How Does a Waste Water Treatment Plant Work?
- Pretreatment Phase. Squander water plants eliminate the 'obvious targets' during the pretreatment stage. ...
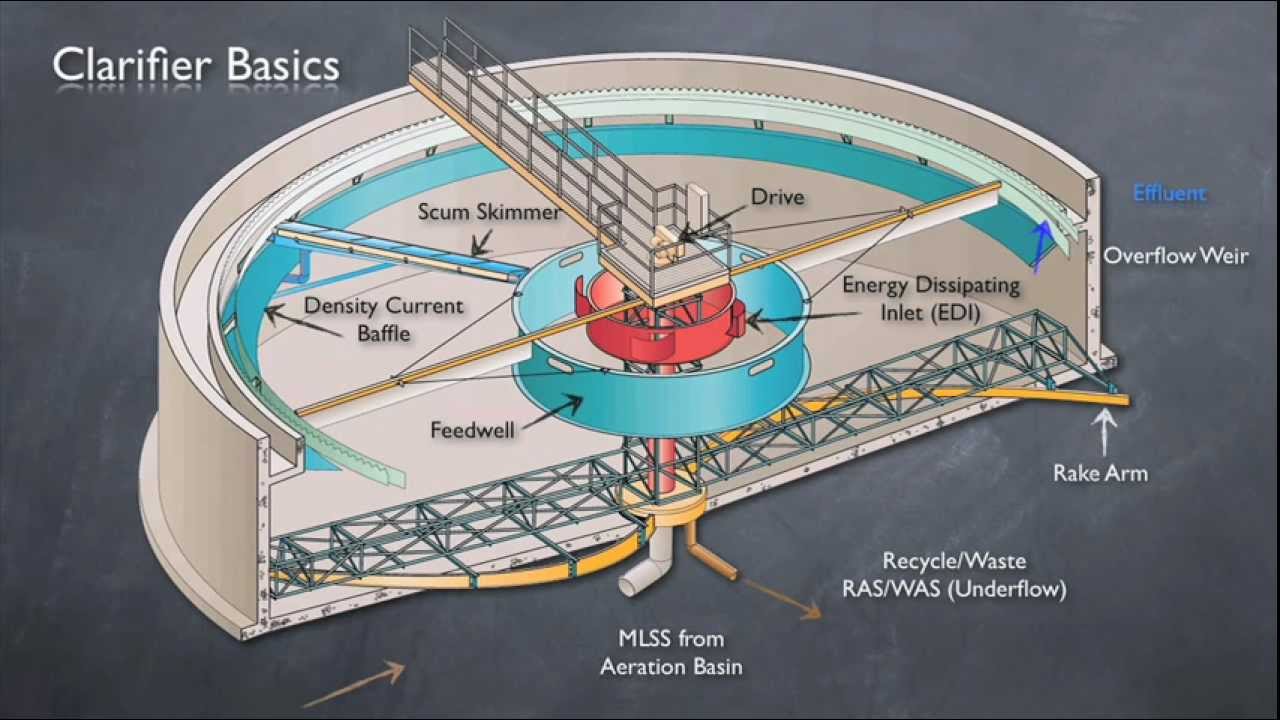
- Primary Treatment. After pretreatment, the waste water gathers in essential clarifiers, which are enormous bowls and sedimentation tanks.
- Secondary Treatment. ...
- Sludge Treatment. ...
Full Answer
What are the disadvantages of a waste water treatment plant?
The basic function of wastewater treatment is to speed up the natural processes by which water is purified. There are two basic stages in the treat-ment of wastes, primary and secondary, which are outlined here. In the primary stage, solids are allowed to settle and removed from wastewater. The secondary stage uses biological processes to
What is the purpose of a waste water treatment plant?
Dec 13, 2018 · Wastewater Treatment Process The Primary Wastewater Treatment Process. Before a wastewater treatment plant lets in any volume of sewage, it must pass the new influx through a screen. The screening process, which is the first, removes large objects in the mixture.
