What is haloperidol used to treat?
The following medications may increase the risk of heart problems when used with haloperidol: Antipsychotics including chlorpromazine (Thorazine®), thioridizine (Mellaril®), iloperidone (Fanapt®), paliperidone... Antiarrhythmics (heart rhythm …
How long does it take for haloperidol to work?
Feb 07, 2022 · Severe behavioral disorders in children: Haloperidol is effective for treating combative, explosive hyperexcitability (which cannot be accounted for by immediate provocation). Haloperidol should be reserved for children only after failure to respond to psychotherapy or medications other than antipsychotics.
What is Haldol used to treat?
Haloperidol is employed in the treatment of schizophrenia and other psychoses. It is used in the treatment of mania and in the short-term adjunctive management of severe anxiety, psychomotor agitation, excitement, and dangerous behavior. It may …

What is haloperidol used to treat?
How effective is haloperidol?
What is the therapeutic effect of Haldol?
What is the mode of action for haloperidol?
The active mechanism of Haldol is to block postsynaptic dopamine (D2) receptors in the mesolimbic system of the brain.
Can Haldol cause death?
How long does haloperidol stay in your system?
How often can haloperidol be given?
Is 5mg of Haldol a lot?
Does Haldol cause brain damage?
What are the main side effects of haloperidol?
How is haloperidol eliminated?
What should be monitored when taking haloperidol?
What is Haloperidol used for?
Haloperidol is a first-generation (typical) antipsychotic that is a commonly used drug worldwide. Haloperidol is used for positive symptoms of schizophrenia, such as hallucinations and delusions.
How to treat haloperidol toxicity?
Since there is no specific antidote, supportive treatment is the mainstay of haloperidol toxicity. If a patient develops signs and symptoms of toxicities, the clinician should consider gastric lavage or induction of emesis as soon as possible, followed by the administration of activated charcoal. Maintenance of Airway, Breathing, and circulation are critical factors for survival. A patent airway is ensured by using an oropharyngeal airway or endotracheal tube. Comatose patients with a difficult airway or upper airway obstruction require a tracheostomy. Supplemental oxygen is administered via nasal prongs or facemask. Patients with refractory hypoxia often require intubation and mechanical ventilation. Hypotension and circulatory collapse need aggressive treatment with intravenous fluids, concentrated albumin, and vasopressor agents such as norepinephrine or phenylephrine. Epinephrine should not be used as it can decrease blood pressure.
What are the symptoms of a haloperidol overdose?
Haloperidol overdose is also associated with ECG changes known as torsade de pointes, which may cause arrhythmia or cardiac arrest.
How often should you monitor haloperidol levels?
Blood levels should be monitored at 12-hour or 24-hour intervals or after the last dose of haloperidol use in a patient. Toxicity. Toxicities are the exaggerated symptoms of known pharmacologic effects and known adverse reactions.
What is the first generation of Haloperidol?
Haloperidol is a first-generation (typical) antipsychotic that is a commonly used drug worldwide. Haloperidol is used for positive symptoms of schizophrenia, such as hallucinations and delusions.
Is haloperidol a cholinergic drug?
Haloperidol is a first-generation (typical antipsychotic) which exerts its antipsychotic action by blocking dopamine D2 receptors in the brain. When 72% of dopamine receptors are blocked, this drug achieves its maximal effect.[11] Haloperidol is not selective for the D2 receptor. It also has noradrenergic, cholinergic, and histaminergic blocking action. The blocking of these receptors is associated with various adverse drug reactions. [12]
Is haloperidol a parenteral solution?
For oral administration, it is available as a tablet form and oral concentrate form. It is also available in a nasal spray formulation. Haloperidol lactate is used as a short-acting parenteral solution available for use intramuscularly and intravenously. Haloperidol decanoate is available for long-acting intramuscular preparation. [11]
What is a haloperidol?
Haloperidol is an antipsychotic medication that may be used in the treatment of schizophrenia and Tourette syndrome. Detrimental effects on cognitive function and movement-related side effects are common.
How does haloperidol work?
Interactions. 1. How it works. Haloperidol may be used to treat psychotic thoughts or symptoms. Experts aren't sure exactly how haloperidol works to reduce psychotic thoughts or symptoms or control tics in Tourette syndrome, but suggest it helps to rebalance neurotransmitters such as dopamine in the brain.
What medications interact with haloperidol?
Common medications that may interact with haloperidol include: antibiotics, such as erythromycin, isoniazid, quinupristin/dalfopristin, or rifampin. anticoagulants (blood thinners) such as apixaban, dabigatran, heparin, or warfarin. anticholinergics, such as scopolamine.
How long does it take for haloperidol to absorb?
6. Response and effectiveness. Haloperidol is absorbed quickly but it may take a few days to a few weeks for psychotic symptoms or symptoms of Tourette syndrome to abate.
