
About 20% of H. pylori treatment fails after initial treatment. Make sure that the patient is compliant with medications. Since the patient has failed an initial course of treatment, we will use an alternate regimen (triple or quadruple therapy) using a different combination of antibiotics for 14 days.
How to treat H pylori naturally at home without antibiotics?
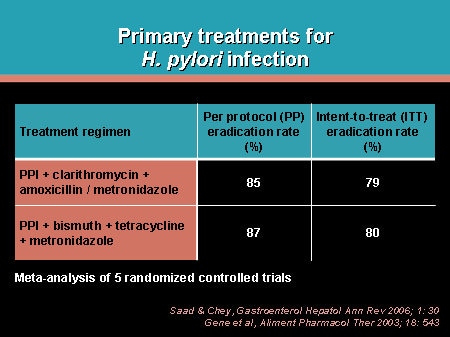
3 rows · Recommended regimens for patients who have failed treatment. Levofloxacin (250 mg), amoxicillin ...
What is a natural cure for H pylori?
Sep 21, 2008 · Thus, we prospectively evaluated 10 patients with three consecutive H pylori eradication failures (1st treatment with PPI-clarithromycin-amoxicillin, 2nd treatment with RBC-tetracycline-metronidazole, and 3rd treatment with PPI-amoxicillin-rifabutin). A fourth eradication regimen with 10 d levofloxacin, amoxicillin and PPI was prescribed, and intention-to …
How long does H pylori take to heal?
Aug 14, 2021 · Causes of h. pylori treatment failure: Poor compliance with the medications. Resistant h. pylori strains. Prior use of the prescribed anti-h. pylori antibiotics. For example, taking clarithromycin for another infection carries higher risk of h. pylori treatment failure. Inadequate suppression of stomach acid during the h. pylori treatment.
How to heal after H pylori?
Helicobacter pylori (H pylori) infection is the main cause of gastritis, gastroduodenal ulcer disease, and gastric cancer. After more than 20 years of experience in H pylori treatment, in my opinion, the ideal regimen to treat this infection is still …
What happens if antibiotics don't work for H. pylori?
When multiple treatment regimens fail, salvage therapy regimens such as bismuth or furazolidone quadruple therapy (a bismuth and tetracycline HCl 4 times a day along with a proton pump inhibitor twice a day, and either metronidazole 400 or 500 mg three times daily or furazolidone 100 mg three times daily for 14 days) ...
What is the second treatment for H. pylori?
The Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report recommends bismuth quadruple therapy, or fluoroquinolone-amoxicillin triple/quadruple therapy as the second-line therapy for H. pylori infection.Oct 28, 2018
How many times can you treat H. pylori?
Treatment for H. pylori infection is challenging. It usually involves taking a combination of three or four medications multiple times a day for 14 days.Apr 5, 2017
What causes H. pylori treatment failure?
The H. pylori treatment failure has been linked to infections with antibiotic resistant strains [13,14,15,16], host genetic polymorphism in the cytochrome that may affect proton pump inhibitor pharmacokinetics (CYP2C19), poor adherence, short duration of therapy and smoking [17,18,19].May 21, 2019
Can you still have H. pylori after treatment?
H pylori antibodies can remain present long after successful H pylori eradication. Biopsy-based testing including the rapid urease test or histology also can be used to document H pylori eradication.Jul 18, 2008
What is the third treatment for H. pylori?
Conclusion: Levofloxacin-based rescue therapy constitutes an encouraging empirical third-line strategy after multiple previous H. pylori eradication failures with key antibiotics such as amoxicillin, clarithromycin, metronidazole, and tetracycline.
What happens if antibiotics don't work?
When bacteria become resistant, the original antibiotic can no longer kill them. These germs can grow and spread. They can cause infections that are hard to treat. Sometimes they can even spread the resistance to other bacteria that they meet.
How long does it take to recover from H. pylori?
pylori treatment usually includes several medicines. At least two of the medicines are antibiotics that help to kill the bacteria. The other medication causes the stomach to make less acid; lower acid levels help the ulcer to heal. Most people are cured after finishing two weeks of medicine.Jul 6, 2020
How long do you need to retest after H. pylori?
Wait at least 8 weeks after eradication therapy before retesting for Helicobacter. Ensure that patient has not been taking antibiotics or PPI as outlined above to avoid false negative results. The faecal antigen test is nearly as good as the urea breath test in detecting failure of eradication therapy.
How often does H. pylori treatment fail?
However, even with the current most effective treatment regimens, about 10% of patients will fail a variety of treatments and remainH pylori positive. Patient compliance, bacterial resistance to antibiotics, and the components of the regimen should be assessed when retreatment is considered.
Can Helicobacter come back after treatment?
H. pylori infection recurred in two patients 6 months after eradication therapy, in seven 1 year after, and in one 2 years after. Thereafter, no further cases of H. pylori recurrence were observed.
How successful is H. pylori treatment?
Treatment with a PPI-CM regimen achieved an H pylori cure in 72% to 95% of patients with an overall efficacy of 82% (95% CI 76% to 88%) as shown in Figure 3 (13,16,18,21–23).
1. The Benefits you will get after H. pylori treatment
In 1994, The NIH consensus conference recognized H. pylori as a cause of gastric and duodenal ulcers. In the same year, International Agency for Research on Cancer Identified H. pylori as a risk factor for gastric adenocarcinoma (reference).
