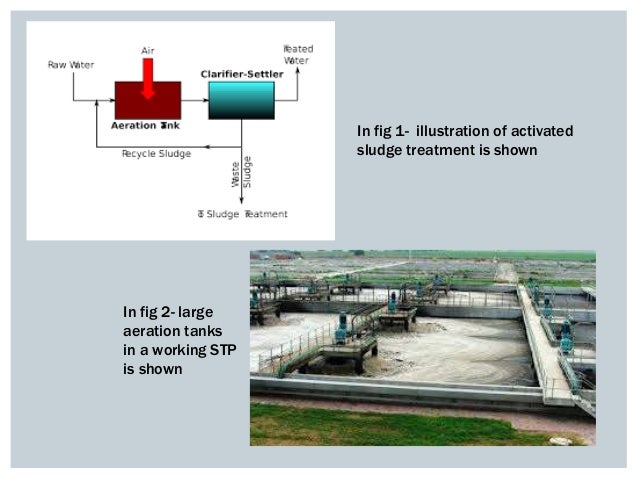
3.2. The Treatment Process
| Treatment Method | Treatment Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Aerobic System | CASP | 1. High reduction of BOD and Pathogens 2 ... | 1. Energy consumption is High 2. Sludge ... |
| Aerobic System | OD | 1. Operation management is easy 2. less ... | 1. Effluent suspended solids concentrati ... |
| Aerobic System | MBR | 1. Treated water is clarified and can be ... | 1. Aeration limitations and membrane pol ... |
| Aerobic System | TF | 1. Low construction and maintenance cost | 1. Poor transparency of treated water. |
Are GMO bacteria safe for wastewater treatment?
Feb 02, 2022 · Which Microbes are Used in Sewage Treatment? Aerobic Bacteria: Aerobic bacteria are most commonly used in aerated environments in modern treatment plants. These... Anaerobic Bacteria: Anaerobic microorganisms are commonly employed in wastewater treatment. Primary function of these... Facultative ...
What microorganisms are used in water treatment?
Aug 13, 2021 · In particular, the filamentous bacteria will especially dominate when specific activated sludge environment supports their growth. Therefore, if you don’t like what has grown, change the aeration tank environment and something different will grow – hopefully settling better in the clarifier. Microbiology of Wastewater Treatment Watch on
Why are bacteria used in sewage treatment?
Biological wastewater treatment is the most common method of sanitation in the world. This technology uses different types of bacteria and other micro-organisms for the treatment and cleaning of polluted water. Wastewater treatment is as essential to human health as it is to environmental protection. Indeed, the use of these bacteria accelerates the treatment of …
How can bacteria produce electricity, treat wastewater?
Apr 09, 2020 · Waste removed during the process is digested by microbes, and what remains is dried and disposed of in landfills, incinerators or applied to soil as a conditioner, depending on the source and process. Large-scale operations manage the bulk of our wastewater and follow a process called activated sludge.
What is a sewage treatment plant and how does it work?
A semi-solid waste or slurry byproduct of sewage treatment is called sewage sludge. Different processes like physical, chemical and biological meth...
What are the main steps in sewage treatment?
a. Primary treatment or Physical process b. Secondary treatment or Biological process
What is the major function of Microbes in Sewage Treatment?
Sewage is treated in sewage treatment plants (STPs) by the heterotrophic microbes present in the sewage before being disposed of in water bodies. M...
Explain types of microbes used in sewage treatment?
Aerobic Bacteria: These bacteria degrade the contaminants in the wastewater using free oxygen in the water, then turn into the energy that can be u...
Why is sewage treatment important?
Sewage treatment helps in reducing the rate of harmful contaminants that cause pollution of water and soil. Wastewater that is treated in these STP...
What are the different types of bacteria in wastewater treatment?