Can you take haloperidol with a fever?
Your doctor may have to adjust your haloperidol frequently on initiat ion to find the right dose for you. Tell your doctor if you experience any unexplained fever, muscle rigidity or unusual muscle movements, agitation, irritability, anxiety, or other uncharacteristic mental disturbances while taking haloperidol.
Does haloperidol affect judgment?
Haloperidol may affect your judgment and impair your ability to drive or operate machinery. It may also increase your risk of falls. A 'one-dose fits all' dosage schedule does not apply to haloperidol. Your doctor may have to adjust your haloperidol frequently on initiation to find the right dose for you.
Can haloperidol cause tardive dyskinesia?
Haloperidol may cause tardive dyskinesia (potentially irreversible and untreatable, involuntary movements of the tongue, lips, face, trunk, and extremities). The risk is highest among elderly women, and with longer treatment durations or higher dosages. Because of this risk, the smallest effective dose of haloperidol should be used and ...
What is haloperidol used for?
It is used in the treatment of mania and in the short-term adjunctive management of severe anxiety, psychomotor agitation, excitement, and dangerous behavior. It may also be used in geriatric restlessness and agitation.
How is haloperidol released?
Haloperidol's production and use as an antidyskinetic and an antipsychotic may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams. If released to air, an estimated vapor pressure of 4.85 × 10−11 mmHg at 25 °C indicates haloperidol will exist solely in the particulate phase in the ambient atmosphere. Particulate-phase haloperidol will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. If released to soil, haloperidol is expected to have no mobility based on an estimated Koc of 5200. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based on an estimated Henry's law constant of 2.3 × 10 −14 atm m 3 mol −1. The p Ka of haloperidol is 8.66, indicating that this compound will exist primarily in the protonated form in the environment, and cations generally adsorb more strongly to organic carbon and clay than their neutral counterparts. If released into water, haloperidol is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based on the estimated Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based on this compound's estimated Henry's law constant. Haloperidol will exist almost entirely in the ionized form at pH values of 5–9, and therefore volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process. An estimated bioconcentration factor of 59 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is moderate. Hydrolysis is not expected to be an important environmental fate process since this compound lacks functional groups that hydrolyze under environmental conditions. Occupational exposure to haloperidol may occur through dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where haloperidol is produced or used. Users of haloperidol can be exposed through intravenous injection or oral consumption (tablets and liquid).
What happens if haloperidol is released into water?
If released into water, haloperidol is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based on the estimated Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based on this compound's estimated Henry's law constant.
What is the most widely used antipsychotic?
Haloperidol is one of the most widely used antipsychotic agents in psychiatry. This drug belongs to the butyrophenone class of agents, which have properties similar to the group 3 phenothiazines (e.g., fluphenazine ). Haloperidol is employed in the treatment of schizophrenia and other psychoses.
How long after haloperidol is blood drawn?
Blood samples were drawn repeatedly from an antecubital vein of the volunteers after the doses; and in a similar way from fasting patients in the morning before the first dose of drug, after at least one week of haloperidol treatment.
How long does it take for prolactin to decrease after haloperidol?
As to the reduction in plasma prolactin concentrations 5 and 10 h after treatment with haloperidol, it may be explained by the autoregulation of prolactin secretion (Voogt and Meites, 1973; Dang and Voogt, 1977 ).
Does haloperidol cause rash?
Haloperidol has been reported to have caused rashes.
Is haloperidol better than placebo?
Most studies used haloperidol doses in the range of 4–20 mg/day. Haloperidol was better than placebo for global improvement (table ⇓ ). 1 study reported no statistically significant difference between groups in the number of patients with reduced Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS) scores.
Is haloperidol good for schizophrenia?
In addition to quantifying long standing clinical impressions, this scholarly review by Joy et al reminds us of some sobering clinical facts about the treatment of schizophrenia. Although haloperidol was found to be superior to placebo for the treatment of schizophrenia, many people with the condition did not make an immediate nor complete recovery. Rates of extrapyramidal adverse effects were very high (put more bluntly, unacceptably high).
What is Haldol used for?
Haldol is an antipsychotic medicine that is used to treat schizophrenia. Haldol is also used to control motor and speech tics in people with Tourette's syndrome. Haldol may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide.
Can Haldol cause eye movement?
The longer you use Haldol, the more likely you are to develop this disorder, especially if you are a woman or an older adult. uncontrolled muscle movements in your face (chewing, lip smacking, frowning, tongue movement, blinking or eye movement);
Can Haldol cause heart problems?
Haldol can cause a serious heart problem. Your risk may be higher if you also use certain other medicines for infections, asthma, heart problems, high blood pressure, depression, mental illness, cancer, malaria, or HIV. Using Haldol with other drugs that make you drowsy can worsen this effect.
Can haloperidol cause hives?
