Medication
- Diabetes Complications in Dogs and Cats: Diabetes Ketoacidosis (DKA)
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Increases Risk of Acute Renal Failure in Pediatric Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
Therapy
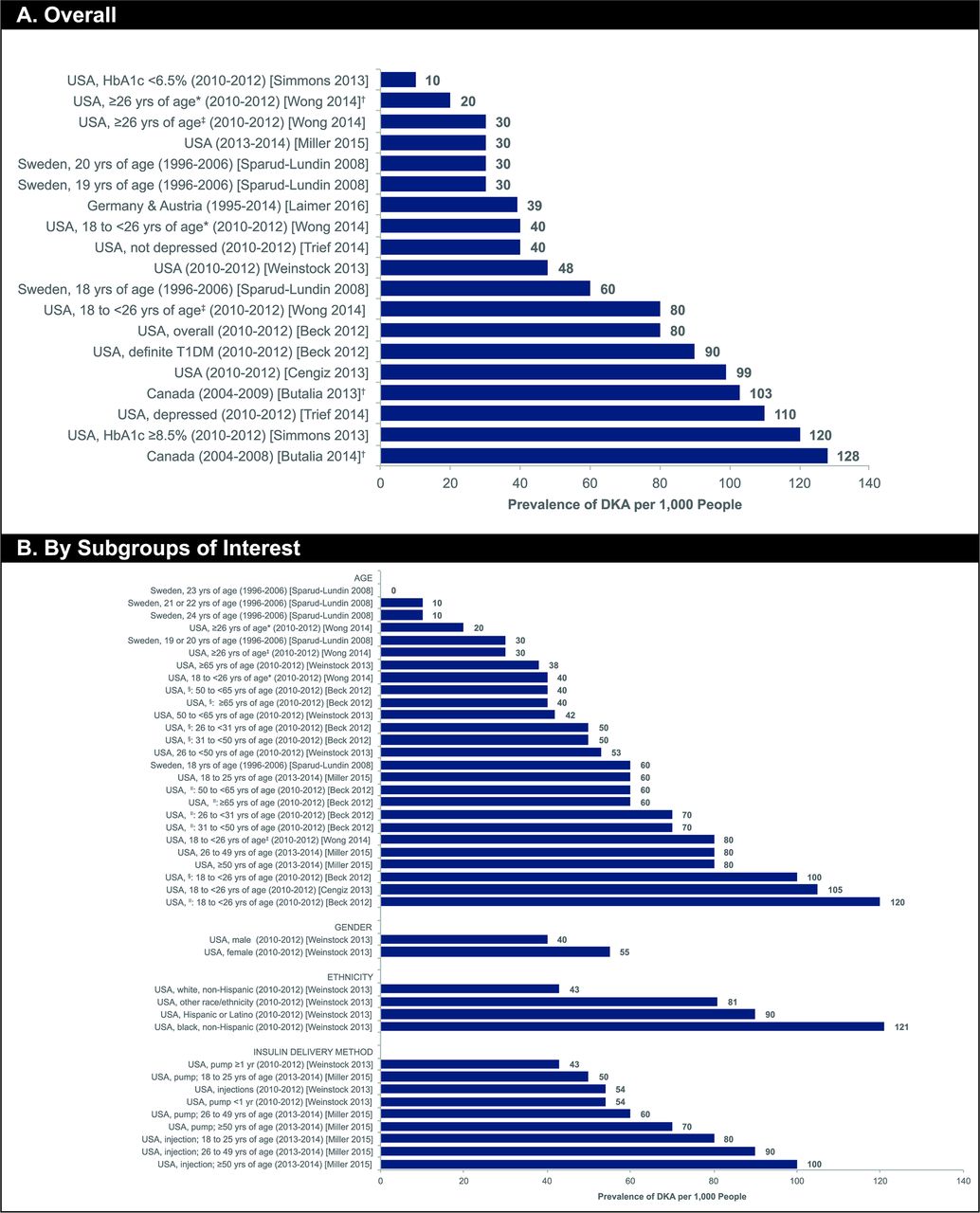
What lab values indicate DKA? Diabetic ketoacidosis is characterized by a serum glucose level greater than 250 mg per dL, a pH less than 7.3, a serum bicarbonate level less than 18 mEq per L, an elevated serum ketone level, and dehydration.
Self-care
Normal insulin levels for non-diabetics are usually between 60 and 100 mg/dl and may rise to 140 mg/dl after eating, reports the University of California. Diabetics may have insulin levels that range from as low as 25 mlU/L at fasting to as high as 30-230 mlU/L after recent glucose administration, reports Medscape.
Nutrition
The types of insulin used for sliding scale therapy include:
- Long-acting insulin (glargine/detemir or neutral protamine Hagedorn)
- Short-acting or rapid-acting insulin (aspart, glulisine, lispro, and regular)
- Premixed insulin (a combination of long-acting and short-acting insulin)
Why are DKA patients NPO?
What lab values indicate diabetic ketoacidosis?
What are normal levels of insulin?
What are the types of insulin therapy?
Explore

What type of insulin is used to treat DKA?
