
Under HIPAA, a covered entity may seek consent to carry out treatment, payment, and health care operations (sometimes referred to as TPO). Remember that state law may be stricter (this guide does not discuss state laws). What are "health care operations"?
What is considered protected health information under HIPAA?
What is PHI?
- Names (Full or last name and initial)
- All geographical identifiers smaller than a state, except for the initial three digits of a zip code if, according to the current publicly available data from the U.S. ...
- Dates (other than year) directly related to an individual
- Phone Numbers
- Fax numbers
- Email addresses
- Social Security numbers
- Medical record numbers
What are the elements of HIPAA authorization?
- (1) Core elements. A valid authorization under this section must contain at least the following elements: (i) A description of the information to be used or disclosed that identifies the ...
- (2) Required statements. ...
- (3) Plain language requirement. ...
- (4) Copy to the individual. ...
What are HIPAA patient rights?
Several provisions of the HIPAA Privacy Rule form the basis of HIPAA Patient Rights. HIPAA protects patients by generally prohibiting the sale of PHI; the use and disclosure of genetic information for underwriting purposes; and the use or disclosure of psychotherapy notes. Do you have an effective HIPAA compliance program?
Can HIPAA authorization be verbal?
The verbal consent/authorization must contain all of the required elements for a valid consent plus HIPAA authorization. The investigator must explain how they will document that the subject gave verbal authorization for the use of PHI. The investigator must make a compelling case that the research would not be practicable without the waiver.
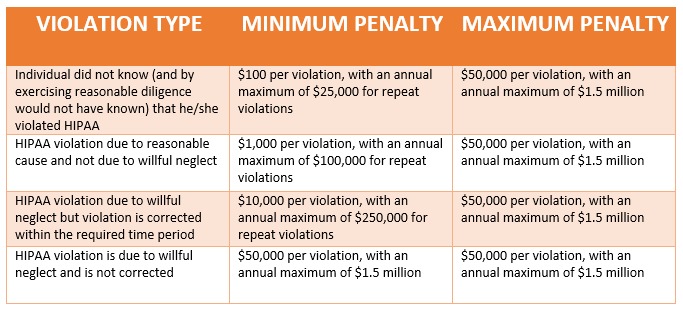
What does HIPAA consent mean?
A HIPAA authorization is consent obtained from an individual that permits a covered entity or business associate to use or disclose that individual's protected health information to someone else for a purpose that would otherwise not be permitted by the HIPAA Privacy Rule.
Is HIPAA a consent for treatment?
HIPAA consent must be separate from the normal informed consent for treatment; 3. The consent must be in plain lan- guage and signed by the patient; and 4. The patient may revoke that consent at any time. And here is an absolute key: the health care entity may condition treat- ment on the patient's consent.
What does a HIPAA authorization include?
The core elements of a valid authorization include: A meaningful description of the information to be disclosed. The name of the individual or the name of the person authorized to make the requested disclosure. The name or other identification of the recipient of the information.
What consent is needed for HIPAA compliance?
Summary – HIPAA Consent Requirements The use and disclosure of PHI requires certain types of consent including; nonverbal consent, or written consent depending on the use case. If you think your information was possibly used or disclosed in an inappropriate manner, the best course of action would be to contact HHS.
What is the difference between HIPAA authorization and informed consent?
A: “Consent” is a general term under the Privacy Rule, but “authorization” has much more specific requirements. The Privacy Rule permits, but does not require, a CE to obtain patient “consent” for uses and disclosures of PHI for treatment, payment, and healthcare operations.
What are 3 major things addressed in the HIPAA law?
The components of 3 HIPAA rules include technical security, administrative security, and physical security. These rules can enhance the efficiency of the healthcare system, improve the portability of healthcare insurance, and ensure the safety of patient information.
Which of the following may be a HIPAA violation?
Releasing Patient Information to an Unauthorized Individual Disclosing PHI for purposes other than treatment, payment for healthcare, or healthcare operations (and limited other cases) is a HIPAA violation if authorization has not been received from the patient in advance.
How long is HIPAA consent good for?
There's no statutory time period within which a release must expire. However, under HIPAA, an authorization to release medical information must include a cutoff date or event that relates to who's authorizing the release and why the information is being disclosed.
What is patient authorization?
An authorization is a detailed document that gives covered entities permission to use protected health information for specified purposes, which are generally other than treatment, payment, or health care operations, or to disclose protected health information to a third party specified by the individual.