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction: hives; difficult breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. High doses or long-term use of haloperidol can cause a serious movement disorder that may not be reversible.
Can you drink alcohol with haldol?
Drinking alcohol with Haldol can cause side effects. Avoid driving or hazardous activity until you know how this medicine will affect you. Your reactions could be impaired. Avoid getting up too fast from a sitting or lying position, or you may feel dizzy.
Is Haldol safe for dementia?
Haldol is not approved for use in older adults with dementia-related psychosis.
What is Haldol?
Haldol has active ingredients of haloperidol. It is often used in schizophrenia. eHealthMe is studying from 21,040 Haldol users for its effectiveness, alternative drugs and more.
What is Schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia (a mental disorder characterized by a breakdown of thought processes) is found to be associated with 1,006 drugs and 634 conditions by eHealthMe.
How to use the study?
You can discuss the study with your doctor, to ensure that all drug risks and benefits are fully discussed and understood.
How the study uses the data?
The study is based on haloperidol (the active ingredients of Haldol) and Haldol (the brand name). Other drugs that have the same active ingredients (e.g. generic drugs) are not considered. Dosage of drugs is not considered in the study neither.
Who is eHealthMe?
With medical big data and proven AI algorithms, eHealthMe provides a platform for everyone to run phase IV clinical trials. We study millions of patients and 5,000 more each day. Results of our real-world drug study have been referenced on 600+ peer-reviewed medical publications, including The Lancet, Mayo Clinic Proceedings, and Nature.
WARNING, DISCLAIMER, USE FOR PUBLICATION
WARNING: Please DO NOT STOP MEDICATIONS without first consulting a physician since doing so could be hazardous to your health.
How long does Olanzapine last?
Olanzapine is a powerful sedative with its effects lasting up to 24 hours.
How to treat rapid tranquilization?
Treatment choice for rapid tranquilization is dependent on a number of factors, including the patient’s presentation, the availability of drugs in a certain setting and the desired effect. The therapeutic endpoint of rapid tranquilization is a matter of debate and in clinical practice, three different approaches are common [2-3]. Certain clinicians consider it best to sedate the patient completely and prefer to increase the dosage of the drug until the patient is asleep. Others may opt for lighter sedation, which retains the patient’s ability to communicate. The final approach, which is also the most suitable for contemporary clinical practice, is to administer drugs at the lowest possible dose which calms the patient and leads to resolution of behavioral symptoms, if possible without inducing sedation or sleep [2-3]. If the initial tranquilization regimen is successful, the patient can be followed up with a regular psychiatric assessment [2-3]. Accounting for the fact that not all available drugs are conducive to all of the aforementioned treatment goals, it becomes obvious that deciding upon which drug to use and at what dosage should be influenced primarily by the stated purpose of the treatment. Suitable drugs include typical antipsychotics (often co-administered with an anticholinergic agent to reduce the incidence of side effects [4], benzodiazepines and, most recently, atypical antipsychotic drugs.
What is the treatment for agitation?
The practice of treating agitation on an acute care basis is also referred to as rapid tranquilization. A variety of psychotropic drugs and combinations thereof can be used. The decision is usually made based on availability and the clinician’s experience, with the typical antipsychotic haloperidol (alone or in combination with antihistaminergic and anticholinergic drugs such as promethazine), the benzodiazepines lorazepam, diazepam and midazolam as well as a variety of atypical antipsychotics being used for this purpose. Haloperidol is associated with extrapyramidal symptoms (which can be controlled by co-administration of promethazine) and may control agitation without inducing sedation, while benzodiazepines have a more pronounced sedating activity. The atypical antipsychotics aripiprazole and ziprasidone are better tolerated, while olanzapine is also a powerful sedative. Clinical trials evaluating the efficacy of different treatment options have been conducted but they are extremely heterogenous and most have numerous methodological flaws, leading to a poor overall quality of evidence upon which guidelines for the appropriate treatment could be based. The combination of haloperidol and promethazine, which combines the sedative properties of the antihistamine with the more selective calming action of haloperidol (with a reduced risk of extrapyramidal effects compared to haloperidol alone because of the anticholinergic properties of promethazine) may be the best choice based on empirical evidence.
Why do people use benzodiazepines?
Benzodiazepine use in the context of rapid tranquilization generally has the goal of calming the patient and ensuring adherence to follow- up treatment. Excessive sedation is generally regarded as an undesirable effect. Compared with antipsychotics such as haloperidol, benzodiazepines pose a far greater risk to the patient as they may cause respiratory depression in high doses, and may also contribute to dangerous drug interactions with other depressants which the patient may have been exposed to [23]. The risk of interactions is much greater when the patient presents to the emergency department with acute agitation, as his previous history is unknown and in many cases unobtainable until the situation is resolved, and for this reason drugs such as ketamine with a lower propensity for such interaction are preferred in the ER setting [24].
