Therapy
Overview. Certain medications also can cause dysarthria. Dysarthria treatment is directed at treating the underlying cause of your condition when possible, which may improve your speech. You may have speech therapy to help improve speech. For dysarthria caused by prescription medications, changing or discontinuing the medications may help.
Nutrition
Common causes of dysarthria include nervous system disorders and conditions that cause facial paralysis or tongue or throat muscle weakness. Certain medications also can cause dysarthria. Treating the underlying cause of your dysarthria may improve your speech. You may also need speech therapy.
What is the treatment for dysarthria?
If you have trouble speaking, you should see a doctor right away. It is important to find out why and make sure it does not get worse. An SLP can test your speech and language. This will help the SLP decide if you have dysarthria or another problem.
What causes dysarthria of the tongue?
Dysarthria doesn't affect your cognitive skills and understanding of speech and writing, but an underlying condition can. Speech therapy session at Mayo Clinic. Your treatment will depend on the cause and severity of your symptoms and the type of dysarthria you have.
When should I see an SLP for dysarthria?
How does dysarthria affect my ability to read and write?

How do you fix dysarthria?
Treating dysarthriastrategies to improve speech, such as slowing speech down.exercises to improve the volume or clarity of speech.assistive devices, such as a simple alphabet board, an amplifier, or a computerised voice output system.
How do you reverse dysarthria?
Dysarthria caused by medicines or poorly fitting dentures can be reversed. Dysarthria caused by a stroke or brain injury will not get worse, and may improve. Dysarthria after surgery to the tongue or voice box should not get worse, and may improve with therapy.
How do you improve dysarthria?
How is dysarthria treated?Exercises to strengthen mouth muscles.Ways to slow down speech.Strategies to speak louder, such as using more breath.Ways to say sounds clearly.Movements to chew and swallow safely.Different communication techniques, such as gestures or writing.
Can you overcome dysarthria?
Your treatment will depend on the cause and severity of your symptoms and the type of dysarthria you have. Your doctor will treat the cause of your dysarthria when possible, which may improve your speech.
What part of the brain is damaged in dysarthria?
There are several types of dysarthria: Flaccid dysarthria—from damage of the cranial nerves or regions of the brainstem and midbrain. Spastic dysarthria—from damage to the motor regions in the cortex, on both sides of the brain.
Can dysarthria be temporary?
The medical term for speech disorders is dysarthria. Speech disorders may develop slowly over time or follow a single incident. Speech problems can be temporary or permanent, depending on the underlying cause.
How do you fix slurred speech?
How is dysarthria treated?Increase tongue and lip movement.Strengthen your speech muscles.Slow the rate at which you speak.Improve your breathing for louder speech.Improve your articulation for clearer speech.Practice group communication skills.Test your communication skills in real-life. situations.
Can ataxic dysarthria be cured?
It's sometimes possible to treat the underlying cause of the condition so it improves or stops getting worse, but in most cases this isn't possible and you'll have treatment to relieve your symptoms.
How can I strengthen my speech muscles?
Here is how to exercise and build your voice muscle:Facial Exercises. Make the following sounds “Ooooh, eeeeee, ahhh” while stretching your lips and mouth.Tongue Exercises. The most important muscle in your mouth is your tongue. ... Strengthen your voice. ... Practice tongue twisters. ... Old fashion tongue twisters:
Which cranial nerve is affected in dysarthria?
Cranial nerves that control the muscles relevant to dysarthria include the trigeminal nerve's motor branch (V), the facial nerve (VII), the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX), the vagus nerve (X), and the hypoglossal nerve (XII).
What medication causes dysarthria?
Dysarthria is most commonly caused by diseases or disorders of the brain or nervous system, such as: Stroke. Multiple sclerosis....Some specific drugs that have been associated with dysarthria include:Carbamazepine.Irinotecan.Lithium.Onabotulinum toxin A (Botox)Phenytoin.Trifluoperazine.
What causes loss of tongue control?
Causes. In a person with dysarthria, a nerve, brain, or muscle disorder makes it difficult to use or control the muscles of the mouth, tongue, larynx, or vocal cords. The muscles may be weak or completely paralyzed. Or, it may be hard for the muscles to work together.
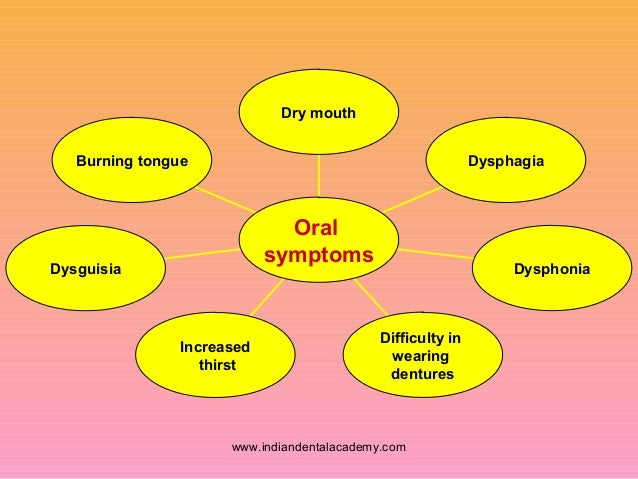
What are the symptoms of dysarthria?
