
Hypochlorite
In chemistry, hypochlorite is an ion with the chemical formula ClO⁻. It combines with a number of cations to form hypochlorites, which may also be regarded as the salts of hypochlorous acid. Common examples include sodium hypochlorite and calcium hypochlorite.
What is chlorination and how does it work?
Chlorination is the process of adding chlorine to drinking water to kill parasites, bacteria, and viruses. Different processes can be used to achieve safe levels of chlorine in drinking water. Using or drinking water with small amounts of chlorine does not cause harmful health effects and provides protection against waterborne disease outbreaks.
What is chlorine in drinking water?
How does chlorine disinfection work? Chlorine kills pathogens such as bacteria and viruses by breaking the chemical bonds in their molecules. Disinfectants that are used for this purpose consist of chlorine compounds which can exchange atoms with other compounds, such as enzymes in bacteria and other cells.
What happens when you add chlorine to tap water?
Apr 04, 2018 · Chlorine is used in drinking water and swimming pool water to kill harmful bacteria. It is also as used as part of the sanitation process for industrial waste and sewage. Household chlorine bleach can release chlorine gas if it is mixed with certain other cleaning agents. Chlorine was used during World War I as a choking (pulmonary) agent.
What is the'chlorine enquiry'of water?
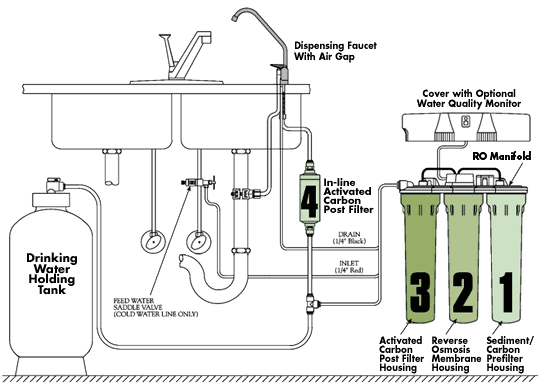
Filtration is another method for removing chlorine from drinking water. Most water filtration systems use reverse osmosis, which uses a permeable membrane to remove chlorine and other particles, ions, and impurities from tap water. Chlorine and other contaminants are left behind when water passes through the membrane.
See more
Because of Chlorine Dioxide's solubility in water, it starts being used as a water treatment. In 1944, Chlorine Dioxide was used by the City of Niagra New York, to control odor and remove phenols from the river water used as the municipal supply to good effect. The city soon changes to Chlorine Dioxide exclusively.
What is the pH of water for disinfection?
The effectivity of disinfection is determined by the pH of the water. disinfection with chlorine will take place optimally when the pH is between 5,5 and 7,5. underchloric acid (HOCl) reacts faster than hypochlorite ions (OCl-); it is 80-100% more effective. The level of underchloric acid will decrease when the pH value is higher.
What is chlorine used for in disinfection?
Chlorine reacts with organic matter to disinfection byporducts, such as trihalomethanes (THM) and halogenated acetic acids (HAA). Chlorine can be added for disinfection in several different ways. When ordinary chlorination is apllied, the chlorine is simply added to the water and no prior treatment is necessary.
How is chlorine produced?
Finally, chlorine can be produced by means of molten salts electrolysis and, mainly in laboratories, by means of hydrochloric acid and manganesedioxide oxidation: MnO2+ 4HCl -> MnCl2+ 2H2O + Cl2. When gaseous chlorine is added to water the following hydrolysis reaction takes place: Cl2+ H2O = H++ Cl-+ HOCl.
How is chlorine broken down?
Chlorine is broken down under the influence of sunlight. UVradiation in sunlight provides energy which aids the break-down of underchloric acid (HOCl) molecules. First, the water molecule(H2O) is broken down, causing electrons to be released which reduce the chlorine atom of underchloric acid to chloride (Cl-).
What disinfectant is used for water disinfection?
Concentrations- Effectivity- Health Effects- Legislation. Chlorine. Chlorineis one of the most commonly used disinfectants for water disinfection. Chlorine can be applied for the deactivation of most microorganisms and it is relatively cheap.
How many electrons does chlorine have?
