Explore
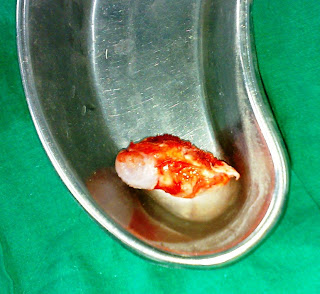
If the cause of exostosis is surfer’s ear, a surgeon can remove the bone in order to give you more comfort and restore hearing. Subungual exostosis — treatment for this type is surgical excision and is very effective. It is done under local anesthesia and once the growth is removed the underlying bone is scraped clean to prevent it from recurring.
What is exostosis and how is it treated?
With dorsal exostosis of the big toe in order to improve foot function you need to do stretching exercises, correct the biomechanics that caused the problem, and orthotics. Any of these will ease the stress on the big toe joint. Again, if non-surgical treatment does not work then you may need surgery to clean the big toe joint up.
What is the treatment for dorsal exostosis of big toe?
Retrocalcaneal exostosis — how it is treated will depend on the severity of the pain. To help with the inflammation of the tendon you may be given a prescription for steroids or an oral NSAID. You may also be given a prescription for an adhesive pain patch or pain gel that you can apply to the back of your heel.
What is the treatment for retrocalcaneal exostosis?
In this type of exostosis, there is an abnormal growth of the bone that forms the sinus cavity. Often you feel no symptoms. But sometimes, even a small growth can cause a lot of pain. The bone growth can block your sinus from draining properly, causing congestion. It may also cause pain by putting pressure on a nearby nerve.
What is sinus exostosis?
How is exostosis treated?
The treatment for hereditary multiple exostosis is surgical removal of any growths that are causing pain or discomfort, or disrupting the child's movement.
Can exostosis be removed?
An exostectomy is the surgical removal of a bony prominence / outgrowth (exostosis). The aim of the surgery is to remove the bony prominence and reduce pain and deformity as a result.
Is exostosis surgery painful?
Exostosis, also called osteoma, is a benign growth of new bone on top of existing bone. It can occur in many parts of the body. When the exostosis is covered with cartilage, it's called an osteochondroma. Exostosis can be painless, or it can cause severe pain and require surgical removal.
Is exostosis a tumor?
What is an osteochondroma? Osteochondroma is the most common type of non-cancerous (benign) bone tumor. An osteochondroma is a hard mass of cartilage and bone that generally appears near the growth plate (a layer of cartilage at the ends of a child's long bones).
How can exostosis be prevented?
The best way to prevent the development or progression of exostosis is to use earplugs while swimming or surfing in ocean waters. At ChEARS Hearing Center, we offer custom earplugs for surfers and swimmers.
Where is exostosis located?
An exostosis, also called a bony spur or osteoma, occurs when a bony growth extend beyond a bone's usual smooth surface. Exostosis can cause chronic pain or irritation, depending on its size and location. Sometimes, cartilage will grow over an area of exostosis, which is called osteochondroma.
Can exostosis cause hearing loss?
External auditory canal (EAC) exostoses are multiple, benign bony growths within the external auditory canal in response to repeated exposure to cold water. They can cause conductive hearing loss and recurrent otitis externa [1].
What causes extra bone growth?
Osteochondroma is an overgrowth of cartilage and bone that happens at the end of the bone near the growth plate. Most often, it affects the long bones in the leg, the pelvis, or the shoulder blade. Osteochondroma is the most common noncancerous bone growth. It most often occurs between ages 10 and 30.
What is the difference between exostosis and osteoma?
Conclusions: Osteomas are benign tumours leading to obstruction of the external auditory canal. Exostosis is the overgrowth of the external auditory canal's compact bone in adults. Osteomas and exostoses may lead to hearing loss.
Should I do surgery for osteochondroma?
Most of the time, an osteochondroma does not require surgery. If the tumor causes pain, it can be removed by surgery.
How do you dissolve bone spurs naturally?
How to dissolve bone spurs naturally1 – Stretching. Stretching your toes, feet, and ankles can alleviate pressure and strain whether you experience a toe bone spur or a heel bone spur. ... 2 – Footwear. ... 3 – Ice packs. ... 4 – Vitamins and supplements. ... 5 – Massage therapy.
What causes extra bone growth?
Osteochondroma is an overgrowth of cartilage and bone that happens at the end of the bone near the growth plate. Most often, it affects the long bones in the leg, the pelvis, or the shoulder blade. Osteochondroma is the most common noncancerous bone growth. It most often occurs between ages 10 and 30.
What is the difference between exostosis and osteoma?
Conclusions: Osteomas are benign tumours leading to obstruction of the external auditory canal. Exostosis is the overgrowth of the external auditory canal's compact bone in adults. Osteomas and exostoses may lead to hearing loss.
