
Precautions
Cycle delay was defined as the duration of the first day of cycle-to-cycle being more than 8 weeks, and dose reduction was defined as the administration of 11 mg/m2every 8 hours, as stated in the prescribing information for decitabine [6]. In the DACO-020 study (5-day regimen), no dose reductions or escalations were allowed.
What is cycle delay in decitabine?
If any of the following nonhematologic toxicities are present, decitabine treatment should not be restarted until the toxicity is resolved: 1) serum creatinine greater than or equal to 2 mg/dL; 2) SGPT, total bilirubin greater than or equal to 2 times ULN; and 3) active or uncontrolled infection.
When should decitabine be stopped for nonhematologic toxicities?
Objective: Decitabine is reported to be valuable in treating multiple malignant blood diseases. However, the application of decitabine in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDSs) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) has not been fully examined.
Is decitabine effective in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia?
Decitabine is approved to treat: Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Decitabine is also being studied in the treatment of other conditions and types of cancer. Definition from the NCI Drug Dictionary - Detailed scientific definition and other names for this drug.
What is decitabine used to treat?
What does decitabine treat?
Decitabine is used to treat myelodysplastic syndrome (a group of conditions in which the bone marrow produces blood cells that are misshapen and does not produce enough healthy blood cells). Decitabine is in a class of medications called hypomethylation agents.
Will decitabine cure MDS?
Results from phase 2 and phase 3 studies indicate that decitabine is effective in the treatment of MDS, resulting in durable clinical responses and delayed time to AML transformation or death.
How long can you take decitabine?
Decitabine (Dacogen) Azacitidine can be injected under the skin or into a vein (IV), often for 7 days in a row, once a month. Decitabine is often injected into a vein (IV) over 3 hours every 8 hours for 3 days. This is repeated every 6 weeks.
How long does decitabine take to work?
How long does it take for patients to respond to treatment? In the clinical study, the median time for patients to achieve some level of remission for either CR or CRh was 2 months (with a range of 0.8 to 4.2 months).
What happens if MDS is not treated?
In MDS, some cells in the bone marrow don't grow like they should, so there aren't enough of some types of blood cells. This makes it hard for the body to work the way it should. Some people with MDS go on to get leukemia, a cancer of the bone marrow in which blood cells start to grow out of control.
What is the latest treatment for MDS?
FDA Approves New Therapy for Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) That Can Be Taken at Home. Today, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Inqovi (decitabine and cedazuridine) tablets for treatment of adult patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML).
How do you know if chemo is working?
The best way to tell if chemotherapy is working for your cancer is through follow-up testing with your doctor. Throughout your treatment, an oncologist will conduct regular visits, and blood and imaging tests to detect cancer cells and whether they've grown or shrunk.
How often is decitabine administered?
2.1 Recommended Starting Dosage Administer DACOGEN at a dose of 15 mg/m2 by continuous intravenous infusion over 3 hours repeated every 8 hours for 3 days.
Is decitabine a chemotherapy drug?
DECITABINE (dee SYE ta been) is a chemotherapy drug. This medicine reduces the growth of cancer cells. It is used to treat adults with myelodysplastic syndromes.
Is decitabine approved for AML?
Due to this, decitabine did not achieve FDA approval for AML, but continues to be used off-label. Current research is focused on further defining subgroups of elderly AML patients who may derive greater benefit from decitabine therapy and combining it with other low-intensity active agents for AML.
Does decitabine cause hair loss?
However, many people have no side effects or only have minor side effects. Call your doctor or get medical help if any of these side effects or any other side effects bother you or do not go away: Hair loss. Constipation, diarrhea, stomach pain, upset stomach, throwing up, or feeling less hungry.
Can you live a normal life with MDS?
These statistics were published in 2007 based on patients diagnosed between 1982 and 2004. Remember, these survival statistics are only estimates – they can't predict what will happen to any individual person....Survival statistics for MDS.IPSS-R risk groupMedian survivalVery high0.8 years4 more rows•Jan 22, 2018
Is there any cure for MDS?
There's no cure for myelodysplastic syndromes, but some medications can help slow the progression of the disease. If you have no symptoms, treatment might not be needed right away. Instead, your doctor might recommend regular exams and lab tests to monitor your condition and to see if the disease progresses.
How long does decitabine infusion take?
Estimated total infusion time for this treatment: 60 minutes. Infusion times are based on clinical studies, but may vary depending on doctor preference or patient tolerability. Pre-medications and intravenous (I.V.)
