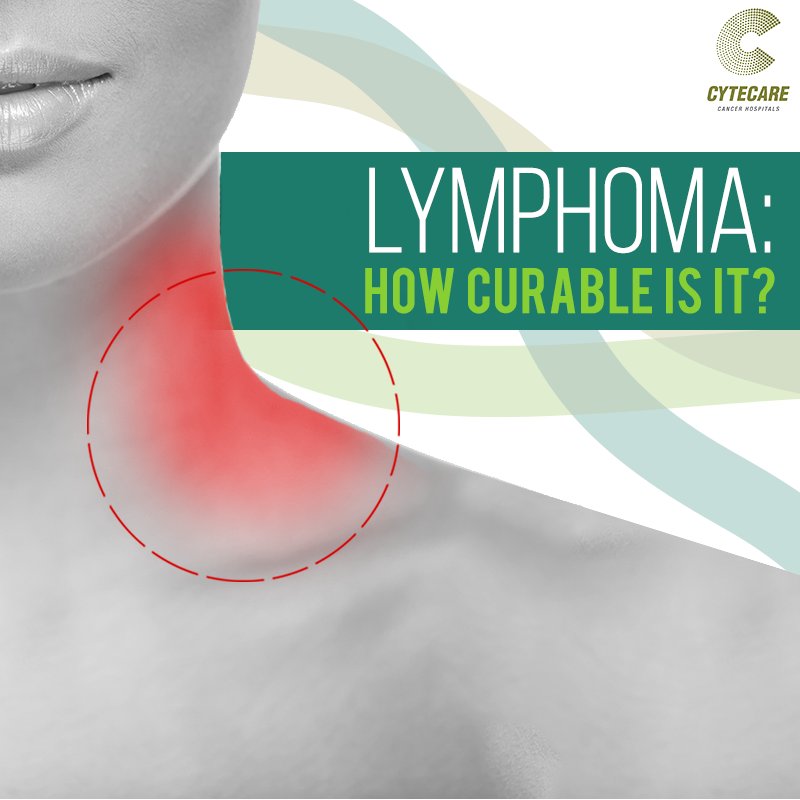
Common tests & procedures
Generally, a lymphoma diagnosis requires a lymph node biopsy. This test is done by removing a sample of your lymph node and checking it for cancer cells. You may also need blood tests and imaging tests. Though diagnosing lymphoma takes time, it’s a very important process.
How is lymphoma diagnosed and treated?
Hematologists are doctors who specialize in blood, bone marrow, and immune cell disorders. Oncologists treat cancerous tumors. Pathologists may work with these doctors to assist in treatment planning and identify if a particular treatment is working. Lymphoma treatments depend upon the cancer’s stage.
What kind of Doctor treats lymphoma?
For lymphoma, some basic questions to ask your doctor include: Do I have lymphoma? What type of lymphoma do I have? What stage is my lymphoma? Is my lymphoma aggressive or slow growing? Will I need more tests? Will I need treatment? What are my treatment options? What are the potential side effects ...
What questions should I ask my doctor about lymphoma?
Chemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses chemicals to kill lymphoma cells. Chemotherapy drugs travel through your bloodstream and can reach nearly all areas of your body. Chemotherapy is often combined with radiation therapy in people with early-stage classical type Hodgkin's lymphoma.
How is Chemo used to treat lymphoma?

Which doctor is best for lymphoma?
Hematologist. This doctor tests and treats blood diseases, including non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. They can help figure out which type of cancer you have and which treatment is best.
Do you have to be hospitalized for lymphoma?
The decision to treat the patient as an inpatient or outpatient depends on how sick the patient is and the subtype of lymphoma. Treatment for most patients with NHL is delivered in an outpatient setting. Bulky tumors and aggressive subtypes are often treated in the hospital.
What doctor Specialises in lymph nodes?
Lymphologists are doctors who are specially trained in the diagnosis of and therapy for diseases of the lymphatic system. Among other things, they examine and treat patients with lymph drainage disorders and lymphoedema (protein-rich accumulation of fluid in the tissue) at all stages of severity.
Does an oncologist treat lymphoma?
A medical oncologist or hematologist: a doctor who treats lymphoma with chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy.
What happens when you are diagnosed with lymphoma?