Which Microbes are Used in Sewage Treatment? 1 Aerobic Bacteria: Aerobic bacteria are most commonly used in aerated environments in modern treatment plants. These bacteria degrade the contaminants in the wastewater using free oxygen in the water, then turn into the energy that can be used to grow and reproduce. This helps the bacteria to complete their tasks, continue to grow and reproduce. 2 Anaerobic Bacteria: Anaerobic microorganisms are commonly employed in wastewater treatment. Primary function of these bacterias in sewage treatment is to reduce sludge volume and create methane gas from it. This gas can be used as an alternative energy source when properly cleaned and managed. This type of bacterias can utilize enough oxygen from its food supply and does not require additional supply of oxygen. Another advantage of anaerobic microorganisms in sewage treatment is that they remove phosphorus from wastewater. Most common anaerobic forms belong to Actinomyces, Bifidobacterium, Clostridium, Propionibacterium and Peptostreptococcus genera. 3 Facultative Bacteria: In sewage treatment, facultative microorganisms are bacteria that can switch between aerobic and anaerobic states depending on their surroundings. These bacteria like to reside in an aerobic environment.
How does sewage treatment help the environment?
Wastewater that is treated in these STPs can be reused for several purposes. Thus, sewage treatment helps in conservation of water as well as the environment.
How to control odor in sewage?
Odour Control in Sewage Treatment 1 Carbon reactors, a contact medium with bio slime, low doses of chlorine, are some examples of processes used to reduce the foul odour. 2 The addition of iron salts, peroxide, nitrate, etc., are some other ways of odour control and managing hydrogen sulfide levels. 3 High-density solids pumps are used for reducing the odour by moving sludge through sealed closed pipework.
Why is sewage treated in STPs?
Hence, sewage has to be treated in Sewage Treatment Plants ( STPs) in order to make it less polluting before disposal. The treatment of waste water is done by the heterotrophic microbes, naturally present in the sewage.
What is the treatment of sewage?
Thus, Microbes Sewage treatment, also known as wastewater treatment, is the removal of impurities from sewage before it enters natural water bodies. Fig: Microbes and Sewage Water Treatment.
What are the two stages of sewage treatment?
Sewage treatment is performed in two stages: 1. Primary treatment.
What is sewage sludge?
Ans: A semi-solid waste or slurry byproduct of sewage treatment is called sewage sludge. Different processes like physical, chemical and biological methods are used to eliminate contaminants from wastewater and produce treated wastewater or effluent which is safe to be released in water bodies or the environment. Q.2.
What is biological wastewater treatment?
Biological wastewater treatment is the most common sanitation method in the world. This technology uses different types of bacteria and other microorganisms for the treatment and purification of polluted water. Wastewater treatment is as essential to human health as it is to the protection of the environment.
Why is wastewater treatment important?
Wastewater treatment is as essential to human health as it is to the protection of the environment. The use of these bacteria accelerates the process of treating pollution on a small surface: the wastewater treatment plant.
What are the causes of anaerobic bacteria?
The presence of bad bacteria (or the absence of good ones) can cause in particular: 1 Low biogas efficiency of the anaerobic digester 2 Poor flocculation and sedimentation 3 An excess of filamentous bacteria 4 Excess of phosphorus 5 Low nitrogen removal efficiency (NH4, NO3) 6 The production of unpleasant odours 7 Excess consumption of chemical products 8 In an anaerobic digester, foam production
How long does it take for bacteria to colonize the environment?
The colonization of an environment by the needed bacteria and microorganisms necessary for the purification generally lasts between 4 and 8 weeks. Once again, it is the temperature that has the most influence on this growth time.
Can chlorine kill bacteria?
If this does not work, then it is possible to destroy these bacteria with chlorine. The problem is that it kills all bacteria. Then it will take a few weeks for normal conditions to be reached again. While the majority of operators continue to inject chlorine, we recommend the injection of dedicated bacteria.
What is lipophilic bacteria?
