic scans in nuclear medicine worldwide. In developed countries (about one-quarter of world population) the frequency of diagnostic nuclear medicine is 1.9% ...
How many people use radioisotopes in a year?
There is widespread awareness of the use of radiation and radioisotopes in medicine, particularly for diagnosis (identification) and therapy (treatment) of various medical conditions. In developed countries (a quarter of the world population) about one person in 50 uses diagnostic nuclear medicine each year, and the frequency ...
What is short range radiotherapy?
This is radionuclide therapy (RNT) or radiotherapy. Short-range radiotherapy is known as brachytherapy , and this is becoming the main means of treatment. Although radiotherapy is less common than diagnostic use of radioactive material in medicine, it is nevertheless widespread, important, and growing.
Why are radioisotopes important?
In combination with imaging devices which register the gamma rays emitted from within, they can study the dynamic processes taking place in various parts of the body.
How many hospitals use radioactive tracer?
Five Nobel Laureates have been closely involved with the use of radioactive tracers in medicine. Over 10,000 hospitals worldwide use radioisotopes in medicine, and about 90% of the procedures are for diagnosis.
How many nuclear procedures are performed annually?
Over 40 million nuclear medicine procedures are performed each year, and demand for radioisotopes is increasing at up to 5% annually. Sterilization of medical equipment is also an important use of radioisotopes.
What is radioisotope used for?
In the hospital setting, radioisotopes are used to treat a range of diseases such as thyroid disease, arthritis, and liver tumours [6]. The most common radioisotopes used in the medical industry are Technetium-99m, Iodine-131, and Molybdenum-99. 85% of all nuclear medical examinations use Mo/Tc generators for diagnosing problems with the liver, bones, or lungs [6].
How long have radioisotopes been used in nuclear medicine?
Radioisotopes have been utilised in nuclear medicine for more than 30 years and remain indispensable in today’s society [2]. But how are they used, and what makes them a practical asset in the medical industry?
How are radioisotopes produced?
Medical radioisotopes are produced from materials bombarded by neutrons in a reactor or alternatively, by protons in a cyclotron, a type of particle accelerator . There are, however, disadvantages and advantages for both methods.
Why are radioisotopes important?
Radioisotopes open an opportunity for doctors to treat patients using less invasive methods, minimising pain, and reducing recovery times . Another benefit of radioisotopes is that treatment can also be applied to unseen areas of the body. In the past, doctors have had to use invasive methods of treatment; however, since the evolution of radioisotopes, this issue has been rectified so that they can avoid risky surgical operations.
What is nuclear imaging?
Have you ever wondered what nuclear medicine expects to accomplish? Well, nuclear imaging is a part of the medical branch involving radiopharmaceuticals, used to diagnose or monitor a patient’s disease. Specifically, radioisotopes make effective tracers, meaning the radiation they emit can be traced and utilised to make a diagnosis. In fact, there are a total of 3,800 known radioisotopes, and their application in medicine has advanced such that 200 of them are used on a daily basis [1].#N#By introducing small amounts of a radioactive substance (i.e. a radioactive tracer) into the patient’s body and taking images, doctors can visualise and assess the function of organ and tissue structures. This ultimately gives a deeper insight into tissues and organs than a traditional x-ray would allow. In some cases, radioisotopes can also be used to treat disease, but this article will focus on their diagnostic applications.
What is the most common isotope of uranium?
One of the most common isotopes is Technetium-99 (Tc-99). Tc-99 is produced by a complex method involving irradiation of uranium in nuclear research reactors for the production of Molybdenum-99 (Mo-99). Sadly, the availability of Tc-99 depends on an unsustainably low number of development reactors. These reactors were installed in the EU during the 1950s and 1960s and are now reaching the end of their lifetime [4]. This creates a growing need for routine maintenance shutdowns and an increasing number of unplanned supply disruptions. The disrupted supply of Mo-99 and its decay product, Tc-99, resulted in the cancellation of critical diagnostic tests for many patients between 2008 and 2010 [4]. It’s clear that there needs to be an amelioration in the availability of Mo-99/Tc-99. If the supply doesn’t enhance, the main medical imaging facilities will be undependable for several patients and the treatment therefore will be ineffective.
Is radioisotope therapy affordable?
A major concern for the health welfare of individuals is that radioisotope therapy is not affordable for everyone, for both the individual patient and at the country level. Health financing and recruitment should be established in the future to ensure everyone has access to treatment as well as greater investment in health personnel in less economically developed countries. The current statistics state that over 40 percent of all countries have fewer than 10 medical doctors per 10,0000 [9]. Not everyone has the opportunity to receive the treatment. But by reinforcing the advancement in technology needed to produce radioisotopes, we can fully realise their role in medicine.
Why is radioactive isotope important?
Radioactive has an important role in complementing human needs in various fields. One of them is in medicine and health. The use of radioactive isotopes in the medical field are for radiodiagnostic and radiotherapy that are also called as nuclear medicine.
