How is coronary fistula treated?
Infants with a larger fistula will need to have surgery to close the abnormal connection. The surgeon closes the site with a patch or stitches. Another treatment option plugs up the opening without surgery, using a special wire (coil) that is inserted into the heart with a long, thin tube called a catheter.
Is a coronary fistula a congenital?
In most cases, coronary artery fistula is congenital, meaning a child is born with the condition. It occurs when one of the coronary arteries doesn't form correctly during the baby's development. Some children can also develop a coronary artery fistula after birth.
What is coronary artery fistula?
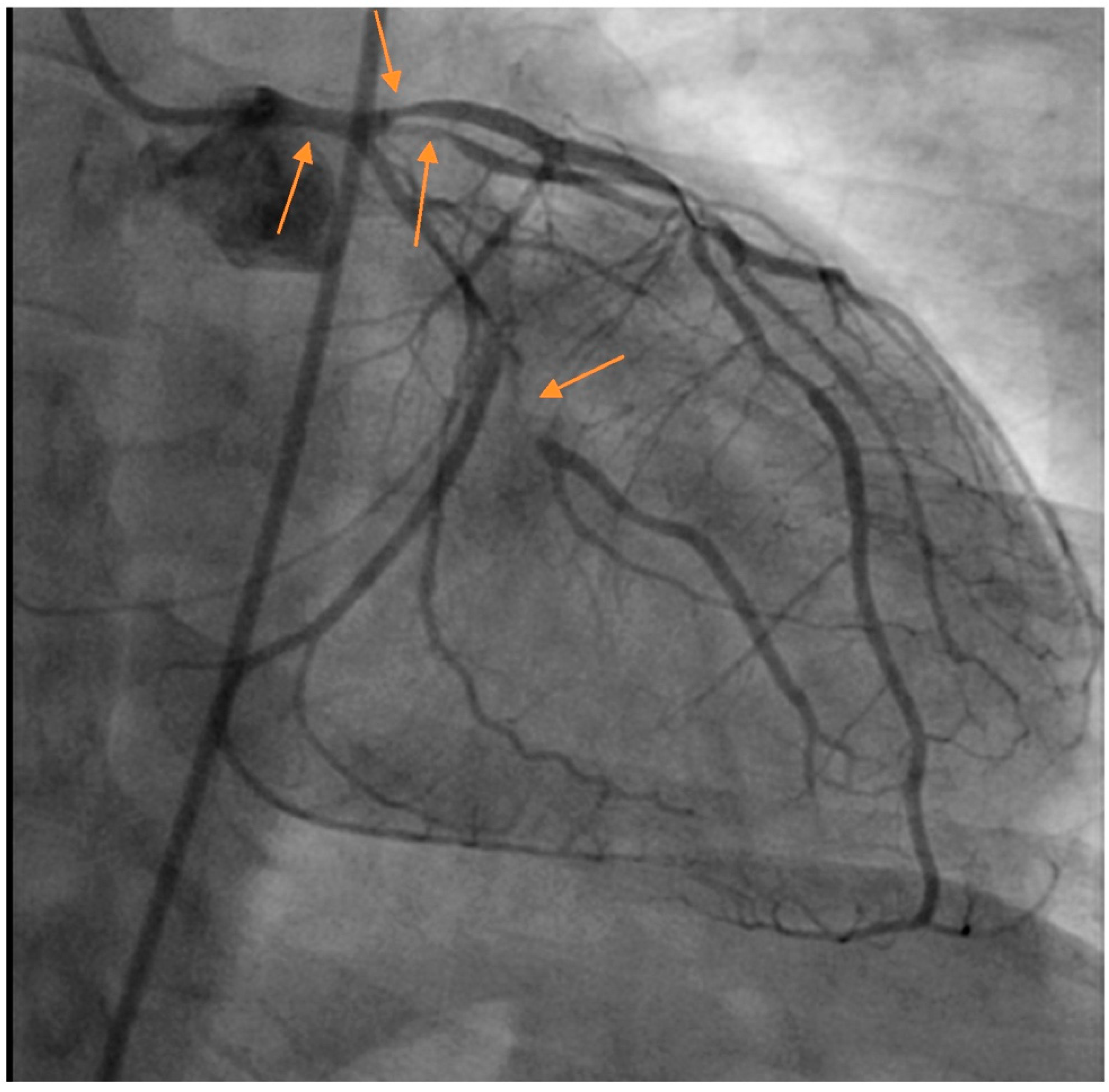
Coronary artery fistulas are aberrant connections between coronary arteries and other structures, such as other branches of arteries or heart chambers. They are largely asymptomatic but can lead to several life-threatening complications.
What does Alcapa stand for?
In anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery (ALCAPA), something goes wrong while the heart is forming in the womb, and the left coronary artery arises from the pulmonary artery instead of the aorta.
What is an AV fistula surgery?
An AV fistula is a surgically placed "shunt"; that is, an artery is directly sutured to a vein. An artery is a high-pressure vessel that carries blood away from the heart and delivers nutrients and oxygen to the tissues.
What is mid LAD myocardial bridging?
Myocardial bridging occurs when the heart is malformed, with a bridge of muscle fibers overlying a section of a coronary artery, usually the left anterior descending (LAD) artery. When the heart beats, the artery is squeezed and normal blood flow is disrupted during both the pumping and relaxed cycles.
What is the most common complication of AV fistula?
Heart failure. This is the most serious complication of large arteriovenous fistulas. Blood flows more quickly through an arteriovenous fistula than it does through typical blood vessels. The increased blood flow makes the heart pump harder. Over time, the strain on the heart can lead to heart failure.
What causes fistula?
A fistula is an abnormal connection between two body parts, such as an organ or blood vessel and another structure. Fistulas are usually the result of an injury or surgery. Infection or inflammation can also cause a fistula to form.
What is the main function of coronary arteries?
Coronary arteries supply blood to the heart muscle. Like all other tissues in the body, the heart muscle needs oxygen-rich blood to function. Also, oxygen-depleted blood must be carried away. The coronary arteries wrap around the outside of the heart.
Why is ALCAPA a problem?
ALCAPA is a problem that occurs when the baby's heart is developing early in the pregnancy. The developing blood vessel to the heart muscle does not attach correctly. In the normal heart, the LCA originates from the aorta.
What is bland white garland syndrome?
Background: Bland-White-Garland syndrome (BWGS) is a very rare disease characterized by anomalous origin of the left coronary artery from the pulmonary trunk (ALCAPA). WBGS affects 1 in every 300 000 live births. Children typically present with dyspnea, pallor, and failure to thrive.
What is alpaca heart?
Anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery (ALCAPA) is a congenital (present at birth) heart defect in which the left coronary artery arises abnormally from the pulmonary artery. Normally, the left and right coronary arteries arise from the aorta and supply blood with oxygen to the heart.