Lipophilic bacteria are specialized in the decomposition of animal and vegetable fats and oils in urban WWTPs and industrial treatment plants. These bacteria are easily adaptable to all current treatment systems.
Can bacteria survive in cold water?
The most common bacteria cannot survive under these conditions. This is why there are effective bacterial mixtures for the treatment of different types of water. Thus, before a cold event, for example, it is possible to pre-seed the biological reactor with specially selected bacteria for these conditions.
Why are biofilms important?
These biofilms help microbiologists monitor when a healthy consortium of bacteria are actively working to digest waste, while signs like excessive foam point to microbes that aren’t team players. If the wrong microbes show up or the process goes off track, then we intervene chemically or remove excess sludge.
What bacteria are in blue?
All bacteria were stained green, and Candidatus Accumulibacter Phosphatis, which accumulates phosphorus, were stained in blue. Courtesy of Connor Skennerton. When things are going well, it’s easy to see. C lumps of bacteria, called flocs, form in the sludge as these microbes help us reclaim the water within.
What is activated sludge?
Sludge comprises an incredibly rich medium, full of organic matter that we find unappetizing, but bacteria find delicious. Once this sludge has been processed by bacteria, it is called activated sludge, which can refer to both the material itself and the waste management process.
What is the process of reducing nitrates and nitrites into nitrogen gas?
Anaerobic bacteria further break down the sludge and reduce nitrate and nitrite into nitrogen gas through a process called denitrification. Biogas (primarily methane and carbon dioxide) produced during this anaerobic digestion is burned off or further purified for sale to energy companies.
What is biological oxygen demand?
Waste management facilities also use biological oxygen demand (a measure of the amount of oxygen being consumed by microbes) to calculate the food to mass ( or microbe) ratio. These values allow scientists to chart their course to the stationary phase when the sludge no longer needs to be aerated.
What is Bacillus Subtilis (Microbes)?
Bacillus subtilis, also known as grass bacillus or hay bacillus, is a rod-shaped bacterium. It is found in soil and the gastrointestional tract of ruminants and humans. As with other members of the genus Bacillus, it can form and endospore to survive extreme environmental conditions of temperature and desiccation.
ClearBlu Dry Microbes
ClearBlu dry microbes are available in blends with all bacillus strains, or with bacillus and two strains of pseudomonas and come freeze-dried on wheat bran or a salt/sugar carrier. Bacillus only blends are effective for municipal or industrial waste streams with minimal oil and grease.
What are the microbes in wastewater treatment plants?
The microbes in the wastewater treatment plant include: Bacteria: As small prokaryotic (no cell nucleus or organelles), bacteria form the "backbone" of the wastewater treatment plant in that they are the most common organisms and they do most of the work in converting pollutants into non-hazardous forms. The species vary according ...
What is wastewater bacteria?
Usually we classify wastewater bacteria based on their ability to grow under various temperatures (psychrophiles, mesophiles, thermophiles) and the ability to utilize oxygen or other electron acceptor for cellular respiration (aerobic, facultative anaerobic, obligate anaerobe). Fungi:
What is the backbone of wastewater treatment?
As small prokaryotic (no cell nucleus or organelles), bacteria form the "backbone" of the wastewater treatment plant in that they are the most common organisms and they do most of the work in converting pollutants into non-hazardous forms.
Is fungus a multicellular organism?
A more complex organism than bacteria, Fungi can be unicellular (yeasts) or multicellular with hyphae. In waste treatment we usually have higher concentrations of fungi under low pH conditions (pH <5.0). Other factors that can favor fungi include complex organics (lignin and other complex biopolymers) and low concentration of macronutrients ...
Why are methanogens important?
The activity of the methanogens is vital for COD/BOD reduction in anaerobic digesters and for production of methane gas. Most other archaea are found in low concentrations in wastewater treatment plants and are secondary to bacteria in importance. 5 Comments.
Where are archaea found?