Other speech conditions can be related to dysarthria: Dysphagia: Trouble swallowing, which may be a symptom of dysarthria. Aphasia: Difficulty understanding others or explaining your thoughts.
How common is dysarthria?
Researchers don’t know exactly how common dysarthria is. It is more common in people who have certain neurological conditions, such as: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): Up to 30% of people with ALS (Lou Gehrig’s disease) have dysarthria.
What is the name of the disorder in which the muscles that are used to produce speech are damaged, paralyzed
Dysarthria. Dysarthria is a motor speech disorder in which the muscles that are used to produce speech are damaged, paralyzed, or weakened. The person with dysarthria cannot control their tongue or voice box and may slur words. There are strategies to improve communication. Appointments 216.444.8500.
What is the difference between central dysarthria and peripheral dysarthria?
The type of dysarthria depends on the part of the nervous system affected: Central dysarthria: Caused by damage to the brain. Peripheral dysarthria: Caused by damage to what the organs needed for speech. Dysarthria can be developmental or acquired:
How many people with MS have dysarthria?
Multiple sclerosis (MS): Around 25% to 50% of people with MS get dysarthria at some point. Parkinson’s disease: Dysarthria affects 70% to 100% of people with Parkinson’s disease. Stroke: About 8% to 60% of people with stroke have dysarthria.
What causes a person to hear a lot of sounds?
Myasthenia gravis. Parkinson’s disease. Peripheral dysarthria develops from damage to the speech organs that changes the way a person sounds. Causes include: Congenital ( being born with) structural problems.
What are the parts of the body that are affected by dysarthria?
Speech problems can cause difficulties in social situations, jobs and school. Dysarthria affects many parts of the body needed for speech, including the: Tongue. Larynx (voice box).
What causes dysarthria?
Causes of Dysarthria. Brain damage causes dysarthria. It can happen at birth or after an illness or injury. Anything that causes brain damage can cause dysarthria, such as: Stroke. Brain injury. Tumors. Parkinson's disease. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS.
Why is it hard to talk?
It is harder to talk when these muscles are weak. Dysarthria happens when you have weak muscles due to brain damage. It is a motor speech disorder and can be mild or severe.
How does SLP test your speech?
An SLP can test your speech and language. This will help the SLP decide if you have dysarthria or another problem. The SLP will look at how well you move your mouth , lips , and tongue and how well you breathe. She will listen to your speech in single words, sentences, and conversation.
What is it called when you have trouble understanding what others say?
You could also have trouble understanding what others say or telling others about your thoughts, called aphasia.
How to reduce the risk of dysarthria?
For example: Exercise regularly. Keep your weight at a healthy level. Increase the amount of fruits and vegetables in. your diet. Limit cholesterol, saturated fat, and salt in. your diet. Limit your intake of alcohol.
What is the best treatment for dysarthria?
If your symptoms are related to an underlying medical condition, your doctor may recommend medications, surgery, speech-language therapy, or other treatments to address it.
What is dysarthria speech?
What is dysarthria? Dysarthria is a motor-speech disorder. It happens when you can’t coordinate or control the muscles used for speech production in your face, mouth, or respiratory system. It usually results from a brain injury or neurological condition, such as a stroke. People with dysarthria have difficulty controlling ...
Why is my speech so slow?
Your speech may become slow or slurred. As a result, it may be difficult for others to understand what you’re trying to say. The specific speech impairments that you experience will depend on the underlying cause of your dysarthria. If it’s caused by a brain injury, for example, your specific symptoms will depend on the location and severity ...
How can a speech pathologist help you?
A speech-language pathologist may be able to help you improve your communication abilities. They may develop a custom treatment plan to help you: Increase tongue and lip movement. Strengthen your speech muscles. Slow the rate at which you speak. Improve your breathing for louder speech.
How do you know if you have dysarthria?
Typical symptoms include: slurred speech. slow speech. rapid speech. abnormal, varied rhythm of speech. speaking softly or in a whisper. difficulty changing the volume of your speech. nasal, strained, or hoarse vocal quality.
What doctor can diagnose dysarthria?
If they suspect you have dysarthria, your doctor may refer you to a speech-language pathologist. This specialist can use several examinations and tests to assess the severity and diagnose the cause of your dysarthria. For example, they will evaluate how you speak and move your lips, tongue, and facial muscles.
