When should hypothyroidism be seen after radioactive iodine therapy for hyperthyroidism?
The presence of hypothyroidism after radioactive iodine therapy is a strong predictor for an adverse outcome of Graves’ ophthalmopathy. This study suggests that patients that receive radioactive iodine therapy for treatment of their hyperthyroidism should be seen earlier than 6 weeks after their treatment...
What is radioactive iodine therapy for thyroid cancer?
Fortunately, radioactive iodine therapy is targeted to treat only your thyroid gland. Thyroid cells are the main cells in the body that can absorb iodine, so there is very little radiation exposure to the rest of your body's cells. When the thyroid cells absorb the radiation, they are damaged or destroyed.
Do I need a second dose of radioactive iodine?
If your symptoms persist 6 months after treatment, you may need a second dose. In the rarest of cases, some patients will not benefit from a second dose and may instead require surgery. The most common side effect of radioactive iodine may seem ironic, yet it makes perfect sense— hypothyroidism.
Why is radioactive iodine stored in the thyroid gland?
Because your thyroid gland concentrates and stores iodine in your body. So when you take radioactive iodine your body will automatically take it up and store it in the thyroid gland.

When do you start levothyroxine after radioactive iodine?
In the intervention arm patients will start levothyroxine therapy at 4 weeks after RAI therapy. The initial dose of levothyroxine will be 25 mcg/day. It will be increased to 50 mcg/day 2 weeks later and then adjusted at 8 weeks post RAI based on a full face-to-face clinical and biochemical evaluation.
What will the TSH level be in a patient who is hyperthyroidism?
A low TSH level—below 0.5 mU/L—indicates an overactive thyroid, also known as hyperthyroidism.
When should I check my TSH after Rai?
American thyroid association guidelines recommend testing for free T4, total T3, and TSH within the first 1–2 months after RAI. Biochemical monitoring should be continued at 4- to 6-week intervals for 6 months, or until the patient becomes hypothyroid and stable on thyroid replacement therapy.
Can thyroid still function after radioactive iodine treatment?
Some patients will still require treatment with antithyroid medication for some weeks or months until the radioactive iodine has been effective and the overactivity has settled. Over two-thirds of those who have radioactive iodine treatment will develop hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid).
What level TSH requires treatment?
If your TSH level is higher than 10 mIU/L, you should start treatment, because you will very likely develop symptoms of an underactive thyroid, even if you don't have them now.
What is the best TSH level?
The American Thyroid Association recommends serum TSH levels stay 0.4-4.0 mIU/L (milli-international units per liter). We recommend keeping that number even lower — below 2.5 mIU/L. However, we recommend keeping TSH levels between 0.5 and 2.5 mIU/L. If your TSH levels are too high, you may be hypothyroid.
Can hyperthyroidism return after radioactive iodine?
Once hypothyroidism has been achieved, it is usually irreversible with the patient requiring lifelong thyroid replacement. Recurrence of hyperthyroidism after RAI therapy may be due to inadequate dosing or early Marine Lenhart syndrome.
What happens when thyroxine is too low?
When the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroxine (called hypothyroidism), many of the body's functions slow down. Some of the most common symptoms of an underactive thyroid gland are: tiredness. feeling cold.
What should thyroid levels be after thyroidectomy?
Current ATA guidelines recommend maintaining TSH levels below 0.1 mU/L in patients with persistent disease indefinitely in the absence of specific contraindications.
Can hyperthyroidism come back?
Even if the disease goes into remission after anti-thyroid treatment, it can come back. Follow-up appointments to check thyroid activity usually are scheduled once every six months for the first two years after the disease goes into remission.
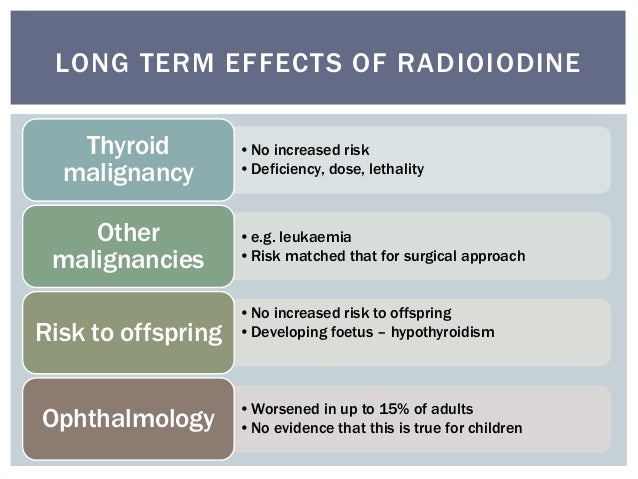
What are the long term side effects of radioactive iodine?
