Symptoms
Is it possible for someone with hepatitis C to get better without treatment Yes. However, less than half of people who are infected with the hepatitis C virus clear it from their bodies without treatment. Experts do not fully understand why this happens for some people. How common is acute hepatitis C in the United States?
Causes
What Might Not Help
- Milk Thistle. This herb is widely used for liver disorders, including hepatitis B. ...
- Acupuncture. This treatment has long been used for ongoing pain. ...
- Colloidal Silver. This product has tiny particles of silver that some people claim can help heal wounds and infections.
- Glycyrrhizin. ...
- Probiotics. ...
Prevention
What’s the outlook for someone with chronic hepatitis C?
- Treatment. Chronic hepatitis C is often treatable. It usually involves taking a combination of medications to reduce the viral load to undetectable levels.
- Genotype. Treatment success for chronic hepatitis C also depends on the genotype of the virus. ...
- Cases of hepatitis C in the United States. U.S. ...
Complications
Well, the good news is hepatitis C is curable. Though it is a chronic infection, recently developed drugs can clear the virus completely from the system. If the viral load (number of virus particles in the blood) is nil after three months of treatment completion, people are considered “cured.”. This is called sustained virologic response (SVR) and data suggest that, in these cases, people will stay virus-free for life.
Can Hep C be cured without treatment?
Is there a natural way to cure Hepatitis C?
When can you expect a cure for hepatitis C?
What is hepatitis C, and can it be cured?

Does Hep C always need treatment?
The infection is likely to return, requiring treatment with antiviral medication to prevent damage to the transplanted liver. Several studies have demonstrated that new, direct-acting antiviral medication regimens are effective at curing post-transplant hepatitis C.
Can people clear hep C without treatment?
Like the human papillomavirus (HPV), early acute hepatitis C can clear on its own without treatment; this happens about 25% of the time. However, it's more likely that the virus will remain in your body longer than six months, at which point it's considered to be chronic hepatitis C infection.
Who qualifies for Hep C treatment?
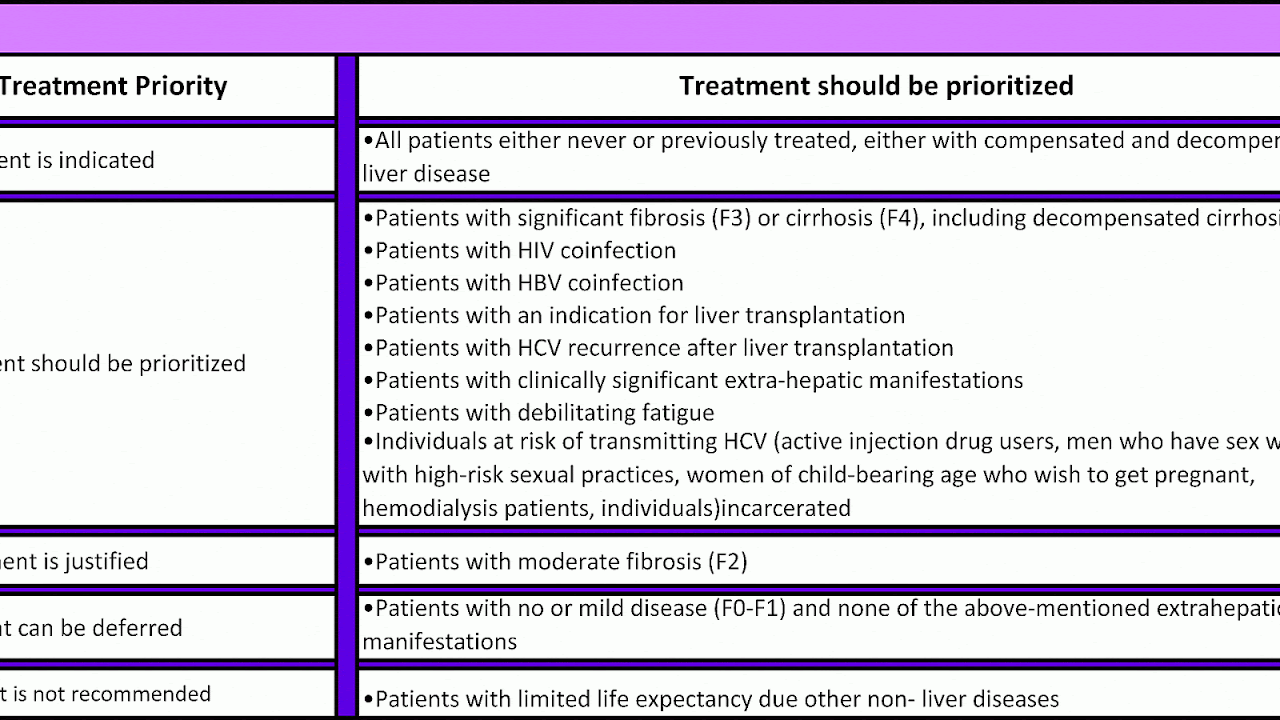
With the exception of pregnant women, the World Health Organization recommends treatment be offered to all individuals aged 12 years or older diagnosed with HCV, regardless of their disease stage.
