What is the maximum number of ECT treatments?
ECT is given as a course of treatments. A common course of ECT consists of 2 to 3 treatments a week for 2 to 7 weeks. The total number of treatments needed depends on how severe the person’s symptoms are and how quickly they improve. Many people with depression begin to notice some improvement after two or three ECT treatments.
How many ECT treatments does it take to work?
Apr 10, 2022 · Continuation ECT is electroconvulsive therapy continued for approximately the six months following the initial index series. 1 Continuation ECT involves a treatment once every 1-6 weeks. 2 Continuation ECT is typically used for patients who have initially positively responded to ECT and can give informed consent for its further use. Often those who do not respond to …
How effective is ECT therapy?
ECT is there-fore often the first-line treatment in an emergency, especially when a person is suicidal, psychotic, not eating, or catatonic (immobile). Some 100,000 Americans undergo ECT treatments each year. Deciding whether ECT is a good treatment option for you or a loved one—and whether it should
Is ECT worth it?
It is recommended that during ECT treatment the following information be documented: 1) Treatment notes, entered at least every two treatments, by the attending physician or designee noting therapeutic response and any substantive change.

How often do you need ECT?
HOW MANY TIMES WILL I NEED TO BE TREATED? People undergoing ECT need multiple treatments. The number needed to successfully treat severe depression can range from 4 to 20, but most people need a total of 6 to 12 treatments. The treatments are usually given three times a week — Monday, Wednesday, and Friday.7 Apr 2021
How long is ECT good for?
Maintenance ECT involves getting treatments every two weeks to every month, usually for a period of six months to a year. But patients have gone on maintenance ECT for up to three years, depending on their response.27 Feb 2008
Can ECT be done twice?
Conclusions: ECT twice a week is an effective schedule for clinical practice and is potentially advantageous in view of a therapeutic outcome identical to that of ECT three times a week and less severe cognitive effects.
Does ECT damage the brain?
Despite many scientific and governmental authorities having concluded that ECT does not cause brain damage, there is significant evidence that ECT has indeed caused brain damage in some patients, both historically and recently, and evidence that it always causes some form or degree of brain damage.
Do you have to do ECT forever?
The ECT taper from an acute series to a maintenance schedule is generally once a week for 4 treatments, then every 2 weeks for 4 treatments, then every 3 weeks for 4 treatments, then every 4 weeks. There is no limit on how long a patient can receive maintenance ECT provided the treatment is effective.
How do you prevent relapse after ECT?
The Royal College of Psychiatrists' current ECT handbook states that “relapse rates are high after remission is achieved in depression, and antidepressants reduce the risk of relapse by about 70%” and that “the combination of lithium/antidepressant may reduce the risk of relapse after ECT.”
What happens when ECT doesn't work?
If nothing else has helped, including ECT, and you are still severely depressed, you may be offered neurosurgery for mental disorder (NMD), deep brain stimulation (DBS) or vagus nerve stimulation (VNS).
Who is ECT Not recommended for?
ECT is not recommended for ongoing management of schizophrenia, or as a routine treatment for mild to moderate depression. You can read full guidelines on the NICE website for using ECT to treat catatonia, mania or schizophrenia, and as one of the treatments for moderate or severe depression.
How long does ECT last?
Generally, ECT is a short-term treatment where the patient receives 6-12 treatments over the course of 2-4 weeks. However, in some cases, continuation ECT or maintenance ECT is used. These two therapies continue ECT beyond the initial 6-12 sessions used in acute treatment.
Why do people need ECT?
Maintenance ECT: Why Some People Need Continuation ECT. Electroconvulsive therapy, once known as shock therapy, is a safe and effective treatment for depression and other mental illnesses. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is most often used in cases of severe, intractable, hard to treat (treatment-resistant) depression.
What is maintenance ECT?
Maintenance ECT consists of ECT treatments given infrequently over a long period of time after the index series and continuation ECT. The goal of maintenance ECT is to prevent the reoccurrence of the mental illness.
Can ECT cause relapse?