What is the difference between exostosis and osteochondroma?
The inherited condition is called hereditary multiple osteochondromas or hereditary multiple exostoses (an exostosis is an external outgrowth of bone). Multiple osteochondromas are also noncancerous, but they pose a greater chance of complications, usually by interfering with the normal growth of your bones.
How do doctors diagnose exostosis?
A doctor will diagnose exostosis by taking a medical history and considering a person’s symptoms. They will take into account the individual’s age, hobbies, and if they have a family history of exostosis.
Where does exostosis develop?
They may also develop around the skull, including inside the mouth and sinuses. Children and young adults are more likely to experience exostosis. In this article, we look at the different types of exostosis, their causes, symptoms, and treatments. We also look at how this condition is diagnosed and possible complications.
What is the condition where the jaw is enlarged?
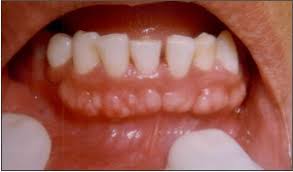
Mouth or jaw. This form of exostosis is a rare condition that causes bony growths from the jaw, usually inside the mouth in the back of the teeth. They are often the result of some trauma or injury to the gums and bones underneath. Exostosis of the mouth or jaw is called buccal exostosis.
What is the term for a tumor that grows under the nail bed?
Exostosis of the nail bed is when a type of bony tumor grows underneath the nailbed. It can be caused by an earlier injury or infection and most commonly affects the big toe. Children and young adolescents are most likely to have this condition. Exostosis of the nail bed is called subungual exostosis.
Can you have exostosis without symptoms?
Some people who have exostosis may have no symptoms at all. They may not be aware of their exostosis until they have an X-ray for another condition, and a doctor identifies an area of bony growth.
Is exostosis pedunculated or sessile?
limbs of different lengths. Exostosis can be either sessile or pedunculated: Sessile exostoses: This type is broad and fixed to the bone. Pedunculated exostoses: These are connected to the bone by a narrow stem.
Is surgery necessary for exostosis?
While treatment is often unneccesary, surgery may be required in the case of severe exostosis. In many cases, no treatment is necessary. If treatment is required, the type of intervention will depend on the location and severity of the exostosis.
How to treat exostosis?
There are some things you can do at home to help, like: Apply ice to help with swelling. Take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen. Use shoe inserts for bone spurs in your feet.
What is the genetic cause of multiple exostosis?
Hereditary multiple exostosis. This type of exostosis, also called diaphyseal aclasis, occurs in children. Caused by a genetic disorder, it's usually diagnosed around the age of 3 or 4. The gene for hereditary multiple exostosis affects bone growth and causes multiple exostoses to form.
What is the term for an extra growth of bone that extends outward from an existing bone?
An exostosis is an extra growth of bone that extends outward from an existing bone. Common types of exostoses include bone spurs, which are bony growths also known as osteophytes. An exostosis can occur on any bone, but is often found in the feet, hip region, or ear canal.
Why do exostoses grow bigger?
The exostoses become bigger as children grow but will stop developing once they reach adulthood. External auditory exostoses. Also called surfer's ear, this type of exostosis is caused by chronic cold water exposure. It's a buildup of bone growth in the external ear canal.
Can exostosis cause pain?
Many people with exostosis don' t have any symptoms. The bone growths themselves don't cause pain, but they can cause problems when they put pressure on nearby nerves, limit your movement, or cause friction by rubbing against other bones or tissues. When symptoms do happen, they can include: Pain near the joint.
Can you get exostosis over 60?
Exostoses develop over time, usually in people with joint damage from arthritis. They are most common in people over 60, but young people can get them, too, especially athletes. Most people with an exostosis don't have symptoms, but it can cause pain in certain situations.
Why do exostoses need to be cleaned?
Other exostoses can trap skin debris in the canal and require routine cleaning in the ear doctor's office to prevent infections. In some cases, large exostoses require surgery to remove the bony overgrowths, and reconstruct the ear canal.
Can you get exostosis from cold water?
Exostoses are most commonly found in people with a history of cold water exposure. However, these bony overgrowths can also occur in people with no prior water history. Multiple smooth, round, bony overgrowths are seen, and often in both ears.
What is the cause of exostosis?
The exostoses are a result of dysplasia in the peripheral part of the growth plate. The bones that are most commonly affected are the lower femur, upper tibia (i.e., around the knee), and upper humerus but may also be found in other bones like the scapula and ilium where they can be missed clinically 14).
Where does exostosis occur?
Exostosis has accounted for 50 % of primary benign bone tumors and has been observed to occur at the metaphysis of long bones or originate from the surface of flat bones 2). Exostosis generally occurs at the proximal femoral or distal tibial metaphysis 3) .
What is retrocalcaneal exostosis?