What is the law of informed consent?
Informed Consent Law covers the legal aspect regarding an individual's right to be informed of and consent to a procedure or treatment suggested by a physician or professional. This written authorization can limit professional liability issues for the individual providing the service.
What are the principles of HIPAA?
Fundamental Principles: HIPAA Authorization & HIPAA Release Requirements. One of the fundamental principles of the Privacy Rule was to create boundaries in an effort to limit the ways that PHI could be disclosed without specific consent such as verbal or written by a covered entity. The Privacy Rule requires that a covered entity disclose PHI is ...
What is the exception to the Privacy Rule?
The exception to the rule is meant to be limited.
What is required by the Privacy Rule for uses and disclosures of protected health information?
Covered entities that do so have complete discretion to design a process that best suits their needs. By contrast, an “authorization” is required by the Privacy Rule for uses and disclosures of protected health information not otherwise allowed by the Rule.
What is authorization in healthcare?
An authorization is a detailed document that gives covered entities permission to use protected health information for specified purposes, which are generally other than treatment, payment, or health care operations, or to disclose protected health information to a third party specified by the individual . An authorization must specify ...
Is voluntary consent required for a patient to use protected health information?
Where the Privacy Rule requires patient authorization, voluntary consent is not sufficient to permit a use or disclosure of protected health information unless it also satisfies the requirements of a valid authorization.
Can covered entities condition treatment?
With limited exceptions, covered entities may not condition treatment or coverage on the individual providing an authorization. Content created by Office for Civil Rights (OCR) Content last reviewed on July 26, 2013.
Does the Privacy Rule require a covered entity to obtain consent for use of protected health information?
The Privacy Rule permits, but does not require, a covered entity voluntarily to obtain patient consent for uses and disclosures of protected health information for treatment, payment, and health care operations. Covered entities that do so have complete discretion to design a process that best suits their needs.#N#By contrast, an “authorization” is required by the Privacy Rule for uses and disclosures of protected health information not otherwise allowed by the Rule. Where the Privacy Rule requires patient authorization, voluntary consent is not sufficient to permit a use or disclosure of protected health information unless it also satisfies the requirements of a valid authorization. An authorization is a detailed document that gives covered entities permission to use protected health information for specified purposes, which are generally other than treatment, payment, or health care operations, or to disclose protected health information to a third party specified by the individual.#N#An authorization must specify a number of elements, including a description of the protected health information to be used and disclosed, the person authorized to make the use or disclosure, the person to whom the covered entity may make the disclosure, an expiration date, and, in some cases, the purpose for which the information may be used or disclosed. With limited exceptions, covered entities may not condition treatment or coverage on the individual providing an authorization.
What is the HIPAA rule?
HIPAA Security Rule. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) is a federal law that required the creation of national standards to protect sensitive patient health information from being disclosed without the patient’s consent or knowledge. The US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) issued ...
Who enforces HIPAA rules?
The HHS Office for Civil Rights enforces HIPAA rules, and all complaints should be reported to that office. HIPAA violations may result in civil monetary or criminal penalties. For more information, visit the Department of Health and Human Services HIPAA website. external icon.
What is the HIPAA Privacy Rule?
The Privacy Rule standards address the use and disclosure of individuals’ health information (known as “protected health information”) by entities subject to the Privacy Rule. These individuals and organizations are called “covered entities.”. The Privacy Rule also contains standards for individuals’ rights to understand ...
What are the types of entities that are covered by HIPAA?
The following types of individuals and organizations are subject to the Privacy Rule and considered covered entities: 1 Healthcare providers: Every healthcare provider, regardless of size of practice, who electronically transmits health information in connection with certain transactions. These transactions include claims, benefit eligibility inquiries, referral authorization requests, and other transactions for which HHS has established standards under the HIPAA Transactions Rule. 2 Health plans: Entities that provide or pay the cost of medical care. Health plans include health, dental, vision, and prescription drug insurers; health maintenance organizations (HMOs); Medicare, Medicaid, Medicare+Choice, and Medicare supplement insurers; and long-term care insurers (excluding nursing home fixed-indemnity policies). Health plans also include employer-sponsored group health plans, government- and church-sponsored health plans, and multi-employer health plans.#N#Exception: A group health plan with fewer than 50 participants that is administered solely by the employer that established and maintains the plan is not a covered entity. 3 Healthcare clearinghouses: Entities that process nonstandard information they receive from another entity into a standard (i.e., standard format or data content), or vice versa. In most instances, healthcare clearinghouses will receive individually identifiable health information only when they are providing these processing services to a health plan or healthcare provider as a business associate. 4 Business associates: A person or organization (other than a member of a covered entity’s workforce) using or disclosing individually identifiable health information to perform or provide functions, activities, or services for a covered entity. These functions, activities, or services include claims processing, data analysis, utilization review, and billing.