Can you live a full life with Hep C?
If the disease is caught early and treated, people with hepatitis C can live a normal life. Approximately 3 to 5 million people in the United States are living with chronic hepatitis C, an infection that causes inflammation and scarring in the liver.
How long does hep C take to damage liver?
On average it takes about twenty years for significant liver scarring to develop. The symptoms experienced and the damage done to the liver vary dramatically from person to person. Some people will have few, if any, symptoms for many years.
What happens if hep C goes untreated?
Hepatitis C can be a short-term illness, but for most people, acute infection leads to chronic infection. Chronic hepatitis C can be a lifelong infection if left untreated. Chronic hepatitis C can cause serious health problems, including liver damage, cirrhosis (scarring of the liver), liver cancer, and even death.
Can your body fight off hep C?
Among those who do have symptoms, the illness is usually so mild that most don't even recognize that they have liver disease. In 15-40% of persons with acute hepatitis C, the immune system successfully fights off the infection, the virus is cleared from the body within 6 months, and the liver heals completely.
When do you initiate hep C treatment?
Because of the many benefits associated with successful HCV treatment, clinicians should treat HCV-infected patients with antiviral therapy with the goal of achieving SVR, preferably early in the course of chronic hepatitis C before the development of severe liver disease and other complications.
What does hep C pain feel like?
Many chronic HCV sufferers also complain of getting aches and pains. Large numbers get sharp pains over the liver (found in the upper right corner of the abdomen) which can sometimes be very alarming. These pains are not necessarily connected with severe liver disease.
Which hepatitis is worse B or C?
Hepatitis B is certainly more virulent and contagious than hepatitis C. Hepatitis B is prevalent around the world and it causes more liver cancer than hepatitis C. People with hepatitis B are more likely to die from complications to their liver than people with any of the other hepatitis infections.
What is the life expectancy of a person with hep C?
Doctor's Response People with hepatitis C can live many years after diagnosis, but the range varies. A 2014 study showed that patients infected with hepatitis C virus died on average 15 years sooner than people who did not have the illness. With hepatitis C, the liver becomes seriously damaged due to inflammation.
How long does it take for hepatitis C to stop?
It’s important to understand how the virus works. After you’re infected, chronic hepatitis C may silently hurt your body. It can take years or even decades to feel symptoms. Once you do, the virus has probably damaged your body in a number of ways. Treatments for hepatitis C can stop the virus, even before it makes you feel sick.
What happens if you have hepatitis C?
Without treatment of a chronic infection, about 75% to 85% of people who have it get a long-term infection called chronic hepatitis C. If the condition goes untreated, it can lead to: Cirrhosis, or scarring of the liver. Liver cancer.
How does hep C spread?
Hepatitis C spreads through blood-to-blood contact. You could infect a loved one if you accidentally use their toothbrush or cut yourself and don’t clean up the blood properly. People who get hep C treatment greatly lower the odds that they will pass the virus to someone else.
How many people will get cirrhosis in 20 years?
The disease affects everyone differently, so there’s no rule. But about 70% to 80% of people with will get chronic help C. Within 20 years, about 20% to 30% of those people will get cirrhosis. From there, it depends on what type of cirrhosis you have, your treatment, and if you can get a liver transplant.