NCI study finds long-term increased risk of cancer death following common treatment for hyperthyroidism. New study findings show an association between the dose of a common treatment for hyperthyroidism and risk of death from solid cancers.
Can you still have Graves disease after radioactive iodine treatment?
Quality of life is worse at 6-10 years after radioactive iodine therapy of Graves' disease compared with treatment with antithyroid drugs or surgery. Quality of life is worse at 6-10 years after radioactive iodine therapy of Graves' disease compared with treatment with antithyroid drugs or surgery.
What is radioactive iodine used for?
Radioactive iodine is a procedure that is often used to treat hyperthyroidism.
Why do people get radioactive iodine?
Most people who get radioactive iodine treatment do so because they are considered to be hyperthyroid ( sometimes people get RAI for thyroid cancer (5) but most people get it for hyperthyroidism).
How long does iodine affect sperm count?
Important to men is the fact that radioactive iodine can cause short-term reductions in sperm count for up to 2 years after your procedure (8).
How long can you live after iodine treatment?
You can expect to live a fairly normal life after radioactive iodine treatment but your life will probably not be exactly as it was before your procedure. For most people, this means that you can expect to live at 80-90% of your 'normal'.
What happens if you destroy your thyroid gland?
And, if you destroy your thyroid gland, it turns out that that may have consequences on your metabolism. Anectodally, you've probably already heard stories about people gaining weight after their procedure.
What happens if you don't have thyroid?
If you don't have thyroid hormone at all then you risk the chance of coma and death.
How long does it take for radioactivity to fade?
The good news is that this radioactivity does fade over a short period of time (usually 5 to 7 days) but the bad news is that you need to stay under certain precautions during this time.
How long does it take for thyroid to return to normal after iodine?
For most people, one dose of radioactive iodine treatment will cure hyperthyroidism. Usually, thyroid hormone levels return to normal in 8 to 12 weeks. In rare cases, the person needs a second or third dose of radioactive iodine. Risks. Some side effects from radioactive iodine treatment include:
How long does it take for iodine to leave your body?
Most people don't feel different after treatment. But a few people may have nausea. Within a few days after treatment, the radioactive iodine will leave your body in your urine and saliva. How long it takes will depend on your age and on the dose you received.
Does radioactive iodine harm thyroid?
After you swallow it, it is taken up by your thyroid gland. Depending on the dosage used, the radioactivity in the iodine destroys most or all of the tissue in your thyroid gland, but it does not harm any other parts of your body.
How to test thyroid for radioactive iodine?
Your doctor will observe your thyroid's activity level by measuring the amount of iodine it absorbs. He or she will do this using a scan of your thyroid, which will show the healthy and diseased tissues.
How to determine the best dose of iodine?
In determining the best dose, the size of the thyroid gland (determined by a physical exam) and results of the uptake test are the two most important factors. The larger the gland, the larger the radioactive iodine dose. The higher the iodine uptake, the smaller the dose.
What is radioactive iodine ablation?
Your doctor may refer to it as radioactive iodine ablation (ablation is a term that refers to destruction or erosion). This article will focus on what you might expect when you are faced with the total elimination of your thyroid gland and its key functions. Graves disease, the most common form of hyperthyroidism, occurs most often in women, ...
What are the side effects of iodine?
Other side effects of radioactive iodine include: 1 Metallic taste in the mouth: This can last for a few weeks. 2 Nausea: This usually subsides one to two days after treatment. 3 Swollen salivary glands: This can last for a few weeks. It is caused by iodine absorbed by the salivary glands, though stimulating saliva flow a day after treatment (by sucking a lemon drop, for instance) is an effective remedy.
How long after iodine treatment can you drink water?