What are covered entities?
The following types of individuals and organizations are subject to the Privacy Rule and considered covered entities: Healthcare providers: Every healthcare provider, regardless of size of practice, who electronically transmits health information in connection with certain transactions.
Can a covered entity disclose health information without an individual's authorization?
A covered entity is permitted, but not required, to use and disclose protected health information, without an individual’s authorization, for the following purposes or situations: Disclosure to the individual (if the information is required for access or accounting of disclosures, the entity MUST disclose to the individual) ...
Does HIPAA apply to PHI?
The Security Rule does not apply to PHI transmitted orally or in writing. To comply with the HIPAA Security Rule, all covered entities must do the following: Ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of all electronic protected health information.
What is HIPAA authorization?
HIPAA authorization is consent obtained from a patient or health plan member that permits a covered entity or business associate to use or disclose PHI to an individual/entity for a purpose that would otherwise not be permitted by the HIPAA Privacy Rule.
When is HIPAA required?
HIPAA authorization is required for: Use or disclosure of PHI otherwise not permitted by the HIPAA Privacy Rule. Use or disclosure of PHI for marketing purposes except when communication occurs face to face between the covered entity and the individual or when the communication involves a promotional gift of nominal value.
What is HIPAA Privacy Rule?
The HIPAA Privacy Rule permits the sharing of health information by healthcare providers, health plans, healthcare clearinghouses, business associates of HIPAA-covered entities, and other entities covered by HIPAA Rules under certain circumstances. In general terms, permitted uses and disclosures are for treatment, payment, ...
What are the requirements for HIPAA?
45 CFR §164.508 details the uses and disclosures of PHI that require an authorization to be obtained from a patient/plan member before information can be shared or used. HIPAA authorization is required for: 1 Use or disclosure of PHI otherwise not permitted by the HIPAA Privacy Rule 2 Use or disclosure of PHI for marketing purposes except when communication occurs face to face between the covered entity and the individual or when the communication involves a promotional gift of nominal value. 3 Use or disclosure of psychotherapy notes other than for specific treatment, payment, or health care operations (see 45 CFR §164.508 (a) (2) (i) and (a) (2) (ii)) 4 Use or disclosure of substance abuse and treatment records 5 Use or disclosure of PHI for research purposes 6 Prior to the sale of protected health information
What happens if you refuse to sign an authorization?
The consequences of a refusal to sign the authorization when the covered entity is permitted to condition treatment, enrollment in the health plan, or eligibility for benefits on a failure to obtain authorization. The individual providing consent must be provided with a copy of the authorization form for their own records.
What does it mean to sign an authorization?
By signing the authorization, an individual is giving consent to have their health information used or disclosed for the reasons stated on the authorization. Any use or disclosure by the covered entity or business associate must be consistent with what is stated on the form.
What is required on an authorization form?
The authorization form must be written in plain language to ensure it can be easily understood and as a minimum, must contain the following elements: Specific and meaningful information, including a description, of the information that will be used or disclosed.
Who must follow HIPAA regulations?
In addition, business associates of covered entities must follow parts of the HIPAA regulations. Often, contractors, subcontractors, and other outside persons and companies that are not employees of a covered entity will need to have access to your health information when providing services to the covered entity.
What are covered entities under HIPAA?
Covered entities include: Health Plans, including health insurance companies, HMOs, company health plans, and certain government programs that pay for health care, such as Medicare and Medicaid.
What is OCR rights?
OCR has teamed up with the HHS Office of the National Coordinator for Health IT to create Your Health Information, Your Rights!, a series of three short, educational videos (in English and option for Spanish captions) to help you understand your right under HIPAA to access and receive a copy of your health information.
What is covered entity?
Covered entities must have contracts in place with their business associates, ensuring that they use and disclose your health information properly and safeguard it appropriately. Business associates must also have similar contracts with subcontractors.
What is the purpose of paying doctors and hospitals?