How does dysarthria affect people?
Communication problems may affect your relationships with family and friends and make social situations challenging. Depression. In some people, dysarthria may lead to social isolation and depression. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
What are the symptoms of dysarthria?
They may include: Slurred speech. Slow speech. Inability to speak louder than a whisper or speaking too loudly. Rapid speech that is difficult to understand. Nasal, raspy or strained voice.
What causes dysarthria in the upper respiratory system?
Conditions that may lead to dysarthria include: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, or Lou Gehrig's disease) Brain injury. Brain tumor. Cerebral palsy.
Why is my speech so slow?
Dysarthria occurs when the muscles you use for speech are weak or you have difficulty controlling them. Dysarthria often causes slurred or slow speech that can be difficult to understand. Common causes of dysarthria include nervous system disorders and conditions that cause facial paralysis or tongue or throat muscle weakness.
Can dysarthria improve speech?
Treating the underlying cause of your dysarthria may improve your speech. You may also need speech therapy. For dysarthria caused by prescription medications, changing or discontinuing the medications may help.
What is dysarthria speech?
Summary. Dysarthria is a speech disorder that occurs due to weakness in the muscles necessary for speech production. People can develop dysarthria after a stroke, brain infection, or brain injury. Certain neurodegenerative diseases can also damage parts of the brain that control the muscles that speech involves.
Why does dysarthria make me quiet?
A person with dysarthria may find it easier to communicate in a quiet place. Dysarthria occurs when damage to the nervous system weakens the muscles that produce speech sounds. It may affect the muscles in one or more of the following areas: face. lips. tongue. throat.
What causes dysarthria in the upper respiratory tract?
upper respiratory tract. The neurological damage that causes dysarthria can occur due to: neurological conditions, such as epilepsy, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and Parkinson’s disease. brain tumors. trauma from injuries to the head or neck, as well as repeated blunt force impacts to the skull.
What is spastic dysarthria?
Spastic dysarthria. People with spastic dysarthria may have speech problems alongside generalized muscle weakness and abnormal reflexes. Spastic dysarthria occurs as a result of damage to the motor neurons in the central nervous system (CNS). The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord.
What is the difference between apaxia and dysarthria?
Apraxia affects a person’s ability to produce speech and results from damage to the part of the brain that plays a role in planning speech. Dysarthria is a distinct speech disorder that specifically involves muscle weakness. Read on to learn more about the causes, types, ...
What causes slurred speech?
Ataxic dysarthria causes symptoms of slurred speech and poor coordination. This type of dysarthria can occur if a person sustains damage to the cerebellum. The cerebellum is the part of the brain responsible for receiving sensory information and regulating movement.
Can dysarthria cause tremors?
As conditions that cause dysarthria also affect the nerves that control muscles, people with dysarthria may experience physical symptoms, such as: tremors or involuntary movements of the jaw, tongue, or lip. overly sensitive or undersensitive gag reflex.
Why do children have dysarthria?
Dysarthria in Children. Dysarthria in children is often misidentified as childhood apraxia of speech. One reason for this is that they may only show weakness in speech associated muscles, without any other evident weakness (unlike what is common in adults). In addition, young children don’t always understand or fully cooperate with ...
What causes hyperkinetic dysarthria?
Hyperkinetic Dysarthria results from diseases like Huntington’s Disease, which attack the basal galangia. You will notice excessive movement, strained or strangled sounding speech, variations in volume, and changes in the rate of speaking.
What is the most common speech disorder?
Dysarthria is one of the more common speech disorders you’ll encounter in this profession. This is a motor-speech disorder, where permanent brain and/or nerve damage impacts speech-related muscles. These muscles either go limp and loose or become tight and rigid, causing slurred or indistinct speech. Individuals know what they want ...
What causes a person to have a slow speech?
Depending on the root cause, the individual may show cognitive decline. Unilateral Upper Motor Neuron Dysarthria most often results from stroke or neurosurgery, although tumors and traumatic brain injury are other possible causes.
Why do children have difficulty speaking?
In addition, young children don’t always understand or fully cooperate with the activities necessary for assessment. Similar to adults with dysarthria, children often have difficulty controlling the volume and pitch of their speech, and may demonstrate slow or slurred speech. Root causes include: Brain injury. Cerebral palsy.
Is dysarthria short term?
This form of dysarthria is often only short-term. Mixed Dysarthria tends to result from multiple strokes or diseases such as ALS, Wilson’s, and MS. Essentially a mixed dysarthria is any combination of the above.
Can dysarthria be triggered by stroke?
Unfortunately this form of dysarthria often comes with cognitive impairment, at times influencing treatment progress. Spastic Dysarthria is most often triggered by a stroke, although other events such as tumors, cerebral palsy, encephalitis and primary lateral sclerosis may also cause it .