For the first 3 days after treatment, stay a safe distance away from others (6 feet is enough). Avoid public places and drink plenty of water (to encourage the removal of radioactive iodine through your urine). For the first three days, do not share items (utensils, bedding, towels, and personal items) with anyone else.
How long does iodine last?
Other side effects of radioactive iodine include: Metallic taste in the mouth: This can last for a few weeks. Nausea: This usually subsides one to two days after treatment. Swollen salivary glands: This can last for a few weeks.
What cells absorb iodine?
Thyroid cells are the main cells in the body that can absorb iodine, so there is very little radiation exposure to the rest of your body's cells. When the thyroid cells absorb the radiation, they are damaged or destroyed. Approximately 90% of patients need only one dose before they are cured of their hyperthyroidism.
What is the name of the substance that is taken up by the thyroid gland?
Symptoms include dry eyes, red eyes, bulging of the eyes and double vision. Radioactive iodine (RAI): this plays a valuable role in diagnosing and treating thyroid problems since it is taken up only by the thyroid gland.
What is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism may be treated with antithyroid meds (Methimazole, Propylthiouracil), radioactive iodine or surgery. Graves’ disease : the most common cause of hyperthyroidism in the United States. It is caused by antibodies that attack the ...
What is the I-123 form?
I-123 is the non-destructive form that does not damage the thyroid and is used in scans to take pictures of the thyroid (Thyroid Scan) or to take pictures of the whole body to look for thyroid cancer (Whole Body Scan). BACKGROUND. Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism in the United States.
What is the most common treatment for Graves disease?
In the United States, radioactive iodine therapy is the most common treatment for Graves’ disease. Occasionally Graves’ disease can affect the eyes, which is known as Graves’ ophthalmopathy. While most cases of ophthalmopathy are mild, in the most severe form it can threaten vision.
Why is iodine important for the thyroid gland?
Iodine is essential for proper function of the thyroid gland, which use s it to make the thyroid hormones. The thyroid is equipped with an active system or “pump” for moving iodine into its cells, where it is concentrated as iodide. The thyroid gland is the only tissue in the body that takes up and holds onto iodine.
WHEN IS RAI USED FOR TREATMENT OF THYROID DISORDERS?
I-131 may occasionally cause mild pain in the neck that can be treated with aspirin, ibuprofen or acetaminophen. The RAI treatment may take up to several months to have its effect. Frequently, the end result of RAI treatment of hyperthyroidism is hypothyroidism, which is treated by thyroid hormone replacement (see Hypothyroidism brochure ).
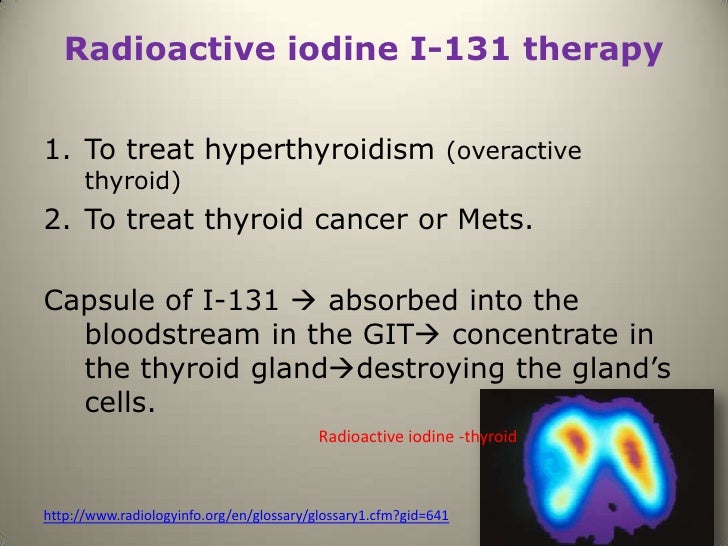
WHAT IS RADIOACTIVE IODINE (RAI)?
Iodine, in the form of iodide, is made into two radioactive forms of iodine that are commonly used in patients with thyroid diseases: I-123 ( harmless to thyroid cells) and I-131 ( destroys thyroid cells ). The radiation emitted by each of these forms of iodine can be detected from outside the patient to gain information about thyroid function and take pictures of the size and location of thyroid tissues. RAI is safe to use in individuals who have had allergic reactions to seafood or X-ray contrast agents, since the reaction is to the compound containing iodine, not the iodine itself. RAI is given by mouth in pill or liquid form.