Retrocalcaneal exostosis also known as Haglund’s deformity, was first described in 1928 by Patrick Haglund 51), is a chronic enlargement of the posterior-superior prominence of the calcaneum, where there is a bony enlargement at the attachment of the Achilles tendon 52). Retrocalcaneal exostosis is a normal anatomical variant often referred to as the Mulholland deformity or ‘pump bump’ as adjoining soft tissues can get irritated when this bony lump rubs against rigid shoes especially by footwear with rigid backs such as pumps leading to insertional Achilles tendinitis 53). Retrocalcaneal exostosis often leads to retrocalcaneal bursitis, calcaneal tendon bursitis, and thickening and inflammation of the calcaneal tendon. This combination of pathology is known as Haglund’s syndrome. Inflammation of the different parts of soft tissue in the area can lead to an isolated condition; however, the treatment options are different in these conditions, and so they should be differentiated.
What is subungual exostosis?
A subungual exostosis is a rare and benign bony overgrowth that is permanently attached to the tip of the toe 39 ). It was first described by Dupuytren, who observed subungual exostosis on toes; Hutchinson later reported subungual exostosis on fingertips 40). The pathology of subungual exostosis differs from that of osteocartilaginous exostoses. Subungual exostosis usually involves the overgrowth of normal bone, which may occur beneath the toenail or on the side of the toe, and can obstruct nail growth 41). While chronic irritation is thought to be the cause of metaplasia in fibrocartilage, the pathogenesis remains unknown. According to the literature, trauma, chronic infection, tumor, hereditary anomalies and the activation of a cartilaginous cyst are all possible causes 42). Some studies have reported that trauma is the main contributing factor in the development of subungual exostosis, with subsequent acute and chronic inflammation causing cartilaginous metaplasia 43). An alternative view is that chronic infection is the result and not the cause of subungual exostosis 44).
Where is subungual exostosis most commonly diagnosed?
Subungual exostosis is most commonly diagnosed in children and young adults; most of these lesions are located in the big toe, although they can occur (albeit infrequently) in other toes 45). Only a small percentage of these lesions occur in the fingers 46).
Where is the buccal exostosis located?
Buccal exostoses are benign bilateral, smooth surface growth occurring on the outer or facial surface of the maxilla and less commonly, the mandible, found usually in the premolar and molar region 62 ).
What is hereditary multiple exostoses?
Hereditary multiple exostoses is a rare autosomal dominant skeletal disorder with almost complete penetrance (95%) due to loss of functional mutations in two genes: exostosin-1 (EXT-1) and exostosin-2 (EXT-2) genotypes 8). Hereditary multiple exostoses is manifested by skeletal deformities caused by abnormal bone growth 9).
What causes exostosis in the ear?
This is caused by frequent flooding of your ear with cold water.
What is the best treatment for metatarsal cuneiform exostosis?
Metatarsal cuneiform exostosis — the best treatment is to wear shoes that put no pressure on the bony bump. These can include low cut dress shoes, flip-flops, or sandals. You can also use a tongue pad to create a small area on the underside of the shoe tongue to relieve pressure on the bump.
Where does subungual exostosis occur?
Subungual exostosis. This type of exostosis involves your fingers and toes. They usually arise from the dorsal, or back, surface of your distal fingers or toes. This means outermost bone on your toe or finger. You will normally find them growing under the nail, especially your toenail of the big toe.
What is the name of the condition where the jaw is facing the upper jaw?
Buccal exostosis. This type of exostosis involves your jawbone. In this case your lower jaw will be more prone than your upper jaw. It forms on your outer cheek facing the side of your upper jaw just above your teeth. It could also affect the cheek-facing side of your lower jaw.
Can you have surgery for a big toe?
Having surgery would be the final treatment if nothing else works or the pain becomes unbearable. With dorsal exostosis of the big toe in order to improve foot function you need to do stretching exercises, correct the biomechanics that caused the problem, and orthotics.
Can osteochondroma be removed?
With osteochondroma, this non-cancerous tumor can be removed or left in place. It all depends on whether it interferes with your quality of life. If the cause of exostosis is surfer’s ear, a surgeon can remove the bone in order to give you more comfort and restore hearing.
Can exostosis cause pain?
Exostosis Symptoms. Other than it could become painful the symptoms that exostosis might cause would be related to the cause. The pain a person feels from having any form of exostosis can range from mild to debilitating severe. The pain depends on where the exostosis is located, the size, and shape. Surfer’s ear – with this cause, which is ...
Why does exostosis occur?
Age is another common reason for Exostosis to occur. Cartilage, the tissue that cushions the end of bone inside the joints, breaks down during the aging process. As it continues to wear away, a person can develop osteoarthritis. This is also a factor in the discs of the spine.
What is the best treatment for bone spurs?