How much energy does a wastewater treatment plant use?
Oct 08, 2018 · The wastewater enters an aeration tank, where it is mixed with sludge. Air is then pumped into the aeration tank to facilitate the growth of bacteria and other small organisms within the sludge. The bacteria and other microorganisms break down the organic matter in the water into harmless byproducts.
How does a sewage treatment plant actually work?
Feb 28, 2022 · Wastewater treatment plants operate on three fundamental operations; primary, secondary and tertiary treatment. The primary treatment is a process that breaks down solids (which floats to the bottom of the tank) into sludge and release treated water for secondary treatment. The process takes place in large sedimentation tanks.

How a waste water treatment plant works?
As sewage enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen, which removes large floating objects such as rags and sticks that might clog pipes or damage equipment. After sewage has been screened, it passes into a grit chamber, where cinders, sand, and small stones settle to the bottom.
What are the 5 stages of wastewater treatment?
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake. ... Sludge Treatment.
What are the 3 stages of wastewater treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
How a treatment plant works?
4:3910:03How Do Wastewater Treatment Plants Work? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSimply it's the breakdown of organic matter along with the use of excess oxygen. Some older plantsMoreSimply it's the breakdown of organic matter along with the use of excess oxygen. Some older plants will add in another step before aeration basins referred to as bio filters or trickling filters.
What are the 7 steps in wastewater treatment?
The Wastewater Treatment ProcessStage One — Bar Screening. ... Stage Two — Screening. ... Stage Three — Primary Clarifier. ... Stage Four — Aeration. ... Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier. ... Stage Six — Chlorination (Disinfection) ... Stage Seven — Water Analysis & Testing. ... Stage Eight — Effluent Disposal.Mar 5, 2021
How do water treatment plants treat water?
During coagulation, chemicals with a positive charge are added to the water. The positive charge neutralizes the negative charge of dirt and other dissolved particles in the water. When this occurs, the particles bind with the chemicals to form slightly larger particles.
Why is wastewater treated with chlorine or UV light?
This includes new plants as well as existing ones that have converted from chlorine. UV is the most effective, safe and environmentally friendly way to disinfect wastewater. Unlike chemical approaches to water disinfection, UV light provides rapid, effective inactivation of microorganisms through a physical process.Sep 1, 2020
What are the 4 steps of water treatment?
4 Steps of Community Water TreatmentCoagulation and Flocculation. ... Sedimentation. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection. ... Learn More. ... Recommended Readings.
Which bacteria is used in aeration tank?
With a normal influent load of pollutants, the dissolved oxygen content in the aerated section of most plants should be kept between 3 and 5 MG/L. Anaerobic bacteria are normally used in an anaerobic digester to reduce the volume of sludge to be disposed of and to produce methane gas.Jun 14, 2012
How is wastewater treated in a wastewater treatment plant?
Primary Treatment As wastewater enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen. This removes large floating objects, such as rags and sticks, which clog pipes or damage equipment. Once the wastewater has been screened, it passes into a grit chamber, where cinders, sand, and small stones settle to the bottom.Mar 6, 2020
How do you make a wastewater treatment plant?
Design Parameters: The overall design of the wastewater treatment plant consists of 4 stages: i) Primary treatment which consists of screening, grit removal and sedimentation ii) Secondary treatment consists of a bioreactor iii) Tertiary treatment consists of nitrogen removal, adsorption and pH control.Oct 31, 2018
1. Pre-treatment Phase
The pre-treatment phase that occurs at a wastewater treatment plant is designed to get rid of the larger and easier to remove items from the water. These items can include everything from tree branches and cans to plastic bottles and rags.
2. Primary Treatment Phase
Once the pre-treatment phase concludes, the primary treatment phase can begin. The wastewater will be collected in sedimentation tanks and large basins at this point, which is done to allow contaminants to sink to the bottom of the water.
3. Secondary Treatment Phase
This is a very important phase of the wastewater treatment process that involves the agitation and aeration of the water within secondary basins. It’s at this point in the process that microorganisms are added to the water in order to break down any organic matter into sludge that can be more readily discarded.