Does hepatitis C cause cancer?
Cancers. People with hepatitis C are more likely to get non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. That’s a type of cancer that starts in the immune system. The virus also raises your odds of liver cancer and bile duct cancer.
Does Hepatitis C cause high blood sugar?
High Blood Sugar. Hepatitis C can make it hard for your body’s cells to take in sugar from the food you eat. Your pancreas will pump out more insulin, a hormone that helps move sugar into your cells. That means too much sugar will stay in your blood. Over time, your body could stop responding to the effects of insulin.
Can hepatitis C cause swelling?
They can build up in vessels and block blood flow, which causes swelling and damage. The condition can affect your skin, organs, nerves, and joints. Hepatitis C also can cause problems with blood itself. You may not make enough white blood cells, which fight infections, or platelets, which help your blood clot.
How long after hepatitis C treatment can you be cured?
Sustained virologic response (or SVR): If the hepatitis C virus is not detected in your bloodstream three months after treatment, you are considered cured. This is called a sustained virologic response and the data has indicated that you will stay free of the virus indefinitely.
What is the purpose of taking hepatitis C medication?
The purpose of taking medications to treat hepatitis C is to: Clear the virus from your bloodstream. Slow the advancement of inflammation and scarring of your liver. Lower your chances of developing cirrhosis or liver cancer.
What is a non responder for hepatitis C?
Nonresponse: When the hepatitis C virus does not become undetectable as a result of treatment, you are considered a non-responder. There are two types, 1) partial response is where the viral load decreases, and 2) null-response is where the viral load never drops.
What are the factors that affect hepatitis C?
The most important factors that impact treatment results include: 1 Taking medications as prescribed and not missing doses 2 Your hepatitis C genotype 3 The presence of cirrhosis (severe scarring of the liver)
Can you breastfeed while on hepatitis C?
Other medical conditions, including liver disease not related to HCV. If you are currently breastfeeding or if you plan to breastfeed while on therapy; it is not currently known if hepatitis C medications pass into the breast milk. If you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
How rare is hepatitis C?
Now that more advanced screening tests for hepatitis C are used in blood banks, the risk of transmission to recipients of blood or blood products is considered extremely rare, at <1 case per 2 million units transfused.
What is the risk of cirrhosis in the following year?
Patients who develop cirrhosis have a 1%–4% annual risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma and a 3%–6% annual risk of hepatic decompensation; for the latter patients, the risk of death in the following year is 15%–20% ( 7 ).
What is the aseptic technique for HCV?
All health-care personnel, including those who are HCV positive, should follow a strict aseptic technique as described by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and the CDC, including appropriate hand hygiene, use of protective barriers, and safe injection practices.
Can hepatitis C cause liver enzymes to fluctuate?
Yes. It is common for patients with chronic hepatitis C to have fluctuating liver enzyme levels, with periodic returns to normal or near normal levels. Liver enzyme levels can remain normal for over a year despite chronic liver disease ( 28 ).
Does dental surgery spread hepatitis C?
As long as Standard Precautions and other infection-control practices are consistently implemented, medical and dental procedures performed in the United States generally do not pose a risk for the spread of hepatitis C.
Is hepatitis C test complete?
If a person tests positive for HCV antibodies, hepatitis C testing is not considered complete unless the initial positive anti-HCV test is followed by a test for HCV RNA as per CDC guidelines. A positive test for HCV RNA is needed before a patient can be diagnosed with current HCV and begin receiving treatment.
What drugs can be hard on the liver?
What’s more, some drugs can be hard on your liver, including over-the-counter ones such as acetaminophen.
Is hepatitis C treated with alcohol?
When treating Hepatitis C it is important to stay hydrated and avoid alcohol. iStock (2) Thanks to recent advances in medication, hepatitis C, a viral infection that affects the liver, is now highly treatable. But you still have to do your part during treatment, which means following a few important recommendations.
Do you need to take hepatitis C medication?
For hepatitis C medications to be effective, they need to be taken as prescribed. Missing doses increases the risk of the virus becoming resistant to medications, according to the American Liver Foundation (ALF).