An effective bone spur treatment is EPAT Therapy, a non-invasive method for increasing the speed of healing and limiting bone spur-related downtime. EPAT Therapy is also known as Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) and it is quickly becoming a popular method of treating a wide number of sports-related injuries.
Is EPAT therapy a surgical procedure?
Because EPAT Therapy is non-s urgical, there is no anesthesia necessary, no scarring, and no risk of infection. In some cases, athletes or workers can actually undergo treatment sessions for bone spurs or exostosis while still maintaining high levels of performance and continuing their normal routine.
What is Exostosis?
An exostosis is a benign or non-cancerous growth of bone on top of other bone. An example of exostosis is a bone spur, also known as an osteophyte. Exostosis is among the most common non-cancerous tumors that affect the bone — 3% of people have one or more.
What Causes Exostosis?
An exostosis can form at a site on a bone that was previously injured, or it can arise from chronic irritation to a bone. There is also a hereditary form of exostosis — called hereditary multiple exostoses — passed down from parent to child. With this type, the bony growths usually appear during childhood and there may be many of them.
Risk Factors for Exostosis
People who have had an injury to a bone or have joint damage from arthritis are at higher risk of developing one or more exostoses.
Symptoms of Exostosis
Common symptoms of exostosis include intermittent pain, stiffness, or limitation of movement in the area of the growth. If the exostosis pushes on a nerve, it may cause numbness or tingling. Some people can feel the bony overgrowth as a lump or thickening when they press on the area.
Diagnosis
Doctors can sometimes diagnose exostosis based on physical examination. They may recommend imaging studies, such as an x-ray. More advanced imaging, such as CT scans or MRI, can provide a detailed look at the bone. In some cases, exostosis shows up on a routine x-ray in a person with no symptoms.
Treatment of Exostosis
Unless exostosis is causing symptoms, many people don't require any treatment for their growths. For painful exostoses, a doctor may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications to reduce inflammation and tenderness.
Home Therapy
Applying ice to areas that are tender or swollen may decrease pain and tenderness when symptoms flare up. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications are also effective for reducing pain and inflammation, but patients should always speak with their doctor before taking new medications.
Overview
A bone island is a small, dense boney growth that can develop in another section of bone.
Symptoms and Causes
Experts are unsure what causes bone islands. They may be present at birth (congenital) or may develop over time.
Diagnosis and Tests
Healthcare providers usually discover a bone island by accident. Often, they’re taking an X-ray or CT scan for a completely different reason and notice the bone island. They can tell it’s a bone island by the shape, type of bone and density of the tissue.
Management and Treatment
You don’t need any treatment for your bone island unless it’s causing you pain. If you’re in pain, your healthcare provider might order a repeat imaging study like a CT scan to see if your bone island has grown. If it gets larger by 50% in one year or 25% in six months, your healthcare provider might do a biopsy (retrieve a sample) of your tissue.
Prevention
Neither you nor your healthcare provider can prevent a bone island. But a bone island causes no harm. There’s no reason to try preventing one.
Living With
You don’t need to do anything about your bone island. There aren’t any treatments.
Frequently Asked Questions
Bone islands are benign, which means they aren’t cancerous. Talk to your healthcare provider if you’re concerned about cancer or other conditions.
How to treat exostosis in mouth?
Treatment for Exostosis in your Mouth. If your exostosis is one of the rare growths in which treatment is recommended, it can be removed in a dental professional's office – usually by an oral surgeon. Using local anesthesia (numbing the specific area around a surgical operation), the surgeon will make an incision and lift ...
How to practice oral hygiene with exostosis?
How to Practice Good Oral Hygiene With an Exostosis. As always, practice good oral hygiene by brushing at least twice a day. Floss or clean between your teeth with interdental brushes or water flossers at least once a day, and use antimicrobial mouthrinses and tongue scrapers.
Where is exostosis found in the mouth?
The most commonly occurring bone growths are found in the mouth's roof ( torus palatinus) and beneath the tongue ( torus mandibularus ).
When do exostoses appear in mouth?
It's common for people to have exostoses in their mouths for years before they even notice they are there.
Can exostosis cause problems?
Issues and Treatment for Exosto sis Mouth. Although these growths are benign, occasionally they can cause problems, especially if they become large enough to interfere with functions of the mouth. TM, if very large, can inhibit proper speaking, and all types of exostosis can interfere with denture placement.
Can exostosis interfere with dentures?
Also, if you have missing teeth and are considering dentures, all types of exostosis can potentially interfere with the placement of your artificial teeth. Some people may want a growth removed due to aesthetic concerns.
Can you have an exostosis without surgery?
There are rare circumstances when exostoses have interfered with oral function or denture placement and have required surgery, but that is not the norm. Most often, by practicing good oral hygiene, your mouth can be as healthy as if you had no exostoses at all.