It can also cause an extra eletron to form (a covalent bond; a chlorine bond), causing the outer shell to complete. Figure 2: chlorine atoms contain 17 electrons. Chlorine can form very stable substances, such as kitchen salt (NaCl). Chlorine can also form very reactive products, such as hydrogenchloride (HCl).
How much chlorine is needed to kill bacteria?
To kill bacteria little chlorine is required; about 0,2-0,4 mg/L. the concentrations of chlorine added to the water are usually higher, because of the chlorine enquiry of the water. Nowadays chlorine gas is only used for large municipal and industrial water purification installations.
How is chlorine treated?
Treatment consists of removing the chlorine from the body as soon as possible and providing supportive medical care such as inhaled breathing treatments for wheezing in a hospital setting.
How to get rid of chlorine in clothing?
If the chlorine release was indoors, get out of the building. If you think you may have been exposed, remove your clothing, rapidly wash your entire body with soap and water, and get medical care as quickly as possible. Removing and disposing of clothing: Quickly take off clothing that has liquid chlorine on it.
How does chlorine poisoning work?
The extent of poisoning caused by chlorine depends on the amount of chlorine a person is exposed to, how the person was exposed, and the length of time of the exposure. When chlorine gas comes into contact with moist tissues such as the eyes, throat, and lungs, an acid is produced that can damage these tissues.
How does chlorine gas change?
Chlorine gas can be pressurized and cooled to change it into a liquid so that it can be shipped and stored. When liquid chlorine is released, it quickly turns into a gas that stays close to the ground and spreads rapidly. Chlorine gas can be recognized by its pungent, irritating odor, which is like the odor of bleach.
Why is chlorine used in swimming pools?
Chlorine is used in drinking water and swimming pool water to kill harmful bacteria. It is also as used as part of the sanitation process for industrial waste and sewage. Household chlorine bleach can release chlorine gas if it is mixed with certain other cleaning agents.
What happens if you breathe chlorine gas?
Fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema) that may be delayed for a few hours. Nausea and vomiting. Watery eyes.
How to protect yourself from chlorine?
How people can protect themselves, and what they should do if they are exposed to chlorine. Leave the area where the chlorine was released and get to fresh air. Quickly moving to an area where fresh air is available is highly effective in reducing exposure to chlorine.
What is chlorine dioxide?
Chlorine Dioxide is the product of lowering the pH of a sodium chlorite solution with an approved acid.. It exists as a greenish gas at normal temperatures. The concentrated gas being formed in the mixed solution gives it an amber aspect.
Does chlorine dioxide kill pathogens?
This is the real focus of the issue, and the answer is really pretty simple. While both kill pathogens well.... Chlorine Dioxide does it differently, and more efficiently, without creating toxic byproducts. Chlorine Dioxide kills by oxidation, whereas Chlorine kills by substitution, (in this case called chlorination).#N#Chlorine Dioxide has a lower oxidation strength than chlorine, but more than twice the oxidative capacity. Reduction/Oxidation Strength or "Redox" is a measure of how strongly an oxidizer reacts with with organic material, the higher the redox potential, the more substances the oxidizer will react with. Chlorine Dioxide has a lower redox potential than ozone, chlorine, or hypochlorus acid. Because of this lower redox potential, Chlorine DIoxide is more selective in what it reacts to.#N#Typically Chlorine DIoxide will only react with compounds that have active carbon bonds, sulfides, cyanides, and compounds with reduced iron or manganese. Chlorine has a higher redox, and will react with a wider range of compounds, including ammonia. Because of this difference Chlorine DIoxide does not create toxic by products like chlorine does. This is why Chlorine is limited as a biocide in it's overall effectiveness as opposed to Chlorine DIoxide.#N#The higher oxidation capacity means that Chlorine Dioxide will remove 5 electrons from the target, whereas chlorine can only remove 2. Chlorine will bind to a pathogen, and other chemicals and compunds that may be present. Chlorine DIoxide being more selective, will not bind with other compounds. Because of this capacity, Chlorine Dioxide is more efficient than Chlorine, Ozone, or Hypochlorus Acid when used as a disinfectant.#N#After the reaction is complete, Chlorine Dioxide reverts to chloride (salt). Chlorine forms Tri-halomathanes from reaction to ammonia, plus other byproducts from other chemicals and compounds as may be present.
