While many actinomycotic abscesses respond to appropriate antibiotic therapy, some may require surgical excision. Imaging studies will also enable the provider to monitor response to treatment. Systemic medications are critical to treatment success.
Full Answer
What is actinomycosis and how is it treated?
Actinomycosis is a long-term infection that causes sores, or abscesses, in the body’s soft tissues. Actinomycosis is usually found in the: Actinomycosis rarely appears elsewhere in the body. However, it can spread from the initial infected area to other parts of the body if illness or injury damages your tissue. Actinomycosis isn’t contagious.
What is the best way to diagnose actinomycete infection?
Culture of an actinomycete from affected site is the gold standard of diagnosis. This is challenging for several reasons. Actinomyces spp. are microaerophilic and grow best when cultured anaerobically. This can be difficult for many clinical laboratories. Even anaerobic transport can be challenging to find in many office settings.
What is the treatment for IUD associated actinomycosis?
Removal of the IUD is crucial in patients with IUD-associated actinomycosis.74,78Open surgical resection, often required for the definite diagnosis of genitourinary tract actinomycosis, facilitates the cure, but may be mutilating, especially if hysterectomy or bladder resection is performed.72–77
Which serologic tests are used in the workup of actinomycosis?
Serologic tests for the agents of actinomycosis are appealing, but their utility is limited. False positive and false negative results are common. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests for actinomycosis are not commercially available but might be helpful in the future.

Can actinomycosis be cured?
If you get proper treatment for actinomycosis, it's highly curable and you'll likely make a full recovery.
How long does it take Actinomyces to grow?
Growth of Actinomyces is slow; it appears within at least 5 days and may take up to 15–20 days. Thus, incubation of at least 10 days is required before conclusion of a negative culture. Most Actinomyces spp. are facultative anaerobes, but some relevant species (such as A.
What is the most common area for actinomycosis to occur?
Infection typically involves the neck and face, lungs, or abdominal and pelvic organs. Microscopically, Actinomyces appears as distinctive "sulfur" granules (rounded or spherical particles, usually yellowish, and ≤ 1 mm in diameter) or as tangled masses of branched and unbranched wavy bacterial filaments.
Is actinomycosis painful?
Symptoms may include any of the following: Draining sores in the skin, especially on the chest wall from lung infection with actinomyces. Fever. Mild or no pain.
How long does it take for actinomycosis to heal?
Actinomycosis can persist for a long time. Long-term treatment with antibiotics, such as penicillin, is common. It may last from 8 weeks to over 12 months. In some cases, a surgeon may drain an abscess or remove an infected part.
How do I get rid of actinomycetes?
In most cases of actinomycosis, antimicrobial therapy is the only treatment required, although surgery can be adjunctive in selected cases. Penicillin G is the drug of choice for treating infections caused by actinomycetes. Parenteral antibiotics are administered initially via PICC line, with transition to oral agents.
Can actinomycosis recur?
Recurrence of endobronchial actinomycosis is an extremely rare condition. It was observed that new endobronchial lesions kept appearing at different sites and that the previously detected lesions had completely disappeared at the completion of the antibiotic course.
Is actinomycosis serious?
Actinomycosis is a rare type of bacterial infection. It can be very serious but can usually be cured with antibiotics.
Does doxycycline treat Actinomyces?
Good drug for actinomycosis. The agents are susceptible and clinical experience seems good. An advantage is the availability of oral and parenteral forms. Some clinicians will start therapy with high IV doses of penicillin or clindamycin, and use doxycycline for a prolonged oral maintenance phase.
Can actinomycosis be fatal?
Local actinomycosis in head and neck lesions can be an intractable and sometimes fatal disease. Initial treatment is extremely important. Insufficient dose or intermittent dosage of antibiotics may not be able to control an Actinomyces infection in a patient in an immunocompromised state.
Can infection move around the body?
Some infections may have complications even when they are treated early. The infection can spread from one place in your body to the entire body through your bloodstream. Early diagnosis and treatment may prevent complications such as bacteremia, sepsis, and septic shock.
