When is bradycardia considered dangerous?
Feb 03, 2020 · In fact, in most people, bradycardia does not require treatment unless patients have symptoms that are clearly due to a slow heartbeat. The following are conditions that produce bradycardia that requires treatment: Cardiac arrhythmias resulting from sinus node dysfunction. Similarly, how do you treat bradycardia naturally?
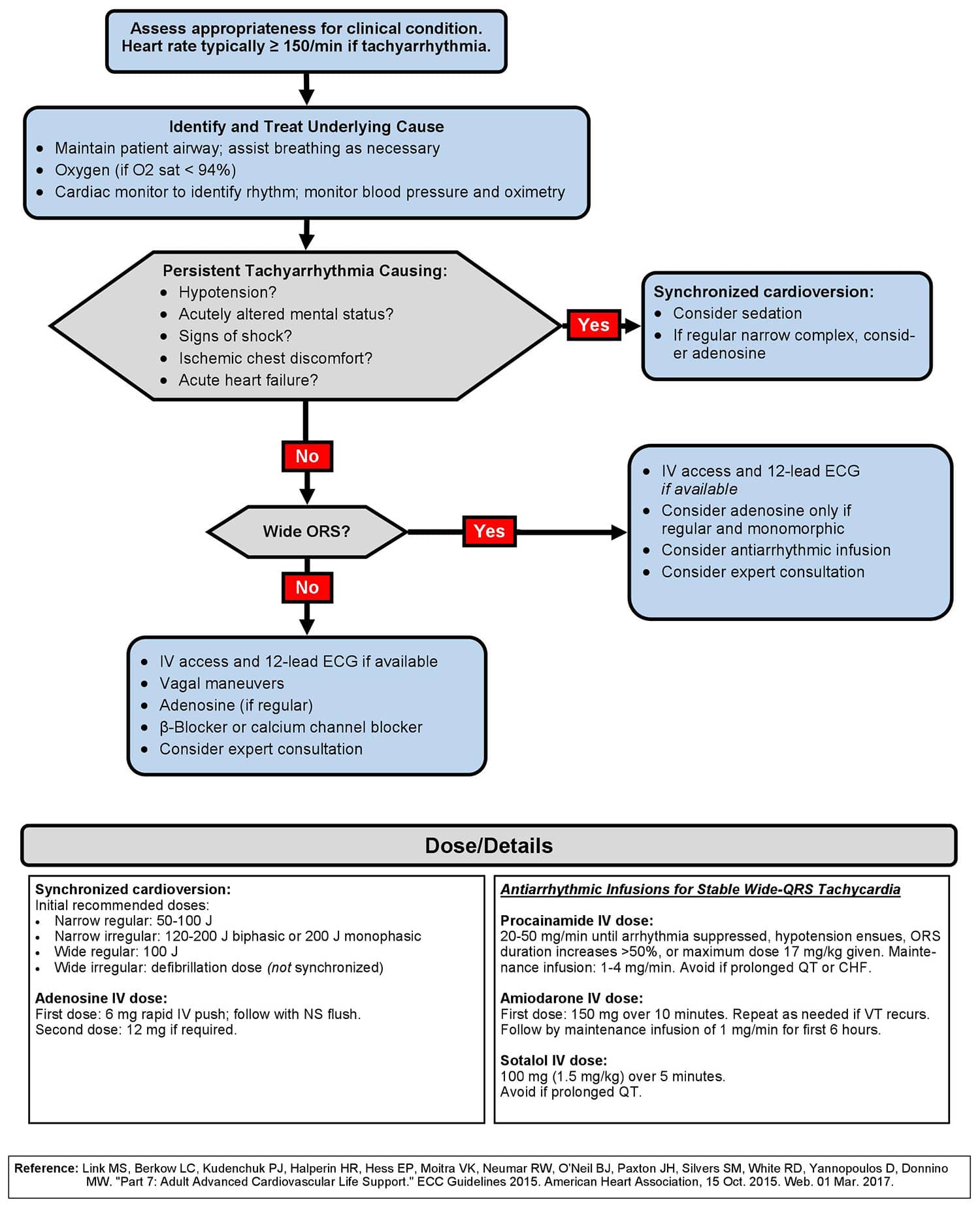
When does bradycardia require treatment ACLS?
Severe or prolonged bradycardia can be treated in a few ways. For instance, if medication side effects are causing the slow heart rate, then the medication regimen can be adjusted or discontinued. In many cases, a pacemaker can regulate …
When does an elevated heart rate become dangerous?
Aug 27, 2019 · When does bradycardia require treatment ACLS? Symptomatic bradycardia, heart rate typically <50 beats per minute with presence of symptoms, is identified and treated directed at the underlying cause. Maintain a patent airway with assisted breathing as necessary.
When does a fast heartbeat need treatment?
Sometimes bradycardia is a good thing and is the goal of treatment. If you need treatment, it will be based on the cause of the condition. If you have an electrical problem in your heart, you will need a pacemaker to keep your heart beating as it should.

When should bradycardia be treated?
When to see a doctor See your health care provider if you or your child has symptoms of bradycardia. If you faint, have difficulty breathing or have chest pain lasting more than a few minutes, call 911 or emergency medical services. Seek emergency care for anyone with these symptoms.Oct 20, 2021
In what situation does bradycardia require treatment ACLS?
Regardless of the patient's rhythm, if their heart rate is too slow and the patient has symptoms from that slow heart rate, the bradycardia should be treated to increase the heart rate and improve perfusion, following the steps of the bradycardia algorithm below.
What is the initial treatment for bradycardia?