Is bleach a chemical?
Bleach is a relative term. Many chemicals including oxidizers such as Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2), can be considered a bleach. Bleaching means they remove color, and yes, Chlorine Dioxide will remove color, like most oxidizers,#N#One industrial use for Chlorine Dioxide is as a bleach for wood pulp, (used in conjunction with sodium hypochlorite), and as a bleach for flour in some countries including the US. The reason it it used in the paper mills is also because of the fact the chlorine dioxide gas prohibits the growth of bio-film as well as for it's bleaching properties.
Who discovered chlorine dioxide?
Chlorine Dioxide was discovered by Sir Humphrey Davy in 1844. The British chemist combined potassium chlorite with sulfuric acid. It will soon be discovered that this green gas would be a more effective disinfectant than chlorine.
What is the combination of free chorine and hypochlorite?
At lower pH levels, the hypochlorous acid will dominate. The combination of hypochlorous acid and hypochlorite ions makes up what is called ‘free chorine.’. Free chlorine has a high oxidation potential and is a more effective disinfectant than other forms of chlorine, such as chloramines.
What is chlorine breakpoint?
Residual Chlorine, Breakpoint. Any type of chlorine that is added to water during the treatment process will result in the formation of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and hypochlorite ions (OCl-), which are the main disinfecting compounds in chlorinated water. More detail is provided later on in this fact sheet.
How is calcium hypochlorite made?
Calcium hypochlorite (CaOCl) is made up of the calcium salts of hypochlorous acid. It is produced by dissolving chlorine gas (Cl 2) into a solution of calcium oxide (CaO) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH). Calcium hypochlorite is a white, corrosive solid that comes either in tablet form or as a granular powder. Calcium hypochlorite is very stable, and when packaged properly, large amounts can be purchased and stored until needed. The chemical is very corrosive however, and thus requires proper handling when being used to treat water. Calcium hypochlorite needs to be stored in a dry area and kept away from organic materials. It cannot be stored near wood, cloth or petrol because the combination of calcium hypochlorite and organic material can create enough heat for an explosion. It must also be kept away from moisture because the tablets/granular powder readily adsorb moisture and will form (toxic) chlorine gas as a result. Calcium hypochlorite has a very strong chlorine odour – something that should be kept in mind when placing them in storage.
What is the purpose of adding chlorine to water?
The main objective of this chlorine addition is to disinfect the water and maintain chlorine residuals that will remain in the water as it travels through the distribution system.
What happens after chlorine demand is met?
After the breakpoint, any additional chlorine added will result in a free chlorine residual proportional to the amount of chlorine added.
How much calcium hypochlorite is needed for water treatment?
Compared to the 1-16 mg/L required with chlorine gas, only 0.5-5 mg/L of calcium hypochlorite is required. When calcium hypochlorite is added to water, hypochlorite and calcium ions are produced.
Why is chlorination important in water treatment?
In order to combat waterborne diseases, different disinfection methods are used to inactivate pathogens. Along with other water treatment processes such as coagulation, sedimentation, and filtration, chlorination creates water that is safe for public consumption.
What disinfectant kills microorganisms?
Chlorine and chlorine-based compounds are the only disinfectants that can efficiently kill microorganisms during water treatment, and maintain the quality of the water as it flows from the treatment plant to the consumer's tap.
How does ozonation kill organisms?
Both chlorination and ozonation kill organisms by oxidation. Ultraviolet treatment, another method, uses UV radiation to kill microorganisms. For chlorine to be effective against microorganisms, it must be present in a sufficient quantity, and it must have a sufficient amount of time to react.
What are the possible sequence of events during chlorination?
A possible sequence of events during chlorination would be: disruption of the cell wall barrier by reactions of chlorine with target sites on the cell surface. release of vital cellular constituents from the cell. termination of membrane-associated functions. termination of cellular functions within the cell.
What is the reaction of chlorine to biomolecules in bacteria?
Researchers postulated that chlorine, which exists in water as hypochlorite and hypochlorous acid, reacts with biomolecules in the bacterial cell to destroy the organism. Further work led to the so-called "multiple hit" theory of chlorine inactivation.