Common symptoms of having lymphoma include swelling of lymph nodes in your neck, in your armpits or your groin. This is often but not always painless and often could be associated with fevers, or unexplained weight loss, or drenching night sweats, sometimes chills, persistent fatigue.
What were your first signs of lymphoma?
The best way to find lymphoma early is to pay attention to possible signs and symptoms. One of the most common symptoms is enlargement of one or more lymph nodes, causing a lump or bump under the skin which is usually not painful. This is most often on the side of the neck, in the armpit, or in the groin.
What type of doctor handles lymphedema?
Since the lymphatic vessels are the third (but lesser-known) component of the circulatory system, patients who need medical care for lymphedema are likely to be referred to vascular specialists, who treat arteries, veins and diseases of the circulatory system.
When is lymphoma suspected?
Most people with lymphoma first notice enlarged lymph nodes in their neck, armpits or groin. They also may have a fever, weight loss, and other vague symptoms that can mimic other diseases. 1 Your healthcare provider may suspect lymphoma based on the symptoms you have or from scans of affected parts of your body.
Should I go to ER for swollen lymph nodes?
In some cases, swollen neck lymph nodes may occur with other symptoms that might indicate a serious or life-threatening condition that should be immediately evaluated in an emergency setting. Seek immediate medical care (call 911) if you, or someone you are with, have any of these symptoms: Difficulty swallowing.
Which hospital is best for lymphoma?
Nationally recognized expertise. Mayo Clinic is recognized for high-quality lymphoma care and research by national organizations.
What doctor looks after lymphoma?
Medical oncologist. It's a doctor who treats cancer with chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and other drugs. This person may be the main doctor you see for B-cell lymphoma.
What can be mistaken for lymphoma?
Conditions that non-Hodgkin Lymphoma is commonly misdiagnosed as include:Influenza.Hodgkin's lymphoma.Cat scratch fever.HIV.Infections.Mononucleosis.
What is the treatment for non-Hodgkin lymphoma?
Many people treated for non-Hodgkin lymphoma will receive some form of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, biologic therapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of these. Bone marrow, stem cell transplantation, or CAR T-cell therapy may sometimes be used.
How long does non-Hodgkin lymphoma last?
Although “indolent” or slow growing forms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma are not currently curable, the prognosis is still very good. Patients may live for 20 years or more following an initial diagnosis. In certain patients with an indolent form of the disease, treatment may not be necessary until there are signs of progression.
Is lymphoma a heterogeneous disease?
Blood cancers, including lymphoma, are extremely heterogeneous, and can involve a variety of treatment options, often in combination. Some form of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, or a combination is typically used to treat Hodgkin lymphoma. Bone marrow or stem cell transplantation may also sometimes be done under special ...
Lymphoma Prognosis
The outlook for people with lymphoma has never been better, thanks to advances in molecular and genetic tumor testing and improvements in understanding the biology of different lymphoma types.
Why choose Memorial Sloan Kettering for lymphoma treatment?
At Memorial Sloan Kettering, we are committed to providing all our patients with access to the most effective and innovative treatments. Our lymphoma patients have excellent outcomes and receive superior care.
What tests are done to detect Hodgkin's lymphoma?
Tests may include X-ray, CT and positron emission tomography. Removing a lymph node for testing. Your doctor may recommend a lymph node biopsy procedure to remove a lymph node for laboratory testing.
What is the goal of Hodgkin's lymphoma treatment?
The goal of treatment is to destroy as many cancer cells as possible and bring the disease into remission.
What is the procedure to remove Hodgkin's lymphoma?
A bone marrow biopsy and aspiration procedure involves inserting a needle into your hipbone to remove a sample of bone marrow. The sample is analyzed to look for Hodgkin's lymphoma cells. Other tests and procedures may be used depending on your situation.
What are the stages of Hodgkin's lymphoma?
Stages of Hodgkin's lymphoma include: Stage I. The cancer is limited to one lymph node region or a single organ. Stage II. In this stage, the cancer is in two lymph node regions or the cancer has invaded one organ and the nearby lymph nodes.
How does chemotherapy work?
Chemotherapy drugs can be taken in pill form or through a vein in your arm, or sometimes both methods of administration are used. Several combinations of chemotherapy drugs are used to treat Hodgkin's lymphoma. Side effects of chemotherapy depend on the drugs you're given. Common side effects are nausea and hair loss.