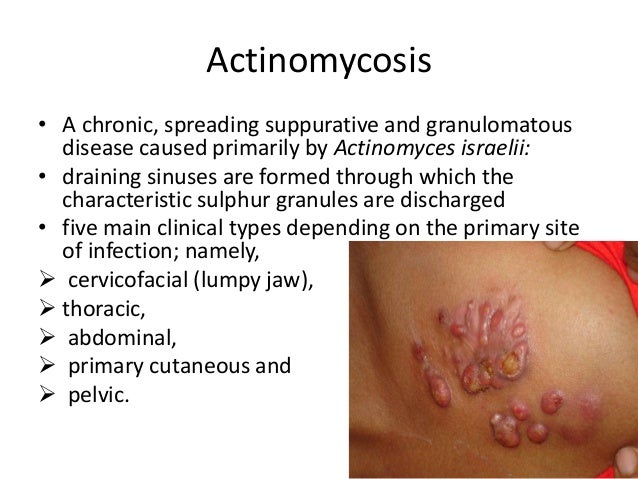
Why is actinomycosis called lumpy jaw?
The mandible is affected more commonly than the maxilla. The defining feature of actinomycosis is the presence of a non-painful swelling under the jaw. This swelling can rupture and drain pus-type, smelly fluid which contaminates the environment.
How to prevent actinomycosis?
One of the best ways to prevent actinomycosis is to practice good oral hygiene. Schedule regular visits with your dentist so that they can spot potential problems. If you get proper treatment for actinomycosis, it’s highly curable and you’ll likely make a full recovery.
What causes actinomycosis?
One of the most common causes of actinomycosis is an oral or a dental abscess. If you’ve recently had an oral abscess, you should see your doctor right away. Women who’ve used an intrauterine device (IUD) for birth control are also considered at higher risk.
How long does it take for penicillin to cure actinomycosis?
If you’re allergic to penicillin, your doctor can give you other antibiotics, such as: It can take up to a year for the antibiotics to completely cure the infection.
Can actinomycosis cause a locked jaw?
Actinomycosis can also cause muscle spasms in the jaw or a “locked jaw.”. If this happens, the mouth cannot open in a normal way. The other symptoms of actinomycosis are: a fever. weight loss. lumps on the neck or face. draining sores on the skin. excess sinus drainage. coughing.
Can actinomycosis be left untreated?
Potential Long-Term Complications. Actinomycosis starts in the soft tissues of the body, but it can infect any surrounding bone if it’s left untreated. Surgery may be necessary to remove any infected bone. If the infection resides in the nasal sinuses, surgery may be required to remove damaged bone and tissue.
Is actinomycosis a fungal infection?
Ac tinomycosis is a rare infection, especially in the United States. Since the infection spreads so slowly, actinomycosis was first thought to be a fungal infection. But a family of bacteria known as Actinomycetaceae causes it. The bacteria in this family include: Actinomyces israelii. Actinomyces naeslundii.
What is the clinical manifestation of actinomycosis?
Actinomycosis has clinical manifestations that depend on where the infection is present. The largest number of patients will have a slow or moderately slow progression process involving the face/neck. One of the hallmarks is a draining lesion that may have been preceded by a localized swelling.
What diseases mimic actinomycosis?
Beware: there are other diseases that can mimic actinomycosis: Because of the subacute to chronic pace of actinomycosis, it is most likely to be confused with malignancy, benign tumor or granulomatous disease (e.g., mycobacterial or fungal).
Why are actinomycetes hard to grow?
Because actinomycetes are present in the environment and in humans as saprophytes, there may not be a clear source of infection from the environment. Actinomycetes are hard to grow in the clinical laboratory and may be present more than is documented by laboratory tests.
Can Actinomyces be gram stained?
Actinomyces can be easily gram stained. Their characteristic appearance as thin, filamentous gram-positive rods can be an excellent clue in the right clinical setting. Acid-fast staining of Actinomyces either from culture or from clinical specimens is negative. This helps to distinguish them from mycobacteria.
Can Actinomyces grow slower than co-pathogens?
Third, Actinomyces are often present in mixed infections and may grow slower than the co-pathogens . Fourth, it can be challenging to confirm the presence of Actinomyces or provide species level identification even in labs that can grow the organism.
Can Actinomyces spp. be inhibited?
Second, the growth of Actinomyces spp. can be inhibited by prior anti-bacterial treatments. This is often the case when clinicians evaluating the patient suspect “infection” and treat empirically. Third, Actinomyces are often present in mixed infections and may grow slower than the co-pathogens.
Is actinomycosis more likely to occur with an IUD?
There is little characteristic epidemiology for actinomycosis in general. Pelvic disease is much more likely when an intrauterine device (IUD) is in place . Orofacial diseases may occur in the presence of underlying tooth pathology, trauma or surgery, but many cases occur in people with healthy dentition and no obvious trauma.
How is actinomycosis diagnosed?