Does decitabine cause hair loss?
However, many people have no side effects or only have minor side effects. Call your doctor or get medical help if any of these side effects or any other side effects bother you or do not go away: Hair loss. Constipation, diarrhea, stomach pain, upset stomach, throwing up, or feeling less hungry.
Does dacogen work?
Hematologic (blood) improvement occurred in 12% of patients treated with Dacogen, compared with 7% of patients treated with supportive care. Anticancer responses lasted for a median of 10.3 months.
Usual Adult Dose for Myelodysplastic Syndrome
TREATMENT REGIMEN OPTION 1: 15 mg/m2 IV over 3 hours; repeat every 8 hours for 3 days; repeat this cycle every 6 weeks; patients may be premedicated with standard antiemetic therapy If hematologic recovery (ANC 1,000/mcL or greater and platelets 50,000/mcL or greater) from a previous treatment cycle requires more than 6 weeks, then the next cycle should be delayed and dosing temporarily reduced by following this algorithm: -Recovery requiring more than 6, but less than 8 weeks: Delay dosing for up to 2 weeks and temporarily reduce the dose to 11 mg/m2 IV every 8 hours (33 mg/m2/day, 99 mg/m2/cycle) when restarting therapy -Recovery requiring more than 8, but less than 10 weeks: Assess patient for disease progression (by bone marrow aspirates); in the absence of progression, the dose should be delayed up to 2 more weeks and then reduced to 11 mg/m2 IV every 8 hours (33 mg/m2/day, 99 mg/m2/cycle) when restarting therapy, then maintained or increased in subsequent cycles as clinically indicated TREATMENT REGIMEN OPTION 2: 20 mg/m2 IV over 1 hour; repeat daily for 5 days; repeat this cycle every 4 weeks; patients may be premedicated with standard antiemetic therapy If myelosuppression is present, subsequent treatment cycles should be delayed until there is hematologic recovery (ANC 1,000/mcL or greater and platelets 50,000/mcL or greater) Comments: -With either regimen, it is recommended that patients be treated for a minimum of 4 cycles; however, a complete or partial response may take longer than 4 cycles. -Perform complete blood and platelet counts prior to each cycle and as needed to monitor response and toxicity. -Perform liver chemistries and serum creatinine prior to initiation of therapy. Use: For the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) including previously treated and untreated, de novo and secondary MDS of all French-American-British subtypes (refractory anemia, refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts, refractory anemia with excess blasts, refractory anemia with excess blasts in transformation, and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia) and intermediate-1, intermediate-2, and high-risk International Prognostic Scoring System groups.
Dose Adjustments
If any of the following nonhematologic toxicities are present, decitabine treatment should not be restarted until the toxicity is resolved: 1) serum creatinine greater than or equal to 2 mg/dL; 2) SGPT, total bilirubin greater than or equal to 2 times ULN; and 3) active or uncontrolled infection. Geriatric patients were generally dosed at the same level as younger adult patients.
Precautions
Safety and efficacy have not been established in patients younger than 18 years. Consult WARNINGS section for additional precautions.
Other Comments
Administration advice: -Once prepared, the final product should be given as a continuous IV infusion over one hour; a central venous catheter is not required. -Premedication for prevention of nausea and vomiting is not typically required, but may be administered if necessary. Storage requirements: The manufacturer's product information should be consulted. Reconstitution/preparation techniques: The manufacturer's product information should be consulted. Patient advice: -Decitabine may cause adverse effects such as anemia during treatment; therefore, caution should be exercised if you are driving or operating machinery..
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
Why are drugs studied?
Drugs are often studied to find out if they can help treat or prevent conditions other than the ones they are approved for. This patient information sheet applies only to approved uses of the drug. However, much of the information may also apply to unapproved uses that are being studied.
Is the drug information on this page educational?
Important: The drug information on this page is meant to be educational. It is not a substitute for medical advice. The information may not cover all possible uses, actions, interactions, or side effects of this drug, or precautions to be taken while using it. Please see your health care professional for more information about your specific medical condition and the use of this drug.
Is decitabine safe for cancer?
Use in Cancer. Decitabine is approved to treat adults with: Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), including chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML). Decitabine is also being studied in the treatment of other conditions and types of cancer. Decitabine is also available in a tablet form. For more information, see the Drug Information Summary ...
What is decitabine used for?
Decitabine is used in treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS).
How does decitabine work?