What tests can you do to see if you have cancer?
A physical exam. Your doctor checks for swollen lymph nodes, including in your neck, underarm and groin, as well as a swollen spleen or liver. Blood tests. A sample of your blood is examined in a lab to see if anything in your blood indicates the possibility of cancer. Imaging tests.
Where is Hodgkin's lymphoma stage IV?
Cancer may also be in one portion of tissue or an organ near the lymph node groups or in the spleen. Stage IV. This is the most advanced stage of Hodgkin's lymphoma. Cancer cells are in several portions of one or more organs and tissues.
What is the treatment for lymphoma?
Treatments offered to people with lymphoma include bone marrow transplant, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy and CAR-T cell therapy, among others. And because Mayo Clinic is a leader in lymphoma research, you also have access to the latest treatments by way of clinical research studies (clinical trials).
What is early cancer therapy?
The Early Cancer Therapeutics Group at Mayo Clinic offers people whose cancers haven't responded to standard chemotherapy or other treatments the opportunity to join an early-phase clinical trial of a potential new treatment.
How many people do Mayo Clinic hematologists treat?
Each year Mayo Clinic doctors care for more than 7,600 people with lymphoma.
Who is the Mayo Clinic hematopathologist?
Mayo Clinic pathologists who specialize in diseases of the blood (hematopathologists) are experienced with all types of lymphomas. They work closely with your care team to ensure an accurate diagnosis of this complex disease, which has many variations and rare forms. Research shows that expert review by pathologists who see many lymphoma cases is key to developing an appropriate treatment plan.
Does Mayo Clinic have lymphoma?
Mayo Clinic offers services for people who have completed lymphoma treatment through cancer survivor ship clinics. Follow-up medical care is important. The lymphoma survivorship clinic offers evaluation for physical and psychological side effects, as well as provides plans for follow-up care and healthy living after cancer treatment. Sometimes follow-up care involves blood tests or imaging studies.
Does Mayo Clinic require a referral?
In most cases, Mayo Clinic doesn't require a physician referral. Some insurers require referrals, or may have additional requirements for certain medical care.
What tests can be done to detect lymphoma?
Imaging tests. Your doctor may recommend imaging tests to look for signs of lymphoma cells elsewhere in your body. Tests may include CT, MRI and positron emission tomography (PET). Lymph node test. Your doctor may recommend a lymph node biopsy procedure to remove all or part of a lymph node for laboratory testing.
What tests can be done to check for swollen lymph nodes?
Physical exam. Your doctor checks for swollen lymph nodes, including in your neck, underarm and groin, as well as for a swollen spleen or liver. Blood and urine tests. Blood and urine tests may help rule out an infection or other disease. Imaging tests.
What is the best way to kill cancer cells?
Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy uses high-powered energy beams, such as X-rays and protons, to kill cancer cells. During radiation therapy, you lie on a table and a large machine moves around you, directing the energy beams to specific points on your body.
How does immunotherapy work?
Immunotherapy uses your immune system to fight cancer. Your body's disease-fighting immune system may not attack your cancer because the cancer cells produce proteins that help them hide from the immune system cells. Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process.
Can radiation kill lymphoma?
For certain types of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, radiation therapy may be the only treatment you need, particularly if your lymphoma is slow growing and located in just one or two spots. More commonly, radiation is used after chemotherapy to kill any lymphoma cells that might remain.
Can immunotherapy be used for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma?
Immunotherapy drugs may be an option for certain types of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma if other treatments haven't helped. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Review/update the information highlighted below and resubmit the form.
Can a doctor see non-Hodgkin lymphoma?
Many types of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma exist, including rare forms that some doctors may have never seen . Research shows that having your tissue samples reviewed by an experienced doctor may result in a more accurate diagnosis. If you have any concerns about your diagnosis, consider seeking a second opinion.
What is the diagnosis of lymphoma?
Also called cutaneous lymphoma, skin lymphoma diagnosis requires a skin biopsy. Bone marrow lymphoma. If lymphoma starts or spreads in the bone marrow, you’ll need a bone marrow biopsy. You might also need additional tests to determine the stage of your lymphoma.
What to do after a physical for lymphoma?