2. The next step after the H. pylori Treatment course
After you complete the 7-14 day course of h. pylori treatment, your doctor usually prescribes a proton pump inhibitor for another 4-8 weeks.
3. When and how your doctor will confirm the eradication
Your doctor will confirm the eradication fro H. pylori after at least four weeks after the end of the treatment course (reference).
4. Treatment failure rate (and its causes)
You should expect a 20% risk of failure of initial h. pylori treatment (reference). In such a case, Your doctor may attempt another course of h. pylori treatment (salvage therapy).
5. Symptoms of h. pylori treatment failure
The most important sign of a good h. pylori treatment is the resolution of your symptoms. The persistence of symptoms may indicate the failure of treatment.
How effective is triple therapy for H pylori?
PPI based triple therapy is significantly more effective for H pylori eradication than dual therapy consisting of two antibiotics or a PPI plus an antibiotic. 2 28 PPI given twice daily is significantly more effective than once daily in combination with clarithromycin and amoxicillin or nitroimidazole. 11 38 PPI based triple therapy may eradicate more H pylori infections when given for 10–14 days than for seven days. 39 Therefore, a good combination therapy should include full doses of medications, optimal dosing frequency, and adequate treatment duration.
What are the factors that contribute to treatment failure?
Several factors contribute to treatment failure. These include patient compliance, bacterial resistance to antibiotics, and treatment related issues. Treatment failure leads to the development of bacterial resistance to metronidazole and clarithromycin. Retreatment can be undertaken after considering several different strategies: to repeat ...
Is clarithromycin resistant to metronidazole?
Bacterial resistance to metronidazole or clarithromycin is an important factor leading to treatment failure. There is a good correlation between bacterial resistance to clarithromycin and eradi cation failure ; however, the clinical relevance of H pylori resistance to nitroimidazoles detected in vitro has been controversial. Some studies suggest that triple therapy consisting of a PPI, clarithromycin, and a nitroimidazole are effective at eradicating H pylori infection in patients harbouring metronidazole resistant strains 13-15; others show that the efficacy is significantly decreased when metronidazole resistance is present. 16-19 Several factors might have contributed to these differences, including different methods used for diagnosing metronidazole resistance, 20 21 different cut off values for determining the minimum inhibitory concentrations, 22 23 and probably different locations where biopsy samples were taken. 24 In patients who harbour metronidazole resistant strains, the eradication rate is about 30% lower than in those infected with metronidazole sensitive strains, when treated with bismuth, metronidazole, and tetracycline or amoxicillin triple therapy. 8 Although a PPI can overcome partially the impact of metronidazole resistance on H pylori eradication, 25 the eradication rate achieved with PAM in patients infected with metronidazole resistant strains is about 30% lower than in those who are infected with metronidazole sensitive strains. 8 23 26 27 A similar difference is also seen when patients are treated with the PMC combination. 8 28
Is H pylori cured?
H pylori infection was cured in 67% (6/9) of the evaluable patients. 40 This result suggests that retreatment of H pylori infection with the same combination is still a choice when the status of bacterial resistance to antibiotics is not known. However, full doses and a longer treatment duration must be used.
What is the treatment for H. pylori?
Phytotherapy is another treatment option that has been explored in research. Many compounds have shown promising anti-H.pylori effect. Micro and nano-technology is another area that has been researched to study its promise in treating and eradicating H.pylori infection.
What is the failure rate of Helicobacter pylori?
The failure rate of current treatment regimens is 25 percent to 40 percent as the bacterial resistance to clarithromycin and metronidazole has been growing steadily.
What are the best antibiotics for bacterial resistance?
In recent years, there has been ongoing research on developing many newer agents to overcome bacterial resistance to traditional drugs. Some of these agents are mentioned below: 1 Cathelicidins and defensins are human antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) and it has been shown that they limit H.pylori growth in mice. 2 Oligo-acyl-lysyl peptides are similar to AMPs structurally and functionally and their antibacterial effect and anti h.pylori effect have been documented. 3 SQ109 is another compound that has shown anti-H. pylori activity and has been shown to be safe in many trials. 4 Phytotherapy is another treatment option that has been explored in research. Many compounds have shown promising anti-H.pylori effect. 5 Micro and nano-technology is another area that has been researched to study its promise in treating and eradicating H.pylori infection.
What is the most common pathogen in humans?
Helicobacter pylori are one of the most common disease-causing pathogens in humans. According to some estimations, about 50 percent of the human population is infected with helicobacter pylori. There are differences in its prevalence geographically as it is more prevalent in developing countries than in the developed world.
How long does amoxicillin stay in your system?
This treatment regimen has been shown to improve eradication rates when it is extended to 14 days. There is ongoing research in this area and further studies may prove or refute its effectiveness against H.pylori infection.
What is Helicobacter pylori?
Image Courtesy of Yutaka Tsutsumi, M.D. Helicobacter pylori are involved in causing inflammation in the stomach and various diseases related to it. H.pylori causes stomach ulcers, stomach cancer, metaplasia and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), and other conditions like iron deficiency, vitamin B12 deficiency, ...
How long does levofloxacin last?
It is a combination of amoxicillin, a proton pump inhibitor, and levofloxacin. It is given for 10 to 14 days. Levofloxacin is an antibiotic that has a wide range of antimicrobial activity against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria including H.pylori.