Relapse after a positive response to ECT is common. Most frequently, prevention of relapse is accomplished through the use of medication but continuation ECT has also been shown effective for the prevention of illness relapse.
How long does it take for ECT to work?
ECT works much faster than medications. On average, ECT takes two tothree weeks to take effect. By contrast, medications usually take six to eightweeks for improvements to become apparent.
What is consent before ECT?
Before the first ECT treatment, a patient will have a thorough psychiatricevaluation as well as a complete physical exam. The patient must also signinformed consent documents authorizing the use of ECT. “Consent” meansthat you understand the procedure as well as its risks and benefits. (See pages33–35 to review the informed consent forms we use at Johns Hopkins.)
How long does it take for a patient to wake up after a syringe?
Patients awaken three to five minutes after the treatment is over. For any-where from five to 45 minutes, patients may experience a period of acute post-treatment delirium. They are typically very confused, and some experienceheadache, muscle stiffness, and disorientation.
Who is Irving Reti?
Irving M. Reti, M.B.B.S., is the director of the Electroconvulsive Therapy Service at TheJohns Hopkins Hospital and an assistant professor in the Department of Psychiatry andBehavioral Sciences at The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. He has receivednumerous honors in his distinguished career, including The Johns Hopkins UniversitySchool of Medicine Clinician Scientist Award, and his research work is funded by theNational Institutes of Health. His research papers have been published in such medicaljournals asNeuropsychopharmacology, the Journal of Neurochemistry, and theEuropean Journal of Neuroscience.
What is HRQOL in medical terms?
Health-related quality of life (HRQOL) is a measure of a person’s perceivedphysical and mental health over time. People with major depression sufferfrom poorer HRQOL than people with hypertension, arthritis, angina, orother common medical conditions. Not surprisingly, HRQOL is especiallycompromised in severely depressed patients who are referred for ECT.
What are the guidelines for ECT?
Guidelines: Providers should assure review of medical conditions that may substantially increase risk during the delivery of ECT. A medical history and physical examination are essential before prescribing of ECT to determine risk factors and minimize risks.
What are the side effects of intubation?
The treatment area should contain resources for maintaining an airway for an extended period and for intubating patients if indicated. Headache, muscle soreness, and nausea: The recognition of these systemic side effects should be addressed and include symptomatic treatments that may be considered.
Is ECT a pharmacologic treatment?
Pregnant women and nursing mothers may receive ECT during all trimesters of pregnancy, puerperium and nursing. ECT may be less risky than alternate pharmacologic treatment or non-treatment of mental illness during pregnancy.
How long does an ECT last?
A single ECT session usually lasts one hour. This includes the time the patient will be in the treatment room (approximately 15-20 minutes) and the time spent in the recovery room (approximately 20-30 minutes). Typically, ECT (whether inpatient or outpatient) is given two to three times a week for a total of six to twelve sessions.
How does ECT work?
Why does ECT work? No one is sure how ECT helps certain psychiatric disorders. It may promote changes in how brain cells communicate with each other at synapses and it may stimulate the development of new brain cells. ECT may flood the brain with neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which are known to be involved in conditions like ...
What are the side effects of a syringe?
The immediate side effects of the procedure which may last for about an hour include: 1 Headaches 2 Nausea 3 Muscle aches and soreness 4 Disorientation and confusion
What is ETC therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ETC), uses electricity to stimulate the brain to produce a seizure. ECT has been found to decrease and relieve depression and other mental health symptoms.
Does ECT work for depression?
If other forms of treatment have not been helpful, often ECT will work. When medicines to treat depression have not helped or if you can’t use them, you may try ECT. ECT may also be used for psychosis, mania, or catatonia when other forms of treatment have not helped.
What is ECT therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy ( ECT) is utilized worldwide for various severe and treatment-resistant psychiatric disorders. Research studies have shown that ECT is the most effective and rapid treatment available for elderly patients with depression, bipolar disorder and psychosis.
When is C-ECT required?