Possessing unique cell membranes and chemistry, archaea microbes are found in such environments as ocean thermal vents, hot springs, anaerobic digesters, ruminant digestive systems, and other diverse environments. In waste treatment we most often see archaea in methane producing microbes in anaerobic digesters.
What are microorganisms in wastewater?
By Per Halkjær Nielsen. Microorganisms are the workhorses of wastewater treatment systems and anaerobic digesters, where they are responsible for removal of pollutants and pathogens, recovery of nutrients and energy, and producing clean water. Numerous different microbes exist in these systems; however, just how many is unknown, ...
What is the work of Denmark?
Work in Denmark has laid the foundations for identifying all the microbes in wastewater treatment systems and anaerobic digesters around the world with the aid of genetic fingerprinting. By Per Halkjær Nielsen.
What is Midas project?
The MiDAS project is a collaborative scheme that has taken place since 2006 between more than 50 wastewater treatment plants, consultants and the Center for Microbial Communities, Aalborg University. It includes regular DNA and FISH analyses of the microbial community composition, in-depth studies of focus topics, and workshops and reports for plant operators. It also includes development and maintenance of the MiDAS field guide, and various MiDAS-curated taxonomies to promote a common language between researchers in the field. The newest is MiDAS 3.6, which is a comprehensive 16S RNA gene reference database based on high-quality sequences derived from activated sludge and anaerobic digester systems, and an improved taxonomy.
What is MiDAS database?
We have now made a new ecosystem-specific database that contains sequences from nearly all microbes present in Danish wastewater treatment plants and digesters, called MiDAS (Microbial Database for Activated Sludge). Since most of the microorganisms are new and undescribed, we have also developed a new MiDAS taxonomy – an identification system that allows all species to be given a unique ID, so they can be recognised in future studies in any part of the world. We know that many of the microbes in Danish plants are also abundant across the world, so use of the new identification systems (the reference database and taxonomy) is useful for all working in the field. Furthermore, we are currently working on a global survey that will enable us to make a near-complete reference database for microbes found in wastewater treatment plants and digesters worldwide. We expect this to be available in early 2020.
What is the role of bacteria in wastewater treatment?
Bacteria are primarily responsible for removing organic nutrients from the wastewater. 2. Protozoa play a critical role in the treatment process by removing and digesting free swimming dispersed bacteria and other suspended particles. This improves the clarity of the wastewater effluent.
What happens to bacteria in wastewater?
In addition, the bacteria develop a sticky layer of slime around the cell wall that enables them to clump together to form bio-solids or sludge that is then separated from the liquid phase. The successful removal of wastes ...
What is activated sludge?
In the activated sludge process, microorganisms are mixed with wastewater. The microorganisms come in contact with the biodegradable materials in the wastewater and consume them as food. In addition, the bacteria develop a sticky layer of slime around the cell wall that enables them to clump together to form bio-solids or sludge ...
How efficient is activated sludge?
The activated sludge process, under proper conditions, is very efficient. It removes 85 to 95 percent of the solids and reduces the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) about the same amount. The efficiency of this system depends on many factors, including wastewater climate and characteristics.
What are filamentous bacteria?
Filamentous bacteria are present when operational conditions drastically change. These bacteria grow in long filaments begin to gain an advantage. Changes in temperature, pH, DO, sludge age, or even the amounts of available nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, oils & grease can affect these bacteria.
What are the factors that affect bacteria growth?
These bacteria grow in long filaments begin to gain an advantage. Changes in temperature, pH, DO, sludge age, or even the amounts of available nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, oils & grease can affect these bacteria.
What happens after aeration?
After the aeration basin, the mixture of microorganisms and wastewater (mixed liquor) flows into a settling basin or clarifier where the sludge is allowed to settle . Some of the sludge volume is continuously recirculated from the clarifier, as Returned Activated Sludge (RAS), back to the aeration basin to ensure adequate amounts ...