4. Sludge Treatment Phase
The final phase of the wastewater treatment process is referred to as the sludge treatment phase. During the secondary treatment phase, the solids and organic matter that remain in the water are converted into sludge that can be treated and recycled.
What is wastewater treatment?
admin-seo. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), wastewater treatment is one of the most common forms of pollution control in the U.S. Lakeside Equipment Corporation is proud to supply equipment and systems that are used across the country at wastewater treatment plants, which are facilities that clean wastewater ...
How does wastewater enter the primary stage of treatment?
Sewage enters the primary stage of treatment as soon as it arrives at a wastewater treatment facility. First, it is sent through a screen that is designed to remove large pieces of debris that could damage Lakeside equipment used elsewhere in the facility. Some facilities have multiple screens in place to remove objects and materials ...
How does wastewater get into an aeration tank?
The wastewater enters an aeration tank, where it is mixed with sludge. Air is then pumped into the aeration tank to facilitate the growth of bacteria and other small organisms within the sludge. The bacteria and other microorganisms break down the organic matter in the water into harmless byproducts.
What happens when wastewater is pumped into a sedimentation tank?
The wastewater slowly flows through a sedimentation tank, and as it flows, the solids that remain in the water start to drift towards the bottom of the tank. This is the final step in the primary stage of the wastewater treatment process. At this point, the majority of the solids have been removed from the water.
What is the secondary stage of wastewater treatment?
The secondary stage of the treatment process is designed to remove up to 85% of organic matter that remains in the wastewater. There are a number of different ways to achieve this goal, but many facilities use either the trickling filter or activated sludge process.
What is grit in sewage?
After passing through the screen, the sewage water moves into the grit chamber. Grit can include sand, gravel, eggshells, or any other type of solid material that makes it through the screening process.
Can bacteria keep up with sewage?
But, the bacteria and other organisms could not keep up with the increase in population and production of sewage. Wastewater is now sent to wastewater treatment plants—many of which use the same purification process found in nature to clean water. Most wastewater treatment plants prepare wastewater for reuse in two separate stages: ...
What is the primary stage of wastewater treatment?
The primary stage mainly involves removal of large floating objects in the waste water. As sewer or water from other sources such as rivers enters into a treatment plant, it passes through a screen.
Why is water important to humans?
Water is a basic resource for daily operations for human beings. It is also a home to millions of aquatic creatures. Water pollution can lead to diseases and death to animals, human beings and aquatic life.
What is a trickling filter?
A trickling filter is made up of 3 to 6 feet deep bed of stones, synthetic media or meshing pieces of wavy plastic. Bacteria gather and multiply on the trickling filter beds. As the effluent is passed through the trickling filter beds, these bacteria consume most of the organic matter in the sewer.
What is wastewater treatment?
A wastewater treatment plant treats sewage water from various sources and makes it reusable. It comprises several processes that address specific needs for wastewater treatment. The treatment system treats the sewage from domestic use, rainwater, runoff, and other pollutants that go down the street gutters. The sewage also includes water ...
How does sewage water work?
The sewage water is first allowed to pass through a primary wastewater treatment plant. At this stage, the treatment uses screens and settling tanks to remove most of the floating materials from the wastewater. Solid materials account for around 35% of the wastewater. Hence, removing the solid waste at the primary stage makes ...
What happens when you remove grit from a sedimentation tank?
Once the settled grit is removed, the wastewater is passed to the sedimentation tanks, settling tanks , or clarifiers. This step removes organic and inorganic matter and suspended solids. By properly adjusting the water flow in the sedimentation tank, the suspended particles start to sink to the bottom and form a solid mass.
What is the mass of wastewater called?
The solid mass is called raw primary biosolids or sludge. Scum is formed on the top of the wastewater and is skimmed off from the top. The primary treatment process removes around 90% of suspended solids, 55% of fecal coliforms, and 50% of biological oxygen demand (BOD).