When were radioactive isotopes first used in medicine?
The use of radioactive isotopes in biology and medicine was actually started in 1901 by Henri Danlos using radium for the treatment of tuberculosis in the skin, but the application of radioisotope as tracers in biology and medicine was pioneered by George de Hevesy in the 1920s when radioactive isotopes were used naturally. In the next development they used synthetic radioactive isotopes. So that in 1943 George Hevesy was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. The first radioisotope used extensively in nuclear medicine is I-131, which was discovered by Glenn Seaborg in 1937.
What are the two types of radioactive isotopes?
Based on the source, natural radioactive isotopes can be broadly divided into two types. The first is primordial radioactive isotopes, which exist in the earth’s crust since the formation of the universe, and the second is the cosmogenic radioisotope which is the result from the interaction between cosmic radiation and air. In addition to these two types, there are also radioactive isotopes that arise because of spontaneous decay of nuclides that can be split or due to the neutron catch nuclear reaction of cosmic radiation, and there are also extinct radioactive isotopes that are no longer present due to short half life, but because of the very small quantity it can be ignored.
What is the name of the radioactive isotopes that Seaborg discovered?
Followed by its use for the treatment of hyperthyroidism in 1940. The next discovery of the Seaborg radioactive isotopes Tc-99m and Co-60, which is a milestone in the field of Nuclear Medicine. Thanks to his services, Seaborg was awarded the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1951.
What is the name of the material that emits radiation a, b, g or neutron?
Artificial radioactive isotopes can be grouped into radioactive isotopes arising from nuclear power generation, radioactive isotopes produced for medicine, industry, or radioactive isotopes arising from nuclear experiments. Radioactive material is a material that emits radiation a, b, g or neutron.
What is a synthetic radioisotope?
Synthetic radioisotope is a radioisotope that is formed and made by humans. Synthetic radioactive isotopes are generated from the use of nuclear energy for peaceful and military purposes. Below we will discuss the number of radioactive isotopes due to nuclear power generation as well as nuclear experiments.
Why is Cobalt 60 used in radiation?
Cobalt-60 (Co-60) and Scandium-137 (Cs-137), the radiation is used to sterilize medical instruments.
Why were radioactive isotopes used in medicine?
This device helped to make the use of radioactive isotopes in the field of medicine, mainly for diagnoses and treatment of possible illness or diseases. The first isotopes were used as a tool to diagnose, detect, and treat thyroid disorders like goiter.
What is the purpose of radioactive isotopes?
It is the branch of medicine, which uses radiation to provide information, regarding the functioning of a specific organ in the human body, or the treatment of a disease. This collected data gives an accurate and immediate diagnosis of the patient’s illness. Radioactive isotopes are used to form images of the thyroid, bones, heart, liver, ...
What is radionuclide therapy?
Radionuclide Therapy (RNT) The use of radioactive isotopes in medicine involves radionuclide therapy. Cancerous cells can be controlled or even eliminated by irradiating the tumor growth region. Teletherapy, also known as external irradiation is carried out by gamma beams emitted from radioactive cobalt-60 source.
How do radioactive tracers work?
Most of the techniques uses radioactive tracers, which emits gamma rays from within the body. These are short-lived ones that are linked to chemical compounds, and they help in scrutinizing specific physiological processes. The mode of administering these tracers is by injections, inhalation, or oral ways.
What is the purpose of cyclotrons?
Cyclotrons are used to manufacture proton rich radioactive isotopes. The nucleus of an isotope emits particles like alpha, beta or positron, and photons like gamma rays, to achieve energetic stability during radioactive decay.
Why is the half life of radioactive isotopes important?
The dosage and half-life requires study of many factors. The use of radioactive isotopes in medicine is increasing day by day with accurate results. It also helps in early diagnosis, and is a mode of treatment for patients, especially for those suffering from cancer and tumors.
What are the types of elements that have the same atomic number?
Isotopes are defined as the types of an element, which have the same atomic number and position in the periodic table. They share similar chemical behavior but have different atomic mass and physical properties. Radioactive ones are those that have an unstable number of protons and neutrons. This instability is created by neutron activation, ...
What is the purpose of isotopes?
Medical isotopes are radioactive substances used in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. The energy emitted by these radioactive substances can be detected using special cameras and imaging software that helps evaluate organ size, location, and function.
What is nuclear medicine?
Nuclear medicine is a branch of medicine involving the use of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. These include, but are not limited to, the treatment of cancer, heart disease, endocrine disease, gastrointestinal disease, and neurological disorders. It offers the potential to recognize diseases in their earliest ...
What is iodine 131 used for?
Iodine-131 is regularly used to evaluate the kidney’s blood flow, evaluate liver function, and diagnose urinary tract obstruction. If is also used to gather images of the thyroid and to treat thyroid cancer. While it is used for beta therapy it is also a strong gamma emitter.
