Drugs commonly recommended for simple UTIs include:
- Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra, others)
- Fosfomycin (Monurol)
- Nitrofurantoin (Macrodantin, Macrobid)
- Cephalexin (Keflex)
- Ceftriaxone
What are the safest antibiotics for UTI?
11 rows · May 28, 2021 · First-line antibiotics for UTIs include fosfomycin, nitrofurantoin and trimethoprim. ...
What is first line drug for UTI?
antibiotic use when selecting empiric therapy. Tailor therapy to culture results. Inpatient, uncomplicated 1st line therapy: Ampicillin* 50 mg/kg/DOSE IV q6h (max: 1 g/DOSE) + Gentamicin* 7.5 mg/kg/DOSE IV q24h (max initial: 300 mg/DOSE) Alternative for low/medium1-risk penicillin allergy, OR high-risk allergy3/contraindication4 to beta-lactam:
What are the first line antibiotics?
Guidelines for Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) in Adults Dosing Recommendations Antibiotic Dose* Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (160 mg/800 mg) 1 1 DS tablet po BID Nitrofurantoin1 100 mg po BID Fosfomycin 3 g dose (see tables for complicated and uncomplicated lower UTI) Amoxicillin-clavulanate1 875mg po BID
Can you use amoxicillin for UTI?
Apr 21, 2021 · Antibiotic treatment French guidelines issued by the French Language Infectious Pathology Society recommend sequential administration of fosfomycin, nitrofurantoin, and quinolones to treat cystitis, and third-generation cephalosporins to treat pyelonephritis [ 33 ].

What is a cystoscopy?
Cystoscopy allows your doctor to view your lower urinary tract to look for abnormalities, such as a bladder stone. Surgical tools can be passed through the cystoscope to treat certain urinary tract conditions. Male cystoscopy. Open pop-up dialog box. Close.
What is the first line of treatment for urinary tract infections?
Antibiotics usually are the first line treatment for urinary tract infections. Which drugs are prescribed and for how long depend on your health condition and the type of bacteria found in your urine.
What is urine culture?
Growing urinary tract bacteria in a lab. Lab analysis of the urine is sometimes followed by a urine culture. This test tells your doctor what bacteria are causing your infection and which medications will be most effective. Creating images of your urinary tract.
What kind of imaging is used to detect urinary tract infections?
If you are having frequent infections that your doctor thinks may be caused by an abnormality in your urinary tract, you may have an ultrasound, a computerized tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Your doctor may also use a contrast dye to highlight structures in your urinary tract.
How long does it take for a UTI to clear up?
Often, UTI symptoms clear up within a few days of starting treatment. But you may need to continue antibiotics for a week or more.
How to get rid of a urinary infection?
Avoid drinks that may irritate your bladder. Avoid coffee, alcohol, and soft drinks containing citrus juices or caffeine until your infection has cleared. They can irritate your bladder and tend to aggravate your frequent or urgent need to urinate.
Why do doctors ask for urine samples?
Your doctor may ask for a urine sample for lab analysis to look for white blood cells, red blood cells or bacteria. To avoid potential contamination of the sample, you may be instructed to first wipe your genital area with an antiseptic pad and to collect the urine midstream. Growing urinary tract bacteria in a lab.
Why are women more prone to UTIs than men?
Women are much more prone to UTIs than men, mainly due to the female lower urinary tract anatomy and its proximity to the reproductive organs.
What is OM-89?
OM-89 oral immunomodulatory treatment for the prevention of recurring UTIs is recommended both by the European Association of Urology (EAU) in uncomplicated UTIs in women (strong evidence, highest recommendation level, 1a) [12] and by the Polish Association of Urology in prevention of recurring urinary tract infections.
What are the factors that contribute to UTIs?
Factors conducive to UTIs in the perimenopausal period include urinary incontinence (impeding proper hygiene), atrophy of vaginal mucous membranes (increasing the risk of vaginal infections that may spread into the urinary tract), and anterior vaginal prolapse (precluding complete voiding of the bladder).
What is a UTI?
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common infections afflicting women. UTI often accompanies vaginal infections and is frequently caused by pathogens originating in the digestive tract. The paper discusses the prevalence of UTI in various patient populations, including postmenopausal, pregnant, diabetic, epileptic, ...
What is the prevalence of asymptomatic bacteriuria?
Prevalence of asymptomatic bacteriuria increases in the peri- and postmenopausal period, reaching levels of 4–19% as compared to 1.5% in premenopausal women [12]. In peri- and postmenopausal women, oestrogen deficiency may be conducive to both urinary incontinence and urinary tract infections.
How long does a urinary tract infection treatment last?
Outside of pregnancy, a 3-day treatment course is as effective as 5-day or 10-day courses. In older women , the treatment may continue for 3 to 6 days.
How often should you take a urine culture for cystitis?
