What is Atraumatic Restorative Treatment for dental decay?
Alternative Restorative Treatment. Atraumatic restorative treatment (ART) is a minimally invasive treatment technique for restoring teeth by means of hand instrumentation for decay removal and fluoride-releasing adhesive materials (glass ionomer) for filling. 1 ART has been promoted by the World Health Organization as a means of delivering care in underdeveloped countries that do …
Is Atraumatic Restorative Treatment effective for pit and fissure caries?
Abstract. Atraumatic restorative treatment (ART) is a method of managing dental caries based on 2 pillars: sealants for preventing carious lesions in pits and fissures, and restorations for cavitated dentine carious lesions. ART uses only hand instruments for opening/enlarging the cavity and for removing carious tissue.
What are the types of restorative treatment in dentistry?
Supported by results of research undertaken in economically developed countries, a 15-step treatment module for dental caries is presented. This technique, which is called Atraumatic Restorative Treatment (ART), is based on removing decalcified tooth tissue using only hand instruments and restoring the cavity with an adhesive filling material.
What should I know before I start the Atraumatic Restorative Treatment?
Mar 07, 2019 · Atraumatic Restorative Treatment 2.1. Indications for Use ART is used in cases when routine dental treatment cannot be performed because of a lack of facilities or accessibility to a dental clinic [ 17 ]. In addition, ART can be used in schools as a community measure to control caries in a large number of children [ 18 ].

How helpful is atraumatic restorative treatment?
Atraumatic restorative treatment is acceptable and effective to control and prevent decay in a socioeconomically deprived community. Dental caries is the most widely spread oral disease in the world, yet it tends to go untreated in underserved communities in both developing and industrialized countries.Dec 5, 2004
What type of restorative material is used for the atraumatic restorative treatment of caries?
Conventional glass polyalkenoate (ionomer) restorative cement (GIC) is the material of choice that has been used for ART and ITR. This is because of its fluoride release properties, including its ability to bond to enamel and dentine, its pulpal biocompatibility, and its ease of manipulation.Mar 7, 2019
What is ITR pediatric dentistry?
An Interim Therapeutic Restoration (ITR) is a restoration placed on teeth to prevent the progression of caries. To provide treatment without local anesthetic using fluoride-releasing glass ionomer on teeth diagnosed with neither necrotic nor irreversible pulpitis.
Which procedures can glass ionomers be used for?
Glass ionomer cements may be used for abrasion and erosion cavities, restoration of deciduous teeth, restoration of class III and class V carious lesions, and tunnel restorations, and may also be combined with resin composite in the laminate or 'sandwich' technique.
Who introduced atraumatic restorative treatment?
Atraumatic Restorative Treatment (ART) was initiated in the mid-eighties in Tanzania in response to an inappropriately functioning community oral health programme that was based on western health care models and western technology.
Who introduced ART in dentistry?
ART was firstly introduced by the dentist Jo Frencken in 1985, Tanzania (Frencken et al., 1996), where the management of decayed teeth in children living in a deprived area was challenging because access to dental treatments using drills was restricted by limited dentist availability and a lack of electricity and/or ...
What is the difference between art and ITR?
ART is used in cases when there are obstacles to reaching dental care units and has been proven to have high success rates in primary and permanent dentitions. ITR is used as a temporary restoration that will be replaced with a more definitive one.Mar 7, 2019
What does art stand for in dentistry?
Atraumatic Restorative Treatment (ART) is an alternative approach for managing dental decay, which involves removal of decayed tissue using hand instruments alone, usually without the use of anaesthesia (injected painkiller) and electrical equipment.Dec 28, 2017
What is an interim restoration?
Interim restoration protects abutment teeth and periodontal tissues until prosthetic treatment ends with the fabrication of a definitive prosthesis, restores and maintains the functions and morphology of the stomatognathic system, and preserves the occlusal contact relationship.Jun 18, 2019
Is composite better than GIC?
While they are less durable than harder wearing fillings, like silver amalgams or gold fillings, composite fillings are significantly more durable than its glass ionomer counterpart. The downside being, after many years of use composite fillings can chip.Dec 19, 2018
Do composite fillings release fluoride?