How much organic matter is removed from sewage?
Around 85% of organic matter from sewage is removed during secondary wastewater treatment. The process involves forcefully mixing the wastewater with bacteria and oxygen, bacteria digest organic matter with the help of oxygen. These processes are performed by the trickling filter and activated sludge tank.
What is tertiary treatment?
This treatment is employed when the water from the secondary treatment has an undesirable amount of dissolved substances like metals, color, nutrients, and organic chemicals. Several physical, chemical, and biological treatment processes are performed for tertiary treatment.
How high is a trickling filter?
Trickling Filter. A trickling filter forms a bed of stones placed at a height of 6 feet. The sewage is allowed to pass through this stone layer once it is out of the sedimentation tank. The bacteria gather on these stones and start to multiply and develop until they completely consume organic matter in the sewage.
How is wastewater drained?
Waste water is drained through pipe systems and thus enters the public sewerage system . Here we differentiate between two types of drainage. In the combined sewer system, domestic and commercial wastewater is fed into a sewer together with rainwater that accumulates on sealed surfaces (e.g. streets and roofs).
What is the process of removing nutrient from wastewater?
In the actual clarifier, bacteria and fungi have the task of metabolising organic components in the wastewater into its individual parts. This process is called Biological nutrient removal. Oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor areas provide optimal conditions for breaking down all carbon and phosphate compounds and urea from the urine.
How does a separate sewer system work?
The separate sewer system divides the media. Dirty water is fed into one sewer, surface water into another. Because of the low dirt load, the collected surface water is usually discharged into neighbouring waters (lakes or rivers). The wastewater and the combined sewer both end up at the treatment plant. Of course, in the case of combined sewer ...
What is the function of a primary clarifier?
The primary clarifier then has the function of filtering further components from the waste water. Suspended solids, which are lighter than water, such as plastic parts but also oils and fats, float up and are removed at the surface. Due to the very low speed in the basin, further heavier particles sink to the bottom.
What is the process of cleaning a toilet called?
Rakes filter everything that is not permeable as solid matter in the wastewater. This can be toilet paper, wet wipes, but also a toothbrush or other things that do not belong in a toilet. This process is called pretreatment.
Where does wastewater end up in a combined sewer system?
The wastewater and the combined sewer both end up at the treatment plant. Of course, in the case of combined sewer systems, the sewage treatment plant has more work to do, as all the surface water has to be cleaned as well.
What happens to clarified water?
In the end, the clarified water is returned to the natural water cycle, usually lakes or streams. Very modern sewage treatment plants have additional treatment stages for further phosphorus elimination or the killing of pathogens.

Pre-Treatment Phase
- http://www.instagram.com/p/CBuVtZ1DbHv/ The pre-treatment phase that occurs at a wastewater treatment plant is designed to get rid of the larger and easier to remove items from the water. These items can include everything from tree branches and cans to plastic bottles and rags. Some of the operations that can occur during this phase include collection of the wastewa…
Primary Treatment Phase
- http://www.instagram.com/p/B-WWIQHlkY8/ Once the pre-treatment phase concludes, the primary treatment phase can begin. The wastewater will be collected in sedimentation tanks and large basins at this point, which is done to allow contaminants to sink to the bottom of the water. Once the smaller particles in the water have settled, scrapers are used to collect the solids and send t…
Secondary Treatment Phase
- http://www.instagram.com/p/B_ZLcJVhNJD/ This is a very important phase of the wastewater treatment process that involves the agitation and aeration of the water within secondary basins. It’s at this point in the process that microorganisms are added to the water in order to break down any organic matterinto sludge that can be more readily discarded. Certain plants will grow a sub…
Sludge Treatment Phase
- http://www.instagram.com/p/B5CI6DapAH8/ The final phase of the wastewater treatment process is referred to as the sludge treatment phase. During the secondary treatment phase, the solids and organic matter that remain in the water are converted into sludge that can be treated and recycled. The sludge treatment phase involves the treatment of the remaining water as well as a…