Actinomycosis is diagnosed based on the clinical history, exam, and specific laboratory tests. The most commonly used test is a tissue biopsy of the infected area to look for the presence of the bacteria that cause this infection. [1]
How do you know if you have actinomycosis?
When it occurs in the pelvic area, symptoms may include pain, vaginal bleeding, and swelling. Actinomycosis mainly affects adults but has been reported in children as well. The first symptom is usually the presence of a soft mass in the neck. Once a diagnosis is made, treatment with antibiotics usually leads to recovery.
What is the name of the bacterial infection that causes a mass in the neck and throat?
Actinomycosis is a bacterial infection that occurs most often in the face and neck. Symptoms of actinomycosis include a neck mass, jaw or face pain, and formation of pockets of pus (abscess). When actinomycosis occurs in other parts of the body, symptoms can include cough, chest or stomach pain, fever, and weight loss. It is usually caused by bacteria called Actinomyces israelii. These bacteria are found normally in the mouth, gastrointestinal tract, and female genital tract, and do not cause an infection unless there is a break in the skin or mucosa. The infection is not contagious. Actinomycosis is diagnosed based on the history and clinical exam, and through specific laboratory tests. It is treated with antibiotics. [1] [2] [3]
How long does actinomycosis treatment last?
Treatment may last several weeks and usually results in full recovery. Sometimes surgery is done to reduce the size of the mass. [3] [5] Specialists involved in the care of someone with actinomycosis include: Infectious disease specialist. Dentist or oral surgeon. Last updated: 6/4/2020.
What are the symptoms of actinomycosis?
Difficulty opening jaw (lockjaw or trismus) When actinomycosis occurs in chest or stomach, symptoms may include cough, chest or stomach pain, fever, and weight loss. When it occurs in the pelvic area, symptoms may include pain, vaginal bleeding, and swelling.
Where are Actinomyces bacteria found?
These bacteria are found normally in the mouth, gastrointestinal, and genital tract of most people. They only causes an infection when there is a break in the skin or mucous membranes. [3] Risk factors for an infection from actinomyces bacteria include a history of diabetes, alcoholism, seizure disorder, or surgical procedure.
Can actinomycosis cause chest pain?
This list does not include every symptom or feature that has been described in actinomycosis. When actinomycosis occurs in chest or stomach, symptoms may include cough, chest or stomach pain, fever, and weight loss.
How to treat actinomycosis?
Treatment of actinomycosis consists of. Draining abscesses with a needle (usually inserted through the skin) or with surgery. Giving high doses of antibiotics. Antibiotics such as penicillin or tetracycline must be taken for at least 2 months and may be needed for more than 12 months.
Where does Actinomycosis occur?
This species of bacteria normally resides in the crevices between the teeth and gums, on the tonsils, and on mucus membranes lining the intestines and vagina.
How do you get infected with a sputum infection?
They lose weight and cough, sometimes bringing up sputum. People probably become infected when they inhale fluids that contain bacteria from their mouth. Abscesses may form in the lungs and eventually spread to the membrane between the lungs and chest wall (pleura).
How long does it take for a fistula to drain?
As the infection spreads, scar tissue and abnormal channels (called fistulas or tracts) form. After months to years, fistulas may eventually reach the skin and allow pus to drain. Pockets of pus (abscesses) may develop in the chest, abdomen, face, or neck.
What is the procedure to take a sample from an abscess?
Often, a needle is inserted through the skin to take a sample from an abscess or infected tissue. Sometimes computed tomography (CT) or ultrasonography is used to help doctors place the needle in the infected area. Sometimes surgery is necessary to remove a sample.
Can you recover from actinomycosis?
If actinomycosis is diagnosed early and treated appropriately, most people recover fully. Recovery is related to which parts of the body are affected. Recovery is best when only the face and neck are affected and worst when the infection is generalized, especially if it affects the brain.
What is the presentation of actinomycosis?
The classic presentation of actinomycosis typically is the indolent development of a firm mass, which often develops fistulous tracts that drain purulent material or sulfur granules. The masses often take on an extremely firm or “woody” texture such that they are often confused with malignancy.
What is anaerobic actinomycosis?
OVERVIEW: What every practitioner needs to know. Actinomycosis refers to the disease entity caused by any one of the organisms of the genus. Actinomyces. These organisms are filamentous gram-positive, facultative anaerobic rods that are frequent commensals of the human gastrointestinal, respiratory, and female genitourinary tract.
What are the adverse events of -lactam?