These days various restorative materials containing fluoride in their formulation are available in the market. These materials such as glass ionomer cements, Resin modified glass ionomers, compomers and composites are able to release fluoride ions in the oral environmental.
Does GIC bond better to enamel or dentine?
This study followed other results presented in the literature, which established that the GICs have higher bond strength to enamel, than to dentine (8,9).May 1, 2011
What is ART in dentistry?
Atraumatic restorative treatment (ART) is a method of managing dental caries based on 2 pillars: sealants for preventing carious lesions in pits and fissures, and restorations for cavitated dentine carious lesions.
How does art work?
ART uses only hand instruments for opening/enlarging the cavity and for removing carious tissue. The amount of carious tissue that should be removed depends mainly on the cavity depth. In cavities of shallow and medium depth, carious tissue is removed up to firm dentine.
What is ITR in dentistry?
ITR is used as a temporary restoration that will be replaced with a more definitive one. ITR is used in cases when the ideal dental treatment cannot be performed. Conventional glass polyalkenoate (ionomer) restorative cement (GIC) is the material of choice that has been used for ART and ITR.
Why is art used in dentistry?
ART is used in cases when routine dental treatment cannot be performed because of a lack of facilities or accessibility to a dental clinic [17]. In addition, ART can be used in schools as a community measure to control caries in a large number of children [18]. ART can be used in both primary and permanent teeth [1].
What is ITR used for?
ITR, on the other hand, is used for treating patients in dental clinics in order to control the progression of caries or to manage certain health characteristics of the patient . A high-viscosity glass ionomer performed better than low and medium-viscosity glass ionomers in ART.
How long does it take for ITR to be replaced?
Generally, ITR should be replaced with a more definitive restoration within six months of the placement to ensure maximum benefit to the patient and to reduce the risk of failure, as the levels of oral cariogenic bacteria might return to pre-treatment levels after six months of treatment [82]. 3.5.
What is carisolv made of?
Carisolv is a gel composed of 0.5% sodium hypochlorite and three amino acids, including lysine , leucine , and glutamic acid [66]. Papacarie and Carisolv are used to dissolve carious tooth structures by breaking the collagen fibrils infected by caries, with the ability to preserve sound tissues [56,65].
Is fluoride good for ART?
The fluoride-release from GIC seems to be advantageous for ART. Fluoride that is released from GIC makes the tooth structures (enamel and dentine) more resistant to acidic invasion by bacteria [7,8,23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. Fluoride can be released from glass ionomers for up to five years [24,27].
Abstract
This review highlights the importance of atraumatic restorative treatment (ART) as a minimal intervention procedure for managing dental caries (pit and fissures caries) and restoring cavitated dentin carious lesions using restorative materials such as glass-ionomer cement. ART technique uses only hand instruments and requires no electricity.
INTRODUCTION
Globally, dental caries has the highest prevalence amongst all oral diseases. It is estimated that 2.3 billion adults and over 530 million children are afflicted by dental caries. [ 1]
DEFINITION AND ART CONCEPT
ART is defined as a minimally invasive approach in preventing dental caries and arresting its further progression.
RATIONALE OF ART
Using a biological approach requires a minimal preparation of the cavity that retains sound tooth tissues and causes less damage to the teeth
GLASS IONOMER AS RESTORATIVE MATERIAL IN ART
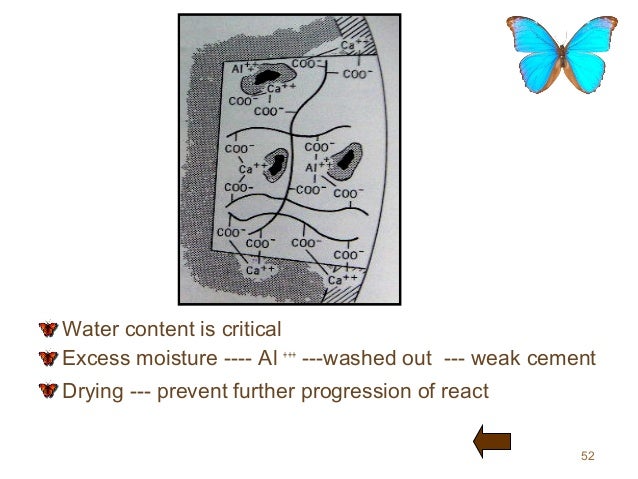
ART is best performed using GIC. Fluoride releasing properties in GIC makes the tooth structure more resistant to dentinal caries. GIC that is specifically designed for ART is the high-viscosity materials (such as Ketac Molar Easymix ®, GC Fuji IX, 3M ESPE, Seefeld, Germany).