What is the problem with chlorinated water?
One concern with chlorinated water is its tendency to form trihalomethanes (THMs), carcinogenic by-products of the disinfection process. In 1979, the EPA adopted the THM regulation, limiting their allowable level in drinking water supplies.
How long does it take for chlorine to react with water?
This reaction time is called the contact time. For most water systems, the best contact time is usually 30 minutes. To ensure continued protection against harmful organisms, a certain amount of chlorine must remain in the water after treatment. The remaining chlorine is known as a residual chlorine.
When did chlorine start in drinking water?
Health officials began treating drinking water with chlorine in 1908 . Previously, typhoid fever had killed about 25 out of 100,000 people in the U.S. annually, a death rate close to that now associated with automobile accidents. Today, typhoid fever has been virtually eliminated.
How long does chlorine need to be in water?
In water supplies, if the water is at 18°C or above, the chlorine will need to be in contact with it for at least 30 minutes. If the water is colder, you will need to increase this contact time. This is why the normal process is to add chlorine ...
What is the role of chlorine in disinfecting?
Chlorine, as a disinfectant, can kill a large variety of microbial waterborne pathogens.
Why add chlorine to water?
This is why the normal process is to add chlorine to water as it enters a storage tank or long delivery pipeline, to give it time to act before the water supply reaches the consumer. However, chlorine will work faster against some bacteria and germs than others, depending on its concentration.
What are the disadvantages of chlorine?
For chlorine to be effective against some organisms, it requires higher doses and longer contact times. It will not be effective penetrating silt and other organic particles suspended in water. It cannot remove the pathogen cryptosporidium, which requires other disinfection methods.
How much chlorine should I use for a hot tub?
In drinking water, this is 0.2mg–1mg per litre. In hot tubs, it is 1mg–3mg per litre.
How long does it take for E. coli to die from chlorine?
For example, according to the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), E coli will die in less than a minute when exposed to chlorine in a swimming pool; but it takes 16 minutes to kill the hepatitis A virus. Chlorine solutions should vary in concentration, depending on their application.
What is the best way to disinfect water?
There are various alternative ways of sterilising water, particularly for use with livestock. These include applying UV radiation and reverse osmosis. An alternative chemical disinfectant is hydrogen peroxide, and now there is a method of stabilising this chemical that ensures it is both food-safe and highly effective.
How are chlorine and ozone different?
Ozone and chlorine are often compared because both have strong disinfectant properties, but they differ in speed, chemical presence, and overall effectiveness. Ozone water treatment systems disinfect water about three times faster than chlorination and require a shorter contact time with water to be effective.
How does ozone water work?
Ozone water treatment begins with the creation of ozone in an ozone generator. Then, ozone is injected into water, and immediately starts oxidizing and eliminating contaminants, such as bacteria, viruses, and metals. Ozone oxidizes organic material in the membranes of bacteria, viruses, and parasites. This weakens, ruptures, and kills their cells, ...
How is ozone produced in a UV light?
In a UV ozone generator, ozone is produced as oxygen is passed between the lamp and the quartz sleeve of a UV light. The ozone is then drawn into water using a venturi and the water treatment process begins. However, UV ozone generators are not as powerful as electrical ozone generators and produce ozone at lower concentrations.
What is ozone water treatment?
Ozone water treatment is used in commercial, industrial, and municipal water treatment systems, as well as in home systems. Major beverage companies rely on ozone water treatment technology and it is often used to disinfect bottled water. Ozone is also employed by cities to treat and disinfect municipal water supplies.
What are the disadvantages of ozone water treatment?
1. Cost. Ozone water treatment is expensive compared to more well-known water treatment methods, such as chlorination. It has high equipment and operational costs, and it may be difficult to find a professional who is proficient in ozone water treatment.
What is the most common way to treat water?
Ozone can also be produced by electrolytic and chemical reactions, but UV and electrical ozone generators are the most common for water treatment.
What is the role of ozone in the atmosphere?
In the upper atmosphere, ozone filters the sun’s ultraviolet light and protects earth from harmful radiation, but here on the surface, ozone plays a role in ensuring clean drinking water ...