Is haloperidol dose dependent?
The drug saturates D2 receptors even at very low dosages, thus its effects are not dose-dependent [9].
Is haloperidol a selective drug?
It is by no means selective and may also bind to other receptors in the central nervous system (CNS), including a1 adrenergic and sigma receptors [5]. Its effects have been thoroughly documented in the literature. It is available both in oral and parenteral formulations (designed for intramuscular (IM) administration, though intravenous (IV) administration is also possible). When administered orally, the effects are noticeable within an hour, while 10-15 minutes are required for the onset of action after IM administration. For this reason, the IM route is preferred in the setting of rapid tranquilization [6].
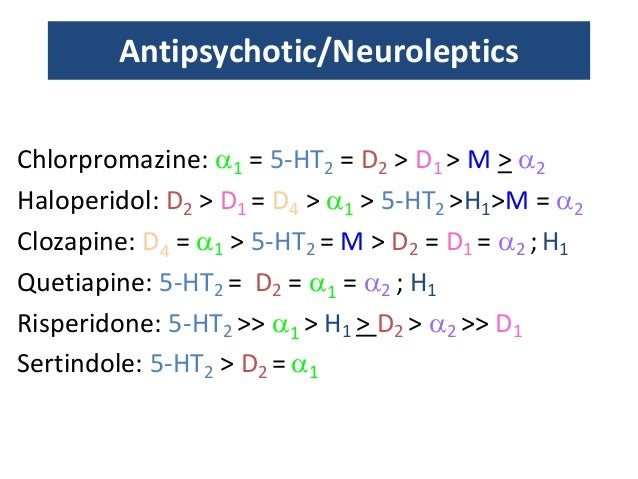
How It Works
- Haloperidol may be used to treat psychotic thoughts or symptoms. Experts aren't sure exactly how haloperidol works to reduce psychotic thoughts or symptoms or control tics in Tourette syndrome, but...
- Haloperidol belongs to the class of medicines known as butyrophenone antipsychotics. It may also be referred to as a typical, conventional, or miscellaneous antipsychotic.
Upsides
- May be used in the treatment of schizophrenia.
- May help control tics and vocal utterances of Tourette syndrome. Some studies have reported a 78-91% reduction in tics.
- Available as oral tablets and as an injection. The injection is not approved for intravenous administration.
- May be used in the treatment of schizophrenia.
- May help control tics and vocal utterances of Tourette syndrome. Some studies have reported a 78-91% reduction in tics.
- Available as oral tablets and as an injection. The injection is not approved for intravenous administration.
- Generic haloperidol is available.
Downsides
- If you are between the ages of 18 and 60, take no other medication or have no other medical conditions, side effects you are more likely to experience include: 1. Extrapyramidal side effects such as akathisia (a feeling of inner restlessness), Parkinsonism (eg, mask-like face, restlessness, shuffling gait), blurred vision, breast discharge, constipation, dry mouth, dystonia (prolonged abn…
Bottom Line
- Haloperidol is an antipsychotic medication that may be used in the treatment of schizophrenia and Tourette syndrome. Detrimental effects on cognitive function and movement-related side effects are common.
Tips
- Take as directed by your doctor. Haloperidol is usually dosed two to three times daily.
- Avoid alcohol while taking haloperidol as it may contribute to the side effects of haloperidol including low blood pressure.
- Haloperidol may affect your judgment and impair your ability to drive or operate machinery. It may also increase your risk of falls.
- Take as directed by your doctor. Haloperidol is usually dosed two to three times daily.
- Avoid alcohol while taking haloperidol as it may contribute to the side effects of haloperidol including low blood pressure.
- Haloperidol may affect your judgment and impair your ability to drive or operate machinery. It may also increase your risk of falls.
- A 'one-dose fits all' dosage schedule does not apply to haloperidol. Your doctor may have to adjust your haloperidol frequently on initiation to find the right dose for you.
Response and Effectiveness
- Haloperidol is absorbed quickly but it may take a few days to a few weeks for psychotic symptoms or symptoms of Tourette syndrome to abate. The maximum effects are usually seen within four to six weeks.
Interactions
- Medicines that interact with haloperidol may either decrease its effect, affect how long it works for, increase side effects, or have less of an effect when taken with haloperidol. An interaction between two medications does not always mean that you must stop taking one of the medications; however, sometimes it does. Speak to your doctor about how drug interactions sh…
References
- Haloperidol [Package Insert]. Revised 05/2021. Cardinal Health https://www.drugs.com/pro/haloperidol.html
Further Information
- Remember, keep this and all other medicines out of the reach of children, never share your medicines with others, and use haloperidol only for the indication prescribed. Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances. Copyright 1996-2022 Drugs.com. Revision date: April 6, 2022. Medical Disclaimer