To pay doctors and hospitals for your health care and to help run their businesses. With your family, relatives, friends, or others you identify who are involved with your health care or your health care bills, unless you object. To make sure doctors give good care and nursing homes are clean and safe.
What to do if you believe your health information is being denied?
If you believe your rights are being denied or your health information isn’t being protected, you can. File a complaint with your provider or health insurer. File a complaint with HHS. You should get to know these important rights, which help you protect your health information.
Can health information be shared without your permission?
To make required reports to the police, such as reporting gunshot wounds. Your health information cannot be used or shared without your written permission unless this law allows it. For example, without your authorization, your provider generally cannot: Give your information to your employer.
Why is information important in healthcare?
Physicians, medical professionals, hospitals and other clinical institutions generate, use and share it to provide good care to individuals, to evaluate the quality of care they are providing, and to assure they receive proper payment from health plans.
Why do health plans use and share care?
Health plans generate, use and share it to pay for care, to assure care for their members is well coordinated and that populations of individuals with chronic conditions are receiving appropriate care.
What is the capability of relevant players in the health care system?
The capability for relevant players in the health care system – including the patient – to be able to quickly and easily access needed information to make decisions, and to provide the right care at the right time, is fundamental to achieving the goals of health reform.
Is HIPAA a privacy law?
For more than a decade, the HIPAA regulations have provided a strong privacy and security foundation for the health care system. Although the regulations have been in effect for quite some time, health care providers frequently still question whether the sharing of health information, even for routine purposes like treatment or care coordination, ...
What is a HIPAA release form?
Simply: HIPAA release forms give patients full power over choosing who can access their health information (parent s, children, spouses, friends , etc.) In order for an release form to be legally valid, it must inform the patient of the following: • The patient has the right to revoke an authorization at any time.
What is HIPAA disclosure?
Specifically singled out by HIPAA, healthcare providers that have a direct treatment relationship with patients are required by law to disclose their privacy practices. These disclosures come in the form of a “notice of privacy practices.”.
What are the two most common HIPAA forms?
The two most standard HIPAA forms are privacy forms (a.k.a. “notices of privacy practices”) and authorization forms (a.k.a. “release forms”). The HIPAA privacy form is by far the most common of the two. In fact, according to HIPAA’s Privacy Rule, all covered entities should be making an effort to obtain patient signatures on privacy forms.
What are HIPAA forms?
HIPAA Forms Explained: Privacy and Authorization. Whether you are a patient or a covered entity (e.g. health organization), you will undoubtedly come into contact with a variety of HIPAA forms. To understand your legal duties as a covered entity, or your rights as a patient, you should become very familiar with these legal documents.
Why can't I sign a HIPAA form?
One potential reason for refusing to sign a HIPAA privacy form is to keep your options open in the case of a violation. If you signed a privacy form, it will be much harder to sue the health provider if the confidentiality of your PHI was broken. Although this is an unlike possibility, it is a possibility nonetheless.
What is the default mode of health privacy?
The default mode of health privacy is this: unless the patient makes a conscious effort to give someone access, the PHI will remain private. Even if you are the spouse of a patient, PHI will be inaccessible to you until your husband/wife authorizes you.
What happens if an acknowledgment cannot be obtained?
If an acknowledgment cannot be obtained, the provider must document his or her efforts to obtain the acknowledgment and the reason why it was not obtained. Source: HHS. In practical terms, if this rule applies to you, you must provide every patient with a privacy form and request his or her signature. 1.

Hipaa Privacy Rule
Covered Entities
- The following types of individuals and organizations are subject to the Privacy Rule and considered covered entities: 1. Healthcare providers: Every healthcare provider, regardless of size of practice, who electronically transmits health information in connection with certain transactions. These transactions include claims, benefit eligibility inquiries, referral authorizatio…
Permitted Uses and Disclosures
- A covered entity is permitted, but not required, to use and disclose protected health information, without an individual’s authorization, for the following purposes or situations: 1. Disclosure to the individual (if the information is required for access or accounting of disclosures, the entity MUST disclose to the individual) 2. Treatment, payment, and healthcare operations 3. Opportunity to ag…
Hipaa Security Rule
- While the HIPAA Privacy Rule safeguards protected health information (PHI), the Security Rule protects a subset of information covered by the Privacy Rule. This subset is all individually identifiable health information a covered entity creates, receives, maintains, or transmits in electronic form. This information is called “electronic protected health information” (e-PHI). The …