
What is the effects model for one way ANOVA?
The effects model for one way ANOVA is a linear additive statistical model which relates the response to the treatment and can be expressed as where μ is the grand mean, τ i (i = 1,2,...,T) are the deviations from the grand mean due to the treatment levels and ϵ i j are the error terms.
What is ANOVA based on?
In Lesson 2 we learned that ANOVA is based on testing the effect of the treatment relative to the amount of random error. In statistics, we call this the partitioning of variability (due to treatment and due to random variability in the measurements).
What is the analysis in two factor ANOVA?
The analysis in two-factor ANOVA is similar to that illustrated above for one-factor ANOVA. The computations are again organized in an ANOVA table, but the total variation is partitioned into that due to the main effect of treatment, the main effect of sex and the interaction effect.
What is a one-factor ANOVA?
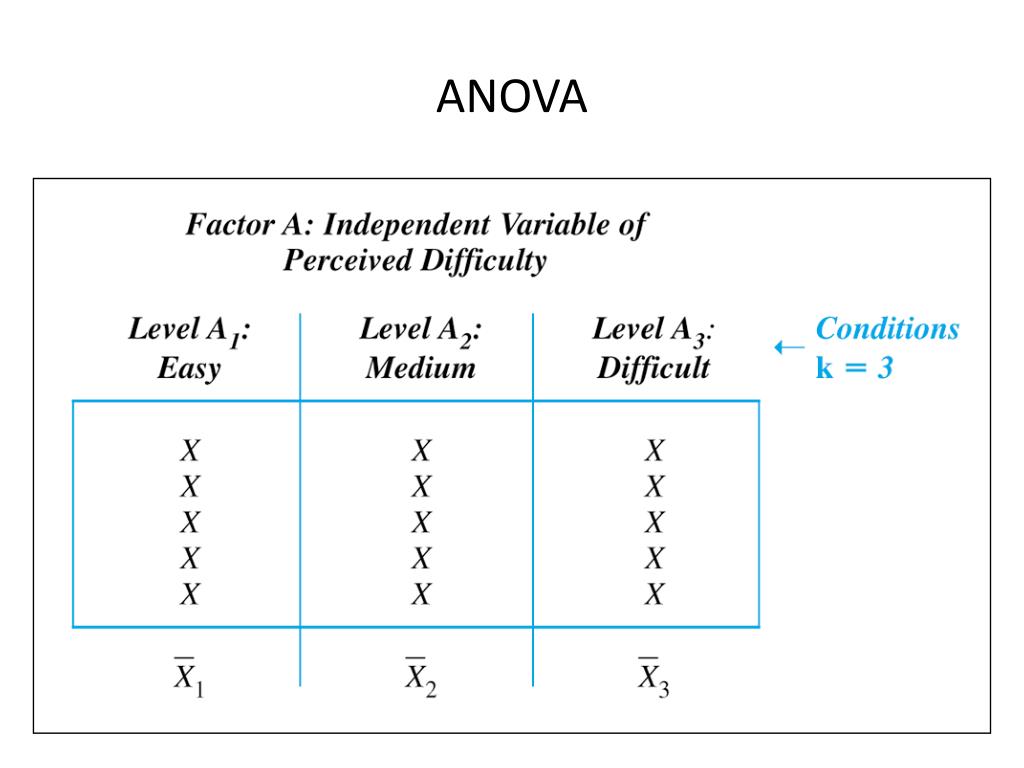
The ANOVA tests described above are called one-factor ANOVAs. There is one treatment or grouping factor with k > 2 levels and we wish to compare the means across the different categories of this factor.
What does between-treatments variability signify in an ANOVA?
In ANOVA it is called the mean square between. For these data: Within-Treatment Variability: In addition to the between-treatments variability, there is variability within each treatment. The within treatments variability will provide a measure of the variability inside each treatment condition.
How do you know if there is a significant effect in ANOVA?
In ANOVA, the null hypothesis is that there is no difference among group means. If any group differs significantly from the overall group mean, then the ANOVA will report a statistically significant result.
What is number of treatments in ANOVA?
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for comparing means of three or more variables. Background. If we have, say, 3 treatments to compare (A, B, C) then we would need 3 separate t-tests (comparing A with B, A with C, and B with C). If we had seven treatments we would need 21 separate t-tests.
What is treatment in one way ANOVA?
The term one- way, also called one-factor, indicates that there is a single explanatory variable (“treatment”) with two or more levels, and only one level of treatment is applied at any time for a given subject.