OTHER MATERIALS USED WITH ART
Resin composite, compomer, and resin-modified glass ionomer have also been used for restorations. However, autocured high-viscosity glass ionomer seems to be the most appropriate adhesive restorative material for use with ART. [ 6]
CLINICAL TRIALS
Various clinical trials have evaluated ART since its initial trial in 1986. [ 2, 7]
What is ART in dentistry?
Atraumatic restorative Treatment (ART) Technique, Indications, Advantages and Disadvantages. A General dental treatment for restorative procedures requires a lot of equipment involving Electricity in every Dental clinic, but in developing and backward countries some places do not have access to basic amenities like electricity, etc.
How long to chew on a tooth restoration?
Advice the patient to not eat or drink for 1 hour and not to chew on the side of the filling for 24 hours. For class two cavities using a matrix band and wedge is a must after tooth preparation.
What is the material used in art?
Restorative material used in ART is Glass Ionomer cement (GIC) as it bonds chemically to both enamel and dentin which reduces the need for removing sound tooth structure to achieve retention. GIC releases Fluoride which helps in arresting caries. It does not harm the pulp tissue.
How to prepare for a cavity?
Cavity Preparation: Dry the tooth surface using a dry cotton pellet, now using the spoon excavator to remove Soft caries in a spooning movement. If you are not able to remove entire caries with the excavator you need to widen the cavity entrance with the help of the enamel hatchet or carver.
What are the goals of art?
The three Goals of the ART technique are Avoiding discomfort, Reducing infection and preserving the tooth structure. The Principles of ART – Removing the carious lesions using hand instruments and restoring the cavity with a restorative material that bonds (Glass Ionomer Cement) to the tooth.
How to clean a cavity with GIC?
Use a dentine conditioner or tooth cleaner (10% polyacrylic acid) to remove any tooth debris left, removing this smear layer helps in the bonding of GIC. You can use GIC liquid to clean the cavity as well. Filling the Cavity: Glass Ionomer cement is taken and mixed on a mixing pad along with a plastic spatula.
What is the art technique?
In situations like the Coronavirus Pandemic, the ART technique is the way to go as it doesn’t lead to the production of Aerosols. ART Definition: By the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry, “A dental caries treatment procedure involving the removal of soft, demineralized tooth tissue using hand instrument alone, ...

Indications & Contraindications –
Armamentarium –
- The armamentarium of ART includes hand instruments which can be classified based on the classification given by G.V Black – 1. Exploring instruments– used in the confirmation of depth and invasion of the caries along with their existence which include 1. mouth mirror 2. straight probes 3. shepherd’s hook or explorer of no. 21 and 4. a periodontalprobe. 2. Hand cutting instru…
Technique –
- It is often noted that the queries about success of this technique always remain on the surface in the school of thoughts. Estimating success of a particular technique lies in the practical implementation of the technique. The implementation procedures are nothing but a serious of simple steps. 1. To begin with, understanding the patient and diagnosis is the first process, it is r…
Limitations –
- Apart from being an absolute perfect alternative for the mechanical restoration, ART is time consuming and effort oriented. It is a conventional technique to be used as an alternative to machine based advanced dentistry. Even though the chances of pulp exposure are minimal but cutting down to the exact cavity shape and size, preserving all its preparation features is challen…
Conclusion –
- This restorative technique is one of the early techniques to be used for prevention for extension of the cavity. It is not only minimally invasive but to a larger extent it is atraumatic and that serves as an advantage in the patient circle but to practise this conventional art, a dentist is required to be skill oriented with an established practis...