In the case of cystitis in the patient’s history, repeat urine cultures should be taken every 1–2 months. Fluoroquinolones are contraindicated throughout the pregnancy, and co-trimoxazole should not be used in the first trimester. Conclusions. Urinary tract infection is one of the most common infections afflicting women.
What is the most common bacterial infection in women?
Urinary tract infections are the most common bacterial infections in women. Most urinary tract infections are acute uncomplicated cystitis. Identifiers of acute uncomplicated cystitis are frequency and dysuria in an immunocompetent woman of childbearing age who has no comorbidities or urologic abnormalities.
What imaging is used for cystitis?
Patients who present with atypical symptoms of acute uncomplicated cystitis and those who do not respond to appropriate antimicrobial therapy may need imaging studies, such as computed tomography or ultrasonography, to rule out complications and other disorders.
What is the first line of treatment for cystitis?
Guidelines recommend three options for first-line treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis: fosfomycin, nitrofurantoin, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (in regions where the prevalence of Escherichia coli resistance does not exceed 20 percent).
How long does it take for pyelonephritis to recur?
A urine culture is recommended for women with suspected acute pyelonephritis, women with symptoms that do not resolve or that recur within two to four weeks after the completion of treatment, and women who present with atypical symptoms. C. 11.
Why are beta-lactam antibiotics not recommended for initial treatment?
Beta-lactam antibiotics, amoxicillin/clavulanate, cefaclor, cefdinir, and cefpodoxime are not recommended for initial treatment because of concerns about resistance.
Does nitrofurantoin have a high in vitro activity?
Fosfomycin and nitrofurantoin have retained high rates of in vitro activity in most areas. 16. Because results of urine cultures are not routinely reported when treating acute uncomplicated cystitis, local resistance rates may not be available.
Can beta-lactam be used for cystitis?
Beta-lactam antibiotics are not recommended as first-line therapy for acute uncomplicated cystitis because of widespread E. coli resistance rates above 20 percent. Fluoroquinolone resistance usually is found to be below 10 percent in North America and Europe, but with a trend toward increasing resistance over the past several years. 16 To preserve the effectiveness of fluoroquinolones, they are not recommended as a first-tier option. Fosfomycin and nitrofurantoin have retained high rates of in vitro activity in most areas. 16
What is the 1.1.11 antibiotic?
1.1.11 Offer an immediate antibiotic prescription (see the recommendations on choice of antibiotic) for children and young people under 16 years with lower UTI. Take account of: previous urine culture and susceptibility results. previous antibiotic use, which may have led to resistant bacteria.
What age should I take antibiotics for pyelonephritis?
First choices for children aged 3 months and over. If there are symptoms of pyelonephritis (such as fever) or a complicated UTI, see the NICE guideline on acute pyelonephritis for antibiotic choices. If 2 or more antibiotics are appropriate, choose the antibiotic with the lowest acquisition cost.
How long should I take second choice for UTI?
Second choices (if no improvement in lower UTI symptoms on first choice taken for at least 48 hours, or when first choice is not suitable) If there are symptoms of pyelonephritis (such as fever) or a complicated UTI, see the NICE guideline on acute pyelonephritis for antibiotic choices.
How long should I take trimethoprim for pyelonephritis?
If there are symptoms of pyelonephritis (such as fever) or a complicated urinary tract infection (UTI), see the NICE guideline on acute pyelonephritis for antibiotic choices. Trimethoprim: 200 mg twice a day for 7 days.
What is the 1.1.16 UTI?
1.1.16 Refer people aged 16 years and over with lower UTI to hospital if they have any symptoms or signs suggesting a more serious illness or condition (for example, sepsis). 1.1.17 Refer children or young people with lower UTI to hospital in line with the NICE guideline on urinary tract infection in under 16s.