Decitabine's anticancer effects are believed to be twofold. One way that it works is by demethylation or interfering with the methylation of DNA. By this process of demethylation, normal function to the tumor suppressor genes is restored, thus restoring control over cell growth.
What is the name of the drug that is used to kill cancer cells?
Decitabine also belongs to the category of chemotherapy called antimetabolites. Antimetabolites are very similar to normal substances within the cell. When the cells incorporate these substances into the cellular metabolism, they interact with a number of targets within the cell to produce a direct cytotoxic effect that causes death of rapidly dividing cancer cells.
What is the function of demethylating DNA?
Decitabine is a member of a new class of drugs known as DNA "demethylating" agents. Methylation of DNA is a major mechanism that regulates gene expression in cells. When there is an increase in DNA methylation this can result in the blockage of the activity of "suppressor genes" that regulate cell division and growth. When suppressor genes are blocked, cell division becomes unregulated, allowing or promoting cancer.
How long after a child is on decitabine can you father?
Males should avoid fathering a child while on Decitabine therapy and for 2 months after treatment.
Can you take aspirin with decitabine?
Do not take aspirin, products containing aspirin unless your doctor specifically permits this.
Does Decitabine have CBC?
You will be checked regularly by your doctor while you are taking Decitabine, to monitor side effects and check your response to therapy. Periodic blood work will be obtained to monitor your complete blood count (CBC) as well as the function of other organs (such as your kidneys and liver) will also be ordered by your doctor.
What is the treatment for MDS?
A number of emerging therapeutic options are currently being evaluated for the treatment of MDS that will, it is hoped, add to the treatment options for patients who are ineligible to receive HSCT or intensive chemotherapy. Lenalidomide, an immunomodulatory drug derived from thalidomide, has been recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and is indicated for the treatment of MDS in patients with chromosome 5q deletion. Other agents such as imatinib and tipifarnib are currently being evaluated in clinical trials (Cortes et al 2003; Feldman 2005; Sekeres 2005; Jabbour and Giles 2005). Some of the therapies farthest along in development are the hypomethylating agents decitabine and azacitidine, both of which have been recently approved by the FDA for the treatment of MDS.
What is DNA methylation?
DNA methylation is a common epigenetic modification that plays an important role in gene expression in mammalian cells (Leone et al 2002; Das and Singal 2004). As part of normal development, certain genes may be silenced through methylation of cytosine residues in their promotor regions (CpG islands). However, in some hematopoietic neoplasms including MDS, DNA hypermethylation can inactivate genes essential for the control of normal cell growth, differentiation, or apoptosis. A group of enzymes called DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) catalyze the methylation of cytosine residues in newly synthesized DNA, thus replicating the methylation signal. In recent years, there has been interest in pharmacologic therapies that target this mechanism by inhibiting DNMT, resulting in hypomethylation of the DNA and re-expression of tumor suppressor genes. Cytosine analogues such as decitabine have been shown to inhibit DNMT and are being used against MDS, as well as AML and other cancers (Leone et al 2002; Das and Singal 2004).
Does decitabine inhibit cell proliferation?
Decitabine is believed to have a dual mechanism of action depending on dose. At both lower and higher doses, decitabine incorporates into DNA; however, at higher doses, decitabine inhibits cell proliferation through nonreversible covalent linking with DNA methyltransferase and blocking of DNA synthesis (Leone et al 2002). At lower doses, decitabine induces hypomethylation, thereby promoting cell differentiation, re-expression of tumor suppressor genes, stimulation of immune mechanisms, and suppression of tumor growth (Leone et al 2002; Mund et al 2005).
How long does it take for AML to transform?
Median time to AML transformation, 25% of patients (yrs)
Is decitabine safe for a patient?
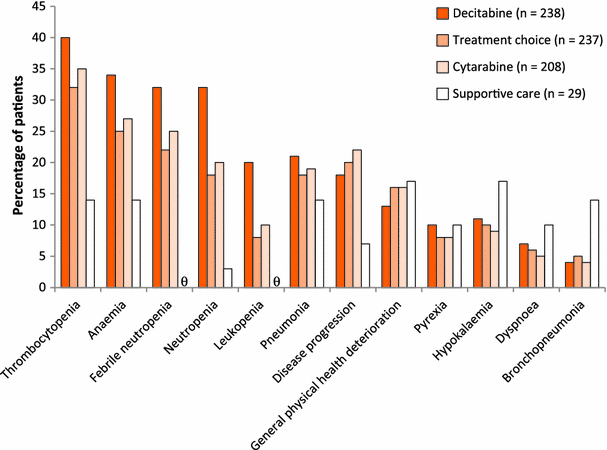
Safety data were evaluated for 83 patients treated with decitabine and 81 patients who received supportive care only. Overall, decitabine therapy was well tolerated with manageable adverse effects. The most common adverse effects included myelosuppression (neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia), pyrexia, fatigue, nausea, cough, petechiae, diarrhea, and constipation (Table 3). Febrile neutropenia occurred in 28% of patients who received decitabine. The authors noted that neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, and leukopenia appeared to diminish in incidence over the first four cycles of decitabine treatment; however, these toxicities remained frequent, most likely owing to the continuing presence of underlying disease and myelosuppression.