After the physical exam, the doctor will likely order a blood test. This looks for specific markers in your blood that might indicate lymphoma. It also helps your doctor rule out other possible causes of your symptoms.
What is the most accurate test for follicular lymphoma?
It’s often combined with an endoscopic ultrasound, which takes pictures of organs and lymph nodes deep inside the body. Follicular lymphoma. Typically, FISH is the most accurate test for diagnosing follicular lymphoma. Skin lymphoma. Also called cutaneous lymphoma, skin lymphoma diagnosis requires a skin biopsy.
What type of biopsy is used to determine the type of lymphoma?
The sample may also help your doctor determine the type of lymphoma and how fast it’s growing. Types of lymph node biopsies include: excision biopsy, which removes all of one lymph node. incisional biopsy, which removes part of a lymph node. core needle biopsy, which only removes a small lymph node sample.
What is the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system is a major part of your body’s immune system. It includes your lymph nodes, bone marrow, spleen, and thymus. Lymphoma occurs if cancer forms in the lymphatic system. The two main types include: Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
What to look for in a physical exam?
During a physical exam, a doctor will: look for swollen lymph nodes in the neck, groin, and underarms. check for swelling in the spleen and liver. ask about your medical history. examine any other physical symptoms.
What is the purpose of antibodies in lymphoma?
In this test, antibodies are used to check a tissue sample for specific proteins. The antibodies stick to the proteins, which activates an enzyme or fluorescent dye. This shows up under a microscope, which allows a specialist to determine the type of lymphoma cells.
What tests can be done to check lymphedema?
If the cause of your lymphedema isn't as obvious, your doctor may order imaging tests to get a look at your lymph system. Tests may include: MRI scan. Using a magnetic field and radio waves, an MRI produces 3-D, high-resolution images. CT scan.
How to treat lymphedema?
Treatment focuses on reducing the swelling and controlling the pain. Lymphedema treatments include: Exercises. Light exercises in which you move your affected limb may encourage lymph fluid drainage and help prepare you for everyday tasks, such as carrying groceries.
How to help lymphedema in arm?
A certified lymphedema therapist can teach you exercises that may help. Wrapping your arm or leg. Bandaging your entire limb encourages lymph fluid to flow back toward the trunk of your body.
How to find obstructions in lymphatic system?
Ultrasound can help find obstructions. Radionuclide imaging of your lymphatic system (lymphoscintigraphy). During this test you're injected with a radioactive dye and then scanned by a machine. The resulting images show the dye moving through your lymph vessels, highlighting blockages.
How to get lymph fluid out of arm?
Long sleeves or stockings made to compress your arm or leg encourage the flow of the lymph fluid out of your affected limb. Wear a compression garment when exercising the affected limb. Obtain a correct fit for your compression garment by getting professional help.
What can CT scans reveal?
CT scans can reveal blockages in the lymphatic system. Doppler ultrasound. This variation of the conventional ultrasound looks at blood flow and pressure by bouncing high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) off red blood cells. Ultrasound can help find obstructions.
How to treat a swollen arm?
Do your best to prevent complications in your arm or leg. Clean your skin daily, looking over every inch of your affected limb for signs of trouble, such as cracks and cuts. Apply lotion to prevent dry skin. Take care of your whole body.
How long can you wait to get treatment for NHL?
"About half of all patients can put off treatment for at least 3 years," Abetti says. "Some patients can be in watch-and-wait mode for 10 years or more .". It's possible you'll never need treatment.
How often should I have a checkup?
If you choose to delay treatment, your doctor will keep a close eye on you and look for changes. You'll have checkups every 3-6 months, or even more often . The major benefit of watch and wait is that you don't have to deal with treatment side effects, Tsai says.
Can you wait to see a doctor for lymphoma?
Also, if you aren't very good about visiting your doctor, watch and wait may not be a good choice. If you wait too long to set up an appointment, your lymphoma may get worse. Pagination. 1.
Is it hard to accept that you're not actively treating your cancer?
There's a risk that your cancer may change to a fast-growing type. It may also be hard to accept that you're not actively treating your cancer. Tsai says many of his patients struggle with this, but they feel better when they learn that watch and wait is an accepted strategy.
Can you wait to get treatment for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma?
It's an approach called "watch and wait," and it might be a choice for you if you don't have any pain or other symptoms. Your doctor will keep a close eye on your disease, and they won't start treatment ...