Can you drink alcohol with hepatitis C?
Don’t drink alcohol. Alcohol is processed through the liver as a toxin and can be a source of inflammation in your liver, just like hepatitis C. When you’re undergoing treatment, it’s counterproductive to drink alcohol, Lee says, because it blunts the immune response to the virus and increases the severity of liver damage, ...
Can you take vitamins with hepatitis C?
Dietary supplements haven’t been shown to be effective treatments for hepatitis C, according to the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, and, in fact, some of them may even have harmful side effects and interact poorly with medications. If you take vitamins or supplements, or are considering taking them for other health reasons, make sure your doctor knows. In some cases, your doctor may recommend a particular brand or suggest a different approach if the potential interactions or risks are too high.
Can hepatitis C be taken as prescribed?
3. Do follow your doctor’s exact instructions for treatment. For hepatitis C medications to be effective, they need to be taken as prescribed.
How long does it take for hepatitis C to be cured?
The virus is considered cured when it is not detected in your blood 12 weeks after treatment is completed. This is otherwise known as a sustained virologic response (SVR).
What is the benefit of taking antiviral drugs for hepatitis C?
Recent research indicates that the antiviral drugs used for treating hepatitis C may have the additional benefit of helping to prevent serious complications of the virus, such as cirrhosis from chronic liver damage .
Why do you need a liver transplant?
If you develop chronic hepatitis C and it leads to liver cancer or liver failure, you may need a liver transplant. Hepatitis C is one of the most common reasons for a liver transplant. A liver transplant removes a damaged liver and replaces it with a healthy one.
What is the best antiviral for hepatitis C?
Current, recommended antiviral treatments for different genotypes of hepatitis C include: ledipasvir-sofosbuvir (Harvoni) elbasvir-grazoprevir (Zepatier) ombitasvir-paritaprevir-ritonavir (Technivie) ombitasvir-paritaprevir-ritonavir ...
Can hepatitis C go away without treatment?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Trusted Source. reports less than half of people who contract the hepatitis C virus may clear it from their bodies without treatment. For this group of people, the virus will be a short-term acute condition that goes away without treatment.
Is there a universal screening for hepatitis C?
universal screening for all individuals over 18 years of age and pregnant women during every pregnancy. Subsequent testing (and frequency of testing) is based on risk. Talk to your doctor about your needs. Per the CDC, these populations are at a higher risk for hepatitis C.
Can you get hepatitis C from a condom?
Hepatitis C isn’t usually transmitted through sexual contact, but it’s possible . Limit your exposure by practicing sex with a condom or other barrier method. It’s also important to openly communicate with sexual partners and to get tested if you suspect you’ve been exposed to the hepatitis C virus.
How old do you have to be to get hepatitis C?
People between ages of 20 and 40 are primarily acquiring hepatitis C through injection drug use, says Douglas Dieterich, MD, a professor of medicine with the division of liver diseases at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City.
How long does it take to cure hepatitis C?
More than 90 percent of people who have hepatitis C can be cured with an 8- to 12-week course of direct-acting antivirals, according to the CDC.
How many people have hepatitis C?
An estimated 2.4 million Americans have hepatitis C, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). This viral infection attacks the liver and, if left untreated, can lead to serious health consequences, including cirrhosis (permanent damage to the liver) and liver cancer. For those who have hepatitis C ...
What percentage of hepatitis C cases are in the baby boomers?
Although baby boomers used to account for the bulk of hepatitis C cases (36.3 percent), the disease has been rapidly spreading among young adults — so much so that in 2020, the CDC reported that younger adults (and particularly millennials) now make up the majority of newly reported chronic hepatitis C infections.
Why is early detection of hepatitis C important?
Early detection of hepatitis C can help prevent serious health consequences and the spread of the disease to others. But even people with a later diagnosis can benefit from treatment.
Do baby boomers have hepatitis C?
Baby boomers account for a fair number of all newly reported cases of hepatitis C, according to the CDC, but a large proportion of them don’t even know they have it, because they haven’t been tested, they don’t have symptoms, or both.
How many people die from hepatitis C?
Without antiviral treatment, an estimated 67 to 91 percent of people with hepatitis C-related liver scarring die from liver cancer, liver failure, or other liver-related causes.