Does decitabine go through the body?
Decitabine distributes extensively throughout human tissues. In a phase 1 pharmacokinetic study of decitabine in 21 patients with advanced solid tumors, the mean value of volume of distribution was found to be 4.59 L/kg ± 1.42 (van Groeningen et al 1986). Although the exact route of elimination and metabolic fate of decitabine is unknown in humans, high total body clearance values and a total urinary excretion of less than 1% of the administered dose suggest that decitabine is eliminated rapidly and primarily through enzymatic metabolism (van Groeningen et al 1986).
Is decitabine soluble in water?
Decitabine is slightly soluble in ethanol/water (50/50), methanol/water (50/50), and methanol; sparingly soluble in water; and soluble in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO). Decitabine (Dacogen™ for Injection) is a white to almost-white sterile lyophilized powder supplied in a clear, colorless glass vial (Dacogen 2006).
What is the purpose of decitabine?
Decitabine is designed to help the bone marrow produce more healthy and normal functioning cells. Decitabine is given to help increase blood cell counts, reduce the risk of infection, reduce the amount of blood transfusions needed, decrease the risk of bleeding, and to prevent MDS from transforming to acute leukemia.
How often is decitabine given?
On occasion, decitabine may be given in the hospital if someone is too sick. Decitabine is repeated every 28 days. This is known as one cycle.
How long does it take for decitabine to work?
Treatment is continued until decitabine is no longer working or it is stopped because of unacceptable side effects. Estimated total infusion time for this treatment: 60 minutes. Infusion times are based on clinical studies, but may vary depending on doctor preference or patient tolerability.
How to minimize the cost of cancer treatment?
One way to minimize costs associated with cancer treatment is to ask your doctor what types of tests they are ordering. If they are expensive, ask if they are covered by insurance before getting the test. If you are concerned about costs, you can also ask your doctor to only order tests that are absolutely necessary and to minimize the ones that are unlikely to change the plan. Some anti-cancer and supportive care medications are now available as generic formulations and preferred by insurance companies. If these medications are still expensive, ask your doctor to work with your pharmacist to find cheaper alternatives. Some drugs have co-pay cards or patient assistance programs that can help reduce the cost.
How many people discontinue decitabine?
Side effects sometimes have percentage ranges [example 1 – 4%] because they differed between in clinical studies: On average, 8 - 17% of patients discontinue decitabine due to unacceptable side effects.
Can you travel to a clinical trial?
It is possible, but it will depend upon the clinical trial requirements and whether you are willing to travel periodically for monitoring. Some, but not all, clinical trials require daily laboratory work as part of the monitoring requirements. Usually monitoring is more frequent at the start of the trial and decreases as time goes on. Most clinical trials cover the cost of the experimental medication and some help to cover travel costs as well as scans when needed. If you cannot afford a standard treatment, a clinical trial may be a way to receive treatment while minimizing out-of-pocket costs.
How long should you take decitabine?
Decitabine should usually be given for at least four cycles but may be continued if your doctor decides that you will benefit from additional treatment. Your doctor may also need to delay your treatment and reduce your dose if you experience certain side effects.
What is the purpose of decitabine?
Decitabine is used to treat myelodysplastic syndrome (a group of conditions in which the bone marrow produces blood cells that are misshapen and does not produce enough healthy blood cells). Decitabine is in a class of medications called hypomethylation agents. It works by helping the bone marrow produce normal blood cells and by killing abnormal cells in the bone marrow.
How should this medicine be used?
Decitabine comes as a powder to be to be added to fluid and injected slowly over 3 hours intravenously (into a vein) by a doctor or nurse in a medical office or hospital outpatient clinic. It is usually injected every 8 hours for 3 days. This treatment period is called a cycle, and the cycle may be repeated every 6 weeks for as long as your doctor recommends. Decitabine should usually be given for at least four cycles but may be continued if your doctor decides that you will benefit from additional treatment.