Regular and glulisine insulin are equally effective during the acute treatment of DKA. A transition to subcutaneous glargine and glulisine after resolution of DKA resulted in similar glycemic control but in a lower rate of hypoglycemia than with NPH and regular insulin.
What is the most appropriate treatment for DKA?
Insulin reverses the processes that cause diabetic ketoacidosis. In addition to fluids and electrolytes, you'll receive insulin therapy — usually through a vein.
Why is regular insulin used in DKA?
Insulin administration is essential in DKA treatment because it promotes glucose utilization by peripheral tissues, diminishes glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, and suppresses ketogenesis.
How is insulin administered in DKA?
A mix of 24 units of regular insulin in 60 mL of isotonic sodium chloride solution usually is infused at a rate of 15 mL/h (6 U/h) until the blood glucose level drops to less than 180 mg/dL; the rate of infusion then decreases to 5-7.5 mL/h (2-3 U/h) until the ketoacidotic state abates.
What is DKA in diabetes?
DKA is most common among people with type 1 diabetes. People with type 2 diabetes can also develop DKA. DKA develops when your body doesn’t have enough insulin to allow blood sugar into your cells for use as energy. Instead, your liver breaks down fat for fuel, a process that produces acids called ketones. When too many ketones are produced too ...
What does DKA mean in Spanish?
Español (Spanish) minus. Related Pages. Elevated ketones are a sign of DKA, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated right away. Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening. DKA is most common among people with type 1 diabetes.
What causes DKA in diabetics?
Missing insulin shots, a clogged insulin pump, or the wrong insulin dose. Other causes of DKA include: Heart attack or stroke. Physical injury, such as from a car accident. Alcohol or drug use. Certain medicines, such as some diuretics (water pills) and corticosteroids (used to treat inflammation in the body).
How to prevent DKA?
Prevent DKA. DKA is a serious condition, but you can take steps to help prevent it: Check your blood sugar often, especially if you’re sick. Keep your blood sugar levels in your target range as much as possible. Take medicines as prescribed, even if you feel fine.
What happens when you have too many ketones?
When too many ketones are produced too fast, they can build up to dangerous levels in your body. Read on to learn more about DKA, how you can prevent DKA, and how to treat it if needed.
Can you test for ketones if you have DKA?
You should also test for ketones if you have any of the symptoms of DKA. Call your doctor if your ketones are moderate or high. Elevated ketones are a sign of DKA, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately.
What causes DKA in a patient?
However, DKA can be caused by any source of physiologic stress. Occasionally, DKA is the presentation of a serious underlying problem, such as occult sepsis. Common causes of DKA include: Insulin non-adherence, inadequate dosing, or insulin pump failure.
How many units of insulin can be given in a bolus?
The main advantage of an insulin bolus is that this can usually be given immediately (most units have 10-unit insulin vials immediately available, whereas an insulin infusion needs to be mixed up in pharmacy). Insulin infusion is usually started at 0.1 U/kg/hour (up to a max of 15 units/hour in morbid obesity).
What causes nagma in the urine?
NAGMA commonly develops at this phase, caused by two factors: (a) Resuscitation with normal saline or half-normal saline. (b) Excretion of ketoacid in the urine (once ketoacid is in the sewer system, it can no longer be converted back into bicarbonate) Development of NAGMA may be revealed by the following:
How long does a pneumothorax line last?
Patients may be delirious and unable to stay still enough to facilitate safe placement of a jugular/subclavian line. The line will only be needed for 24-48 hours (until DKA resolves), so infection risk is minimal.
What is glucose used for?
Thus, glucose levels are often used as a surrogate measurement of the biological efficacy of insulin (for example, during the initial phase of resuscitation, if the glucose level isn't falling that indicates that insulin isn't working and should be up-titrated).
How much fluid is needed for DKA?
Most patients will require ~2-4 liters of crystalloid up front. For young DKA patients with normal cardiorenal function, if the patient's heart rate is >100 b/m then they probably need more fluid.
Can DKA cause potassium to drop?
DKA resuscitation will cause the potassium to drop like a stone. If the patient is hyperkalemic, then this should resolve rapidly. For critical hyperkalemia IV calcium may be considered, but the real key here is IV insulin . Critical hyperkalemia is an indication for an immediate 10 unit IV insulin bolus.
What is mild volume depletion?
Mild to moderate volume depletion is indicated by the absence of orthostatic hypotension or supine hypotension, dry mucous membranes, and poor skin turgor. The goal is to gradually replace half of the fluid deficit over 12-24 hours, to prevent complications such as cerebral edema.
What is the goal of intravenous fluid depletion?
The goal is to gradually replace half of the fluid deficit over 12-24 hours, to prevent complications such as cerebral edema.
How long does it take for a fluid deficit to be replaced?
The goal is to gradually replace half of the fluid deficit over 12 to 24 hours, to prevent complications such as cerebral edema.
What is the potassium level of insulin?
For this reason, insulin therapy should be withheld until the serum potassium level reaches 3.3 mEq/L. Likewise, if plasma potassium falls <3.3 mEq/L at any point of therapy, insulin should be discontinued.