What is the purpose of I-131?
THYROID CANCER – Large doses of I-131 are used to destroy thyroid cancer cells (see Thyroid Cancer brochure ). This is performed after the remaining thyroid cells ( including any cancer cells) are stimulated by raising TSH levels by either withdrawing the thyroid hormone pills or by treating with recombinant human TSH.
Is rai safe for thyroid?
In general, RAI is a safe and effective treatment for the thyroid disorders mentioned above. Hypothyroidism is a common side effect of RAI for hyperthyroidism and always seen after RAI for thyroid cancer. This is usually easily treated with thyroid hormone replacement (see Hypothyroidism brochure ). Some studies suggest a slight increase in thyroid cancers may be seen after RAI treatment for hyperthyroidism. Loss of taste and dry mouth due to salivary gland damage may be seen. The use of lemon drops, vitamin C or sour stimulation to potentially decrease the exposure of the salivary glands to RAI is controversial and should be discussed with your physician. Importantly, once you have been treated with RAI, regular medical follow-up is lifelong.
Is 131-I radiation safe?
Although the treatments with 131-I are generally safe, RAI produces radiation so patients must do their best to avoid radiation exposure to others, particularly to pregnant women and young children. The amount of radiation exposure markedly decreases as the distance from the patient increases. Patients who need to travel in the days after I-131 RAI treatment are advised to carry a letter of explanation from their physician. This is because radiation detection devices used at airports or in federal buildings may pick up even very small radiation levels. Details should be discussed with a physician prior to, and at the time of, the RAI treatment.
DOES RAI FOR THYROID IMAGING PROVIDE THE BEST RESULTS?
No special radiation precautions are necessary after a thyroid scan or RAIU using I-123. I-131 can also be used to take pictures of the thyroid gland, although it is rarely used due to the harmful effects it has on thyroid cells.
How is radioiodine administered?
Radioiodine is administered orally as sodium iodide (131-I) in solution or a capsule. The radioiodine is rapidly incorporated into the thyroid, and its beta emissions result in extensive local tissue damage. The net effect is ablation of thyroid function over a period of 6 to 18 weeks.
What is the treatment for Graves disease?
Graves' disease — The therapeutic approach to Graves' hyperthyroidism consists of both rapid amelioration of symptoms with a beta blocker and measures aimed at decreasing thyroid hormone synthesis with either the administration of a thionamide, radioiodine ablation, or surgery [ 4 ]. Because all three treatment modalities are effective, the choice of therapy should involve active discussion between clinician and patient ( table 1 ).
Is radioiodine used for hyperthyroidism?
Radioiodine had been the most popular treatment for hyperthyroidism in the United States [ 1 ]; however, the use of thionamides has been increasing [ 3 ]. Radioiodine is less popular outside of the United States [ 1,5-7 ]. The choice of therapy for Graves' disease is reviewed separately. (See "Graves' hyperthyroidism in nonpregnant adults: Overview of treatment", section on 'Choice of therapy' .)
Is it safe to take antithyroid medication?
Data subsequently have shown that long-term antithyroid drug use is safe [ 2 ], and an updated analysis using insurance claims data in the United States suggests that antithyroid drugs are used as initial therapy for 60 percent of patients, while only 33 percent of patients receive radioiodine [ 3 ].
Is radioiodine good for Graves' thyroid?
Radioiodine in the treatment of hyperthyroidism. Radioiodine is an effective treatment for Graves' hyperthyroidism. It had been the therapy of choice in the United States, selected by 60 percent of thyroid specialists who responded to a survey in 2011 [ 1 ].
Is UpToDate a substitute for medical advice?
The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your own physician or other qualified health care professional regarding any medical questions or conditions. The use of UpToDate content is governed by the UpToDate Terms of Use. ©2021 UpToDate, Inc. All rights reserved.
Does thionamide withdrawal cause hyperthyroidism?
Kubota S, Ohye H, Yano G, et al. Two-day thionamide withdrawal prior to radioiodine uptake sufficiently increases uptake and does not ex acerbate hyperthyroidism compared to 7-day withdrawal in Graves' disease. Endocr J 2006; 53:603.