Drug-induced neutropenia and thrombocytopenia are not uncommon with β-lactams. Other adverse events include renal insufficiency, drug allergy, drug rash, and central-line infection if the patient is being treated with IV therapy.
What is the term for aspiration of foreign bodies?
Thoracic actinomycosis: This type of actinomycosis is much more common in adults and is frequently associated with aspiration of oral secretions or foreign bodies, which then disrupt the normal bronchial mucosal barriers.
What is the most common predisposing factor for cervicofacial actinomycos
Cervicofacial actinomycosis: The most common predisposing factor for cervicofacial actinomycosis is some kind of disruption of the gingiva (35% in some series), typically as a consequence of dental caries (33%), extractions (12%), or trauma. Thoracic actinomycosis: This type of actinomycosis is much more common in adults ...
How common is cervicofacial actinomycosis?
Cervicofacial actinomycosis is overwhelmingly the most common form in pediatrics. It accounts for up to 49.1% of cases in some series, with as many as 75% of patients having symptoms for 6 months or longer. It frequently presents with the indolent development of a painless firm neck or mandibular mass.
Where does abdominopelvic actinomycosis occur?
The abscess most commonly develops in the ileocecal region (right lower quadrant)and presents as a hard, irregular right lower quadrant mass on examination. It may suppurate with fistulae to skin.
Why should pus be collected for culture?
Optimally, pus with granular material should be collected for culture to detect antibiotic sensitivity prior to the administration of antibiotics. Selective resistance to penicillin has been described, although rarely. Obtaining culture and sensitivities will also reveal synchronous infectious species and enable appropriate therapy.
Is actinomycosis an immunocompetent infection?
Most infections occur in immunocompetent hosts. Actinomycosis has been recognized as an indicator of poor prognosis in cases of infected osteoradionecrosis and bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw. Death from Actinomycosis is exceedingly rare.
Can actinomycosis be treated with antibiotics?
Treatment of cutaneous actinomycosis is relatively straightforward, especially when microbiologic susceptibility studies have been performed prior to antibiotic therapy. If the disease does not respond to treatment, consider co-infection or an alternative diagnosis.
What is actinomycosis?
Actinomycosis is a chronic bacterial disease that usually affects the face and neck and typically caused by the bacteria Actinomyces israelii. These bacteria are found in the nose and throat and normally don't cause infection in healthy tissues. They become dangerous if they spread beyond their usual environment.
9 symptoms of actinomycosis
While symptoms of actinomycosis depend on the type and location of the infection, general symptoms may include:
How do doctors diagnose actinomycosis?
To diagnose actinomycosis, a sample of sputum, pus, or tissue may be sent to a lab for microscopic examination. Sometimes, the lab will make a culture of the sample bacteria.
What is the treatment of actinomycosis?
Actinomycosis grows gradually but can severely affect your health. Seeking early treatment is crucial.
OVERVIEW: What every practitioner needs to know
Actinomycosis refers to the disease entity caused by any one of the organisms of the genus Actinomyces. These organisms are filamentous gram-positive, facultative anaerobic rods that are frequent commensals of the human gastrointestinal, respiratory, and female genitourinary tract.
Are you sure your patient has actinomycosis? What are the typical findings for this disease?
The classic presentation of actinomycosis typically is the indolent development of a firm mass, which often develops fistulous tracts that drain purulent material or sulfur granules. The masses often take on an extremely firm or “woody” texture such that they are often confused with malignancy.
What caused this disease to develop at this time?
Disruption of the normal mucosal barriers is often an inciting event for infection with this organism. One of the hallmarks of actinomycosis is its potential to dissect through tissue planes, disregarding normal anatomic barriers.
What laboratory studies should you request to help confirm the diagnosis? How should you interpret the results?
The diagnosis of actinomycosis is based primarily on culture results and histopathologic evaluation of tissue specimens. Histologic analysis may reveal filamentous clusters of organisms in a mat-like configuration; grossly macroscopic sulfur granules may be seen as well.
Would imaging studies be helpful? If so, which ones?
Imaging is useful to evaluate the extent of disease and possibly the response to therapy.
If you are able to confirm that the patient has actinomycosis, what treatment should be initiated?
The cornerstone of treatment of actinomycosis includes extensive surgical debridement combined with administration of long-term antimicrobial agents.
What are the adverse effects associated with each treatment option?
Given the long duration of treatment, adverse drug events are not uncommon. Drug-induced neutropenia and thrombocytopenia are not uncommon with β-lactams. Other adverse events include renal insufficiency, drug allergy, drug rash, and central-line infection if the patient is being treated with IV therapy.