What are the side effects of a syringe injection?
change in skin color. hair loss. joint or muscle pain. chest discomfort or chest wall pain. swelling of the hands, feet, ankles, lower legs, or stomach. pain, swelling, or redness at injection spot. Some side effects can be serious.
Can you get pregnant while on decitabine?
You or your partner should not become pregnant while you are using decitabine. You should use birth control to prevent pregnancy in yourself or your partner during your treatment with decitabine and for 2 months afterwards. Talk to your doctor about birth control methods that will work for you.
Can decitabine cause blurred vision?
frequent urination. extreme hunger. weakness. blurred vision. Decitabine may cause other side effects. Call your doctor if you have any unusual problems while receiving this medication.
Indications and Usage For Decitabine
This medication is used to treat a group of blood/bone marrow disorders (myelodysplastic syndromes-MDS) in which the bone marrow does not produce enough healthy blood cells.
May Treat: Acute myeloid leukemia · Myelodysplastic syndrome
Brand Names: Dacogen
Drug Class: Antineoplastic - Antimetabolite - Pyrimidine Analogs
Availability: Prescription Required
Pregnancy: Consult your doctor. This medication may be harmful to an unborn child.
Lactation: This drug should not be given to breastfeeding mothers
Decitabine Dosage and Administration
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Warnings and Precautions
Adverse Reactions
Drug Interactions
- Recommended Dosage
Pre-Medications and Baseline Testing 1. Consider pre-medicating for nausea with antiemetics. 2. Conduct baseline laboratory testing: complete blood count (CBC) with platelets, serum hepatic panel, and serum creatinine. Decitabine for Injection Regimen Options Three Day Regimen Admi… - Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Hematologic Toxicity If hematologic recovery from a previous Decitabine for injection treatment cycle requires more than 6 weeks, delay the next cycle of Decitabine for injection therapy and reduce Decitabine for injection dose temporarily by following this algorithm: 1. Recovery requirin…
Use in Specific Populations
- For Injection: 50 mg of Decitabine as a sterile, white to almost white lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution.
Overdosage
- Myelosuppression
Fatal and serious myelosuppression occurs in Decitabine-treated patients. Myelosuppression (anemia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia) is the most frequent cause of Decitabine dose reduction, delay, and discontinuation. Neutropenia of any grade occurred in 90% of Decitabine-tr… - Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from human data, animal studies and its mechanism of action, Decitabine can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. In preclinical studies in mice and rats, Decitabine caused advers…
Decitabine Description
- The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling: 1. Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Decitabine - Clinical Pharmacology
- Drug interaction studies with Decitabine have not been conducted. In vitro studies in human liver microsomes suggest that Decitabine is unlikely to inhibit or induce cytochrome P450 enzymes. In vitro metabolism studies have suggested that Decitabine is not a substrate for human liver cytochrome P450 enzymes. As plasma protein binding of Decitabine is negligible (<1%), interacti…
Usual Adult Dose For Myelodysplastic Syndrome
- Pregnancy
Risk Summary Based on findings from human data, animal studies, and the mechanism of action, Decitabine can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. Limited published data on Decitabine u… - Lactation
Risk Summary There are no data on the presence of Decitabine or its metabolites in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from Decitabine in a breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed …
Dose Adjustments
- There is no known antidote for overdosage with Decitabine. Higher doses are associated with increased myelosuppression including prolonged neutropenia and thrombocytopenia. Standard supportive measures should be taken in the event of an overdose.
Precautions
- Decitabine is a nucleoside metabolic inhibitor. Decitabine is a fine, white to almost white powder with the molecular formula of C8H12N4O4 and a molecular weight of 228.21. Its chemical name is 4-amino-1-(2-deoxy-β-D-erythro-pentofuranosyl)-1,3,5-triazin-2(1H)-one and it has the following structural formula: Decitabine is slightly soluble in ethanol/water (50/50), methanol/water (50/50…
Other Comments
- Mechanism of Action
Decitabine is believed to exert its antineoplastic effects after phosphorylation and direct incorporation into DNA and inhibition of DNA methyltransferase, causing hypomethylation of DNA and cellular differentiation or apoptosis. Decitabine inhibits DNA methylation in vitro, which is ac… - Pharmacodynamics
Decitabine has been shown to induce hypomethylation both in vitro and in vivo. However, there have been no studies of Decitabine-induced hypomethylation and pharmacokinetic parameters.
Further Information