C-ECT may be required in the first 6 months after a remission with acute ECT treatment . The recommended post-ECT continuation pharmacotherapy is combined lithium and antidepressant. If a patient fails standard pharmacotherapy following a successful course of ECT, C-ECT should be considered in order to decrease the likelihood of relapse [ 244 ]. The goal of C-ECT is to prevent relapse while M-ECT, beginning 6 months after C-ECT, is used to prevent recurrence. Kellner and colleagues [ 245] evaluated the comparative efficacy of C-ECT and the combination of lithium plus nortriptyline (continuation pharmacotherapy) after a successful acute ECT course. There were 201 depressed patients in the study, including 66 elderly patients. This multisite randomized trial found that both C-ECT and continuation pharmacotherapy reduced relapse rates, and had no age differences in the rates of response and symptom remission [ 245 ].
When was ECT introduced?
History of ECT. Convulsive therapy was reintroduced in 1934 by the neuropsychiatrist Meduna, who, based on his theory of “a biological antagonism between epilepsy and schizophrenia”, chemically induced a therapeutic generalized seizure in a catatonic schizophrenia patient [ 17 ].
What is electroconvulsive therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a biological treatment procedure involving a brief application of electric stimulus to produce a generalized seizure. ECT is utilized worldwide as one of the most effective biological treatment modalities for various severe, treatment-refractory or treatment-resistant psychiatric disorders, in particular, ...
Is ECT a non-pharmacologic treatment?
Currently, ECT is still the most widely available nonpharmacologic treatment procedure for severe mental illness, although newer neuromodulation therapies are being developed. These newer brain stimulation modalities include more invasive procedures, such as vagal nerve stimulation, deep brain stimulation and epidural cortical stimulation, and less invasive procedures, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation, transcranial direct current stimulation and magnetic seizure therapy (MST). Only transcranial magnetic stimulation and vagal nerve stimulation are US FDA approved. As discussed elsewhere in this review, the cardiac and cognitive side-effect profiles of ECT are the major concerns of practicing ECT in the geriatric population. MST is an experimental brain stimulation technique that involves a magnetically induced seizure. MST presumably has a better localization of the site of initiation and focalization of propagation [ 249 ], which could cause fewer cognitive side effects and possibly have less impact on parasympathetic and sympathetic outflow, which cause HR and BP fluctuation [ 250 ]. However, the efficacy of MST in the treatment of depression has not been established [ 251 ], although MST has been found to be associated with rapid reorientation and intact anterograde and retrograde memory [ 252 ]. Elderly patients may benefit from MST because of its favorable side-effect profile compared with ECT if antidepressant effect of MST is comparable with or superior to ECT, and the treatment becomes FDA approved.
What are the causes of major depression in 2030?
The three leading causes of disease burden in 2030 are projected to be HIV/AIDS, unipolar depressive disorders and ischemic heart disease . Unipolar depression was ranked the fourth cause of disease burden in 2002; and it is projected to be the second worldwide and the first in high-income countries (e.g., USA) in 2030 [ 47 ]. Depression is highly comorbid with the other two leading causes, HIV/AIDS and ischemic heart disease [ 48, 49 ]. The prevalence of major depression was 5.5% in individuals over 65 years of age [ 50 ]. The highest prevalence of major depression was in nursing homes and other residential settings [ 51 ]. Untreated and undertreated elderly with major depression have higher rates of mortality and morbidity [ 52, 53 ]. Although it is a treatable illness, major depression can be chronic and recurrent.
When did the sine wave stimulus stop?
Sine wave stimulus has been replaced by brief pulse stimulus since 2001, when professional organizations recommended discontinuing use of sine wave stimulation. Ultrabrief pulse was reintroduced in the late 1990s and in RCTs [ 188 – 190 ]. Ultrabrief pulse has been shown to be a more efficient method of delivering electrical dose regardless of anatomical positioning of electrode placement [ 188 ]. The use of ultrabrief pulse stimulation allows a wide range of effective stimulus dose on currently marketed devices ( Table 1 ). There is growing data on the efficacy of ultrabrief pulse ECT, which appears to be effective while reducing adverse cognitive effects. It is currently not advised to practice ultra-brief BL ECT outside of research settings [ 191 ].
How long does an ECT treatment last?