Can you wait to see your doctor if you have a slow growing NHL?
Also, if you aren't very good about visiting your doctor, watch and wait may not be a good choice.
What kind of doctor treats lymphoma?
A number of medical specialists collaborate to treat lymphoma. Hematologists are doctors who specialize in blood, bone marrow, and immune cell disorders. Oncologists treat cancerous tumors. Pathologists may work with these doctors to assist in treatment planning and identify if a particular treatment is working.
Where are lymphoma cells found?
The cancer cells of SLL are found mostly in the lymph nodes. SLL is identical to chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), but with CLL, the majority of cancer cells are found in the blood and bone marrow.
What is lymphoma in the body?
What is lymphoma. The lymph system is a series of lymph nodes and vessels that move lymph fluid through the body. Lymph fluids contain infection-fighting white blood cells. Lymph nodes act as filters, capturing and destroying bacteria and viruses to prevent infection from spreading. While the lymph system typically protects your body, ...
What are the two types of lymphoma?
The two major lymphoma types are Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL). A pathologist in the 1800s named Dr. Thomas Hodgkin identified the cells in what is now called Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Those with Hodgkin’s lymphoma have large cancerous cells called Reed-Sternberg (RS) cells.
What is the difference between a stage 1 and stage 4 lymphoma?
Doctors will “stage” a tumor to signify how far the cancerous cells may have spread. A stage 1 tumor is limited to a few lymph nodes, while a stage 4 tumor has spread to other organ s, such as the lungs or bone marrow.
What is the most aggressive type of lymphoma?
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most aggressive type of NHL. This fast-growing lymphoma comes from abnormal B cells in the blood. It can be cured if treated, but if left untreated, it can lead to death. The stage of DLBCL helps determine your prognosis. Read more about the stages and how this lymphoma is treated.
How does radiation help with Hodgkin's lymphoma?
Treatment for Hodgkin’s lymphoma includes radiation therapy to shrink and kill cancerous cells. Doctors also prescribe chemotherapy medications to destroy cancerous cells. Read more about these chemotherapy medications and other drugs used to treat lymphoma. Chemotherapy and radiation are also used to treat NHL.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Alternative Medicine
Coping and Support
Diagnosis
- Which lymphoma treatments are right for you depends on the type and stage of your disease, your overall health, and your preferences. The goal of treatment is to destroy as many cancer cells as possible and bring the disease into remission. Lymphoma treatments include: 1. Active surveillance.Some forms of lymphoma are very slow growing. You and your doctor may decide t…
Treatment
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Clinical Trials
- No supplements have been found to treat lymphoma. But integrative medicine may help you cope with the stress of a cancer diagnosis and the side effects of cancer treatment. Talk to your doctor about your options, such as: 1. Physical activity 2. Art therapy 3. Meditation 4. Music therapy 5. Relaxation exercises 6. Acupuncture 7. Massage
Alternative Medicine
- A lymphoma diagnosis can be overwhelming. With time you'll find ways to cope with the stress and uncertainty of cancer. Until then, you may find it helps to: 1. Learn about lymphoma.If you'd like to know more about your lymphoma, ask your doctor for the details of your cancer — the type, the stage and your prognosis. Ask for good sources of up-to-date information on your treatment …
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
Lymphoma Care at Mayo Clinic
The Mayo Clinic Experience and Patient Stories
Expertise and Rankings
Locations, Travel and Lodging
- Make an appointment with your health care provider if you have any signs or symptoms that worry you. If your provider suspects that you have a type of lymphoma, he or she may refer you to a doctor who specializes in diseases that affect the blood cells (hematologist). Because appointments can be brief, and because there's often a lot of information...
Costs and Insurance
- Your Mayo Clinic care team
Mayo Clinic specialists provide expert, personalized care to people with lymphoma, including very rare types of the disease. Your care team might include: 1. Hematologists 2. Pathologists 3. Radiation oncologists 4. Radiologists 5. Bone marrow transplant specialists 6. Surgeons 7. Dem… - Advanced diagnosis and treatment
Mayo Clinic pathologists who specialize in diseases of the blood (hematopathologists) are experienced with all types of lymphomas. They work closely with your care team to ensure an accurate diagnosis of this complex disease, which has many variations and rare forms. Researc…