How is hepatitis C transmitted?
Hepatitis C is transmitted from one person to another through blood-to-blood contact. Today, the most common routes of transmission include: 1 being born to a mother with hepatitis C 2 sharing needles or syringes that have been used to inject recreational drugs 3 being accidentally stuck with a used needle while working as a healthcare provider
Is it safe to delay hepatitis C treatment?
It can take time for chronic hepatitis C to cause serious symptoms. But that doesn’t mean it’s safe to delay treatment. Starting treatment early may lower your risk of developing complications from the illness, including liver scarring and liver cancer.
How often should I get hepatitis C?
Universal hepatitis C screening (new recommendations): Hepatitis C screening at least once in a lifetime for all adults aged ≥18 years, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection (HCV RNA-positivity) is <0.1%.
What age should I be tested for hepatitis C?
CDC recommends hepatitis C screening of all adults aged ≥18 years once in their lifetimes, and screening of all pregnant women (regardless of age) during each pregnancy. The recommendations include an exception for settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is demonstrated to be <0.1%; however, few settings are known to exist with a hepatitis C prevalence below this threshold ( 2, 9 ). The recommendation for testing of persons with risk factors remains unchanged; those with ongoing risk factors should be tested regardless of age or setting prevalence, including continued periodic testing as long as risks persist. These recommendations can be used by health care professionals, public health officials, and organizations involved in the development, implementation, delivery, and evaluation of clinical and preventive services.
What is the goal of hepatitis C screening?
The goal of hepatitis C screening is to identify persons who are currently infected with HCV. Hepatitis C testing should be initiated with a U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved anti-HCV test. Persons who test anti-HCV positive are either currently infected or had past infection that has resolved naturally or with treatment. Immunocompetent persons without hepatitis C risks who test anti-HCV negative are not infected and require no further testing. Persons testing anti-HCV positive should have follow-up testing with an FDA-approved nucleic acid test (NAT) for detection of HCV RNA. NAT for HCV RNA detection determines viremia and current HCV infection. Persons who test anti-HCV positive but HCV RNA negative do not have current HCV infection. CDC encourages use of reflex HCV RNA testing, in which specimens testing anti-HCV positive undergo HCV RNA testing immediately and automatically in the laboratory, using the same sample from which the anti-HCV test was conducted. Hepatitis C testing should be provided on-site when feasible.
What is the best treatment for HCV?
The treatment for HCV infection has evolved substantially since the introduction of DAA agents in 2011. DAA therapy is better tolerated, of shorter duration, and more effective than interferon-based regimens used in the past ( 39, 40 ). The antivirals for hepatitis C treatment include next-generation DAAs, categorized as either protease inhibitors, nucleoside analog polymerase inhibitors, or nonstructural (NS5A) protein inhibitors. Many agents are pangenotypic, meaning they have antiviral activity against all genotypes ( 20, 21, 40 ). A sustained virologic response (SVR) is indicative of cure and is defined as the absence of detectable HCV RNA 12 weeks after completion of treatment. Approximately 90% of HCV-infected persons can be cured of HCV infection with 8–12 weeks of therapy, regardless of HCV genotype, prior treatment experience, fibrosis level, or presence of cirrhosis ( 39 – 41 ).
How long does it take for hepatitis C to show symptoms?
Fulminant hepatic failure following acute hepatitis C is rare. The average time from exposure to symptom onset is 2–12 weeks (range: 2–26 weeks) ( 25, 26 ). HCV antibodies (anti-HCV) can be detected 4–10 weeks after infection and are present in approximately 97% of persons by 6 months after exposure.
How is hepatitis C transmitted?
HCV is transmitted primarily through parenteral exposures to infectious blood or body fluids that contain blood, most commonly through injection drug use.
What is the most efficient mode of transmission of hepatitis C?
Percutaneous exposure is the most efficient mode of hepatitis C virus (HCV) transmission, and injection drug use (IDU) is the primary risk factor for infection ( 1 ). National surveillance data revealed an increase in reported cases of acute HCV infection every year from 2009 through 2017 ( 1 ).

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Preparing For Your Appointment