How long does a Caesium 131 X-ray last?
Caesium-131. Caesium-131 provides soft x-rays which makes it suitable for brachytherapy. It has a half-life of 9.7 days.
How many nuclear procedures are performed annually?
Nuclear medicine also provides therapeutic procedures for specific diseases. Over 40 million nuclear medicine procedures are performed annually with the demand for medical isotopes increasing 5% each year. Fundamentally, medical isotopes are used to target and destroy harmful cells in the body.
What is the difference between Caesium 137 and Chromium 51?
Chromium-51. Chromium-51 is most regularly used to quantify the loss of gastro-intestinal proteins or to quantify blood loss. It is also used to label and monitor red blood cells.
Nuclear Medicine Diagnosis, Nuclear Imaging
- Radioisotopes are an essential part of medical diagnostic procedures. In combination with imaging devices which register the gamma rays emitted from within, they can be used for imaging to study the dynamic processes taking place in various parts of the body. In using radiopharmaceuticals for diagnosis, a radioactive dose is given to the patient an...
Nuclear Medicine Therapy
- The uses of radioisotopes in therapy are comparatively few, but nevertheless important. Cancerous growths are sensitive to damage by radiation. For this reason, some cancerous growths can be controlled or eliminated by irradiating the area containing the growth. This may be called radiosurgery. External irradiation (sometimes called teletherapy) can be carried out using …
Sterilization
- Many medical products today are sterilized by gamma rays from a Co-60 source, a technique which generally is much cheaper and more effective than steam heat sterilization. The disposable syringe is an example of a product sterilized by gamma rays. Because it is a 'cold' process radiation can be used to sterilize a range of heat-sensitive items such as powders, ointments, an…
Supply of Radioisotopes
- The main world isotope suppliers are Curium (France & USA), MDS Nordion (Canada), IRE (Europe), NTP (South Africa), JSC Isotope (Russia), and ANM(ANSTO Australia). Most medical radioisotopes made in nuclear reactors are sourced from relatively few research reactors, including: 1. HFR at Petten in Netherlands (supplied via IRE and Curium). …
Notes & References
- OECD Nuclear Energy Agency, A Supply & Demand Update of the Mo-99 Market (August 2012) OECD-NEA, The Supply of Medical Radioisotopes: An Economic Diagnosis and Possible Solutions (2019) International Atomic Energy Agency, Feasibility of Producing Molybdenum-99 on a Small Scale Using Fission of Low Enriched Uranium or Neutron Activation of Natural Molybdenum, Tec…
Radioactive Isotopes
- Isotopes are defined as the types of an element, which have the same atomic number and position in the periodic table. They share similar chemical behavior but have different atomic mass and physical properties. Radioactive ones are those that have an unstable number of protons and neutrons. This instability is created by neutron activation, wherein a neutron capture…
What Is Nuclear Medicine?
- It is the branch of medicine, which uses radiation to provide information, regarding the functioning of a specific organ in the human body, or the treatment of a disease. This collected data gives an accurate and immediate diagnosis of the patient’s illness. Radioactive isotopes are used to form images of the thyroid, bones, heart, liver, and many ...
Diagnostic Techniques
- Most of the techniques uses radioactive tracers, which emits gamma rays from within the body. These are short-lived ones that are linked to chemical compounds, and they help in scrutinizing specific physiological processes. The mode of administering these tracers is by injections, inhalation, or oral ways. Single photons are detected by a gamma camera that provides a view o…
Radionuclide Therapy
- The use of radioactive isotopes in medicine involves radionuclide therapy. Cancerous cells can be controlled or even eliminated by irradiating the tumor growth region. Teletherapy, also known as external irradiation is carried out by gamma beams emitted from radioactive cobalt-60 source. In developed countries, the use of versatile linear accelerators is being utilized. Internal radionuclid…
Biochemical Analysis
- Radioactive isotopes can be easily detected even if they are present in low concentration. This has helped in the use of these isotopes in medicine, for labeling molecules of biological samples in vitro. There are many tests that help to detect the constituents of blood, serum, urine, hormones, antigens, and drugs by linking them with the isotopes. This type of tests are called ra…
Diagnostic Radio-Pharmaceuticals
- All organs in the body act differently due to the presence of specific chemicals absorbed by them. This knowledge has helped in developing diagnostic radio-pharmaceuticals, to examine the blood flow to the brain, and functioning of organs like heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, bones (excess growth), etc. It also helps in predicting the effects of surgery and assessing changes since the start of tre…
Therapeutic Radio-Pharmaceuticals
- Radiation has the ability to weaken or destroy malfunctioning cells under certain medical conditions. A radioactive element that can generate radiation is localized on the target organ with the help of its usual biological path or attaching an element to a suitable biological compound. Beta-radiation is commonly used to destroy damaged cells. This is known as radionuclide thera…