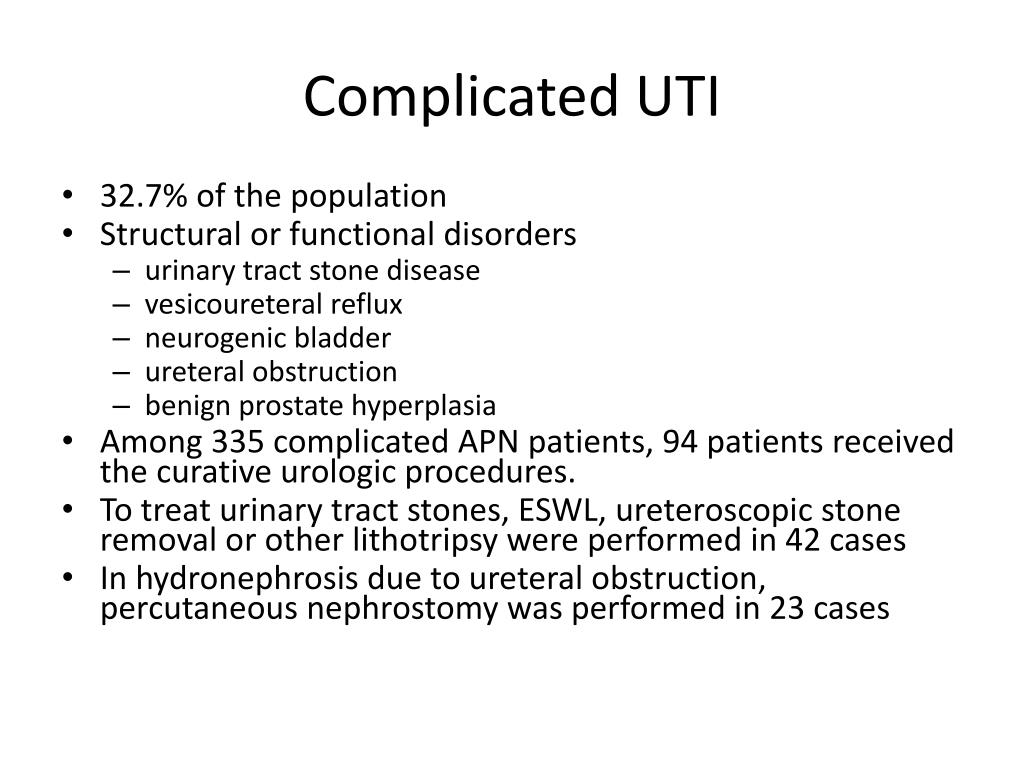
What is the risk of developing complications, which is higher in people with known or suspected structural or functional abnormality of the
the risk of developing complications, which is higher in people with known or suspected structural or functional abnormality of the genitourinary tract or immunosuppression. the evidence for back-up antibiotic prescriptions, which was only in non-pregnant women with lower UTI where immediate antibiotic treatment was not considered necessary.
What is asymptomatic bacteriuria?
1.2.1 Be aware that asymptomatic bacteriuria: is significant levels of bacteria (greater than 10 5 colony forming units/ml) in the urine with no symptoms of UTI. is not routinely screened for, or treated, in women who are not pregnant, men, young people and children.
What are the symptoms of UTI in newborns?
In infants and young children, typical signs and symptoms include fever, strong-smelling urine, hematuria, abdominal or flank pain, and new-onset urinary incontinence.
How common is UTI in children?
Acute UTIs are relatively common in children. By seven years of age, 8 percent of girls and 2 percent of boys will have at least one episode. 1 In a study of infants presenting to pediatric emergency departments, the prevalence of UTI in infants younger than 60 days with a temperature greater than 100.4°F (38°C) was 9 percent.
What is the best antibiotic for UTI?
The recommended initial antibiotic for most children with UTI is trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra). Alternative antibiotics include amoxicillin/clavulanate (Augmentin) or cephalosporins, such as cefixime (Suprax), cefpodoxime, cefprozil (Cefzil), or cephalexin (Keflex).
How old do you have to be to get a urinary tract infection?
Clinical signs and symptoms of a urinary tract infection depend on the age of the child, but all febrile children two to 24 months of age with no obvious cause of infection should be evaluated for urinary tract infection (with the exception of circumcised boys older than 12 months).
What is the most sensitive test for UTI?
Dipstick tests for UTI include leukocyte esterase , nitrite, blood, and protein. Leukocyte esterase is the most sensitive single test in children with a suspected UTI. The test for nitrite is more specific but less sensitive.
How long does it take to cure pyelonephritis?
19 – 21. Children with acute pyelonephritis can be treated effectively with oral antibiotics (e.g., amoxicillin/clavulanate, cefixime, ceftibuten [Cedax]) for 10 to 14 days or with short courses (two to four days) of intravenous therapy followed by oral therapy.
What is the most common pathogen in children?
The most common pathogen is Escherichia coli, accounting for approximately 85 percent of urinary tract infections in children. Renal parenchymal defects are present in 3 to 15 percent of children within one to two years of their first diagnosed urinary tract infection. Clinical signs and symptoms of a urinary tract infection depend on the age ...
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Antibiotics usually are the first line treatment for urinary tract infections. Which drugs are prescribed and for how long depend on your health condition and the type of bacteria found in your urine.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Urinary tract infections can be painful, but you can take steps to ease your discomfort until antibiotics treat the infection. Follow these tips: 1. Drink plenty of water.Water helps to dilute your urine and flush out bacteria. 2. Avoid drinks that may irritate your bladder.Avoid coffee, alcohol, and soft drinks containing citrus juices or caffeine until your infection has cleared. They can irrit…
Alternative Medicine
- Many people drink cranberry juice to prevent UTIs. There's some indication that cranberry products, in either juice or tablet form, may have infection-fighting properties. Researchers continue to study the ability of cranberry juice to prevent UTIs, but results are not conclusive. If you enjoy drinking cranberry juice and feel it helps you prevent UTIs, there's little harm in it, but w…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Your family doctor, nurse practitioner or other health care provider can treat most urinary tract infections. If you have frequent recurrences or a chronic kidney infection, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in urinary disorders (urologist) or kidney disorders (nephrologist) for an evaluation.