What does the p-value in ANOVA mean?
The p-value is the area to the right of the F statistic, F0, obtained from ANOVA table. It is the probability of observing a result (Fcritical) as big as the one which is obtained in the experiment (F0), assuming the null hypothesis is true. Low p-values are indications of strong evidence against the null hypothesis.
What does F value mean in ANOVA?
The F value is used in analysis of variance (ANOVA). It is calculated by dividing two mean squares. This calculation determines the ratio of explained variance to unexplained variance. The F distribution is a theoretical distribution.
What are treatments and blocks in ANOVA?
Blocks are individuals who donated a blood sample. Treatments are different methods by which portions of each of the blood samples are processed.
What is treatment variation?
The treatment variance is based on the deviations of treatment means from the grand mean, the result being multiplied by the number of observations in each treatment to account for the difference between the variance of observations and the variance of means.
How do you find treatments in statistics?
2:584:15What is a Statistical Treatment? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou might also be asked for a statistical treatment when writing a thesis or conducting anMoreYou might also be asked for a statistical treatment when writing a thesis or conducting an experiment. Basically it means to summarize your results. You'll want to include measurements.
Is the between treatments variance?
– Thus, the between-treatments variance simply measures how much difference exists between the di i treatment conditions. the differences have been caused by the treatment effects.
Which sum of squares measure the treatment effect?
The within-treatments sum of squares measures treatment effects as well as random_ unsystematic differences within each of the samples assigned to each of the treatments_ These differences represent all of the variations that could occur in study; therefore_ they are sometimes referred to as error: In ANOVA, the test ...
What is K in ANOVA test?
k represents the number of independent groups (in this example, k=4), and N represents the total number of observations in the analysis. Note that N does not refer to a population size, but instead to the total sample size in the analysis (the sum of the sample sizes in the comparison groups, e.g., N=n1+n2+n3+n4).
7.1 Can playing Tetris reduce intrusive memories?
After a traumatic experience, some people experience flashbacks, which are intrusive and involuntary memories that involve vivid imagery related to the traumatic event. These intrusive memories can be highly distressing and are a hallmark of acute stress disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
7.2 Comparing two groups
To start with a relatively straightforward example, let’s first focus only on the data from the Tetris+Reactivation and the Reactivation-Only conditions. We are interested in whether playing Tetris during reactivation reduces the number of memory intrusions on later days, in comparison to when the traumatic memory was reactivated only.
7.3 The ANOVA model
The dummy coding procedure above can be generalized to the situation in which you want to compare more than two groups. In the Tetris study, there were four conditions. To allow a linear model to represent the means in all four conditions, you need to use more than one dummy-coding predictor. In fact, you would need 3 dummy-coding predictors.
7.4 Contrast coding
As in the case of two groups, the approach to testing group differences in the GLM is to construct new predictor variables, which we might call contrast-coding predictors, that represent differences between groups.
7.5 Default orthogonal coding schemes
While orthogonal contrasts provide benefits in terms of straightforward interpretation of the parameters, and, in the case of equally sized groups, independent predictors and and a neat division of the whole model SSR to the SSR terms for the predictors, orthogonality is not a strict requirement.
7.6 Multiple testing and post-hoc tests
Using contrast codes, you can test a total of g − 1 comparisons within a single analysis. At times, this may suffice to test all hypotheses of interest. At other times, you would like to test more hypotheses.
What is the effects model for ANOVA?
The effects model for one way ANOVA is a linear additive statistical model which relates the response to the treatment and can be expressed as,
What is ANOVA based on?
In Lesson 2 we learned that ANOVA is based on testing the effect of the treatment relative to the amount of random error. In statistics, we call this the partitioning of variability (due to treatment and due to random variability in the measurements). This partitioning of the deviations can be written mathematically as:
What are the assumptions being made to employ the ANOVA model?
So what are these assumptions being made to employ the ANOVA model? The errors are assumed to be independent and identically distributed ( iid) with a normal distribution having a mean of 0 and unknown equal variance.
What does failure to meet assumptions mean?
Failure to meet these assumptions means any conclusions drawn from the model are not to be trusted.
What software is used to conduct an ANOVA?
Use statistical software to conduct an ANOVA (in SAS, R, and Minitab).
What is residual vs predicted value plot?
Most useful is the residual vs. predicted value plot, which identifies the violations of zero mean and equal variance. Residuals are also plotted against the treatment levels to examine if the residual behavior differs among treatments.