Atropine. In the absence of reversible causes, atropine remains the first-line drug for acute symptomatic bradycardia (Class IIa).Nov 28, 2005
Is bradycardia an emergency?
Asymptomatic bradycardia generally does not require any emergency treatment.Apr 6, 2021
What is a first line treatment for a patient with unstable bradycardia?
The American Heart Association recommends atropine sulfate as the first line of treatment for symptomatic bradycardia, regardless of whether it is due to AVB or not.Nov 23, 2019
How is symptomatic bradycardia treated?
Symptomatic, stable bradycardia: Most patients can be observed and will not require intervention.Patients with severe symptoms: Administer atropine.If second-degree AV block, Mobitz II, or third-degree AV block is present and the patient is symptomatic: Start transcutaneous pacing or transvenous pacing.Aug 2, 2021
Is a heart rate of 48 too low?
A normal resting heart rate for most people is between 60 and 100 beats per minute (bpm). A resting heart rate slower than 60 bpm is considered bradycardia.May 7, 2018
What is the priority intervention for symptomatic bradycardia?
Note: If dealing with primary bradycardia (defined above), atropine is preferred as the first-choice treatment of symptomatic AV block. If dealing with secondary bradycardia, atropine is not indicated for the treatment of AV block, and epinephrine should be used.
Is a heart rate of 55 too low?
Bradycardia is a heart rate that's too slow. What's considered too slow can depend on your age and physical condition. Elderly people, for example, are more prone to bradycardia. In general, for adults, a resting heart rate of fewer than 60 beats per minute (BPM) qualifies as bradycardia.Sep 30, 2016
What causes bradycardia?
Causes for bradycardia include: 1 Problems with the sinoatrial (SA) node, sometimes called the heart’s natural pacemaker 2 Problems in the conduction pathways of the heart that don’t allow electrical impulses to pass properly from the atria to the ventricles 3 Metabolic problems such as hypothyroidism (low thyroid hormone) 4 Damage to the heart from heart disease or heart attack 5 Certain heart medications that can cause bradycardia as a side effect
What is the SA node?
Problems with the sinoatrial (SA) node, sometimes called the heart’s natural pacemaker. Problems in the conduction pathways of the heart that don’t allow electrical impulses to pass properly from the atria to the ventricles.
Can bradycardia be treated?
Borderline or occasional bradycardia may not require treatment. Severe or prolonged bradycardia can be treated in a few ways. For instance, if medication side effects are causing the slow heart rate, then the medication regimen can be adjusted or discontinued.
How to tell if you have bradycardia?
You may not have any symptoms of bradycardia. But if you do have a slow heart rate and any of these symptoms, call your doctor: 1 Syncope/passing out 2 Dizziness 3 Weakness 4 Confusion 5 Heart palpitations/fluttering 6 Feeling short of breath 7 Chest pain 8 Lack of energy
What does it mean when your heart beats slow?
Bradycardia means your heart rate is slow. This can be completely normal and desirable, but sometimes it can be an abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia). If you have bradycardia and you have certain symptoms along with the slow heart rate, then it means your heartbeat is too slow.
What is the normal heart rate for a person?
A normal resting heart rate for most people is between 60 and 100 beats per minute (bpm). A resting heart rate slower than 60 bpm is considered bradycardia. Athletic and elderly people often have a heart rate slower than 60 bpm when they are sitting or lying down, and a heart rate less than 60 bpm is common for many people during sleep.
What is the heart's electrical system?
To understand bradycardia, it helps to understand the heart’s electrical system, which is what makes the heart beat. Your heart has a natural pacemaker called the sinus node (SA node), which is made of a small bunch of special cells.
Why do you need a heart monitor?
You will keep track of any symptoms you have. Your doctor will match up the symptoms with the activity on the monitor to see if a heart rhythm problem is the cause and if your heart rate is related to your symptoms.
What is the purpose of a pacemaker?
A pacemakers is a small device that is placed under your skin to monitor your heart’s rate and rhythm.
Where is the AV node?
Next, the impulse travels down an electrical pathway to the AV node. The AV node is in the center of your heart, in between the atria and ventricles. The AV node acts like a gate that slows the electrical signal before it moves into the ventricles.
Why does bradycardia happen?
The most common cause for bradycardia is a malfunction in the heart’s natural pacemaker, the sinus node. It controls how quickly the top and bottom heart chambers pump blood through the body. Another cause is atrioventricular block ( AV Block ), in which the top and bottom chambers don’t communicate well and the heart rate drops as a result.
How to tell if your heart rate is slow?
Consult your doctor if you are experiencing some of these symptoms and you have an associated slow heart rate: 1 Lack of energy. 2 Low stamina. 3 Dizziness. 4 Weakness. 5 Chest pains. 6 Confusion/memory problems. 7 Heart palpitations or flutters.
Can you have a slow heart rate?
It is very possible to have a slow heart rate and experience no symptoms. However, if you have symptoms but ignore them, it can sometimes cause more serious problems. Consult your doctor if you are experiencing some of these symptoms and you have an associated slow heart rate: Lack of energy. Low stamina.
Is age a risk factor for bradycardia?
In fact, age is the most common risk factor for developing bradycardia. The condition is most common among men and women over age 65. Illness or other conditions also may prompt it. These other causes include:
Is bradycardia a problem?
A low heart rate, called bradycardia, occurs frequently in older adults, cardiologist Jose Baez-Escudero, MD, says. It’s not always a problem, but it does require treatment in some cases. “As people get older, there is occasional normal wear and tear on the electrical system of the heart,” he says.