ECT treatments now usually last up to eight seconds.
What is ECT therapy?
ECT. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT or “electroshock”) is a psychiatric procedure that is frequently used to treat depression and other mental disorders. Psychiatrists long ago got the idea that having a convulsion could be therapeutic for patients with mental illness.
Why is psychiatry so bad?
First, psychiatrists assume that all of human behavior is simply the result of brain function, steadfastly ignoring the possibility of any spiritual aspect of or holistic approach to human existence.
What is electroporation used for?
Toxic material rushes in, and the cell dies. In biological research, electroporation is used to force drugs into cells through temporary pores. In medicine it is used to kill cancer cells. In psychiatry brain cell damage by electroporation is a likely byproduct of ECT.
How does a pump work?
The pump generates pressure, which forces the water to move. The higher the pressure, the faster the water will flow. The pressure can be measured in pounds per square inch. The rate of flow can be measured in gallons per minute. The pressure is the cause, and the water flow is the effect.
When was ECT first used?
ECT was first used in 1938 when an Italian psychiatrist, Ugo Cerletti, observed pigs in a Rome slaughterhouse being anesthetized with electroshock before being butchered. His first human patient begged Cerletti, “Non una seconda! Mortifierel” (“Not another one! It will kill me!”).
Who is Kenneth Castleman?
Kenneth Castleman has a PhD in biomedical engineering. He has served on the faculty at Caltech and The University of Texas and on the research staff at USC and UCLA. He has published three books and over sixty scientific articles. He has also served on advisory committees for several universities and government agencies, including The National Institutes of Health, NASA, and the FBI.

Why It's Done
Risks
Self help information for family, friends and colleagues
- Loosen tight clothing
- Protect the person from injury
- If they have fallen, place something soft under their head
- Stay with them until they recover fully
Do not:
- Try to restrain the person
- Put anything between their teeth
- Move them, unless they are in danger
- Give them food to eat or drink
Person who have had seizure
- Avoid triggers
- Avoid unprotected heights and unsupervised areas of water
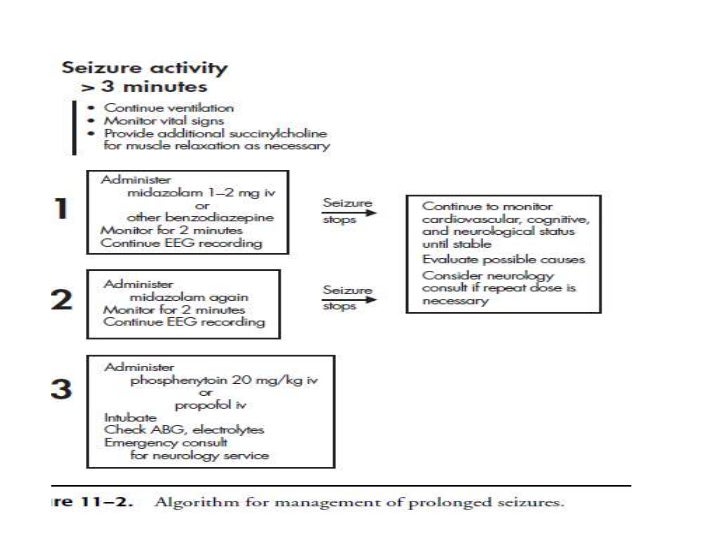
- Seizure lasts less than 5 minutes
- None of the below mentioned incidents occur during the episode
See a doctor immediately if you notice:
- Seizure lasts longer than five minutes
- Breathing or consciousness doesn't return after the seizure stops
- A second seizure follows immediately
- The seizure happened in water
- High fever
- Heat exhaustion
- Person is pregnant
- Person has diabetes
- Person is injured during the seizure
How You Prepare
What You Can Expect
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: 1. Severe depression,particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. 2. Treatment-resistant depression,a severe depression that doesn't improve with medications o…
Results
- Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: 1. Confusion.Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. You may not know where you are or why you're there. Rarely, confusion may last several days or longer. Confusion is generally more noticeable in older adults. 2. Memory loss.Some people hav…