What is the diagnostic test for model assumptions?
As the model residuals serve as estimates of the unknown error, diagnostic tests to check for validity of model assumptions are based on residual plots, and thus, the implementation of diagnostic tests is also called ‘ Residual Analysis ’ .
When is ANOVA used?
The ANOVA technique applies when there are two or more than two independent groups. The ANOVA procedure is used to compare the means of the comparison groups and is conducted using the same five step approach used in the scenarios discussed in previous sections.
What is the fundamental strategy of ANOVA?
The fundamental strategy of ANOVA is to systematically examine variability within groups being compared and also examine variability among the groups being compared.
Why is the test statistic more involved?
Because there are more than two groups, however, the computation of the test statistic is more involved. The test statistic must take into account the sample sizes, sample means and sample standard deviations in each of the comparison groups.
What is the test of hypothesis?
The specific test considered here is called analysis of variance (ANOVA) and is a test of hypothesis that is appropriate to compare means of a continuous variable in two or more independent comparison groups.
What is the null hypothesis in ANOVA?
The null hypothesis in ANOVA is always that there is no difference in means. The research or alternative hypothesis is always that the means are not all equal and is usually written in words rather than in mathematical symbols. The research hypothesis captures any difference in means and includes, for example, the situation where all four means are unequal, where one is different from the other three, where two are different, and so on. The alternative hypothesis, as shown above, capture all possible situations other than equality of all means specified in the null hypothesis.
What is the rejection region of the F test?
If the null hypothesis is false, then the F statistic will be large. The rejection region for the F test is always in the upper (right-hand) tail of the distribution as shown below.
What is hypothesis testing?
This module will continue the discussion of hypothesis testing, where a specific statement or hypothesis is generated about a population parameter, and sample statistics are used to assess the likelihood that the hypothesis is true. The hypothesis is based on available information and the investigator's belief about the population parameters. The specific test considered here is called analysis of variance (ANOVA) and is a test of hypothesis that is appropriate to compare means of a continuous variable in two or more independent comparison groups. For example, in some clinical trials there are more than two comparison groups. In a clinical trial to evaluate a new medication for asthma, investigators might compare an experimental medication to a placebo and to a standard treatment (i.e., a medication currently being used). In an observational study such as the Framingham Heart Study, it might be of interest to compare mean blood pressure or mean cholesterol levels in persons who are underweight, normal weight, overweight and obese.
What is the significance of a one way ANOVA?
A one-way ANOVA revealed that there [was or was not] a statistically significant difference in [dependent variable] between at least two groups (F (between groups df, within groups df) = [F-value], p = [p-value]).
What is one way ANOVA?
A one-way ANOVA is used to determine whether or not there is a statistically significant difference between the means of three or more independent groups. When reporting the results of a one-way ANOVA, we always use the following general structure: A brief description of the independent and dependent variable.
Do you report post hoc results in ANOVA?
Only report post-hoc results if necessary. If the overall p-value of the ANOVA is not statistically significant, then you will not conduct post-hoc multiple comparisons between groups. This means you obviously don’t have to report any post-hoc results in the final report.
What is ANOVA in science?
In Part 1 we mentioned ANOVA is a way to keep track of the variation in a response variable. Figure 3.1 provides a schematic for how we can think about this for our InsectSprays data set example introduced in Part 2.
What is an ANOVA in R?
ANOVA compares the variability due to the treatment to that due to error to generate a test statistic. We will now see how we can compute these variance quantities and do ANOVA in R by applying a model to our data.
What is an effect in the context of this model?
An effect in the context of this model is the difference between the mean for the ith i t h treatment and the grand mean. We operate under the constraint that all our estimated effects sum to 0, viz.,
How to calculate F-statistics in ANOVA?
Lastly, our ANOVA F-statistic is calculated by taking the ratio of our mean sum of squares treatment (between treatment group variation) and mean sum of squares error (within treatment group variation). A high F-statistic is our measure to suggest the variation is largely explained by our explanatory variable rather than random variation. In the context of the means model, it allows us to conclude that at least one of our treatment means is significantly different from 0. The value of our F-statistic for our InsectSprays example computed above is:
Is the F-statistic the same as the means model?
Our F-statistic remains the same as what it was for the means model when computing with the effects model. It is again 34.7. The interpretation changes from what we said in the means model- it suggests that at least one of the effects of the ith i t h insect spray on insect count are not equal to 0.
